All Solutions
Page 742: Assessment
dual nature, wave properties, mass, momentum.
.
b( We can estimate the electron’s mass by using the magnetic field in the same way the mass spectrometer is working by balancing the electric field by the magnetic field and knowing the charge of the electron one can estimate its mass in a straight-forward manner.
c) We can aim a beam of electrons into a crystal and then observe the diffraction patterns to get the wavelength.
b) We use the magnetic force.
c) We diffract electrons on a crystal to get the angles of the diffraction.
b) We can measure the change in the wavelength when X-rays are scattered by some object.
c) We can take a prism with a known index of refraction and measure how much the light bands when passing through the prism.
b) X-ray scattering.
c) Bending through the prism.
$$
f(4000textrm{ K})=2.5times 10^{14}textrm{ Hz}
$$
$$
f(5800textrm{ K})=3.5times 10^{14}textrm{ Hz}
$$
$$
f(8000textrm{ K})=4.5times 10^{14}textrm{ Hz}
$$
b) We see that the frequency of the peak intensity increases linearly with the temperature.
c) The intensity in the red part of the spectrum rises from 0.5 to 9 which is a 18-fold increase.
textrm{a) }f(4000textrm{ K})=2.5times 10^{14}textrm{ Hz}
$$
$$
textrm{a) }f(5800textrm{ K})=3.5times 10^{14}textrm{ Hz}
$$
$$
textrm{a) }f(8000textrm{ K})=4.5times 10^{14}textrm{ Hz}
$$
$$
textrm{ b) It increases with the temperature.}
$$
$$
textrm{c) It increases 18 times.}
$$
b) The same holds for radiation of energy, the bright orange bar is radiating more energy.
b) Bright orange bar
b) The same reasoning goes for the work function which is directly proportional to the threshold frequency so the answer is tungsten again.
b) Tungsten
$$
lambda=frac{h}{mv}=frac{6.63times 10^{34}}{0.2times 21}
$$
which gives that
$$
lambdaapprox10^{-34}textrm{ m}
$$
Which is $10^{33}$ times less than the diameter of the ball.
$$
E=nhf
$$
from where we can express the frequency as
$$
f=frac{E}{nh}=frac{5.44times 10^{-19}}{1times 6.63times 10^{-34}}
$$
Finally, we have that
$$
boxed{f=8.21times 10^{14}textrm{ Hz}}
$$
f=8.21times 10^{14}textrm{ Hz}
$$
$$
K=-qV_0
$$
Therefore the stopping potential is given as
$$
V_0=-frac{K}{q}=frac{4.8times 10^{-19}}{1.6times 10^{-19}}
$$
Finally,
$$
boxed{V_0=3textrm{ V}}
$$
V_0=3textrm{ V}
$$
$$
p=frac{h}{lambda}=frac{6.63times 10^{-34}}{4times 10^{-7}}
$$
Finally, one gets that
$$
boxed{p=1.7times 10^{-27}, frac{textrm{kg}cdottextrm{m}}{textrm{s}}}
$$
p=1.7times 10^{-27}, frac{textrm{kg}cdottextrm{m}}{textrm{s}}
$$
$$
K_{max}=eV_0
$$
a) So in electron-volts we simply have that
$$
K_{max}=etimes5textrm{ V}
$$
$$
boxed{K_{max}=5textrm{ eV}}
$$
b) In joules, the same energy has the following value
$$
K_{max}=5times 1.6times 10^{-19}textrm{ J}
$$
$$
boxed{K_{max}=8times 10^{-19}textrm{ J}}
$$
textrm{a) }K_{max}=5textrm{ eV}
$$
$$
textrm{b) }K_{max}=8times 10^{-19}textrm{ J}
$$
$$
K_{max}=E_{ph}-W=hf-hf_0
$$
On the other hand the frequency of the light is given as
$$
f=frac{c}{lambda}=frac{3times 10^8}{650times 10^{-9}}
$$
$f=4.6times 10^{14}textrm{ Hz}$
so we have that
$$
K_{max}=h(f-f_0)=6.63times 10^{-34}times(4.6times 10^{14}-3times 10^{14})
$$
Finally, we have that
$$
boxed{K_{max}=1.06times 10^{-19}textrm{ J}}
$$
K_{max}=1.06times 10^{-19}textrm{ J}
$$
$$
W=hf_0=6.63times 10^{-34}times 4.4times 10^{14}
$$
which gives that
$$
boxed{W=2.9times 10^{-19}textrm{ J}}
$$
W=2.9times 10^{-19}textrm{ J}
$$
$$
K_{max}=E_{ph}-W=hf-hf_0
$$
$$
K_{max}=h(f-f_0)=6.63times 10^{-34}times(1times 10^{15}-4.4times 10^{14})
$$
Finally, we have that
$$
boxed{K_{max}=3.7times 10^{-19}textrm{ J}}
$$
K_{max}=3.7times 10^{-19}textrm{ J}
$$
$$
W=frac{hc}{lambda}=frac{1.24times 10^{-6}}{0.68times 10^{-6}}
$$
This gives that
$$
boxed{W=1.82textrm{ eV}}
$$
W=1.82textrm{ eV}
$$
$$
I=1360times 3600times 3000=14.7times 10^9, frac{textrm{ J}}{textrm{m}^2}
$$
$$
A=frac{E_{home}}{etimes I}=frac{4times 10^{11}}{0.2 times14.7times 10^{9}}=135textrm{ m}^2
$$
textrm{a) }I=14.7times 10^9, frac{textrm{ J}}{textrm{m}^2}
$$
$$
textrm{b) }A=135textrm{ m}^2
$$
$$
lambda=frac{h}{mv}
$$
$$
lambda=frac{6.63times 10^{-34}}{9.11times 10^{-31}times 3times 10^6}
$$
lambda=2.4times 10^{-10}textrm{ m}
$$
$$
lambda=frac{h}{mv}
$$
from where the velocity can be expressed as
$$
v=frac{h}{mlambda}
$$
$$
v=frac{6.63times 10^{-34}}{9.11times 10^{-31}times 3times 10^{-10}}
$$
v=2.4times 10^{6}, frac{textrm{m}}{textrm{s}}
$$
$$
frac{mv^2}{2}=qV
$$
From which the speed is expressed as
$$
v=sqrt{frac{2qV}{m}}=sqrt{frac{2times 1.6times 10^{-19}times 5times 10^3 }{9.11times 10^{-31}}}
$$
Finally, we get that
$$
v=4.2times 10^{7}, frac{textrm{m}}{textrm{s}}
$$
$$
lambda=frac{h}{mv}=frac{6.63times 10^{-34}}{9.11times 10^{-31}times4.2times 10^7}
$$
$$
lambda=1.7times 10^{-11}textrm{ m}
$$
v=4.2times 10^{7}, frac{textrm{m}}{textrm{s}}
$$
$$
lambda=1.7times 10^{-11}textrm{ m}
$$
$$
K=frac{mv^2}{2}
$$
and de Broglie relation
$$
lambda=frac{h}{mv}
$$
$$
v=sqrt{frac{2K}{m}}
$$
After plugging the values
$$
v=sqrt{frac{2times0.025times 1.6times 10^{-19}}{1.67times 10^{-27}}}
$$
Finally
$$
v=2.2times 10^3,frac{textrm{m}}{textrm{s}}
$$
$$
lambda=frac{h}{mv}
$$
After pluging the values
$$
lambda=frac{6.63times 10^{-34}}{1.67times 10^{-27}times2.2times 10^3}
$$
Finally
$$
lambda=1.8times 10^{-10}textrm{ m}
$$
v=2.2times 10^3,frac{textrm{m}}{textrm{s}}
$$
$$
lambda=1.8times 10^{-10}textrm{ m}
$$
$$
K=frac{mv^2}{2}
$$
and de Broglie relation
$$
lambda=frac{h}{mv}
$$
and with the simple geometric formula
$$
C=2pr
$$
$$
v=sqrt{frac{2K}{m}}
$$
After plugging the values
$$
v=sqrt{frac{2times 13.65times 1.6times 10^{-19}}{9.11times 10^{-31}}}
$$
Finally
$$
v=2.19times 10^6,frac{textrm{m}}{textrm{s}}
$$
$$
lambda=frac{h}{mv}
$$
After pluging the values
$$
lambda=frac{6.63times 10^{-34}}{9.11times 10^{-31}times2.19times 10^6}
$$
Finally
$$
lambda=0.33times 10^{-9}textrm{ m}
$$
$$
C=2pi r=2times 3.14times 0.519times 10^{-9}
$$
$$
C=3.26times 10^{-9} textrm{ m}
$$
Which is one order of magnitude more than the de Broglie wavelength.
v=2.2times 10^6,frac{textrm{m}}{textrm{s}}
$$
$$
lambda=1.8times 10^{-10}textrm{ m}
$$
$$
C=3.26times 10^{-9} textrm{ m}
$$
$qV=frac{mv^2}{2}$
from where we can express the voltage as
$$
V=frac{mv^2}{2q}
$$
$$
lambda=frac{h}{mv}
$$
$$
v=frac{h}{lambda m}
$$
$$
V=frac{m}{2q}times frac{h^2}{lambda^2 m^2 }=frac{h^2}{2qmlambda^2}
$$
$$
V=frac{6.63^2times 10^{-68}}{2times 1.6times 10^{-19}times 9.11times 10^{-31}times 0.18^2times 10^{-18}}
$$
Finally, we have that
$$
boxed{V=46.5textrm{ V}}
$$
$$
V=frac{6.63^2times 10^{-68}}{2times 1.6times 10^{-19}times 1.67times 10^{-27}times 0.18^2times 10^{-18}}
$$
Finally, we have that
$$
boxed{V=0.025textrm{ V}}
$$
textrm{a) }V=46.5textrm{ V}
$$
$$
textrm{b) }V=0.025textrm{ V}
$$
$$
K_{max}=-qV_0
$$
$$
K_{max}=-(-1e)times 3.8V
$$
Finally
$$
boxed{K_{max}=3.8textrm{ eV}}
$$
K_{max}=3.8textrm{ eV}
$$
$$
W=hf_0
$$
$$
W=6.63times 10^{-34}times 8times 10^{14}
$$
Finally we have that the work function is given
$$
boxed{W=5.3 times 10^{-19}textrm{ J}}
$$
W=5.3 times 10^{-19}textrm{ J}
$$
In order to solve this problem, we are going to use the photoelectric effect equation which tells us that the maximum kinetic energy is given as
$$
K_{max}=E_{ph}-W=hf-hf_0
$$
$$
K_{max}=h(f-f_0)=6.63times 10^{-34}times(1.6times 10^{15}-8times 10^{14})
$$
Finally, we have that
$$
boxed{K_{max}=5.3 times 10^{-19}textrm{ J}}
$$
K_{max}=5.3 times 10^{-19}textrm{ J}
$$
$$
lambda=frac{h}{mv}
$$
$$
lambda=frac{6.63times 10^{-34}}{3.3times 10^{-27}times 2.5times 10^4}
$$
Finally,
$$
boxed{lambda=8times 10^{12}textrm{ m}}
$$
lambda=8times 10^{12}textrm{ m}
$$
$W=frac{hc}{lambda_0}$
and photoelectric effect equation
$$
K=E_{ph}-W
$$
$$
lambda_0=frac{hc}{W}=frac{1240times 10^{-9}}{4.7}
$$
Finally
$$
boxed{lambda=263times 10^{-9}textrm{ m}}
$$
$$
K_{max}=E_{ph}-W=frac{hc}{lambda}-W=frac{1240times 10^{-9}}{150times 10^{-9}}-4.7
$$
Which gives
$$
boxed{K_{max}=3.57textrm{ eV}}
$$
lambda=263times 10^{-9}textrm{ m}
$$
$$
K_{max}=3.57textrm{ eV}
$$
$$
W=frac{hc}{lambda_0}
$$
From where we can express the threshold wavelength as
$$
lambda_0=frac{hc}{W}
$$
$$
lambda_0=frac{1240times 10^{-9}}{2.48}
$$
Finally, we have
$$
boxed{lambda_0=500times 10^{-9}textrm{ m}}
$$
lambda_0=500times 10^{-9}textrm{ m}
$$
$$
lambda=frac{h}{mv}
$$
$$
v=frac{h}{mlambda}=frac{6.63times 10^{-34}}{9.11times 10^{-31}times 400times 10^{-9}}
$$
Finally, we have that
$$
boxed{v=1.82times 10^3, frac{textrm{m}}{textrm{s}}}
$$
$$
K=frac{mv^2}{2}
$$
$$
K=frac{9.11times 10^{-31}times 1.82^2times 10^6}{2times 1.6times 10^{-19}}
$$
$$
boxed{K=9.43times 10^{-6}{textrm { eV}}}
$$
textrm{a) }v=1.82times 10^3, frac{textrm{m}}{textrm{s}}
$$
$$
textrm{b) }K=9.43times 10^{-6}{textrm{ eV}}
$$
$$
lambda=frac{h}{mv}
$$
so the speed is
$$
v=frac{h}{mlambda}
$$
Now, the kinetic energy is given as
$$
K=frac{mv^2}{2}=frac{m}{2}times frac{h^2}{m^2lambda^2}
$$
$$
K=frac{h^2}{2mlambda^2times 1.6times 10^{-19}}=frac{6.63^2times 10^{-68}}{2times 9.11times 10^{-31}times 20^2times 10^{-18}times 1.6times 10^{-19}}
$$
Finally, we have that
$$
boxed{K=3.8times 10^{-3}textrm{ eV}}
$$
K=3.8times 10^{-3}textrm{ eV}
$$
$$
c=lambda f
$$
$$
lambda=frac{c}{f}=frac{3times 10^{8}}{1.2times 10^{15}}
$$
Which gives that
$$
boxed{lambda=250times 10^{-9}textrm{ m}}
$$
$$
W=hf_0
$$
$$
W=6.63times 10^{-34}times 1.2times 10^{15}
$$
that gives us
$$
W=8times 10^{-19}textrm{ J}
$$
or in eV
$$
W=frac{8times 10^{-19}}{1.6times 10^{-19}}=boxed{5textrm{ eV}}
$$
$$
K_{max}=frac{hc}{lambda}-W
$$
where $hc=1240times 10^{-9}$ eV$cdot$m.
$$
K_{max}=frac{1240times 10^{-9}}{167times 10^{-9}}-5=7.43-5
$$
Finally, we have that
$$
boxed{K_{max}=2.43textrm{ eV}}
$$
lambda=250times 10^{-9}textrm{ m}
$$
$$
W=5textrm{ eV}
$$
$$
K_{max}=2.43textrm{ eV}
$$
$$
E_{ph}=frac{hc}{lambda}
$$
$$
E_{ph}=frac{6.63times 10^{-34}times 3times 10^{8}}{632.8times 10^{-9}}=boxed{3.14times 10^{-19}textrm{ J}}
$$
$$
dot n=frac{P}{E_{ph}}
$$
$$
dot n=frac{5times 10^{-4}}{3.14times 10^{-19}}=boxed{15.9times 10^{14}, frac{textrm{photons}}{textrm{s}}}
$$
textrm{a) }E_{ph}=3.14times 10^{-19}textrm{ J}
$$
$$
textrm{b) }dot n=15.9times 10^{14}, frac{textrm{photons}}{textrm{s}}
$$
$$
P=IA=Ipi r^2=1.5times 10^{-11}times 3.14times 3.5^2times 10^{-6}
$$
$$
boxed{P=5.8times 10^{-16}textrm{ W}}
$$
$$
E_{ph}=frac{hc}{lambda}
$$
$$
E_{ph}=frac{6.63times 10^{-34}times 3times 10^{8}}{550times 10^{-9}}=boxed{3.6times 10^{-19}textrm{ J}}
$$
$$
dot n=frac{P}{E_{ph}}
$$
$$
dot n=frac{5.8times 10^{-16}}{3.6times 10^{-19}}=boxed{1.6times 10^{3}, frac{textrm{photons}}{textrm{s}}}
$$
textrm{a) }E_{ph}=3.6times 10^{-19}textrm{ J}
$$
$$
textrm{b) }dot n=1.6times 10^{3}, frac{textrm{photons}}{textrm{s}}
$$
$$
f=clambda
$$
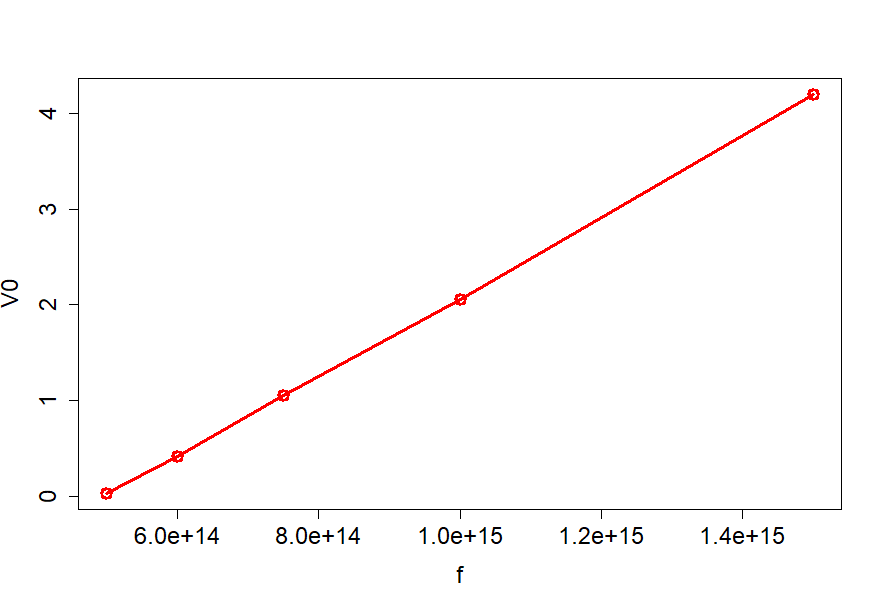
begin{tabular}{|r|r|r|}
hline
multicolumn{1}{|l|}{$lambda$(nm)} & multicolumn{1}{l|}{f(Hz)} & multicolumn{1}{l|}{$V_0$(eV)} \ hline
200 & $15times 10^{14}$ & 4.2 \ hline
300 & $10times 10^{14}$ & 2.06 \ hline
400 & $7.5times 10^{14}$ & 1.05 \ hline
500 & $6times 10^{14}$ & 0.41 \ hline
600 & $5times 10^{14}$ & 0.03 \ hline
end{tabular}
end{table}
$$
Delta V_0=kDelta f
$$
$$
k=frac{Delta V_0}{Delta f}
$$
We can take the last point and the first point that to have
$$
k=frac{4.17}{1times 10^{15}}=4.17times 10^{-15}, frac{textrm{ V}}{textrm{ Hz}}
$$
and since 1V=1J/1C we can write
$$
boxed{k=4.17times 10^{-15}frac{textrm{ J}}{textrm{C}cdottextrm{ Hz}}}
$$
On the other hand the accepted value is set to be
$$
frac{h}{e}=frac{6.63times 10^{-34}}{1.6times 10^{-19}}=boxed{4.14times 10^{-15}frac{textrm{ J}}{textrm{C}cdottextrm{ Hz}}}
$$
we see that the difference is relatively small and equals $approx 10^{-17}$.
$$
lambda_0=frac{c}{f_0}=frac{3times 10^8}{4.99times 10^{15}}
$$
$$
boxed{lambda_0=601times 10^{9}textrm{ m}}
$$
$$
W=hf_0=6.63times 10^{-34}times 4.99times 10^{14}
$$
$$
boxed{W=3.3times 10^{-19}textrm{ J}}
$$
k=4.17times 10^{-15}frac{textrm{ J}}{textrm{C}cdottextrm{ Hz}}
$$
$$
lambda_0=601times 10^{9}textrm{ m}
$$
$$
W=3.3times 10^{-19}textrm{ J}
$$
$$
F=kx
$$
from where we can express the spring constant $k$ as
$$
k=frac{F}{x}=frac{400}{0.15}=boxed{2.7times 10^3, frac{textrm{N}}{textrm{m}}}
$$
k=2.7times 10^3, frac{textrm{N}}{textrm{m}}
$$
$$
F=frac{1}{4pi varepsilon_0}cdotfrac{q_1q_2}{r^2}
$$
From where we can express the second charge as
$$
q_2=frac{4pivarepsilon_0cdot Fcdot r^2}{q_1}
$$
$$
q_2=frac{9times 0.02^2}{9times 10^9times 8times 10^{-7}}
$$
Finally, we have that
$$
boxed{q_2=5times 10^{-7}textrm{ C}}
$$
q_2=5times 10^{-7}textrm{ C}
$$
$$
I=frac{V}{R}
$$
$$
I=12I_s=12frac{V}{R_s}=12timesfrac{120}{24times 6}
$$
Which gives that the total current is
$$
boxed{I=10 textrm{ A}}
$$
I=10 textrm{ A}
$$
$$
F=ILB
$$
$$
I=frac{F}{LB}=frac{1.1times 10^{-3}}{1.2times 5times 10^{-5}}
$$
Finally we have that
$$
boxed{I=18.3textrm{ A}}
$$
I=18.3textrm{ A}
$$

