All Solutions
Page 117: Standardized Test Practice
$$
begin{align*}
v_i&=0 mathrm{m/s} \
v_f&=10 mathrm{m/s} \
t_i&=0 mathrm{s} \
t_f&=4 mathrm{s} \
a&=? \
\
a&=dfrac{v_f – v_i}{t_f – t_i} \
&=dfrac{10 mathrm{m/s}-0 mathrm{m/s}}{4 mathrm{s}-0 mathrm{s}} \
&=2.5 mathrm{m/s^2}
end{align*}
$$
Known:
$$
begin{align*}
t&=4 mathrm{s} \
a&=2.5 mathrm{m/s^2} \
end{align*}
$$
Unknown:
$$
begin{align*}
s&=? \
\
s&=dfrac{acdot t^2}{2} \
&=dfrac{2.5 mathrm{m/s^2}cdot 4^2 mathrm{s^2}}{2} \
&=boxed{20 mathrm{m}}
end{align*}
$$
s=20 mathrm{m}
$$
$v_f = 0.0 + (2.5) (10)$
$v_f = 25 m/s$
We should convert m/s to km/h:
$1 m/s = 3.6 km/h$
$$
==> v_f = (25*3.6) km/h = 90 km/h
$$
90 km/h
$$
The acceleration $a$ stands for change in velocity $v$ over time interval $t$, or: $dfrac{v}{t}$. If we want acceleration to be constant, we want $dfrac{v}{t}$ to be the same value for each point on the graph. This is represented with the straight line given on the graph $-$ so the acceleration
on velocity-time graph is the rise over run of the given line. We can thus calculate this acceleration, and find the velocity for the given time $t=10mathrm{~sec}$.
$$begin{align}
a=mathrm{dfrac{rise}{run}}
end{align}$$
To find this let’s use the points $(0,0)$ and $(4,10)$. Thus, the rise is equal to:
$$mathrm{rise}=10-0=10$$
And run is equal to:
$$mathrm{run}=4-0=4$$
$$begin{align}
a&=mathrm{dfrac{rise}{run}} nonumber
\&=dfrac{10}{4} nonumber
\&=2.5mathrm{~dfrac{m}{s^2}}
end{align}$$
With this acceleration, we can now find the velocity $v$ at given time $t=10mathrm{~sec}$.
$$begin{align}
a=dfrac{v-v_0}{t-t_0}
end{align}$$
Where $v$ is the velocity at time $t$ and $v_0$ is the velocity at $t_0$.
$$begin{align}
a&=dfrac{v-v_0}{t-t_0} nonumber
\&=dfrac{v}{t}rightarrow v=acdot t
end{align}$$
Now we can finally calculate the velocity $v$ using equation $(4)$.
$$begin{aligned}
v&=acdot t
\&=2.5cdot 10
\&={25mathrm{~dfrac{m}{s}}}
end{aligned}$$
Converting to $mathrm{dfrac{km}{h}}$, we get:
$$begin{aligned}
v&={25mathrm{~dfrac{m}{s}}}cdot 3600cdotdfrac{1}{1000}=boxed{90mathrm{~dfrac{km}{h}}}
end{aligned}$$
Known:
$$
begin{align*}
m_c&=30 mathrm{kg} tag{average mass of child} \
m_p&=60 mathrm{kg} tag{ average mass of parent} \
F_c&=150 mathrm{N} tag{average force of child} \
F_p&=475 mathrm{kg} tag{average force of parent} \
N_c&=13 \
N_p&=5 \
end{align*}
$$
Unknown:
$$
begin{align*}
a&=? \
\
F_{net}&=N_pcdot F_p – N_ccdot F_c \
&=5cdot 475 mathrm{N} – 13cdot 150 mathrm{N} \
&=425 mathrm{N hat{E}} tag{ $mathrm{hat{E}}$ is direction (Eastward)} \
\
F&=mcdot a \
a&=dfrac{F}{m} \
&=dfrac{F_{net}}{N_ccdot m_c+N_pcdot m_p } \
&=dfrac{425 mathrm{N hat{E}}}{13cdot 30 mathrm{kg}+5cdot 60 mathrm{kg}} \
&=boxed{0.6159 mathrm{m/s^2 hat{E}}}
end{align*}
$$
$F = (225)*(1.62)$
$$
F = 364 m/s^2
$$
364 m/s^2
$$
– Probe mass: $m=225mathrm{~kg}$
– Acceleration: $a_{moon}=1.62mathrm{~dfrac{m}{s^2}}$
**Objective**
– Find the weight $W$.
The weight of an object $W$ is defined as a force that the object experiences due to gravity $F_g=mcdot a_{grav}$. Where $a_{grav}$ is the acceleration constant at the place of measurement (in case of measuring on Earth: $a_{grav}=gapprox9.81mathrm{~dfrac{m}{s^2}}$).
In our case: $a_{grav}=a_{moon}$. Using definition of weight, we can now simply calculate.
$$begin{aligned}
W=F_g&=mcdot a_{grav}
\&=225cdot 1.62
\&approxboxed{364mathrm{~N}}
end{aligned}$$
So the answer is $mathrm{B}$.
Known:
$$
begin{align*}
m_C&=45 mathrm{kg} \
m_S&=3.2 mathrm{kg} \
g&=9.8 mathrm{m/s^2} \
end{align*}
$$
Unknown:
$$
begin{align*}
F_T&=? \
\
F_T&=F_{gC}+F_{gS} \
&=m_Ccdot g+m_Scdot g \
&=gcdot (m_C+m_S) \
&=9.8 mathrm{m/s^2}cdot (45 mathrm{kg}+3.2 mathrm{kg}) \
&=boxed{472.4 mathrm{N}}
end{align*}
$$
Known:
$$
begin{align*}
F_T&=220 mathrm{N} \
F_G&=472.4 mathrm{N} tag{Note that we included the weight of both the swing and the child in $F_g$} \
end{align*}
$$
Unknown:
$$
begin{align*}
F_n&=? \
\
F_n&=F_g-F_T \
&=472.4 mathrm{N}-220 mathrm{N} \
&=boxed{252.4 mathrm{N}}
end{align*}
$$
Known:
$$
begin{align*}
m&=16 mathrm{kg} \
v_i&=0 mathrm{m/s} \
v_f&=6 mathrm{m/s} \
t_i&=0 mathrm{s} \
t_f&=3 mathrm{s} \
end{align*}
$$
Unknown:
$$
begin{align*}
F&=? \
\
a&=dfrac{v_f-v_i}{t_f-t_i} \
&=dfrac{6 mathrm{m/s}}{3 mathrm{s}} \
&=2 mathrm{m/s^2} \
\
F&=mcdot a \
&=16 mathrm{kg}cdot 2 mathrm{m/s^2} \
&=boxed{32 mathrm{N}}
end{align*}
$$
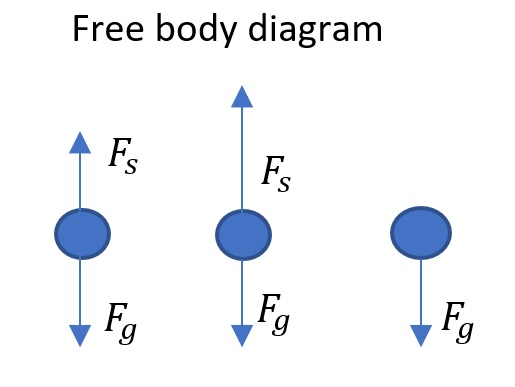
$$
begin{align*}
F_g& tag {weight} \
F_s& tag{force shown on scale} \
\
F_s&=-F_g+F \
F_s&=-mcdot -g +mcdot a\
&=mcdot (g+a)
end{align*}
$$

