
All Solutions
Section 1-2: Function Notation
Simplify substitute the given value of $x$
a) $f(2)=2-3(2)=2-6=-4$
b) $f(0)=2-3(0)=2-0=2$
c) $f(-4)=2-3(-4)=14$
d) $fleft(dfrac{1}{2}right)=2-3left(dfrac{1}{2}right)=dfrac{1}{2}$
e) $f(a)=2-3a$
f) $f(3b)=2-3(3b)=2-9b$
b) $2$
c) $14$
d) $dfrac{1}{2}$
e) $2-3a$
f) $2-9b$
b: $2-3(0)=2$
c: $2-3(-4)=2+12=14$
d: $2-3(0.5)=2-1.5=0.5$
e: $2-3(a)=2-3a$
f: $2-3(3b)=2-9b$
a) when $x=1$, $y=2$ so $f(1)=2$
b) when $x=-2$, $y=-2$ so $g(-2)=-2$
c) $f(4)-g(-2)=-1-4=-5$
d) when $f(x)=-3$, $x=-3$ or $-4$
b) 4
c) $-5$
d) $-3$ or $-4$
a) We set $x=0$ as the time at 11:00 am where the volume is 1.2 L=1200 mL. Since the volume of milk is decreasing by $3$ mL/min.
$f(x)=1200-3x$
b) At 1:00 pm, 2 hours have passed since 11: am, thus $x=2times 60=120$
$f(120)=1200-3(120)=840$ mL
c) We shall find $x$ such that $f(x)=450$
$450=1200-3x$
$3x=1200-450$
$x=dfrac{1200-450}{3}$
$x=250$
Thus, there will be 450 mL left in the carton 250 minutes (4 hours and 10 minutes) after 11:00 which corresponds to 3:10 pm.
b) $840$ mL
c) $3:10$ pm
Let be $x$ number of minutes
We have 1200 mL of milk, every minute leaking from a carton 3 mL
Equation of this situation is :
$$
f(x)=1200-3x
$$
From 11:00 a.m. to 1:00 p.m 120 minutes passed
we know $x$ represent number of minutes, so, how much will be left in the carton at 1:00 p.m can calculate use function in part a)
Substitute $x=120$ in $f(x)=1200-3x$
$f(120)=1200-3cdot120$
$f(120)=1200-360=840$
Solution is: 840 mL will be left in the carton at 1:00 p.m
$1200-3x=450$
$3x=1200-450$
$3x=750$
$x=250$
There are 1200 mL milk in the carton at 11:00 a.m. so when there are 450 mL of milk left, a total of 1200-450 = 750 mL of milk have leaked out. The rate of the leak is 3 mL/min, so it took 250 minutes for that amount to leak out.
1 hour has 60 minutes, so if we divide 250 min by 60 min we get 4 hours and 10 minutes.
So it was 3:10 pm when 450 mL of milk are left in the carton.
i) $f(-1)$ represents the value of the function when the input is $x=-1$.
Substitute $x=-1$ in $f(x)=(x-2)^{2}-1$
$f(-1)=(-1-2)^{2}-1$
$f(-1)=(-3)^{2}-1$
$f(-1)=9-1$
$f(-1)=8$
ii) $f(3)$ represents the value of the function when the input is $x=3$.
Substitute $x=3$ in $f(x)=(x-2)^{2}-1$
$f(3)=(3-2)^{2}-1$
$f(3)=(1)^{2}-1$
$f(3)=1-1$
$f(3)=0$
iii) $f(1.5)$ represents the value of the function when the input is $x=1.5$.
Substitute $x=1.5$ in $f(x)=(x-2)^{2}-1$
$f(1.5)=(1.5-2)^{2}-1$
$f(1.5)=(-0.5)^{2}-1$
$f(1.5)=0.25-1$
$f(1.5)=0.75$
i) $f(-1)$ represents the value of the function when the input is $x=-1$.
Substitute $x=-1$ in $f(x)=2+3x-4x^{2}$
$f(-1)=2+3(-1)-4(-1)^{2}$
$$
f(-1)=2-3-4
$$
$$
f(-1)=-5
$$
ii) $f(3)$ represents the value of the function when the input is $x=3$.
Substitute $x=3$ in $f(x)=2+3x-4x^{2}$
$f(3)=2+3cdot3-4cdot3^{2}$
$f(3)=2+9-4cdot9$
$f(3)=2+9-36$
$$
f(3)=-25
$$
iii) $f(1.5)$ represents the value of the function when the input is $x=1.5$.
Substitute $x=1.5$ in $f(x)=2+3x-4x^{2}$
$f(1.5)=2+3cdot1.5-4(1.5)^{2}$
$f(1.5)=2+4.5-4cdot2.25$
$f(1.5)=-2+4.5-9$
$$
f(1.5)=-2.5
$$
b) $-5$, $-25$, $-2.5$
Substitute $x=-3$ in $f(x)=dfrac{1}{2x}$:
$$
f(-3)=dfrac{1}{2cdot(-3)}=dfrac{1}{-6}=-dfrac{1}{6}
$$
Substitute $x=0$ in $f(x)=dfrac{1}{2x}$:
$f(0)=dfrac{1}{2cdot0}=dfrac{1}{0}$
We know dividing by zero is undefined, so , function $f(x)$ is not defined for $x=0$.
Substitute $x=1$ and $x=3$ in $f(x)=dfrac{1}{2x}$ and calculate:
$$
f(1)-f(3)=dfrac{1}{2cdot1}-dfrac{1}{2cdot3}=dfrac{1}{2}-dfrac{1}{6}=dfrac{1cdot3-1}{6}=dfrac{3-1}{6}=dfrac{2}{6}=dfrac{1}{3}
$$
Substitute $x=dfrac{1}{4}$ and $x=dfrac{3}{4}$ in $f(x)=dfrac{1}{2x}$ and calculate:
$$
f(dfrac{1}{4})+f(dfrac{3}{4})=dfrac{1}{2cdotdfrac{1}{4}}+dfrac{1}{2cdotdfrac{3}{4}}=dfrac{4}{2}+dfrac{2}{3}=dfrac{4cdot3+2cdot2}{6}=dfrac{12+4}{6}=dfrac{16}{6}=dfrac{8}{3}=2dfrac{2}{3}
$$
b) undefined
c) $dfrac{1}{3}$
d) $2dfrac{2}{3}$
Domain of the function is $D_{f}=left{-2,0,2,3,5,7 right}$
Range of the function is $R=left{ 1,2,3,4,5right}$
i) $f(3)=4$
ii) $f(5)=2$
iii) $f(5-3)=f(2)=5$
iv) $f(5)-f(3)=2-4=-2$
If $x=3$, then $y=f(3)=4$
If $x=5$, then $y=f(5)=2$
If $x=2$, then $y=f(2)=5$
b) i) 4 ii) 2 iii) 5 iv) $-2$
b: $2(b+1)-5=2b+2-5=2b-3$
c: $2(3c-1)-5=6c-2-5=6c-7$
d: $2(2-5x)-5=4-10x-5=-10x-1$
b) $2b-3$
c) $6c-7$
d) $-10x-1$
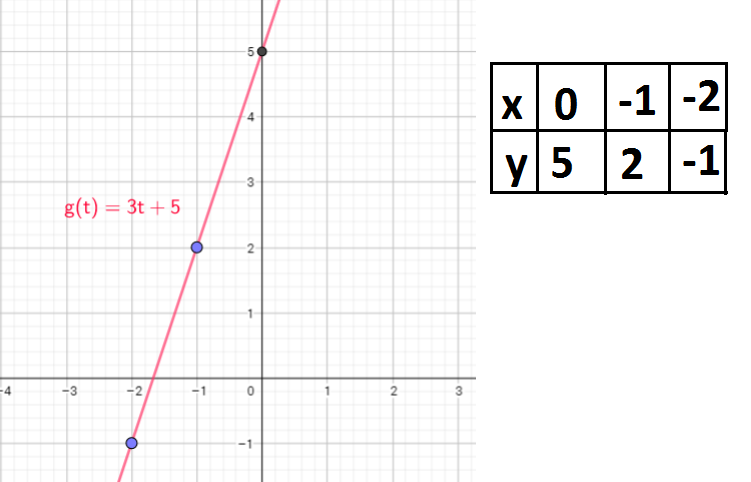
If $x=-2$, then $g(-2)=3(-2)+5=-6+5=-1$
If $x=-1$, then $g(-1)=3(-1)+5=-3+5=2$
If $x=0$, then $g(0)=3cdot0+5=0+5=5$
That means function passes through points $(-2,-1), (-1,2)$ and $(0,5)$
i) $g(0)=3cdot0+5=0+5=5$
ii) $g(3)=3cdot3+5=9+5=14$
iii) $g(1)-g(0)=3cdot1+5-(3cdot0+5)=3+5-(0+5)=8-5=3$
iv) $g(2)-g(1)=3cdot2+5-(3cdot1+5)=6+5-(3+5)=11-8=3$
v) $g(1001)-g(1000)=3cdot1001+5-(3cdot1000+5)=3003+5-(3000+5)=3008-3005=3$
vi) $g(a+1)-g(a)=3(a+1)+5-(3a+5)=3a+3+5-3a-5=3$
b) i) 5
ii) 14
iii) 3
iv) 3
v) 3
vi) 3
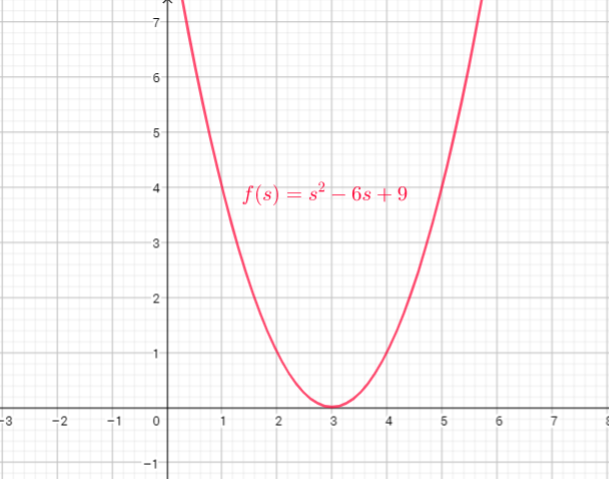
If $x=-2$, then $f(-2)=(-2)^{2}-6(-2)+9=4+12+9=25$
If $x=-1$, then $f(-1)=(-1)^{2}-6(-1)+9=1+6+9=16$
If $x=0$, then $f(0)=(0)^{2}-6cdot0+9=0+0+9=9$
If $x=2$, then $f(2)=(2)^{2}-6cdot2+9=4-12+9=1$
If $x=1$, then $f(1)=(1)^{2}-6cdot1+9=1-6+9=4$
Now, we can create table:
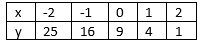
i) To find $f(0)$ , plug in 0 wherever $s$ occures in the equation of $f(s)$ and simplify to get $f(0)$
$f(0)=0^{2}-6cdot0+9=0-0+9=9$
ii) To find $f(1)$ , plug in 1 wherever $s$ occures in the equation of $f(s)$ and simplify to get $f(1)$
$f(1)=1^{2}-6cdot1+9=1-6+9=4$
iii) To find $f(2)$ , plug in 2 wherever $s$ occures in the equation of $f(s)$ and simplify to get $f(2)$
$f(2)=2^{2}-6cdot2+9=4-12+9=1$
iv) To find $f(3)$ , plug in 3 wherever $s$ occures in the equation of $f(s)$ and simplify to get $f(3)$
$f(3)=3^{2}-6cdot3+9=9-18+9=0$
v) $left(f(2)-f(1)right)-left(f(1)-f(0) right)=left(1-4 right)-left( 4-9right)=-3-(-5)=-3+5=2$
vi) $left(f(3)-f(2)right)-left(f(2)-f(1) right)=left(0-1 right)-left( 1-4right)=-1-(-3)=-1+3=2$
constant for a quadratic function.
hline
$s$ & 0 & 1 & 2 & 3 \ hline
$f(s)$ & 9 & 4 & 1 & 0 \ hline
end{tabular}\\
b) i) 9 $text{ }$ ii) 4 $text{ }$ iii) 1 $text{ }$ iv) 0 $text{ }$ v) 2 $text{ }$ vi) 2\
c) They are the same as they represent second differences, which are constant for a quadratic function.\\
To find $f(-2)$ , plug in -2 wherever $x$ occures in the equation of $f(x)$ and simplify to get $f(-2)$
$$
f(-2)=2(-2-3)^{2}-1=2(-5)^{2}-1=2cdot25-1=50-1=49
$$
Now we can conclude $f(-2)$ is the y-coordinate of the point on the graph with x-coordinate -2
many points on the graph there were
for each value of $x$. Any vertical line drawn on the
graph intersects the graph at only
one point. This is the graph of a
function
b) The $y$-coordinate of the point on the graph with $x$-coordinate $-2$
c) domain = ${ xin bold{R}}$ , range = ${ yinbold{R};|;ygeq -1}$
d) It passes the vertical-line test.
$-6=4-5x$
$5x=4+6$
$5x=10$
$dfrac{5x}{5}=dfrac{10}{5}$
$x=2$
$2=4-5x$
$5x=4-2$
$5x=2$
$dfrac{5x}{5}=dfrac{2}{5}$
$$
x=dfrac{2}{5}
$$
$0=4-5x$
$5x=4$
$dfrac{5x}{5}=dfrac{4}{5}$
$$
x=dfrac{4}{5}
$$
$dfrac{3}{5}=4-5x$
$5cdot dfrac{3}{5}=5cdot(4-5x)$
$3=20-25x$
$25x=20-3$
$25x=17$
$x=dfrac{17}{25}$
text{a) 2};;;; ;; text{b)} dfrac{2}{5};;;;;; text{c)} dfrac{4}{5};;;;;;text{d)} dfrac{17}{25}
$$
The daily rental cost as a function of the number of kilometres travelled is $f(x)=0.15x+50$ .
The rental cost :
$f(472)=50+0.15cdot472=50+70.8=120.8$ dollars
$f(x)=0.15x+50$
$80=0.15x+50$
$0.15x=80-50$
$0.15x=30$ divide both side by 0.15
$x=200$.
Solutin is : We can drive 200 km in a day for 80 dollars.
b) $$120.80$
c) 200 km
Function is $f(x)=(24-3x)x$
$f(3)=(24-3cdot3)cdot3=(24-9)cdot3=15cdot3=45$
To find $f(-5)$ , plug in -5 wherever $x$ occures in the equation of $f(x)$ and simplify to get $f(-5)$
$f(-5)=(24-3cdot(-5))cdot(-5)=(24+15)cdot(-5)=39cdot(-5)=-195$
To find $f(10)$ , plug in 10 wherever $x$ occures in the equation of $f(x)$ and simplify to get $f(10)$
$f(10)=(24-3cdot10)cdot10=(24-30)cdot10=-6cdot10=-60$
Our quadratic function is $f(x)=(24-3x)x$ or $f(x)=-3x^{2}+24x$
There is $a=-3,$ and $b=24$. Now can calculate:
$dfrac{-b}{2a}=dfrac{-24}{2(-3)}=dfrac{-24}{-6}=4$
Now we need calculate $f(-dfrac{b}{2a})$:
$f(dfrac{-b}{2a})=f(4)=(24-3cdot4)cdot4=(24-12)cdot4=12cdot4=48$
Now can conclude: Quadratic function
$f(x)=(24-3x)x$ has maximum in the point $(4,48)$. That means, the maximum result possible is 48.
b) 45, $-195$, $-60$
c) 48
(1) the other side of the arch is 281 meters away
(2) the top of the arch is 71 meters above the river
Since the arch is 281 meters wide, the distance from its center to either of its x-intercept is $dfrac{281}{2}=140.5$. Also, the maximum height of 71 m shall occur at $x=0$ (at the axis of symmetry). Therefore, the equation can be written as
$f(x)=71-ax^2$
We must find the value of $a$ such that $f(x)=0$ when $x=140.5$
$0=71-acdot(140.5^2)implies a=dfrac{71}{140.5^2}=0.003596$
Therefore, the equation of the parabola is
$f(x)=71-0.0036x^2$
Note that other forms can be obtained if the axis of symmetry is set differently.
Thus, we can express the function is factored form
$y=a(x-0)(x-281)$
$y=ax(x-281)$
Now, we shall find the value of $a$
Since this is a symmetric parabolic arch, the maximum point must occur halfway between $x=0$ and $281$ which is at $x=140.5$ where $y=71$ m
Substituting this point to the equation to find $a$, we can get
$y=ax(x-281)$
$71=a(140.5)(140.5-281)$
$a=dfrac{71}{(140.5)(140.5-281)}=-0.0036$
Therefore, the equation of the parabola is
$f(x)=-0.0036x(x-281)$ or
$$
f(x)=0.0036x(281-x)
$$
f(x)=0.0036x(281-x)
$$
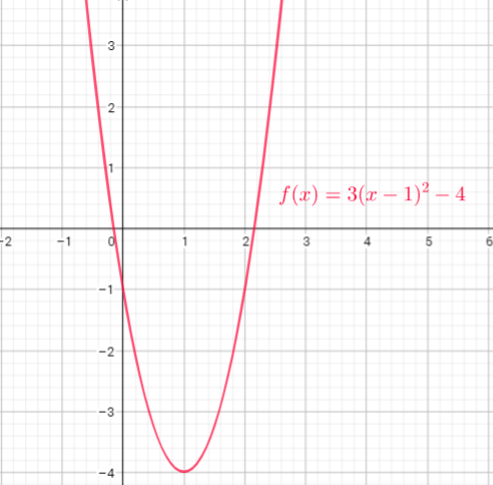
We need start from on x-axis where $x=-1$, move up to curve, then across to y-axis
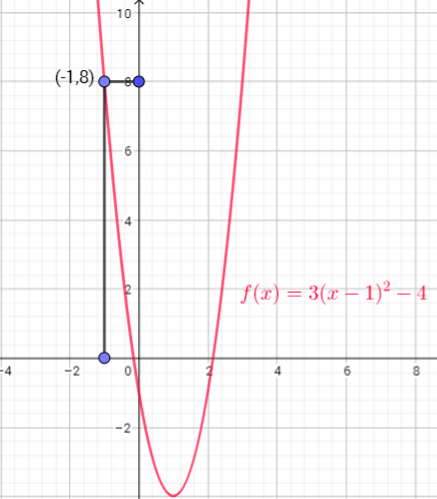
i) To find $f(2)-f(1)$ , plug in 2 and 1 wherever $x$ occures in the equation of $f(x)$ and simplify to get $f(2)-f(1)$
$f(2)-f(1)=[3(2-1)^{2}-4]-[3(1-1)^{2}-4]=[3cdot1^{2}-4]-[3cdot0^{2}-4]=[3-4]-[0-4]=-1+4=3$
ii) To find $2f(3)-7$ , plug in wherever $x$ occures in the equation of $f(x)$ and simplify to get $2f(3)-7$
$2f(3)-7=2cdot(3(3-1)^{2}-4)-7=2cdot(3cdot2^2-4)-7=2cdot(12-4)-7=2cdot8-7=16-7=9$
iii) To find $f(1-x)$ , plug in $1-x$ wherever $x$ occures in the equation of $f(x)$ and simplify to get $f(1-x)$
$$
f(1-x)=3(1-x-1)^{2}-4=3(-x)^{2}-4=3x^{2}-4
$$
b) The expression $f(-1)$ represents the distance of the graph from the $x$-axis when $x=-1$.
We can find it by creating a vertical line at $x=-1$ and the $y$-coordinate of the point that intersects with the graph is $f(-1)$
a) If we wont determine the values of $x$ for $f(x)=0$ we need solve equation $f(x)=0$:
$f(x)=0$
$x^{2}+2x-15=0$
$(x+5)(x-3)=0$
$x+5=0$ or $x-3=0$
$x=-5$ or $x=3$
$f(x)=-12$
$x^{2}+2x-15=-12$
$x^{2}+2x-15+12=0$
$x^{2}+2x-3=0$
$(x+3)(x-1)=0$
$x+3=0$ or $x-1=0$
$x=-3$ or $x=1$
$f(x)=-16$
$x^{2}+2x-15=-16$
$x^{2}+2x-15+16=0$
$x^{2}+2x+1=0$
$(x+1)^{2}=0$
$x+1=0$
$$
x=-1
$$
b) $1,-3$
c) $-1$
$g(x)=2-x$
satisfies the given condition.
$3a+1=2-a$
$3a+a=2-1$
$4a=1$
$dfrac{4a}{4}=dfrac{1}{4}$
$$
a=dfrac{1}{4}
$$
$3(a^2)+1=2-(2a)$
$3a^2+2a-1=0$
$(3a-1)(a+1)=0$
$3a-1=0$ or $a+1=0$
$a=dfrac{1}{3}$ or $-1$
b.) $a=dfrac{1}{3}$ or $-1$
Linear function passes through points $(200,285)$ and $(60,75)$.
Now we can calculate slope
$m=dfrac{200-60}{285-75}=dfrac{140}{210}=dfrac{14}{21}=dfrac{2}{3}$
Use coordinate of one point and slope we can determine $n$:
$200=dfrac{2}{3}cdot285+n$
$n=200-190$
$n=10$
Linear function that will convert 285 to 200 and 75 to 60 is $y=dfrac{2}{3}x+10$
, now we can determine $y$:
$y=dfrac{2}{3}cdot95+10=dfrac{190}{3}+dfrac{30}{3}=dfrac{210}{3}=73dfrac{1}{3}$
If $x=175$, then $y=dfrac{2}{3}cdot175+10$
, now we can determine $y$:
$y=dfrac{2}{3}cdot175+10=dfrac{350}{3}+dfrac{30}{3}=dfrac{380}{3}=126dfrac{2}{3}$
If $x=215$, then $y=dfrac{2}{3}cdot215+10$
, now we can determine $y$:
$y=dfrac{2}{3}cdot215+10=dfrac{430}{3}+dfrac{30}{3}=dfrac{460}{3}=153dfrac{1}{3}$
If $x=255$, then $y=dfrac{2}{3}cdot255+10$
, now we can determine $y$:
$$
y=dfrac{2}{3}cdot255+10=dfrac{510}{3}+dfrac{30}{3}=dfrac{540}{3}=180
$$
Remember that the slope of a line is
$m=dfrac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1}$
$m=dfrac{60-200}{75-285}=dfrac{2}{3}$
Now, we can use the point slope form
$y-y_1=m(x-x_1)$
$y-200=dfrac{2}{3}(x-285)$
$y=dfrac{2}{3}(x-285)+200$
$y=dfrac{2}{3}x-190+200$
$$
y=dfrac{2}{3}x+10
$$
$x=95$ , $y=dfrac{2}{3}(95)+10=73dfrac{1}{3}$
$x=175$ , $y=dfrac{2}{3}(175)+10=126dfrac{2}{3}$
$x=215$ , $y=dfrac{2}{3}(215)+10=153dfrac{1}{3}$
$x=255$, $y=dfrac{2}{3}(255)+10=180$
b) $73dfrac{1}{3}$ , $126dfrac{2}{3}$ , $153dfrac{1}{3}$ , $180$
$f(1)=1$
$f(x+1)=f(x)+3x(x+1)+1$
To evaluate the function at different values of $x$, simply substitute the $x$-values to the function.
$f(x+1)=f(x)+3x(x+1)+1$
$f(2)=f(1+1)=f(1)+3(1)(1+1)+1=1+3(1)(2)+1=8$
$f(3)=f(2+1)=f(2)+3(2)(2+1)+1=8+3(2)(3)+1=27$
$f(4)=f(3+1)=f(3)+3(3)(3+1)+1=27+3(3)(4)+1=64$
$f(5)=f(4+1)=f(4)+3(4)(4+1)+1=64+3(4)(5)+1=125$
$f(6)=f(5+1)=f(5)+3(5)(5+1)+1=126+3(5)(6)+1=216$
$f(x)=x^3$
We can also verify this by
$f(x+1)=(x+1)^3$
$=x^3+3x^2+3x+1$
$=x^3+3x(x+1)+1$
Substitute $x^3=f(x)$
$$
f(x+1)=f(x)+3x(x+1)+1
$$
b) $f(x)=x^3$

