
All Solutions
Page 586: Lesson Check
R/2
$$
-R/2
$$
hline
Real image & Virtual imagetabularnewline
hline
hline
real image can be projected on screen & virtual image can not be projected on screentabularnewline
hline
real image form in front of mirror & virtual image forms behind the mirrortabularnewline
hline
real image are inverted & virtual image is uprighttabularnewline
hline
end{tabular}
Convex mirror always produce virtual image.
tt{According to {color{#4257b2}{Table 16.1}} a convex surface should produce an upright, reduced, virtual image, this is due to the convex surface behavior in reflecting light illustrated in the {color{#4257b2}{Figure 16.25}} as all principle rays are scattered and only their extensions can intersect behind the mirror.}
$$
tt{upright,reduced,virtual image}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
f = -frac{1}{2}R
end{align*}
$$
While the focal length for a concave mirror of radius $R$ is given by
$$
begin{align*}
f = frac{1}{2}R
end{align*}
$$
We plug in the value $R = 0.86;text{m}$ for the convex mirror focal length equation.
$$
begin{align*}
f = -frac{1}{2}(0.86;text{m}) = boxed{-0.43;text{m}}
end{align*}
$$
We plug in the value $R = 0.86;text{m}$ for the concave mirror focal length equation.
$$
begin{align*}
f = frac{1}{2}(0.86;text{m}) = boxed{0.43;text{m}}
end{align*}
$$
(b) $f = 0.43$ m
Hence the radius curvature is $R=2f=2times (15 {rm cm})=30$ cm
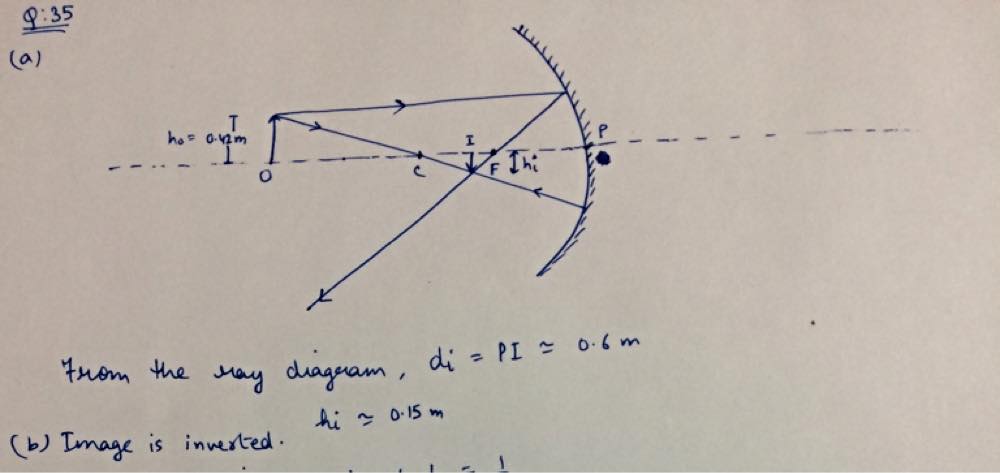
The mirror is concave $Rightarrow f>0$
$d_o>fRightarrow$ The image is real $Rightarrow d_i>0$
$frac{1}{d_i}=frac{1}{f}-frac{1}{d_o}=frac{d_o-f}{d_of}Rightarrow d_i=frac{d_of}{d_o-f}=frac{2*0.5}{2-0.5}=boxed{0.67m}$
The magnification equation states:
$$
m=-frac{d_i}{d_o}=boxed{-0.33}
$$
$$
m=frac{h_i}{h_o}Rightarrow h_i=m*h_o=(-0.33)*42=boxed{14cm}
$$
d_i=0.67m,text{m}=-0.33,h_i=14cm
$$
Haven't found what you were looking for?
Search for samples, answers to your questions and flashcards

