
All Solutions
Section 9-3: Combining Two Functions: Products
$(ftimes g)(x)={(0,2 times -1), (1,5 times -2), (2,7 times 3), (3,12 times 5)}$={(0, -2), (1, -10), (2, 21), (3,60)}
#### (b)
$(ftimes g)(x)={(0,3 times 4), (2,10 times -2)}={(0,12), (2, -20)}$
$(ftimes g)(x)=x(4)=4x$
#### (d)
$(ftimes g)(x)=x(2x)=2x^2$
#### (e)
$(ftimes g)(x)=(x+2)(x^2-2x+1)$
$=x^3-2x^2+x+2x^2-4x+2$
$=x^3-3x+2$
#### (f)
$(ftimes g)(x)=2^x(sqrt{x-2})$
$=2^xsqrt{x-2}$
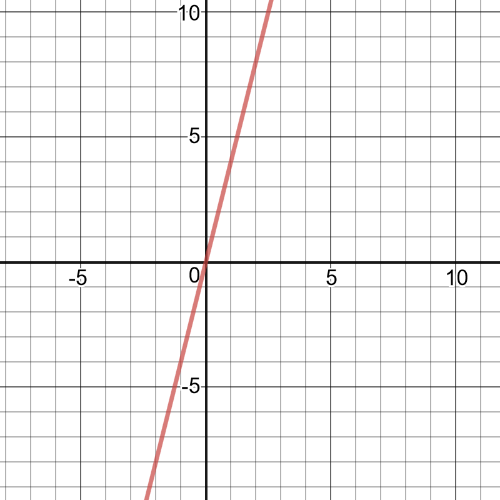
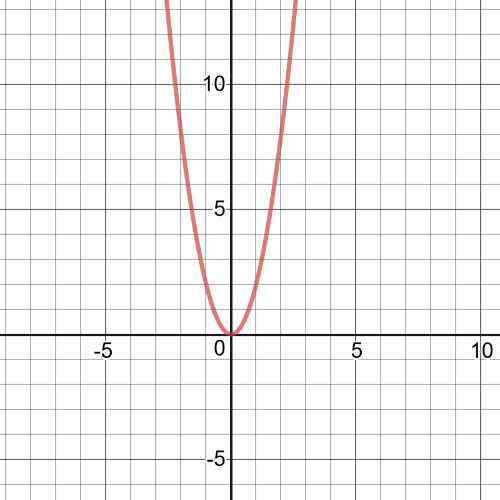
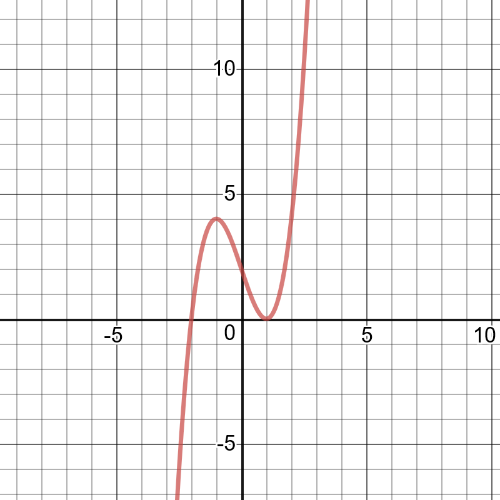
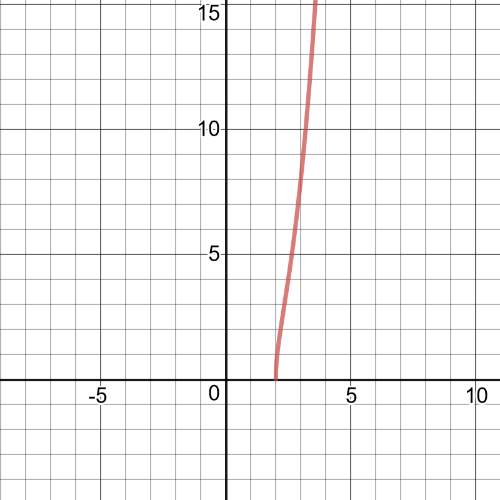
1.task, part (c), red is graph of the function $f(x)$ and blue is of $g(x)$.
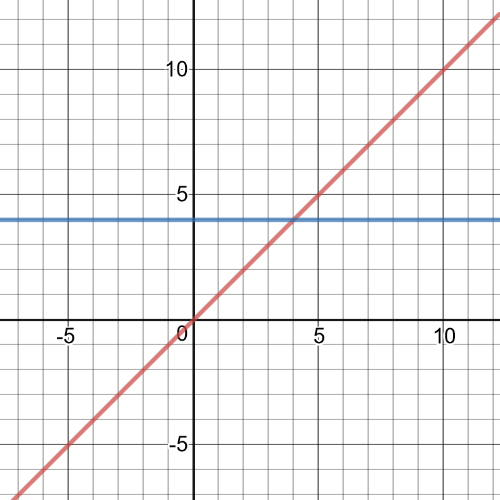
1.task, part (c), $f:left{xinBbb{R} right}$, $g:left{xinBbb{R} right}$
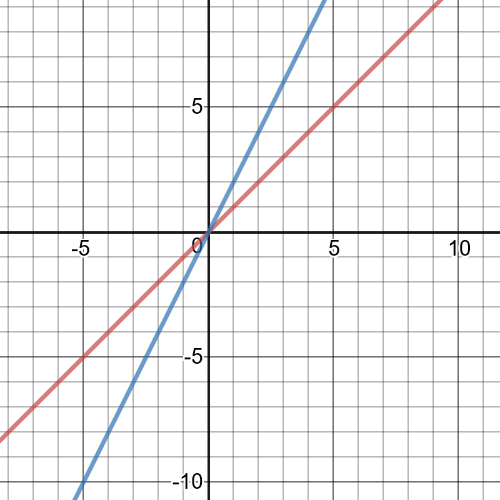
1.task, part (d), $f:left{xinBbb{R} right}$, $g:left{xinBbb{R} right}$
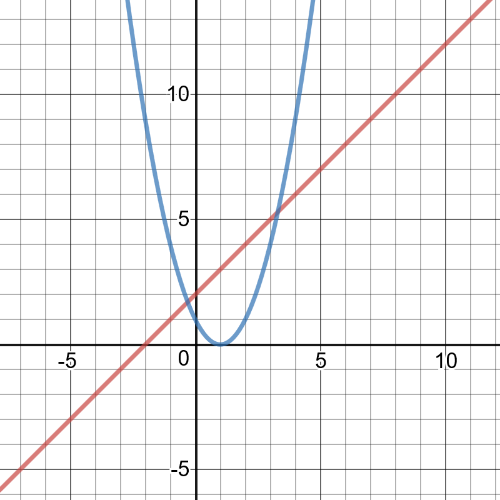
1.task, part (e), $f:left{xinBbb{R} right}$, $g:left{xinBbb{R} right}$
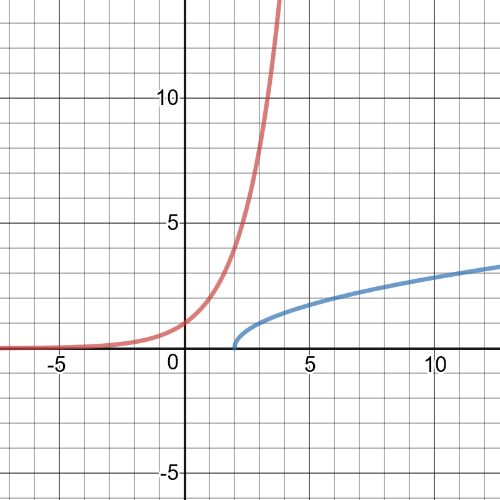
1.task, part (f), $f:left{xinBbb{R} right}$, $g:left{xinBbb{R}|xgeq2 right}$
#### (c)
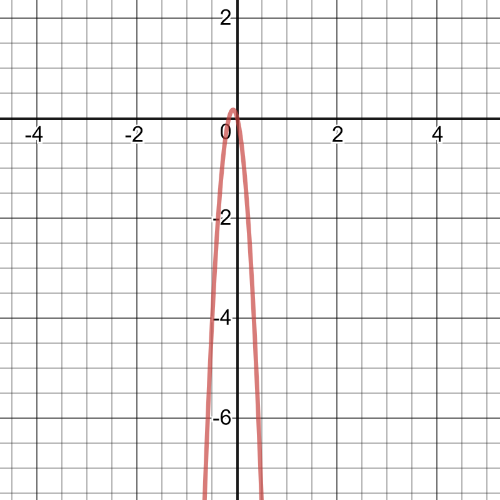
The graph of $ftimes{g}$ can be found by multipliying corresponding $y-coordinates$.
1.task, part (c), on the following picture there is a graph of $ftimes{g}$:
So,$xgeq-1$ and $xleq 1$ since the radicand must be greater than or equal to $0$.
So,the domain is $left{xinBbb{R}|-1leq x leq 1 right}$
$(ftimes g)(x)=(x-7)(x+7)=x^2-49$
#### (b)
$(ftimes g)(x)=(sqrt{x+10})(sqrt{x+10})=x+10$
#### (c)
$(ftimes g)(x)=7x^2(x-9)=7x^3-63x^2$
#### (d)
$(ftimes g)(x)=(-4x-7)(4x+7)=-16x^2-28x-28x-49=16x^2-56x-49$
#### (e)
$(ftimes g)(x)=2sin xleft(dfrac{1}{x-1} right)=dfrac{2sin x}{x-1}$
#### (f)
$(ftimes g)(x)=log (x+4)(2^x)=2^x log (x+4)$
4(b): $D=left{xinBbb{R}|xgeq -10 right}$; $R=left{yin Bbb{R}|ygeq0 right}$
4(c): $D=left{ xinBbb{R}right}$; $R=left{yinBbb{R} right}$
4(d): $D=left{ xinBbb{R}right}$; $R=left{yinBbb{R}|yleq0 right}$
4(e): $D=left{ xinBbb{R} | xne -1right}$; $R=left{yin Bbb{R} right}$
4(f): $D=left{xinBbb{R}|x > -4 right}$; $R=left{yinBbb{R}|ygeq 0 right}$
increasing/decreasing: The function is increasing from $0$to $infty$. The function is is decreasing from $-infty$ to $0$.
zeros: $x=-7, 7$
maximum/minimum: The minimum is at $x=0$.
period: N/A
4(b): symmetry: The function is not symmetric.
increasing/decreasing: The function is increasing from $-10$ to $infty$.
zeros: $x= -10$
maximum/minimum: The minimum is at $x=-10$.
period: N/A
4(c): symmetry: The function is not symmetic.
increasing/decreasing: The function is increasing from $-infty$to $0$ and from $-infty$ to $0$ and from $6$ to $infty$.
zeros: $x=0,9$
maximum/minimum: The relative minimum is at $x=-6$. The relative maximum is at $x=0$.
period: N/A
4(d): symmetry: The function is symmetric about the line $x=-1.75$.
increasing/decreasing: The function is increasing from $-infty$ to $-1.75$ and is decreasing from $-1.75$ to $infty$.
zero: $x=-1.75$
maximum/minimum: The maximum is at $x=-1.75$.
period: N/A
4(e): symmetry: The function is not symmetric.
increasing/decreasing: The function is increasing from $-infty$ to $0$ and from $6$ to $infty$.
zeros: $x=0,9$
maximum/minimum: The relative minima are at $x=-4.5336$ and $4.4286$.The relative maximum is at $x=-1.1323$.
period: N/A
4(f): symmetry: The function is not symmetric.
increasing/decreasing: The function is increasing from $-4$ to $infty$.
zeros: none
maximum/minimum: none
period: N/A
$g(x)=6x+1$
$(ftimes g)(x)= -4x(6x+1)=-24x^2-4x$
$left{xinBbb{R}|xne -2,7, dfrac{pi}{2},or dfrac{3pi}{2} right}$
#### (b)
$left{xinBbb{R}|x>8 right}$
#### (c)
$left{xinBbb{R}|xgeq-81 (and) xne0,pi, or 2pi right}$
#### (d)
$$
left{xinBbb{R}|xleq -1 or x geq 1 (and) xne -3 right}
$$
$R(x)=(20 000-750x)(25+x)$ or $R(x)=500 000+1250x-750x^2$, where $x$ is the increase in the admission fee in dollars
#### (b)
Yes, it’s the product of the function $P(x)=20000-750x$, which represents the number of daily visitors, and $F(x)=25+x$, which represents the admission fee.
#### (c)
Use a graphing calculator. The ticket price that will maximize revenue is 25.83$.
Use a graphing calculator to estimate.
$$
textbf{The amount of contaminated material is at its greatest after about $7.3$s.}
$$
$-40=(m(1)^2+2(1)+5) times(2(1)^2-n(1)-2)$
$-40=(m+2+5)(2-n-2)$
$-40=(m+7)(-n)$
$dfrac{40}{m+7}=n$ EQUATION 1
$24=(m(-1)^2+2(-1)+5)times (2(-1)^2-n(-1)-2)$
$24=(m-2+5)(2+n-2)$
$24=(m+3)(n)$
$dfrac{24}{m+3}=n$ EQUATION 2
$dfrac{40}{m+7}=dfrac{24}{m+3}$
$40(m+3)=24(m+7)$
$40m+120=24m+168$
$16m=48$
$m=3$
$dfrac{24}{3+3}=n$
$dfrac{24}{6}=n$
$4=n$
$$
textbf{So, the equations are $f(x)=3x^2+2x+5$ and $g(x)=2x^2-4x-2$.}
$$
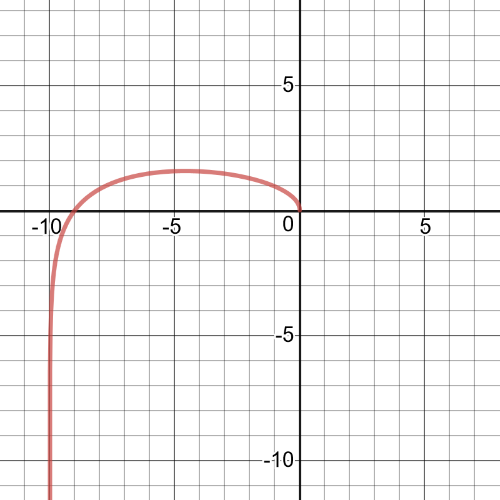
$(ftimes g)(x)=sqrt{-x}log(x+10)$
The domain is $left{xinBbb{R}| -10 < x leq 0 right}$.
#### (b)
One strategy is to create a table of values for $f(x)$ and $g(x)$ and to multiply the corresponding $y$-values together. The resulting values could then be graphed.Another strategy is to graph $f(x)$ and $g(x)$ and to then create a graph for $(ftimes g)(x)$ based on these two graphs. The first strategy is probably better than the second strategy, since the $y$-values for $f(x)$ and $g(x)$ will not be round numbers and will not be easily discernable from the graphs of $f(x)$ and $g(x)$.
#### (c)
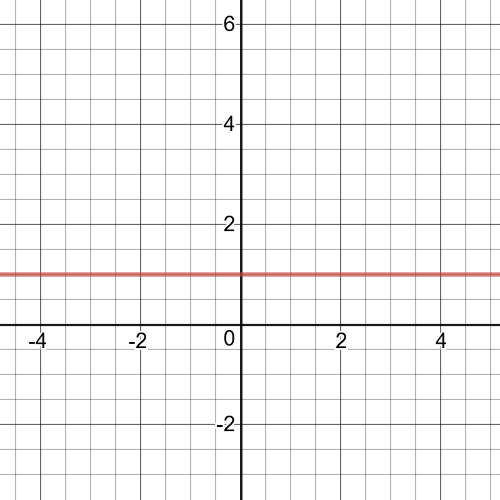
$f(x)times dfrac{1}{f(x)}=(x^2-25)times dfrac{1}{x^2-25}$
#### (b)
The domain of the function is $left{xinBbb{R}|xne -5 (or) 5 right}$.
#### (c)
The range will always be $1$. If $f$ is of odd degree, there will always be at least one value that makes the product undefined and which is excluded from the domain. If $f$ is of even degree, there may be no values that are excluded from domain.
$f(x)=2^x$
$g(x)=x^2+1$
$(ftimes g)(x)=2^x(x^2+1)$
#### (b)
$f(x)=x$
$g(x)=sin(2pi x)$
$(ftimes g)(x)=x sin(2pi x)$
$4x^2-91=(2x+9)(2x-9)$
$f(x)=(2x+9)$
$g(x)=(2x-9)$
#### (b)
$8sin^3 x+27=(2sin x +3)times(4sin^2x-6sin x+9)$
$f(x)=(2sin x+3)$
$g(x)=(4sin^2x-6sin x+9)$
$4x^{dfrac{5}{2}}-3x^{dfrac{3}{2}}+x^{dfrac{1}{2}}=x^{dfrac{1}{2}}(4x^5-3x^3+1)$
$f(x)=x^{dfrac{1}{2}}$
$g(x)=(4x^5-3x^3+1)$
#### (d)
$dfrac{6x-5}{2x+1}=dfrac{1}{2x+1}times 6x-5$
$f(x)=dfrac{1}{2x+1}$
$g(x)=6x-5$

