
All Solutions
Page 78: Chapter Self-Test
corresponding element in the range, so the relation
is a function.
Domain=$left{ -5,-2,0,3right}$
Range=$left{-1, 1,7 right}$.
Answer is: $text{textcolor{#4257b2}{relation is a function}}$.
If we want to find a domain, we put the expression inside the square root greater than or equal to zero and solve the inequality:
$$
begin{align*}
x+2&geq0\
x&geq-2\
end{align*}
$$
So, Domain $=left{xin R| xgeq -2 right}$
Range is a set of all reall positive number
Range=$left{ yin R| ygeq0right}$
Answer is: $text{textcolor{#4257b2}{relation is a function}}$
b) Relation is a function.
a) incandescent bulb: $f(x)=0.65+0.004x$
fluorescent bulb: $g(x)=3.50+0.001x$
domain = ${ xinbold{R};|;xgeq 0}$
The cost does not have upper limit but it cannot be less than the initial cost (greater than or equal to the initial cost)
$f(x)$: range = ${ yinbold{R};|;ygeq 0.65}$
$g(x)$: range = ${ yinbold{R};|;ygeq 3.50}$
$3.50+0.001x< 0.65+0.004x$
$0.001x-0.004x<0.65-3.50$
$-0.003xdfrac{2.85}{0.003}implies x>950$
Thus, the fluorescent is cheaper after 950 hours.
running hours per year = 365$times 6=2190$
incandescent: $f(2190)=0.65+0.004(2190)=$9.41$
fluorescent: $g(2190)=3.50+0.001(2190)=$5.69$
Cost difference = $9.41-5.69=3.72$
Therefore, after one year, the fluorescent lamp is cheaper than incandescent lamp by $$3.72$
b) f: domain = ${ xinbold{R};|;xgeq 0}$ , range = ${ yinbold{R};|;ygeq 0.65}$
g: domain = ${ xinbold{R};|;xgeq 0}$ , range = ${ yinbold{R};|;ygeq 3.50}$
c) 950 hours
d) Fluorescent lamp is $$3.72$ cheaper than incandescent lamp after one year.
$f(x)$ can take real values if the denominator of $f(x)$ is not zero because division by zero is not allowed in mathematics:
$xne2$
Solve the above inequality for to obtain the domain: $x ≠ 2$
So,$text{textcolor{#4257b2}{ Domain= $left{xin R | xne2 right}$}}$
The range of the function is same as the domain of the inverse function. So, to find the range determine the inverse of the function.
Interchange the $x$ and $y$ :
$x=dfrac{1}{y-2}$
Solving for $y$ we get:
$$
begin{align*}
x=&dfrac{1}{y-2}\
y-2=dfrac{1}{x}\
y=dfrac{1}{x}+2\
end{align*}
$$
So, the inverse function is $f^{-1}(x)=dfrac{1}{x}+2$
The excluded value in the domain of the inverse function can be determined byequating the denominator to zero. So, the domain of the inverse function is the set of real numbers except 0 .
$text{textcolor{#4257b2}{Range$=left{yin R | yne0 right}$ }}$.
If we want to find domain we put the expression inside the square root greater than or equal to zero and solve this inequality:
$$
begin{align*}\
&3-xgeq0\
-xgeq-3\
xleq-3\
end{align*}
$$
$text{textcolor{#4257b2}{Domain=$left{ xin R | xleq -3right}$}}$
Now, we need find range of the function:
The range of values of $sqrt{3-x}$ may be written as an inequality:
$sqrt{3-x}geq0$
Then, subtract 4 from both sides of the above inequality to obtain:
$sqrt{3-x}-4leq-4$
The range of values of the expression on the left side of the inequality, which is also the range of the given function, is given by the interval $(-infty, -4]$. So,
$$
text{textcolor{#4257b2}{Range=$left{ yin R | yleq-4right}$}}
$$
Domain of this function is the set of all real numbers.
$$
text{textcolor{#4257b2}{Domain=$left{xin R right}$}}
$$
The range of values of $|x+1|$ may be written as an inequality:
$|x+1|geq0$
Multiply both sides by $-1$ of the above inequality to obtain:
$-|x+1|leq0$
Then,add 3 to both sides of the above inequality to obtain:
$-|x+1|+3leq3$
This means, $text{textcolor{#4257b2}{Range=$left{yin R | yleq-3right}$}}$
b) Domain$=left{ x in R | xleq-3right}$ , Range$=left{yin R | yleq-4 right}$
c) Domain$=left{xin R right}$ , Range$=left{yin R | yleq-3 right}$
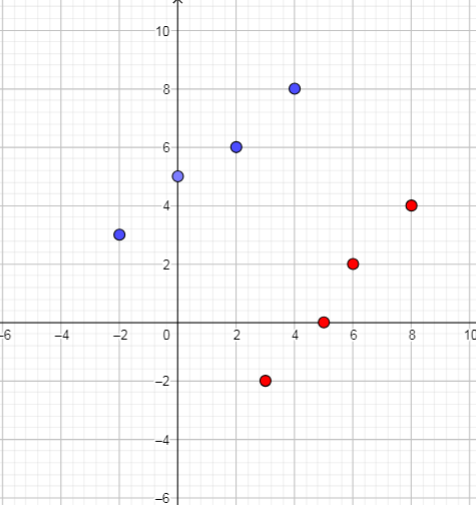
The inverse function we can determine if we switch the $x$ and $y$ coordinates of each point.
$text{textcolor{#c34632}{Inverse function is $left{(3,-2), (5,0), (6,2), (8,4) right}$}}$
We know, the domain is all the $x$-values, and the range is all the $y$-values. Use that, we get:
$text{textcolor{#4257b2}{Function}}$: Domain$=left{-2,0,2,4 right}$, Range$=left{ 3,5,6,8right}$
$text{textcolor{#c34632}{Inverse function}}$: Domain$=left{3,5,6,8 right}$, Range$=left{ -2,0,2,4right}$
This is a linear function.
Now determine the inverse of the function.
Interchange the $x$ and $y$ :
$x=3-4x$
Solving for $y$ we get:
$$
begin{align*}
x&=3-4y\
x-3&=-4y tag{text{subtract 3 from both sides}}\
dfrac{x-3}{-4}&=y tag{text{divide both sides by -4}}\
y&=dfrac{3-x}{4} tag{text{simplify}}\
end{align*}
$$
So, the inverse function is $text{textcolor{#c34632}{ $f^{-1}(x)=dfrac{3-x}{4}$}}$
$text{textcolor{#4257b2}{Function}}$: Domain$=left{xin R right}$, Range$=left{ yin Rright}$
$text{textcolor{#c34632}{Inverse function}}$: Domain$=left{xin R right}$, Range$=left{ yin Rright}$.
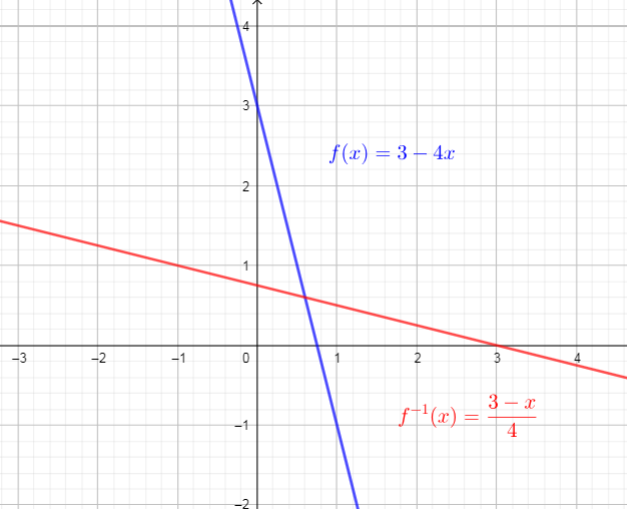
b) Inverse function is: $f^{-1}(x)=dfrac{3-x}{4}$
check for answers
b) $f(x) = 1500+0.04(x-2500)$ for $xgeq 2500$
The domain of the inverse is the range of the original function which is $ygeq 1500$
$y=1500+0.04(x-2500)$
$x=1500+0.04(y-2500)$
$y-2500=dfrac{x-1500}{0.04}$
$y=25(x-1500)+2500$
$f^{-1}(x)=25(x-1500)+2500$ ; $xgeq 1500$
$$
f^{-1}(1740)=25(1740-1500)+2500=$8500
$$
b) $f(x)=0.04(x-2500)+1500$ for $xgeq 2500$
c) The graph has been plotted in the answers.
d) $f^{-1}(x)=25(x-1500)+2500$ for $xgeq 1500$
e) $f^{-1}(x)(1740)=25(1740-1500)+2500=$8500$
b) $k=-3$.
The first, we need determine $a, k, c$ and $d$.
The graph of $f(x)=sqrt{x}$ is vertically compressed by the factor $dfrac{1}{2}$ $longrightarrow$ $y=dfrac{1}{2}sqrt{x}$
then reflected in the $y$-axis $longrightarrow$ $y=dfrac{1}{2}sqrt{-x}$
and then translated 2 units right $longrightarrow$ $y=dfrac{1}{2}sqrt{-(x-2)}=$
Use these steps, we get new function:
$color{#4257b2}{y=dfrac{1}{2}sqrt{-(x-2)}=dfrac{1}{2}f(-(x-2))}$
If we compare this function with $y=af[k(x-d)]+c$, we can conclude that:
$a=dfrac{1}{2}, k=-1, c=0, d=2$
We can identify the domain and range of functions is by using graphs. Because the domain refers to the set of possible input values, the domain of a graph consists of all the input values shown on the $x$-axis. The range is the set of possible output values, which are shown on the $y$-axis.
$text{textcolor{#4257b2}{Domain$=left{xin R | xleq2 right}$}}$
$text{textcolor{#4257b2}{Range$=left{yin R | ygeq0 right}$}}$
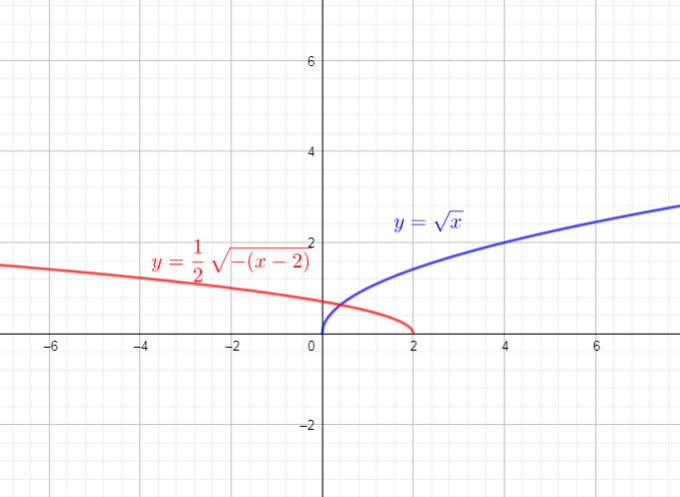
The first, we need determine $a, k, c$ and $d$.
The graph of $f(x)=dfrac{1}{x}$ is stretched vertically by the factor $longrightarrow$ $y=dfrac{4}{x}$
then reflected in the $x$-axis $longrightarrow$ $y=dfrac{-4}{x}$
then translated 2 units left $longrightarrow$ $y=dfrac{-4}{x+2}$
and then translated 3 units down $longrightarrow$ $y=dfrac{-4}{x+2}-3$
Use these steps, we get new function:
$color{#4257b2}{y=dfrac{-4}{x+2}-3=-4f(x+2)-3}$
If we compare this function with $y=af[k(x-d)]+c$, we can conclude that:
$a=-4, k=1, c=-3, d=-2$
$text{textcolor{#4257b2}{Domain$=left{xin R | xne0 right}$}}$
$text{textcolor{#4257b2}{Range$=left{yin R | yne-2 right}$}}$
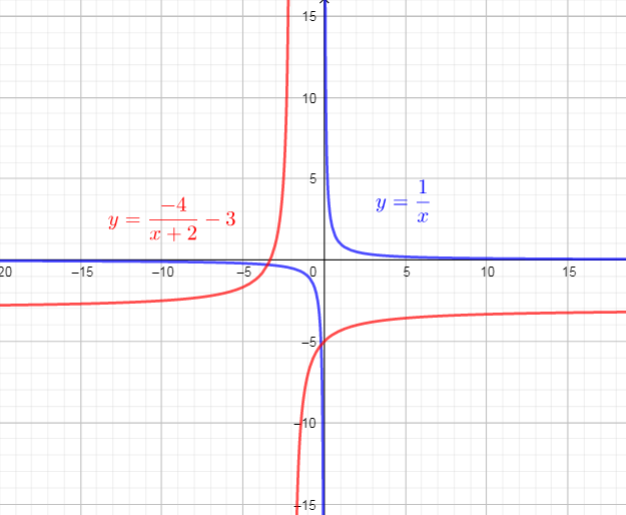
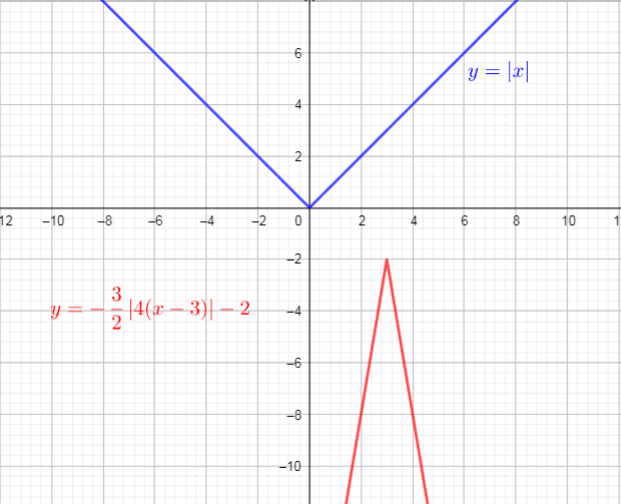
The first, we need determine $a, k, c$ and $d$.
The graph of $f(x)=|x|$ is horizontally compressed by the factor $dfrac{1}{4}$ $longrightarrow$ $y=|4x|$
then, stretched vertically by the factor $dfrac{3}{2}$ $longrightarrow$ $y=dfrac{3}{2}|4x|$
then reflected in the $x$-axis $longrightarrow$ $y=-dfrac{3}{2}|4x|$
and then translated 3 units right $longrightarrow$ $y=-dfrac{3}{2}|4(x-3)|$
and then translated 2 units down $longrightarrow$ $y=-dfrac{3}{2}|4(x-3)|-2$
Use these steps, we get new function:
$color{#4257b2}{y=-dfrac{3}{2}|4(x-3)|-2=-dfrac{3}{2}f(4(x-3))-2}$
If we compare this function with $y=af[k(x-d)]+c$, we can conclude that:
$a=-dfrac{3}{2}, k=4, c=-2, d=3$
We can identify the domain and range of functions is by using graphs. Because the domain refers to the set of possible input values, the domain of a graph consists of all the input values shown on the $x$-axis. The range is the set of possible output values, which are shown on the $y$-axis.
$text{textcolor{#4257b2}{Domain$=left{xin R right}$}}$
$text{textcolor{#4257b2}{Range$=left{yin R | yleq-2 right}$}}$
a) $dfrac{1}{2}f(-(x-2))$
b) $y=-4f(x+2)-3$
c) $y=-dfrac{3}{2}f(4(x-3))-2$
Check the answers.

