All Solutions
Page 478: Assessment
Another type of reflection is diffuse reflection. This type of reflection occurs when the surface is rough relative to the wavelength of light. In this case, the incident rays of light are parallel to each other, but they reflect at different angles because they fall on the different parts of the surface. We can say, the light is scattered off a rough surface. Also, we can see this type of reflection in Figure 17-3c, and Figure 17-3d.

$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f} &= frac{1}{d_{o}}+ frac{1}{d_{i}}\
frac{2}{R} &= frac{1}{d_{o}}+ frac{1}{d_{i}}\
frac{2}{ infty} &= frac{1}{d_{o}}+ frac{1}{d_{i}}\
0 &= frac{1}{d_{o}}+ frac{1}{d_{i}}\
frac{1}{d_{o}}&= – frac{1}{d_{i}}\
d_{i} &= – d_{o}
end{align*}
$$
The position of the object is always real (greater than zero), so the position of the image is lesser than zero. So, the image is always virtual (behind the mirror), and at the same distance from the mirror as the object. We can see this in the diagram below.
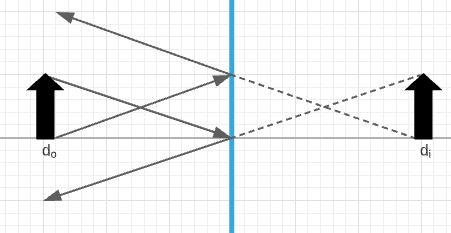
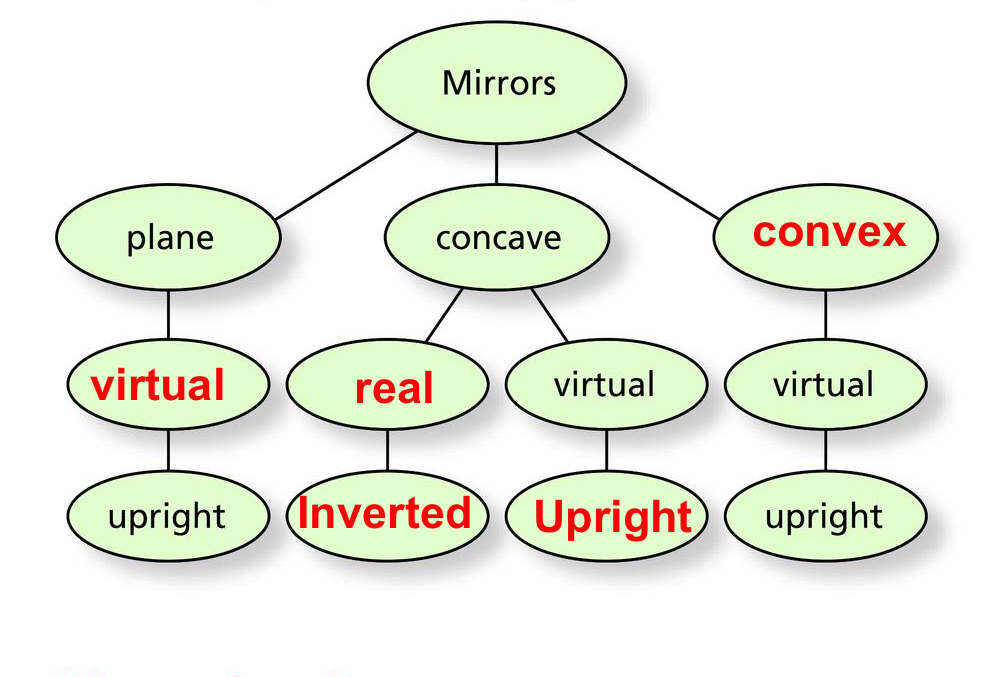
A plane mirror always produces a virtual, upright image behind the mirror.
Magnification of the image produced by plane mirror is always 1, that means image has the same size as that of the object
Distance of image from the mirror is same the object’s distance from mirror
So NO image will be formed and the student will not get anything on the screen.
If the image is real, it will appear on the screen.
If you guess the image location approximately, the image will appear on the screen, but it will be less clear.
$$
begin{align*}
d_{i}&<0\
frac{1}{d_{i}}&<0 / + frac{1}{d_{o}}\
frac{1}{d_{o}}+ frac{1}{d_{i}} &< frac{1}{d_{o}}\
frac{1}{f}&< frac{1}{d_{o}} \
d_{o}&<f
end{align*}
$$
From the previous calculation, we can see that the image is virtual in the case of a concave mirror, only when the position of the object is lesser than the focal length.
This defect is called spherical aberration.
This defect can be minimized by covering the outer edges of the concave mirror
text{Mirror Formula : }dfrac{1}{f}=dfrac{1}{d_o}+dfrac{1}{d_i}
$$
Where $f$ is the focal length, it is negative for convex mirror and positive for concave mirror
$d_o$ is distance of object from mirror, It is always positive for real objects
$d_i$ is the distance of image from mirror, it is negative for virtual images and positive for real images
r=2f
$$
text{Magnification} = -dfrac{d_i}{d_o}
$$
If the magnification is negative, it means that the image is inverted
$$begin{align}
mathrm{Magnification}=dfrac{-d_i}{d_o}
end{align}$$
Note that : Only virtual images can be seen inside a mirror, for a real image you need to place an additional screen at the position of the image (which keeps changing as the object keeps moving !)
On the other hand concave mirrors produce inverted and real images if the object is outside the focal length.
Convex mirrors are used over plane mirrors, because Convex mirrors allow drivers to see more. They provide a greater field of view by scaling down the objects they reflect.
$$
dfrac{1}{d_o}+dfrac{1}{d_i}=dfrac{1}{f}
$$
Therefore
$$
dfrac{1}{d_i}=dfrac{1}{f}-dfrac{1}{d_o}
$$
We know that $d_o$ is always positive for real objects
We also know that $f$ is negative for convex mirrors
Therefore RHS is negative, which makes $d_i$ negative
Which means that the image is formed behind the mirror
Remember that: Only virtual images can be formed behind the mirror. Real images cannot be formed behind the mirror, It is because Light rays cannot meet behind the mirror
This proves that a convex mirror can only produce virtual images
The wet road is the more specular reflector, and in that case, reflected rays are parallel to each other. So, only a small percent of the light rays will come back to us, and the wet road would appear black to us.
Whereas smooth and glossy surfaces produce specular reflection which causes glare, which means not ideal for reading
This defect is called spherical aberration.
Concave mirrors produce a real image only if the object is beyond the focal point.
If the object is positioned on the center of curvature of the mirror, magnification will be $M=1$.
In order to achieve a smaller image, the object needs to be positioned **further** from the image than the **center of curvature**.
Note that : Only virtual images can be seen inside a mirror, for a real image you need to place an additional screen at the position of the image (which keeps changing as the object keeps moving !)
On the other hand concave mirrors produce inverted and real images if the object is outside the focal length.
Convex mirrors are used over plane mirrors, because Convex mirrors allow drivers to see more. They provide a greater field of view by scaling down the objects they reflect.
The angle between the reflected ray and the normal is known as the angle of reflection $(theta_r)$
$$
text{color{#c34632} By Law of reflection : $theta_i = theta_r$}
$$
We are asked for $theta_r$
By Law of reflection, $theta_r = theta_i = 38text{textdegree}$
text{color{#4257b2}$38text{textdegree}$}
$$
$a)$ If the angle of incidence is $ theta_{i}=53 textdegree$ , then the reflected angle is
begin{align*}
theta_{i}&= theta_{r}\
theta_{r}&=53 textdegree
end{align*}
The reflected angle is [ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore theta_{r}=53 textdegree $}]
\
$b)$ From the diagram below, we can see that the angle between the ray of incidence and the reflected ray is a sum of angles $ theta_{i}$ and $ theta_{r}$. So, we can write this as
begin{align*}
theta &= theta_{i}+ theta_{r}\
theta&= 53 textdegree +53 textdegree \
theta&= 106 textdegree
end{align*}
The angle between the incident and the reflected ray is [ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore theta=106 textdegree $}]
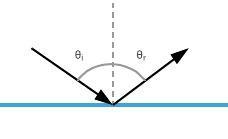
$b)$ $theta= 106 text{textdegree}$
The angle between the reflected ray and the normal is known as the angle of reflection $(theta_r)$
$$
text{color{#c34632} By Law of reflection : $theta_i = theta_r$}
$$
textbf{color{#c34632}(a)}
$$
Given that : $theta_i = 53text{textdegree}$
We are asked for $theta_r$
By Law of reflection, $theta_r = theta_i = 53text{textdegree}$
textbf{color{#c34632}(b)}
$$
Let us call the angle between incident ray and reflected ray as $theta$
Then $theta = theta_i+theta_r = 53text{textdegree}+53text{textdegree} = 106text{textdegree}$
text{color{#4257b2}textbf{color{#c34632}(a)} $53text{textdegree}$
$ $
textbf{color{#c34632}(b)} $106text{textdegree}$}
$$
The angle of incidence is an angle between **normal** of the plane and the ray, which means that the angle of incidence $theta_i$ and the angle between the ray and **mirror** $alpha=36^o$ sum to an angle of $90^o$:
$$alpha + theta_i=90^o$$
$$theta_i=90-alpha$$
$$theta_i=90-36$$
$$theta_i=54^o$$
$$theta_i=theta_r$$
Which means that:
$$theta_r=54^o$$
$$theta=theta_i+theta_r$$
$$theta=54+54$$
$$boxed{theta=108^o}$$
begin{align*}
theta_{i}+ alpha &= 90 textdegree\
theta_{i}&= 90 textdegree – alpha \
theta_{i}&= 90 textdegree – 36 textdegree \
theta_{i}&= 54 textdegree
end{align*}
Now, from the Law of Reflection, we know that the angle of reflection is the same as the angle of incidence [ theta_{r}= 54 textdegree]
So, now we have everything to calculate the angle between the incident and the reflected ray $theta$. We can write
begin{align*}
theta &= theta_{i}+ theta_{r}\
theta&= 54 textdegree +54 textdegree \
theta&= 108 textdegree
end{align*}
The angle between the incident and the reflected ray is [ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore theta=108 textdegree $}]
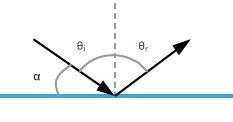
theta = 108 text{textdegree}
$$
Distance between image and the camera is $1.2+1.2 = 2.4$ m
So the camera lens must be focused at 2.4 m
begin{align*}
theta_{r1}+ alpha &= 90 textdegree\
alpha&= 90 textdegree – theta_{r1}\
alpha&= 90 textdegree – 30 textdegree\
alpha&= 60 textdegree
end{align*}
Now, we can calculate $ beta$
begin{align*}
alpha + beta + 90 textdegree &= 180 textdegree \
alpha + beta &=90 textdegree\
beta &= 90 textdegree – alpha \
beta&= 90 textdegree – 60 textdegree \
beta&= 30 textdegree
end{align*}
In the same way as we calculated the angle $ alpha$, we can calculate the angle of incidence on the second mirror
begin{align*}
theta_{i2}+ beta &= 90 textdegree\
theta_{i2} &= 90 textdegree -beta \
theta_{i2} &= 90 textdegree – 30 textdegree \
theta_{i2} &= 60 textdegree
end{align*}
Again, we use the Law of Reflection to find the angle of reflection [ theta_{i2}= theta_{r2}]
So, the angle of reflection from the second mirror is [ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore theta_{r2}=60 textdegree $}]
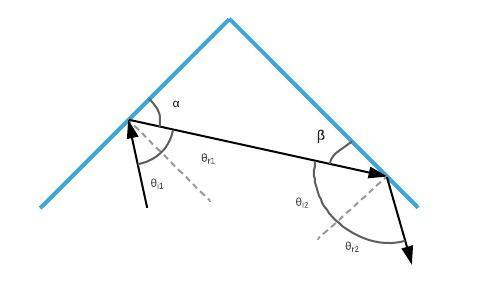
$$
begin{align*}
theta_{i1}&= theta_{r1}\
theta_{i2}&= theta_{r2}\
end{align*}
$$
So, we can say, they have the same value $theta_{i1}= theta_{r1}= theta_{i2}= theta_{r2} = theta$. Now, we can calculate the angles $alpha$ and $beta$
$$
begin{align*}
theta+ alpha &= 90 text{textdegree}\
alpha&= 90 text{textdegree} – theta\
end{align*}
$$
Also, we know that
$$
begin{align*}
alpha + beta + 90 text{textdegree} &= 180 text{textdegree} \
alpha + beta &=90 text{textdegree}\
beta &= 90 text{textdegree} – alpha \
beta &= 90 text{textdegree} – ( 90 text{textdegree} – theta)\
beta &= 180 text{textdegree} + theta\
end{align*}
$$
In the same way as we calculated the angle $alpha$, we can calculate the angle $beta$. And then we can find that the value of $theta$ is $45 text{textdegree}$. And we can draw this on the diagram.

$b)$ All of the angles are equal to $45 text{textdegree}$
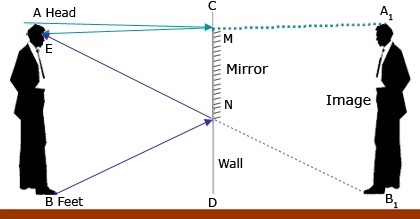
$Delta$ ANC and $Delta$ AB$_1$A$_1$ are similar
By properties of similar triangles
$$
dfrac{A_1B_1}{MN} = dfrac{AA_1}{AC}
$$
$$
text{color{#4257b2}Note that : $A_1B_1 = AB$, Because Height of Image = Height of Object
$ $
And that : $AA_1 = 2AC$, Because the image and object are at the same distance from mirror }
$$
$$
dfrac{AB}{MN} = dfrac{2AC}{AC}
$$
$$
dfrac{AB}{MN} = 2
$$
$$
dfrac{AB}{2} = MN
$$
We conclude that the mirror size should be at least half of the man’s height.
$$
begin{align*}
alpha + beta + 45 text{textdegree} &= 180 text{textdegree} \
alpha + beta &=135 text{textdegree}
end{align*}
$$
Also, from the Law of Reflection, we know that the angle of incidence is the same as the angle of reflection. So, we can write
$$
begin{align*}
theta_{i1}&= theta_{r1}\
theta_{i2}&= theta_{r2}\
end{align*}
$$
We know that the angle of incidence on the first mirror is $theta_{i1}=30 text{textdegree}$, so the angle of reflection from the first mirror is $theta_{r1}=30 text{textdegree}$. Futhermore, the sum of the angles $alpha$ and $theta_{r1}$ is $90 text{textdegree}$, so we can write
$$
begin{align*}
theta_{r1}+ alpha &= 90 text{textdegree}\
alpha&= 90 text{textdegree} – theta_{r1}\
alpha&= 90 text{textdegree} – 30 text{textdegree}\
alpha&= 60 text{textdegree}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
alpha + beta &=135 textdegree\
beta &= 135 textdegree – alpha \
beta&= 135 textdegree – 60 textdegree \
beta&= 75 textdegree
end{align*}
In the same manner as before, we can calculate the angles $ theta_{i2}$ and $ theta_{r2}$
begin{align*}
theta_{i2}+ beta &= 90 textdegree\
theta_{i2} &= 90 textdegree -beta \
theta_{i2} &= 90 textdegree -75 textdegree \
theta_{i2} &= 15 textdegree
end{align*}
So, the angle of reflection from the second mirror is [ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore theta_{r2}=15 textdegree $}]
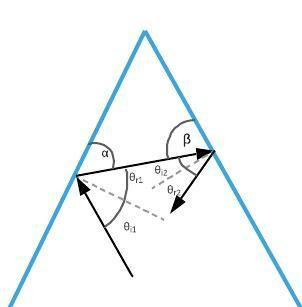
theta_{r2}=15 text{textdegree}
$$
begin{align*}
theta_{i1}&= theta_{i2}+ 18 textdegree \
theta_{i2} &= theta_{i1} – 18 textdegree \
theta_{i2} &= 60 textdegree – 18 textdegree \
theta_{i2} &= 42 textdegree
end{align*}
From the Law of Reflection, we know that the angle of incidence is the same as the angle of reflection relative to the normal [ theta_{i}= theta_{r}= 42 textdegree ]
Now, we can calculate the angle $ theta$ between the reflected ray and the mirror as
begin{align*}
theta + theta_{r}&= 90 textdegree\
theta &= 90 textdegree – theta_{r} \
theta &= 90 textdegree – 42 textdegree \
theta &= 48 textdegree
end{align*}
So, the angle between the reflected ray and the mirror is [ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore theta=48 textdegree $}]
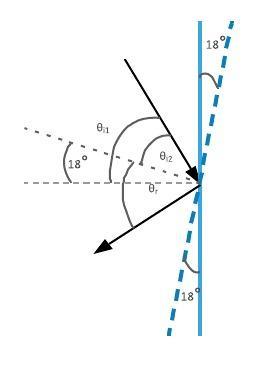
theta=48 text{textdegree}
$$
text{color{#c34632}Recall that : $$text{Radius of Curvature} = 2times text{Focal Length}$$}
$$
Therefore
$$
text{Radius of Curvature} = 2times 10text{ cm} = 20text{ cm}
$$
text{color{#4257b2}$$text{Radius of Curvature} = 20text{ cm}$$}
$$
color{#4257b2}text{Recall that : Magnification} = -dfrac{d_i}{d_o}
$$
Substitute : $d_i = -9$ and $d_o = 18$
Notice the negative sign for $d_i$. It is Important to note that the image is virtual, which means that the image is formed behind the mirror
$$
text{ Magnification} = -dfrac{-9}{18} = 0.5
$$
Magnification of 0.5 means that image is upright and half the size of object
text{color{#4257b2}Magnification = 0.5}
$$
$$M=frac{h_i}{h_o}$$
$$h_o=frac{h_i}{M}$$
Inserting values we get:
$$h_o=frac{0.6}{frac{1}{3}}$$
Finally, the height of an object is:
$$boxed{h_o=1.8,,rm{m}}$$
text{color{#4257b2}Recall that : $$text{Magnification} = dfrac{text{Image Height}}{text{Object Height}}$$}
$$
Substitute : Magnification $=dfrac{1}{3}$ and Image Height = $0.6$
$$
dfrac{1}{3}= dfrac{0.6}{text{Object Height}}
$$
Cross Multiply
$$
text{Object Height}= 3times 0.6 = 1.8
$$
text{color{#4257b2}Boy’s Height is 1.8 meters }
$$
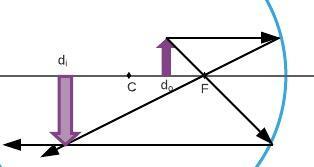
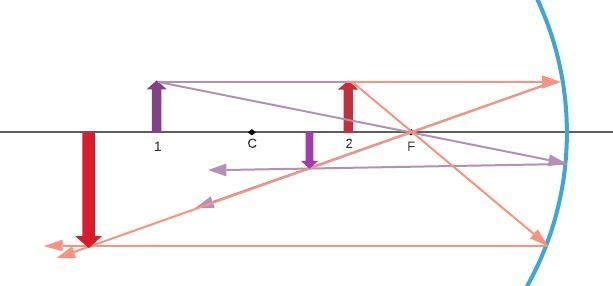
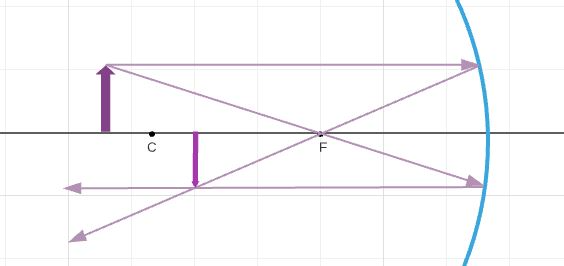
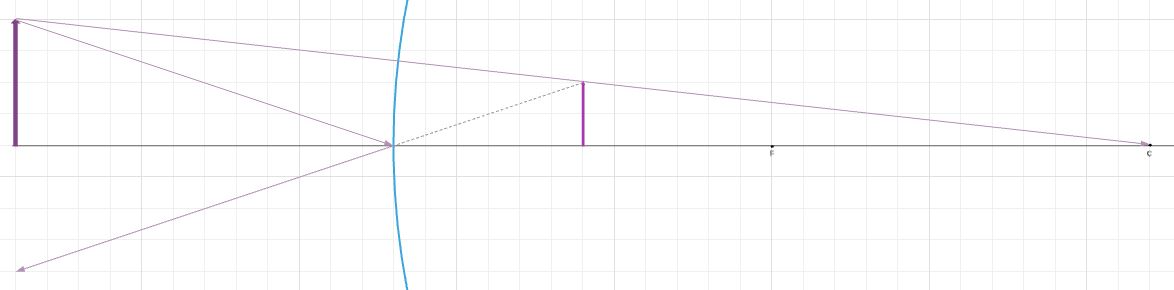
First, we are going to find the characteristic with equations. From Figure 17-21 we know
$$
begin{align*}
d_{o}>f \
frac{1}{d_{o}}< frac{1}{f}\
frac{1}{d_{o}} 0 \
d_{i} >0
end{align*}
$$
From this, we know that that the image is real. Now, we will observe relation between the radius $r=2f$ and the object position $d_{o}$
$$
begin{align*}
r>d_{o} \
2f>d_{o}\
frac{1}{d_{o}}> frac{1}{2f}\
frac{1}{f}- frac{1}{d_{i}} frac{1}{d_{i}} \
frac{1}{2f} > frac{1}{d_{i}}\
d_{i}> 2f\
d_{i}>r
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
M&= -frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}} = frac{h_{i}}{h_{o}}\
h_{i}&= – h_{o} frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}}
end{align*}
$$
We can see that $d_{o}$, $d_{i}$, and $h_{o}$ are greater than zero, then the height of the image is lesser than zero, so the image is inverted.
Also, $d_{i}> d_{o}$, so the magnification is greater than $1$, and the image is larger than the object.
$$frac{1}{d_o}+frac{1}{d_i}=frac{1}{f}$$
From the previous equation we can express $d_i$:
$$frac{1}{d_i}=frac{1}{f}-frac{1}{d_o}$$
$$frac{q}{d_i}=frac{d_o-f}{fd_o}$$
And finally:
$$d_i=frac{fd_o}{d_o-f}$$
$$d_i=frac{16cdot 31}{31-16}$$
$$boxed{d_i=33.1,,rm{cm}}$$
$$M=frac{h_i}{h_o}=-frac{d_i}{d_o}$$
$$h_i=h_ofrac{d_i}{d_o}$$
$$h_i=-3.8cdot frac{33.1}{31}$$
$$boxed{h_o=-4.1,,rm{cm}}$$
$$h_o=-4.1,,rm{cm}$$
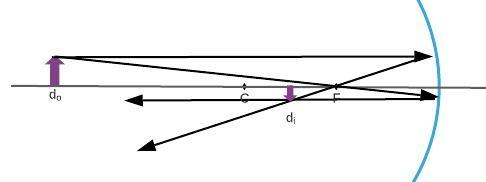
From Figure 17-22, we know the focal length is $f= 16 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}$, the position of the object is $d_{o}= 31 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}$, and the height of the object is $h_{o}= 3.8 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}$\
Now, we are going to find the position of the image with the mirror equation
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{o}}+ frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f}\
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f}- frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}\
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}\
d_{i}&= frac{16 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} cdot 31 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{31 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}- 16 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
d_{i}&=33.1 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
So, the position of the image is [ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore d_{i}=33.1 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} $}]
When we know the position of the image, we can find the height of the image with the magnification equation
begin{align*}
M&= -frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}} = frac{h_{i}}{h_{o}}\
h_{i}&= – h_{o} frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}} \
h_{i}&= – 3.8 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} frac{33.1 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{31 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}} \
h_{i}&= -4.1 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
So, the height of the image is [ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore h_{i}=-4.1 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} $}]
$$
h_{i}=-4.1 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
&f= – 6.00 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
&d_{o}= 10.00 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f} &= frac{1}{d_{o}}+ frac{1}{d_{i}} / – frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f} – frac{1}{d_{o}}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f} – frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}\
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}\
d_{i}&= frac{- 6.00 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} cdot 10.00 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{10.00 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}+ 6.00 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
d_{i}&= frac{- 60.00 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm^{2}}}{16.00 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
d_{i}&=-3.75 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore d_{i}=-3.75 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} $}]
d_{i}=-3.75 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
&f= 15.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
&d_{o}= 30.00 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
&h_{o}=1.8 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f} &= frac{1}{d_{o}}+ frac{1}{d_{i}} / – frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f} – frac{1}{d_{o}}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f} – frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}\
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}\
d_{i}&= frac{15.00 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} cdot 30.00 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{30.00 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}- 15.00 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
d_{i}&= frac{450.00 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm^{2}}}{15.00 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
d_{i}&=30.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore d_{i}=30.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} $}]
begin{align*}
– frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}} &= frac{h_{i}}{h_{o}} / cdot h_{o}\
h_{i}&= -h_{o}frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
h_{i}&= -h_{o}frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}}\
h_{i}&= – 1.8 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m} frac{30.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{30.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
h_{i}&= – 1.8 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m} cdot 1.0\
h_{i}&= – 1.8 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}\
end{align*}
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore h_{i}=-1.8 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m} $}]
$$
h_{i}=-1.8 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
&r= 40 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}\
&d_{o}= 16 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
f&= frac{r}{2}\
f&= frac{40 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}}{2}\
f&= 20 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}
end{align*}
$$
Now, when we have found the focal length, we are going to use it in the mirror equation.
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f} &= frac{1}{d_{o}}+ frac{1}{d_{i}} / – frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f} – frac{1}{d_{o}}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f} – frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}\
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}\
d_{i}&= frac{20 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm} cdot 16 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}}{16 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}- 20 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}}\
d_{i}&= frac{320 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm^{2}}}{-4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}}\
d_{i}&=-80 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}
end{align*}
$$
Now, we use this information in the magnification equation.
$$
begin{align*}
M&=- frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}}\
M&=- frac{-80 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}}{16 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}}\
M&= 5
end{align*}
$$
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore M=5 $}]
M=5
$$
$$
begin{align*}
&r= 34.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
&d_{o}= 22.4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
&h_{o}=3.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
f&= frac{r}{2}\
f&= frac{34.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{2}\
f&= 17.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
Now, when we have found the focal length, we are going to use it in the mirror equation.
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f} &= frac{1}{d_{o}}+ frac{1}{d_{i}} / – frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f} – frac{1}{d_{o}}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f} – frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}\
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}\
d_{i}&= frac{17.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} cdot 22.4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{22.4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}- 17.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
d_{i}&= frac{380.8 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm^{2}}}{5.4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
d_{i}&= 70.5 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
Now, we use this information in the magnification equation.
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore d_{i}=70.5 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} $}]
$$
begin{align*}
– frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}} &= frac{h_{i}}{h_{o}} / cdot h_{o}\
h_{i}&= -h_{o}frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}}
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
h_{i}&= -h_{o}frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}}\
h_{i}&= – 3.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} frac{70.5 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{22.4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
h_{i}&= – 3.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} cdot 3.15\
h_{i}&= – 9.4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
end{align*}
$$
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore h_{i}=-9.4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} $}]
$$
h_{i}=-9.4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
&f= 12.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
&d_{o}= 8.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
&D_{o}=3.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f} &= frac{1}{d_{o}}+ frac{1}{d_{i}} / – frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f} – frac{1}{d_{o}}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f} – frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}\
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}\
d_{i}&= frac{12.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} cdot 8.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{8.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}- 12.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
d_{i}&= frac{96.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm^2}}{-4.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
d_{i}&= -24.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore d_{i}=-24.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} $}]
begin{align*}
– frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}} &= frac{D_{i}}{D_{o}} / cdot D_{o}\
D_{i}&= -D_{o}frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
D_{i}&= -D_{o}frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}}\
D_{i}&= – 3.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} frac{-24.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{8.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
D_{i}&= – 3.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} cdot (-3.0)\
D_{i}&= 9.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
end{align*}
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore D_{i}=9.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} $}]
$b)$ $D_{i}= 9.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}$
$$
begin{align*}
&f= 3.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
&d_{o}= 12.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
&h_{o}=24 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f} – frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}\
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}\
d_{i}&= frac{3.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} cdot 12.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{12.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}- 3.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
d_{i}&= frac{36.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm^{2}}}{9.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
d_{i}&= 4.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore d_{i}=4.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} $}]
$$
begin{align*}
– frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}} &= frac{h_{i}}{h_{o}} / cdot h_{o}\
h_{i}&= -h_{o}frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
h_{i}&= -h_{o}frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}}\
h_{i}&= – 24 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm} frac{4.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{12.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
h_{i}&= -24 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm} cdot frac{1}{3}\
h_{i}&= – 8 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}\
end{align*}
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore h_{i}=-8 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm} $}]
$c)$ $h_{i}= – 8 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}$
$$
begin{align*}
&D= 40.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
&d_{o}= 1.5 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}\
&h_{o}=12.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
f&= frac{d}{4}\
f&= frac{40.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{4}\
f&= 10.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
But, the mirror is convex, so the focal length is lesser than zero $f=-10.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}$ Now, when we have found the focal length, we are going to use it in the mirror equation.
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f} &= frac{1}{d_{o}}+ frac{1}{d_{i}} / – frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f} – frac{1}{d_{o}}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f} – frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}\
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}\
d_{i}&= frac{-0.1 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m} cdot 1.5 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}}{1.5 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}+ 0.1 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}}\
d_{i}&= frac{-0.15 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m^{2}}}{1.6 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}}\
d_{i}&= -9.4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
– frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}} &= frac{h_{i}}{h_{o}} / cdot h_{o}\
h_{i}&= -h_{o}frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
h_{i}&= -h_{o}frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}}\
h_{i}&= – 12 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} frac{-9.4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{150 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
h_{i}&= -12 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} cdot (-0.062)\
h_{i}&= 0.75 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
end{align*}
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore h_{i}=0.75 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} $}]
$$
h_{i}=0.75 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
& theta_{i1}= 28 text{textdegree}\
& Delta theta_{i}=34 text{textdegree}
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
theta_{i2}&= theta_{i1} + Delta theta_{i}\
theta_{i2}&= 28 text{textdegree} + 34 text{textdegree}\
theta_{i2}&= 62 text{textdegree}
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
theta_{i2}&= theta_{r}\
theta_{r}&= 62 text{textdegree}
end{align*}
$$
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore theta_{r}= 62 textdegree $}]
theta_{r}= 62 text{textdegree}
$$

Also, we can see that the height of the image is one third of the height of the object, $frac{1}{3}h_{o}$. The height of the object is $h_{o}=3 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}$, so the height of the image is $h_{i}=1 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}$.
$$
h_{i}=1 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
&r=24.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
&d_{o}=4.4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
f&= frac{r}{2}\
f&= frac{24.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{2}\
f&= 12.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
Now, when we have found the focal length, we are going to use it in the mirror equation.
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f} &= frac{1}{d_{o}}+ frac{1}{d_{i}} / – frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f} – frac{1}{d_{o}}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f} – frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}\
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}\
d_{i}&= frac{12.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} cdot 4.4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{4.4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}- 12.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
d_{i}&= frac{52.8 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm^{2}}}{-7.6 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}}\
d_{i}&= -6.95 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore d_{i}=-6.95 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} $}]
d_{i}=-6.95 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
&r=26.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
&d_{o}=30.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
&h_{o}=2.4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
f&= frac{r}{2}\
f&= frac{26.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{2}\
f&= 13.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
Now, when we have found the focal length, we are going to use it in the mirror equation.
$$
end{document}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f} &= frac{1}{d_{o}}+ frac{1}{d_{i}} / – frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f} – frac{1}{d_{o}}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f} – frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}\
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}\
d_{i}&= frac{13.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} cdot 30.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{30.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}- 13.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
d_{i}&= frac{390.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm^{2}}}{17.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}}\
d_{i}&= 22.94 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}
end{align*}
$$
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore d_{i}=22.94 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} $}]
$$
begin{align*}
– frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}} &= frac{h_{i}}{h_{o}} / cdot h_{o}\
h_{i}&= -h_{o}frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}}
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
h_{i}&= -h_{o}frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}}\
h_{i}&= – 2.4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} frac{22.94 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{30 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
h_{i}&= -2.4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} cdot 0.765\
h_{i}&= -1.84 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
end{align*}
$$
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore h_{i}=-1.84 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} $}]
$b)$ $h_{i}=-1.84 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}$
$$
begin{align*}
&d_{o}=20 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
&M=+3.2
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
M&=- frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}} / cdot (-d_{o})\
d_{i}&=-M d_{o}\
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
d_{i}&=-M d_{o}\
d_{i}&=-(+3.2) cdot 20hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
d_{i}&=-64hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f} &= frac{1}{d_{o}}+ frac{1}{d_{i}} \
frac{1}{f} &= frac{d_{i}+d_{o}}{d_{o}d_{i}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f} &= frac{d_{i}+d_{o}}{d_{o}d_{i}}\
f&= frac{d_{o}d_{i}}{d_{i}+d_{o}}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
f&= frac{d_{o}d_{i}}{d_{i}+d_{o}}\
f&=frac{-64 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} cdot 20 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{-64 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}+20 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
f&=frac{-1280 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm^{2}}}{-44 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
f&=29.1 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
r&=2f\
r&=2 cdot 29.1 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
r&=58.2 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore r=58.2 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} $}]
58.2 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
&d_{o}=-36 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
&M=+0.5
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
M&=- frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}} / cdot (-frac{d_{o}}{M})\
d_{o}&=-frac{d_{i}}{M}\
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
d_{o}&=-frac{d_{i}}{M}\
d_{o}&=-frac{-36 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{0.5}\
d_{o}&=72 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f} &= frac{1}{d_{o}}+ frac{1}{d_{i}} \
frac{1}{f}&= frac{d_{i}+d_{o}}{d_{o}d_{i}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f}&= frac{d_{i}+d_{i}}{ d_{o} d_{i}}\
f&= frac{d_{i} d_{o}}{d_{i}+d_{o}}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
f&= frac{d_{i} d_{o}}{d_{i}+d_{o}}\
f&= frac{(-36hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}) cdot 72 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{- 36hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}+72 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
f&=frac{(- 36hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}) cdot 72 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{36 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
f&=- 72hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore f=-72 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} $}]
f=-72 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
&r=3.8 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}\
&d_{o}=6.5 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}\
&h_{o}=1.7 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
f&= frac{r}{2}\
f&= frac{3.8 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}}{2}\
f&= 1.9 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}
end{align*}
$$
But the mirror is convex, so the focal length is negative $f=-1.9 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}$
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f} &= frac{1}{d_{o}}+ frac{1}{d_{i}} / – frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f} – frac{1}{d_{o}}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f} – frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}\
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}\
d_{i}&= frac{-1.9 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m} cdot 6.5 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}}{6.5 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}+ 1.9 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}}\
d_{i}&= frac{-12.35 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m^{2}}}{8.4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}}\
d_{i}&= -1.47 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}
end{align*}
$$
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore d_{i}=-1.47 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m} $}]
$$
begin{align*}
– frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}} &= frac{h_{i}}{h_{o}} / cdot h_{o}\
h_{i}&= -h_{o}frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}}
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
h_{i}&= -h_{o}frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}}\
h_{i}&= – 1.7 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m} frac{-1.47hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}}{6.5 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}}\
h_{i}&= -1.7 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m} cdot (-0.23)\
h_{i}&= 0.38 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}\
end{align*}
$$
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore h_{i}=0.38 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m} $}]
$b)$ $h_{i}=0.38 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}$
$$
begin{align*}
&M=7.5\
&d_{o}=14.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}\
&h_{i}>0
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
M&= – frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}} / cdot (-d_{o})\
d_{i}&=-M d_{o}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
d_{i}&=-M d_{o}\
M d_{o}&>0\
d_{i}&<0
end{align*}
So, now we know that the image is virtual.
begin{align*}
frac{|d_{i}|}{|d_{o}|}&=M\
frac{|d_{i}|}{|d_{o}|}&>1\
|d_{i}|&>|d_{o}|
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f}&= frac{1}{d_{i}}+frac{1}{d_{o}}\
frac{1}{f}&= frac{d_{o}+d_{i}}{d_{i} d_{o}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f}&= frac{d_{o}+ d_{i}}{d_{i} d_{o}}\
f&= frac{d_{i} d_{o}}{d_{o}+ d_{i}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
d_{i}&=-M d_{o}\
d_{i}&=- 7.5 cdot 14.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}\
d_{i}&=-105.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}\
end{align*}
begin{align*}
f&= frac{d_{i} d_{o}}{d_{o} + d_{i}}\
f&= frac{-105.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm} cdot 14.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}}{14.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}-105.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}}\
f&= frac{-1470.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm^{2}}}{-91.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}}\
f&=16.2 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
r&=2f\
r&= 2 cdot 16.2 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}\
r&= 32.4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}
end{align*}
So, the radius of the curvature is [ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore r=32.4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm} $}]
$b)$ $r=32.4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{mm}$
$$
begin{align*}
d_{o}&=22 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
d_{o_{p}}&=d_{o}\
d_{i_{p}}&=d_{o_{p}}\
d_{i_{p}}&=22 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
d_{i}&=d_{i_{p}}+12 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
d_{i}&=22 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}+12 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
d_{i}&=34 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
[d_{i}=-34 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}]
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f}&= frac{1}{d_{o}} + frac{1}{d_{i}} \
frac{1}{f}&= frac{d_{i} + d_{o}}{d_{o} cdot d_{i}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f}&= frac{d_{i} + d_{o}}{d_{o} cdot d_{i}}\
f&= frac{d_{o} cdot d_{i}}{d_{i} + d_{o}}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
f&= frac{d_{o} cdot d_{i}}{d_{i}+ d_{o}}\
f&= frac{22 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} cdot (-34 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm})}{-34 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}+ 22 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
f&=frac{-748 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm^2}}{-12 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
f&=62.3 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
$$
dfrac{1}{f}=dfrac{1}{d_o}+dfrac{1}{d_i}
$$
Given that : $d_o = 22$
For Images produced by plane mirrors, object and Image are at the same distance from the mirror
That means that the Image is now 22cm behind the mirror. But before the plane mirror was used, the image was $22+12 = 34$ cm behind the mirror
Therefore $d_i = -34$
$$
dfrac{1}{f} = dfrac{1}{22}+dfrac{1}{-34}
$$
$$
dfrac{1}{f} = dfrac{1}{22}times dfrac{34}{34}-dfrac{1}{34}times dfrac{22}{22}
$$
$$
dfrac{1}{f} = dfrac{34}{34times22}-dfrac{22}{34times22}
$$
$$
dfrac{1}{f} = dfrac{12}{34times22}
$$
Take reciprocal of both sides
$$
{f} = dfrac{34times22}{12}approx62.3text{ cm}
$$
The positive sign means that the mirror was concave
$$
begin{align*}
&h_{o}=1.6 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}\
&d_{o}=3.2 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}\
&h_{i}=0.28 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
– frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}}&= frac{h_{i}}{h_{o}} / cdot (-d_{o})\
d_{i}&=-d_{o} frac{h_{i}}{h_{o}}\
end{align*}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
d_{i}&=-d_{o} frac{h_{i}}{h_{o}}\
d_{i}&=-3.2 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m} frac{0.28 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}}{1.6 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}}\
d_{i}&=-3.2 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m} cdot 0.175\
d_{i}&=-0.56 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f}&= frac{1}{d_{i}} + frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{f}&= frac{d_{o}+d_{i}}{d_{i} d_{o}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f}&= frac{d_{o}+d_{i}}{d_{i} d_{o}}\
f&=frac{d_{i} d_{o}}{d_{o}+d_{i}}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
f&=frac{d_{i} d_{o}}{d_{o}+d_{i}}\
f&= frac{-0.56 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m} cdot 3.2 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}}{3.2 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}+(-0.56 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m})}\
f&=frac{-1.792 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m^2}}{2.64 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}}\
f&=-0.68 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}
end{align*}
$$
.
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore f=-0.68 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m} $}]
f=-0.68 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
&d_{o}=12.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
&d_{i}=-6.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
&h_{o}=4.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
&h_{i}=2.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
M&= – frac{d_{i}}{d_{o}}\
M&= -frac{-6.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{12.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
M&=0.5
end{align*}
begin{align*}
M&= frac{h_{i}}{h_{o}}\
M&= frac{2.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{4.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
M&=0.5
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f}&= frac{1}{d_{i}} + frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{f}&= frac{d_{o}+d_{i}}{d_{i} cdot d_{o}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f}&= frac{d_{o}+d_{i}}{d_{i} d_{o}}\
f&=frac{d_{i} d_{o}}{d_{o}+d_{i}}\
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
f&=frac{d_{i} d_{o}}{d_{o}+d_{i}}\
f&= frac{-6.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} cdot 12.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{12.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}- 6.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
f&= frac{-72.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm^{2}}}{6.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
f&= -12 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore f=-12.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} $}]
f=-12.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f} &= frac{1}{d_{o}}+ frac{1}{d_{i}} / – frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f} – frac{1}{d_{o}}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{1}{f} – frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= frac{d_{o}- f}{f cdot d_{o}}\
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}\
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot 2Cf}{2Cf- f}\
d_{i}&= frac{ 2Cf^{2}}{(2C-1) f}\
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
d_{i}&= frac{ 2Cf^{2}}{(2C-1) f}\
d_{i}&= frac{ 2Cf}{2C-1}\
d_{i}&= frac{ d_{o}}{2C-1}\
end{align*}
begin{align*}
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}\
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot Cf}{Cf- f}\
d_{i}&= frac{ Cf^{2}}{(C-1) f}\
end{align*}
begin{align*}
d_{i}&= frac{ Cf^{2}}{(C-1) f}\
d_{i}&= frac{ Cf}{C-1}\
d_{i}&= frac{ d_{o}}{C-1}\
end{align*}
begin{align*}
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}\
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot frac{f}{C}}{frac{f}{C}- f}\
d_{i}&= frac{ frac{f^{2}}{C}}{(frac{1}{C}-1) f}\
end{align*}
begin{align*}
d_{i}&= frac{ frac{f^{2}}{C}}{(frac{1}{C}-1) f}\
d_{i}&= frac{ frac{f}{C}}{frac{1}{C}-1}\
d_{i}&= frac{ d_{o}}{frac{1}{C}-1}\
end{align*}
begin{align*}
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}\
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot 2f}{2f- f}\
d_{i}&= frac{ 2f^{2}}{f}\
d_{i}&=2f\
d_{i}&=d_{o}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}- f}\
d_{i}&= frac{f cdot f}{f- f}\
d_{i}&= frac{ f^{2}}{ 0}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f}&= frac{1}{d_{i}} + frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{f}&= frac{d_{o}+d_{i}}{d_{i} cdot d_{o}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f}&= frac{d_{o}+d_{i}}{d_{i} d_{o}}\
f&=frac{d_{i} d_{o}}{d_{o}+d_{i}}\
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
f&= frac{d_{i} cdot d_{o}}{d_{o}+d_{i}}\
f&= frac{22 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} cdot 22 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{22 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}+22 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
f&= frac{22^{2} hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm^{2}}}{2 cdot 22 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
f&= 11 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}
end{align*}
$$
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore f=11 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} $}]
f=11 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
$$
begin{align*}
f&=frac{r}{2}\
f&=frac{infty}{2}\
f&=infty
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f}&= frac{1}{d_{o}}+ frac{1}{d_{i}}\
frac{1}{infty}&= frac{1}{d_{o}}+ frac{1}{d_{i}}\
0&= frac{1}{d_{o}}+ frac{1}{d_{i}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
0 &= frac{1}{d_{o}}+ frac{1}{d_{i}} / – frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{d_{i}}&= – frac{1}{d_{o}}
end{align*}
$$d_i=d_o+delta_i$$
$$d_i=-6-8$$
$$d_i=-14,,rm{cm}$$
Where we took negative values because the distance is behind mirror.
$$frac{1}{d_o}+frac{1}{d_i}=frac{1}{f}$$
From the previous equation we can express $f$:
$$frac{1}{f}=frac{d_i+d_o}{d_od_i}$$
And $f$ is:
$$f=frac{d_od_i}{d_o+d_i}$$
$$f=frac{6cdot (-14)}{6-14}$$
$$boxed{f=10.5,,rm{cm}}$$
$$
begin{align*}
d_{i}&=d_{i_{p}}-8.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
d_{i}&=-6.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}-8.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}\
d_{i}&=-14.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f}&= frac{1}{d_{i}} + frac{1}{d_{o}} \
frac{1}{f}&= frac{d_{o}+d_{i}}{d_{i} cdot d_{o}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
frac{1}{f}&= frac{d_{o}+d_{i}}{d_{i} d_{o}}\
f&=frac{d_{i} d_{o}}{d_{o}+d_{i}}\
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
f&= frac{d_{i} d_{o}}{d_{o}+ d_{i}}\
f&= frac{-14.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} cdot 6.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}{6.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}- 14.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
f&= frac{-84.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm^{2}}}{-8.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}}\
f&= 10.5 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
end{align*}
$$
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore f=10.5 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm} $}]
f=10.5 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{cm}
$$
After the plane mirror is replaced with concave mirror, the image is now $6+8 = 14$ cm behind the mirror
That means $d_i = -14$ and $d_o = 6$
$$
text{color{#4257b2}Use Mirror Equation : $$dfrac{1}{f} = dfrac{1}{d_o}+dfrac{1}{d_i}$$}
$$
$$
dfrac{1}{f} = dfrac{1}{6}+dfrac{1}{-14}
$$
$$
dfrac{1}{f} = dfrac{1}{6}times dfrac{7}{7}-dfrac{1}{14}timesdfrac{3}{3}
$$
$$
dfrac{1}{f} = dfrac{7}{42}-dfrac{3}{42}
$$
$$
dfrac{1}{f} = dfrac{4}{42}
$$
Take reciprocal of both sides
$$
{f} = dfrac{42}{4} = 10.5text{ cm}
$$
text{color{#4257b2}10.5text{ cm}}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
M&<1\
-frac{d_{i2}}{d_{o2}}&-d_{o2}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
|d_{i2}|&> – (-|d_{o2}|)\
|d_{i2}|&> |d_{o2}|\
end{align*}
begin{align*}
&v_{i}=4.7 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m/s}\
&v_{f}=0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m/s}\
&s=6.2 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}\
&g=9.8hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m/s^2}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
m cdot a& =- F_{friction}\
m cdot a& =- mu N\
m cdot a& =- mu m g\
end{align*}
begin{align*}
m cdot a& =- mu m g/: m\
a&=- mu g
end{align*}
begin{align*}
a&=- mu g / : (-g)\
mu&=- frac{a}{g}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
a&=frac{v_{f}^{2}-v^{2}_{i}}{2s}\
a&=frac{(0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m/s})^{2}-(4.7 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m/s})^{2}}{2 cdot 6.2 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}}\
a&=-1.8 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m/s^2}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
mu&=- frac{-1.8 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m/s^2}}{9.8 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m/s^2}}\
mu&=0.2
end{align*}
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore mu=0.2 $}]
mu = 0.2
$$
begin{align*}
&m=1.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{g} Rightarrow m=1.0 cdot 10^{-3} hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{kg}\
&h=1.0 cdot 10^{4} hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}\
&v=70.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m/s}\
&Q=E_{loss}/2\
&g=9.81cdot 10^{4} hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m/s^{2}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
E_{p}&=mgh\
E_{p}&=1.0 cdot 10^{-3} hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{kg} cdot 9.81cdot 10^{4} hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m/s^{2}} cdot 1.0 cdot 10^{4} hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}\
E_{p}&=98.1 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{J}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
E_{k}&=frac{1}{2} mv^{2}\
E_{k}&=frac{1}{2} cdot 1.0 cdot 10^{-3} hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{kg} cdot (70.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m/s})^{2}\
E_{k}&=2.4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{J}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
E_{i}&=E_{f}\
E_{p}&=E_{k}+E_{loss}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
E_{p}&=E_{k}+E_{loss} / – E_{k} \
E_{loss}&=E_{p}-E_{k}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
E_{loss}&=E_{p}-E_{k}\
E_{loss}&=98.1 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{J}- 2.4 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{J}\
E_{loss}&=95.7hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{J}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
Q&= frac{E_{loss}}{2}\
Q&=frac{95.7hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{J}}{2}\
Q&=47.8 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{J}
end{align*}
[ framebox[1.1width]{$ therefore Q=47.8 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{J} $}]
Q=47.8 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{J}
$$
begin{align*}
&A_{1}=0.25 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m^{2}}\
&A_{2}=2 cdot 10^{-5} hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m^{2}}\
&F_{1}=600 cdot 10^{-5} hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{N}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
P_{1}&= frac{F_{1}}{A_{1}}\
P_{1}&= frac{600 cdot 10^{-5} hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{N}}{0.25 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m^{2}}}\
P_{1}&= 2400 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{Pa}
end{align*}
P_{2}= 2400 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{Pa}
$$
begin{align*}
&l=2.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}\
&M_{Moon}=7.34 cdot 10^{22} hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{kg}\
&R_{Moon}=1.74 cdot 10^{6} hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}\
&g_{Earth}=9.81 cdot 10^{6} hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m/s^{2}}\
&G=6.67 cdot 10^{-11}hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{frac{m^{3}}{kg hspace{0.5mm} s^{2}}}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
mg_{Moon}&=G frac{mM_{Moon}}{R_{Moon}^{2}}
end{align*}
$$
begin{align*}
mg_{Moon}&=G frac{mM_{Moon}}{R_{Moon}^{2}} /: m\
g_{Moon}&=G frac{M_{Moon}}{R_{Moon}^{2}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
g_{Moon}&=G frac{M_{Moon}}{R_{Moon}^{2}}\
g_{Moon}&=6.67 cdot 10^{-11}hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{frac{m^{3}}{kg hspace{0.5mm} s^{2}}} frac{7.34 cdot 10^{22} hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{kg}}{(1.74 cdot 10^{6} hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m})^{2}}\
g_{Moon}&=6.67 cdot 10^{-11}hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{frac{m^{3}}{kg hspace{0.5mm} s^{2}}} cdot 2.42 cdot 10^{10}hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{kg/m^{2}}\
g_{Moon}&=1.62 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m/s^{2}}
end{align*}
begin{align*}
T_{Moon}&=2 pi sqrt{frac{l}{g_{Moon}}}\
T_{Moon}&=2 pi sqrt{frac{2.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}}{1.62 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m/s^{2}}}}\
T_{Moon}&=6.98hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{s}
end{align*}
T_{Earth}&=2 pi sqrt{frac{l}{g_{Earth}}}\
T_{Earth}&=2 pi sqrt{frac{2.0 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m}}{9.81 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{m/s^{2}}}}\
T_{Earth}&=2.84hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{s}
end{align*}
$$
T_{Earth}=2.84 hspace{0.5mm} mathrm{s}
$$
$$
begin{align*}
frac{v}{4L_{closed}}&=frac{v}{2L_{open}}/ : v/2\
L_{open}&=2L_{closed}
end{align*}
$$
$A_{R}$ = $Asin(omega_{GR}t)$;
Beat ferquency = $(omega_{G}-omega_{R})/2$
This resultant is the frequency of yellow light

