
All Solutions
Page 202: Practice Questions
direction of opening:
$a>0implies$ up
$a0implies { f(x)inbold{R};|;f(x)geq k}$
if $a<0implies { f(x)inbold{R};|;f(x)leq k}$
a) Since $a=-3<0$, it opens downward. The vertex is $(2,5)$ and axis of symmetry is $x=2$
b) domain: ${ xin bold{R}}$
range: ${ f(x)inbold{R};|;f(x) leq 5}$
b) domain = ${ xin bold{R}}$ , range = ${ yin bold{R};|;yleq 5}$
c) see graph inside
zeros: $r$ and $s$
direction of opening:
$a>0implies$ up
$a0implies { f(x)inbold{R};|;f(x)geq k}$
if $a<0implies { f(x)inbold{R};|;f(x)leq k}$
a) Since $a=4>0$, it opens upwards and it has zeros at $x=2$ and $-6$.
The value of $x$ at the vertex corresponds to the average of two zeros.
$h=dfrac{2+(-6)}{2}=-2$
$k=f(-2)=4(-2-2)(-2+6)=-64$
and axis of symmetry is $x=-2$
b) domain: ${ xin bold{R}}$
range: ${ f(x)inbold{R};|;f(x) geq -64}$
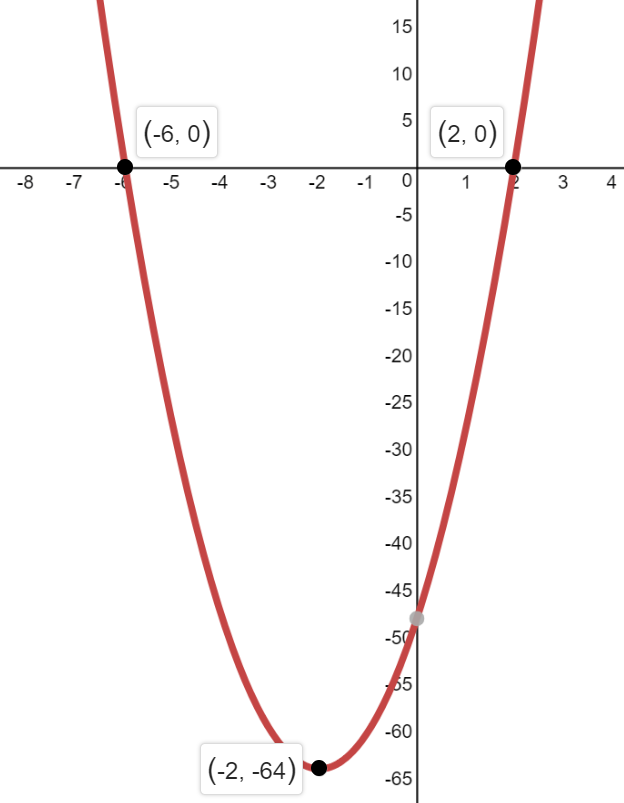
b) vertex $(-2,-64)$
c) domain: ${ xinbold{R}}$ ; range : ${ yin bold{R};|;ygeq -64}$
The two given points $(-5,3)$ and $(3,3)$ has the same value of $y$-coordinate, thus, the average of the $x$-coordinates must correspond to the axis of symmetry.
axis of symmetry: $x=dfrac{-5+3}{2}=dfrac{-2}{2}=-1$
x=-1
$$
a) In vertex form $f(x)=a(x-h)^2+k$
The vertex is at $(h,k)$
In this case, $a=-3<0$,
so the maximum occurs at $(4,7)$
The maximum value is $7$ which occurs at $x=4$
vertex$(h,k)$ where $h=dfrac{r+s}{2}$ and $k=f(h)$
In this case,
$h=dfrac{0+(-6)}{2}=-3$
$k=f(-3)=4(-3)(-3+6)=-36$
With $a=4>0$, the minimum occurs at $(-3,-36)$
The minimum value is $-36$ which occurs at $x=-3$
b) The minimum value is $-36$ which occurs at $x=-3$
$f(x)=ax^2+bx+c$
the vertex is $(h,k)$ where
$h=-dfrac{b}{2a}$
$$
k=f(h)
$$
$h(t)=-4.9t^2+28t+2$
$a=-4.9$ , $b=28$ , $c=2$
Since $a<0$, the vertex corresponds to the maximum.
We shall find the coordinates of the vertex to find the maximum height
$h=-dfrac{b}{2a}=-dfrac{28}{2(-4.9)}=2.86$
$k=f(2.86)=-4.9(2.86)^2+28(2.86)+2=42$ m
Therefore, the maximum height is $42$ m which occurs at about $2.9$ s
Replace $y$ with $x$ and replace $x$ with $y$ (swap the variables), then solve for $y$ in terms of $x$
$x=y^2implies y=pmsqrt{x}$
Therefore, $g(x)=sqrt{x}$ and $h(x)=-sqrt{x}$ are two branches of the inverse of $f(x)=x^2$
The inverse of a quadratic function is a parabola that opens either left or right. It has two branches and it would touch the vertical line twice. Thus, it is not function.
Note that if the domain of the quadratic function is restricted to a single branch of the parabola, then its inverse would be a function since it will only have once branch.
$f(x)=a(x-2)^2+4$
To find $a$, we can use any point on the parabola. We will choose $(1,2)$
$2=a(1-2)^2+4implies a=dfrac{2-4}{(1-2)^2}=-2$
$f(x)=y=-2(x-2)^2+4$
Now, we will find the inverse of this function by swapping $x$ and $y$
$x=-2(y-2)^2+4$
$(y-2)^2=dfrac{x-4}{-2}$
$y-2=pmsqrt{dfrac{4-x}{2}}$
$$
y=2pmsqrt{dfrac{4-x}{2}}
$$
We can sketch the inverse function by swapping the coordinates. Thus, the inverse shall contain the following points.
$(-4,0)$, $(2,1)$ , $(4,2)$, $(2,3)$ , $(-4,4)$
domain = ${ xinbold{R};|;xleq 4}$
The range is the set of all real numbers.
range = ${ yinbold{R}}$
c) The inverse relation cannot pass the vertical line test. For example, the vertical line at $x=-4$ would touch the points $(-4,0)$ and $(-4,4)$, thus, it is not a function.
b) domain = ${ xinbold{R};|;xleq 4}$ ; range = ${ yinbold{R}}$
c) not a function ; does not pass vertical line test
a) $sqrt{98}$
$=sqrt{49times 2}$
$=sqrt{7^2times 2}$
$=7sqrt{2}$
b) $-5sqrt{32}$
$=-5sqrt{16times 2}$
$=-5sqrt{4^2times 2}$
$=(-5times 4)sqrt{2}$
$=-20sqrt{2}$
c) $4sqrt{12}-3sqrt{48}$
$=4sqrt{4times 3}-3sqrt{16times 3}$
$=4sqrt{2^2times 3}-3sqrt{4^2times 3}$
$=8sqrt{3}-12sqrt{3}$
$=-4sqrt{3}$
d) $(3-2sqrt{7})^2$
$=3^2-2(3)(-2sqrt{7})+(2sqrt{7})^2$
$=9-12sqrt{7}+4times 7$
$$
=37-12sqrt{7}
$$
b) $-20sqrt{2}$
c) $-4sqrt{4}$
d) $37-12sqrt{7}$
$a=5$, $b=7$ , $c=10$
$s=dfrac{1}{2}(a+b+c)=dfrac{1}{2}(5+7+10)=11$
$A=sqrt{s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)}$
$=sqrt{11(11-5)(11-7)(11-10)}$
$=sqrt{11(6)(4)(1)}$
$=sqrt{264}$
$=sqrt{4times 66}$
$=sqrt{2^2times 66}$
$=2sqrt{66}$
The area of the triangle is $2sqrt{66}$ square units.
$a=6$ , $b=3$
$c=sqrt{6^2+3^2}$
$c=sqrt{36+9}$
$c=sqrt{45}$
$c=sqrt{9times 5}$
$c=sqrt{3^2times 5}$
$c=3sqrt{5}$
$$
c^2=a^2+b^2
$$
$P=9+3sqrt{5}$
Therefore, the perimeter of the triangle is
$P=9+3sqrt{5}$ cm
$$
P=a+b+c
$$
If $x_1$ and $x_2$ are the zeros of the quadratic function, then the $x$-intercepts are
$(x_1,0)$ and $(x_2,0)$
$f(x)=2x^2+x-15=0$
$(2x-5)(x+3)=0$
$x=dfrac{5}{2}$ or $-3$
Therefore, the $x$-intercepts are
$left(dfrac{5}{2},0right)$ and $(-3,0)$
$t=2020-2007=13$
Now substitute this value of $t$ to the population model
$P(t)=12t^2+800t+40;000$
$P(13)=12(13)^2+800(13)+40;000$
$P(13)=52;428$
$300;000=12t^2+800t+40;000$
$12t^2+800t-260;000=0$
We will use quadratic formula
$a=12$ , $b=800$ , $c=-260;000$
$t=dfrac{-bpmsqrt{b^2-4ac}}{2a}$
$t=dfrac{-800pmsqrt{800^2-4(12)(-260;000)}}{2(12)}$
$t=-184.25$ or $117.59$
We can confirm this by graphing.
$t=-184.25implies text{ year }=2007-184.25=1823$
$t=117.59implies text{ year } = 2007+117.59=2125$
Thus, the population is predicted to be $300,000$ in 1823 and 2125.
$12t^2+800t+40;000=30;000$
$12t^2+800t+10;000=0$
$a=12$ , $b=800$ , $c=10;000$
$x=dfrac{-bpmsqrt{b^2-4ac}}{2a}$
$x=dfrac{-800pmsqrt{800^2-4(12)(10;000)}}{2(12)}$
$x=-50implies 2007-50=19567$
$-$16.67 $implies 2007-16.67=1990.33$
This occurs in year 1957 and 1990.
The population is predicted to be 300 000 in 1823 and 2125
Since the perimeter is $400$ m, we can write
$2x+2w=400$
$x+w=200implies w=200-x$
The area of the triangle is length $times$ width
$x(200-x)=8000$
$200x-x^2=8000$
$200x-x^2-8000=0$
$-x^2+200x-8000=0$
Solve by quadratic formula
$a=-1$ , $b=200$ , $c=-8000$
$x=dfrac{-bpmsqrt{b^2-4ac}}{2a}$
$x=dfrac{-200pmsqrt{(-200)^2-4(-1)(-8000)}}{2(-1)}$
$x=55.28$ or $144.72$
$w=200-55.28=144.72$
Therefore, both values of $x$ would lead to rectangle with dimensions
$55.28$ m by $144.72$ m
Remember that for parabola opening downwards $a<0$, the range is $h(t)leq k$
$h(t)=14t-5t^2$
$a=-5$ , $b=14$, $c=0$
The value of $t$ that corresponds to the vertex is
$t=-dfrac{b}{2a}=-dfrac{14}{2(-5)}=-1.4$
Now we shall evaluate $h(t)$ at $t=-1.4$ to find $k$
$k=h(-1.4)=14(1.4)-5(1.4)^2=9.8$
Therefore, the maximum height is $9.8$, thus, it can reach a height of $9$ m.
$f(x)=ax^2+bx+c$
$b^2-4ac>0implies$ 2 zeros
$b^2-4ac=0implies$ 1 zero
$b^2-4ac0$
$(2k)^2+2(2k)(-3)+(-3)^2-16>0$
$4k^2-12k+9-16>0$
$4k^2-12k-7>0$
$(2k-7)(2k+1)>0$
$k=dfrac{7}{2}$ , $-dfrac{1}{2}$
This is a parabola that opens upward so the function would be greater than zero for values that are on the left of $-dfrac{1}{2}$ and to the right of $dfrac{7}{2}$
$kdfrac{7}{2}$
$f(x)=4x^2-3x+2(-1)x+1$
$f(x)=4x^2-5x+1$
$a=4$ , $b=2(4)-3=5$ , $c=1$
$$
y=4x^2+5x+1
$$
$P(x)=-2x^2+7x+8=0$
We shall use quadratic formula
$a=-2$ , $b=7$ , $c=8$
$x=dfrac{-bpmsqrt{b^2-4ac}}{2a}$
$x=dfrac{-7pmsqrt{7^2-4(-2)(8)}}{2(-2)}$
$x=dfrac{-7pmsqrt{113}}{-4}$
$x=dfrac{7pmsqrt{113}}{4}$
$x=-0.9075$ or $4.408$
Since the number of bikes $x$ (in thousands) cannot be negative, choose only $x=4.408$
which corresponds to $4408$ bikes.
$y=a(x-r)(x-s)$
$y=a[x^2-(r+s)x+rs]$
To evaluate $a$, substitute any point on the parabola to the equation and solve for $a$
$r+s=(2+sqrt{3})+(2-sqrt{3})=4$
$rs=(2+sqrt{3})(2-sqrt{3})=2^2-(sqrt{3})^2=4-3=1$
Thus, the equation becomes
$y=a(x^2-4x+1)$
We are given that $(2,5)$ is a point on the parabola,
$5=a(2^2-4(2)+1)$
$a=dfrac{5}{2^2-4(2)+1}=-dfrac{5}{3}$
Therefore, the equation of the parabola is
$y=-dfrac{5}{3}(x^2-4x+1)$
$$
y=-dfrac{5}{3}+dfrac{20}{3}x-dfrac{5}{3}
$$
y=-dfrac{5}{3}+dfrac{20}{3}x-dfrac{5}{3}
$$
defarraystretch{1.5}%
begin{tabular}{|l|l|}
hline
$bold{Form}$ & $bold{Family; of; Parabola}$ \ hline
begin{tabular}[c]{@{}l@{}}vertex form\ $f(x)=a(x-h)^2+k$end{tabular} & begin{tabular}[c]{@{}l@{}}if $a$ is varied\ $implies$ families with the same vertex and\ axis of symmetryend{tabular} \ hline
begin{tabular}[c]{@{}l@{}}factored form\ $f(x)=a(x-r)(x-s)$end{tabular} & begin{tabular}[c]{@{}l@{}}if $a$ is varied\ $implies$ families with the same $x$-intercepts\ and axis of symmetryend{tabular} \ hline
begin{tabular}[c]{@{}l@{}}standard form\ $f(x)=ax^2+bx+c$end{tabular} & begin{tabular}[c]{@{}l@{}}if $a$ and $b$ are varied\ $implies$ families with the same $y$-interceptend{tabular} \ hline
end{tabular}
end{table}
Now, we shall evaluate $a$ by substituting the coordinates of the point $(-2,6)$
$f(x)=a(x+3)^2-4$
$6=a(-2+3)^2-4$
$a=dfrac{6+4}{(-2+3)^2}=10$
The member that passes through $(-2,6)$ is
$$
f(x)=10(x+3)^2-4
$$
f(x)=10(x+3)^2-4
$$
parabolic arch $implies$ parabola that opens downward, we will arbitrarily choose the axis of symmetry of the parabola at $x=0$
$15$ m high $implies$ the vertex is $(0,15)$
$6$ m wide at a height of $8$ m $implies$ passes through $(-3,8)$ and $(3,8)$
$y=a(x-0)^2+15$
We will find $a$ by substituting the point $(3,8)$
$8=a(3-0)^2+15$
$a=dfrac{8-15}{3^2}=-dfrac{7}{9}$
Therefore, the equation of the parabola is
$$
y=-dfrac{7}{9}x^2+15
$$
$-dfrac{7}{9}x^2+15=0$
$dfrac{7}{9}x^2=15$
$x=pmsqrt{dfrac{15}{7/9}}$
$x=pm 4.4$
Thus, the zeros are at $(-4.4,0)$ and $(4.4,0)$
The distance between these two points is $4.4-(-4.4)=8.8$
Therefore, the arch must be 8.8 m wide at the base.
b) 8.8 m
$$
2x^2+7x-15=0
$$
$$
ax^2+bx+c=0
$$
(x+5)(2x-3)
$$
$$
2x-3=0rightarrow x=frac{3}{2}=1.5
$$
$$
-3(-5)+4=19
$$
$h(t)=g(t)$
$-5t^2+20t+15=3t+3$
$-5t^2+17t+12=0$
$a=-5$, $b=17$, $c=12$
We shall first determine how many zeros are possible
$b^2-4ac=(17)^2-4(-5)(12)=529>0$
Since $b^2-4ac>0$, there will be two solutions.
We shall then use the quadratic formula
$t=dfrac{-bpmsqrt{b^2-4ac}}{2a}$
$t=dfrac{-17pmsqrt{529}}{2(-5)}$
$t=-0.6$ or 4
Time can’t be negative, so choose $t=4$
The height at $t=4$ can be solved using either $h(t)$ or $g(t)$
$g(t)=3(4)+3=15$ m
Therefore, the paintball will hit the baseball after 4 s at a height of 15 m.
If no values of $x$ satisfies the equation $(b^2-4ac<0)$, then $f(x)$ and $g(x)$ does not intersect.
a) $f(x)=g(x)$
$x^2-6x+9=-3x-5$
$x^2-3x+14=0$
$a=1$ , $b=-3$ , $c=14$
$b^2-4ac=(-3)^2-4(1)(14)=-47<0$
Since $b^2-4ac<0$, the parabola and the line do not intersect.
b) $g(x)=3x-5$

