
All Solutions
Section 9-2: Combining Two Functions: Sums and Differences
$f+g=left{(-4, 4+2), (-2.4+1), (1.3+2), (4.6+4) right}$
$=left{(-4,6), (-2,5), (1, 5), (4, 10) right}$
#### (b)
$g+f=left{(-4,2+4), (-2,1+4), (1,2+3),(4,4+6) right}$
$=left{(-4,6),(-2,5), (1,5), (4,10) right}$
#### (c)
$f-g=left{(-4,4-2), (-2,4-1), (1,3-2), (4,6-4) right}$
$=left{(-4,2), (-2,3), (1,1), (4,2) right}$
#### (d)
$g-f=left{(-4,2-4), (-2,1-3), (1,2-3), (4,4-6) right}$
$=left{(-4,-2), (-2, -3), (1,-1), (4,-2) right}$
#### (e)
$f+f=left{(-4,4+4), (-2,4+4), (1,3+3), (3,5+5), (4,6+6) right}$
$=left{(-4,8), (-2,8), (1,6), (3,10), (4,12) right}$
#### (f)
$g-g=left{(-4,2-2), (-2,1-1), (0,2-2), (1,2-2), (2,2-2), (4,4-4) right}$
$=left{(-4,0), (-2,0), (0,0), (1,0), (2,0), (4,0) right}$
$f(4)=4^2-3=16-3=13$
$g(4)=-dfrac{6}{4-2}=-dfrac{6}{2}=-3$
So, $(f+g)(4)=13+-3=10$
#### (b)
$2; (f+g)(x)$ is undefined at $x=2$ because $g(x)$ is undefined at $x=2$
#### (c)
Since $2$ cannot be part of the domain, the domain is $left{xinBbb{R}|xne 2 right}$
So the domain of $f-g$ is $left{xinBbb{R}|-1leq x <1 right}$.
$f(x)=-dfrac{1}{2}(x-6)$
$g(x)=-(x-6)(dfrac{1}{4}x+dfrac{1}{2})$
So, to find $textbf{the graph}$ of $f+g$, add corresponding $y$-coordinates, that graph is on following picture:
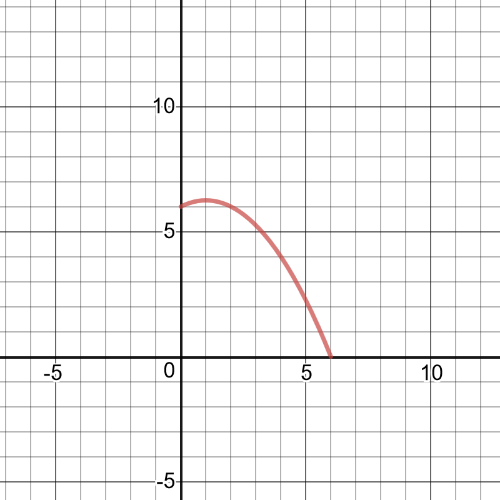
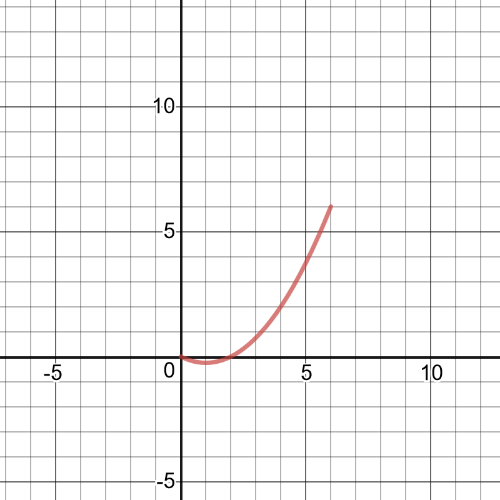
$f+g=|x|+x$
#### (b)
$(f+g)(x)=|x|+x$
$(f+g)(-x)=|-x|+ -x=|x|-x$
$$
textbf{The function is neither even or odd.}
$$
$f+g=left{(-6,1+6), (-3,7+3) right}$
$=left{(-6,7), (-3, 10) right}$
#### (b)
$g+f=left{(-6,6+1), (-3,3+7) right}$
$=left{(-6,7), (-3,10) right}$
#### (c)
$f-g=left{(-6,1-6), (-3,7-3) right}$
$=left{(-6, -5), (-3, 4) right}$
#### (d)
$g-f=left{(-6,6 -1), (-3,3-7) right}$
$=left{-6,5), (-3, -4) right}$
#### (e)
$f-f=left{-9, -2 -(-2)), (-8,5-5),(-6,1-1), (-3,7-7), (-1, -2-(-2)), (0,-10-(-10)) right}$
$=left{(-9,0), (-8,0), (-6,0), (-3,0), (-1,0), (0,0) right}$
#### (f)
$g+g=left{(-7,7+7), (-6,6+6), (-5,5+5), (-4,4+4), (-3,3+3) right}$
$=left{(-7,14), (-6,12), (-5,10), (-4,8), (-3,6) right}$
$(f+g)(x)=dfrac{1}{3x+4}+dfrac{1}{x-2}$
$=dfrac{x-2}{(3x+4)(x-2)}+dfrac{3x+4}{(3x+4)(x-2)}$
$=dfrac{4x+2}{(3x+4)(x-2)}$
$=dfrac{2(2x+1)}{3x^2-2x-8}$
#### (b)
The denominator cannot be $0$, so $3x+4ne 0$ or $xne -dfrac{4}{3}$ and $x-2ne0$ or $xne2$.
So, the domain is $left{xinBbb{R}|xne -dfrac{4}{3} or 2 right}$.
#### (c)
$(f+g)(8)=dfrac{2(2(8)+1)}{3(8)^2-2(8)-8}$
$=dfrac{2(17)}{3(64)-16-8}$
$=dfrac{34}{192-16-8}=dfrac{34}{168}=dfrac{17}{84}$
#### (d)
$$
(f-g)(8)=dfrac{1}{3(8)+4}-dfrac{1}{(8)-2}=dfrac{1}{24+4}-dfrac{1}{6}=dfrac{1}{28}-dfrac{1}{6}=dfrac{3}{84}-dfrac{14}{84}=-dfrac{11}{84}
$$
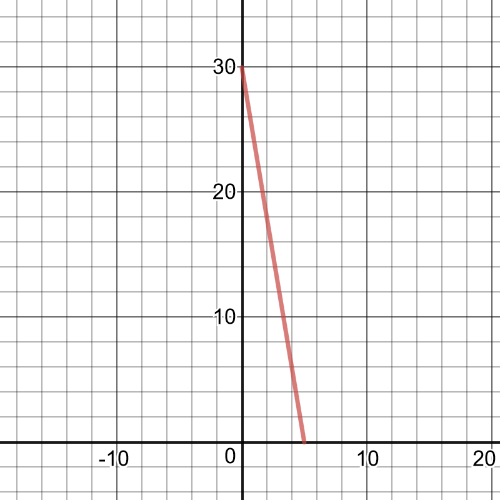
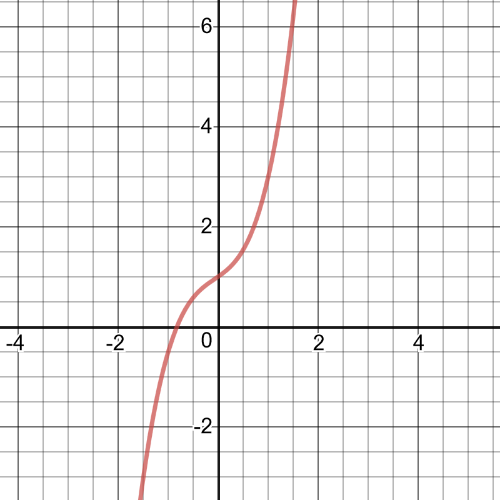
First, we have function $f(x)+g(x)=2^x+x^3$
From the graph we can see following:
$textbf{symmetry}$: The function is not symmetric.
$textbf{increasnig/decreasing}$: The function is always increasing.
$textbf{zeros}$: $-0.8262$
$textbf{maximum/minimum}$: No maximum or minimum
$textbf{period}$: N/A
$textbf{domain and range}$: The domain and range is set $Bbb{R}$.
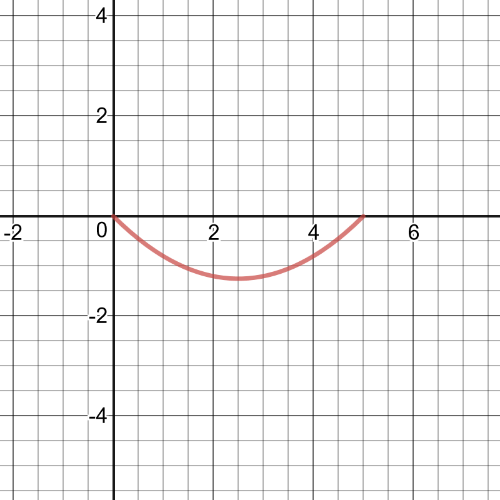
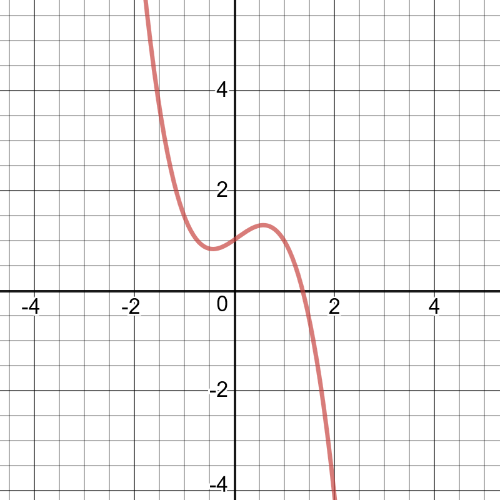
From the graph we can see following:
$textbf{symmetry}$: The function is not symmetric.
$textbf{increasnig/decreasing}$: The function is always decreasing.
$textbf{zeros}$: $1.3735$
$textbf{maximum/minimum}$: No maximum or minimum
$textbf{period}$: N/A
$textbf{domain and range}$: The domain and range is set $Bbb{R}$.
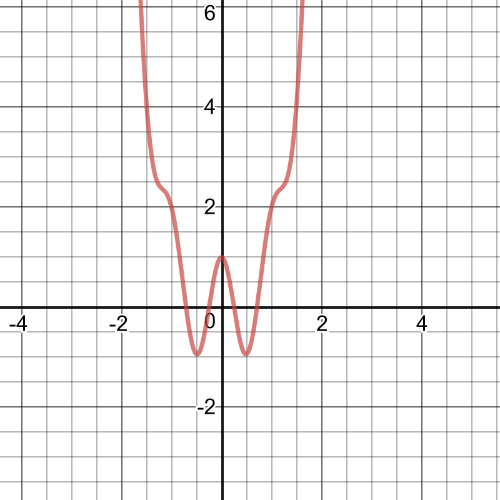
First, we have function $f(x)+g(x)=cos{2pi{x}}+x^4$
From the graph we can see following:
$textbf{symmetry}$: The function is symmetric across the line $x=0$.
$textbf{increasnig/decreasing}$: The function is decreasing on $(-infty,-0.4882)$ and $(0,0.4882)$ and increasing on $(-0.4882,0)$ and $(0.4882,infty)$.
$textbf{zeros}$: $x=-0.7092, x=-0.2506, x=0.2506, x=0.7092$
$textbf{maximum/minimum}$: Relative maximum at $x=0$and relative minimum at $x=-0.4882$.
$textbf{period}$: N/A
$textbf{domain and range}$: The domain is set $Bbb{R}$ and range is all real numbers greater than -0.1308.
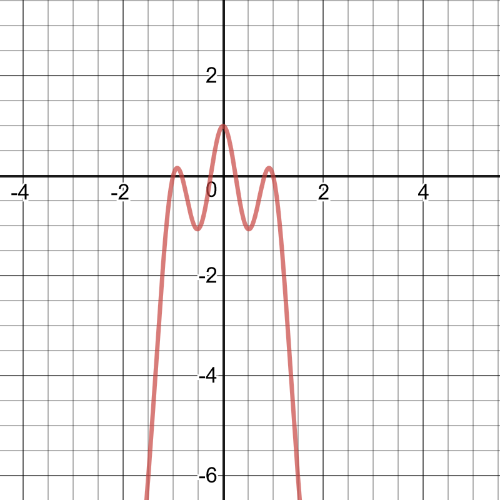
From the graph we can see following:
$textbf{symmetry}$: The function is symmetric across the line $x=0$.
$textbf{increasnig/decreasing}$: The function is increasing on $(-infty,-0.9180)$ and $(-0.5138,0)$ and $(0.5138,0.9180)$ and decreasing on $(-0.9180,-0.5138)$ and $(0.9180,infty)$.
$textbf{zeros}$: $x=-1, x=-0.8278, x=-0.2494, x=0.2494, x=0.8278, x=1$
$textbf{maximum/minimum}$: Relative maximum at $x=-0.9180, x=0 , x=0.9180$ and relative minimum at $x=-0.5138, x=0.5138$.
$textbf{period}$: N/A
$textbf{domain and range}$: The domain is set $Bbb{R}$ and range is all real numbers less than $1$.
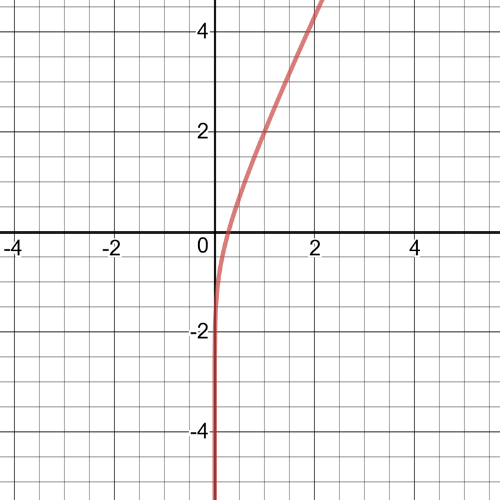
First, we have function $f(x)+g(x)=log{x}+2x$
From the graph we can see following:
$textbf{symmetry}$: The function is not symmetric.
$textbf{increasnig/decreasing}$: The function is increasing on $(0,infty)$.
$textbf{zeros}$: None
$textbf{maximum/minimum}$:None.
$textbf{period}$: N/A
$textbf{domain and range}$: The domain is set of all real numbers greater than $0$ and range is all real numbers.
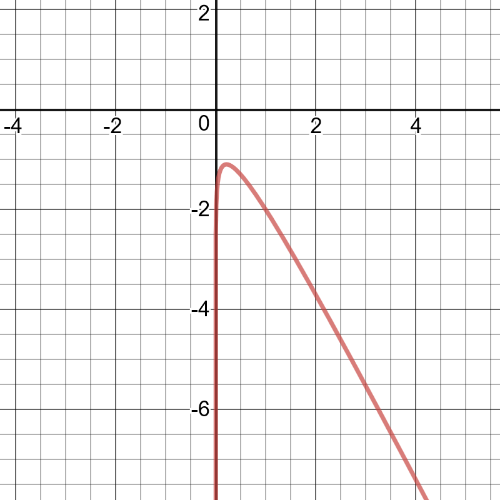
From the graph we can see following:
$textbf{symmetry}$: The function is not symmetric.
$textbf{increasnig/decreasing}$: The function is increasing on $(0,0.2)$ and decreasing on $(0.2, infty)$.
$textbf{zeros}$: None
$textbf{maximum/minimum}$:Maximum at $x=0.2$.
$textbf{period}$: N/A
$textbf{domain and range}$: The domain is set of all real numbers greater than $0$ and range is all real numbers less than or equal to $-1.1$
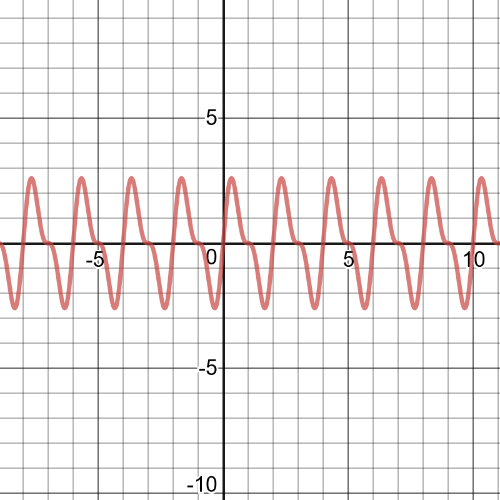
First, we have function $f(x)+g(x)=sin{2pi{x}}+2sin{pi{x}}$
From the graph we can see following:
$textbf{symmetry}$: The function is symmetric about the origin.
$textbf{increasnig/decreasing}$: The function is increasing on $(-0.33+2k,0.33+2k)$ and decreasing on $(0.33+2k,1.67+2k)$.
$textbf{zeros}$: $k$
$textbf{maximum/minimum}$:Minimum at $x=0.33+2k$ and maximum at $x=0.33+2k$ .
$textbf{period}$: 2
$textbf{domain and range}$: The domain is set of all real numbers and range is all real numbers between $-2.598$ and $2.598$.
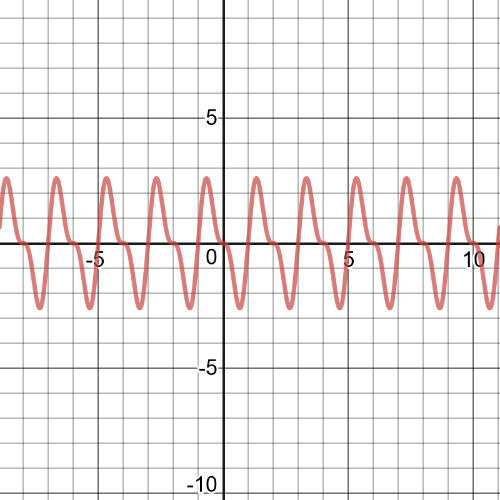
From the graph we can see following:
$textbf{symmetry}$: The function is symmetric about the origin.
$textbf{increasnig/decreasing}$: The function is increasing on $(0.67+2k,1.33+2k)$ and decreasing on $(-0.67+2k,0.67+2k)$.
$textbf{zeros}$: $k$
$textbf{maximum/minimum}$:Minimum at $x=0.67+2k$ and maximum at $x=1.33+2k$ .
$textbf{period}$: 2
$textbf{domain and range}$: The domain is set of all real numbers and range is all real numbers between $-2.598$ and $2.598$.
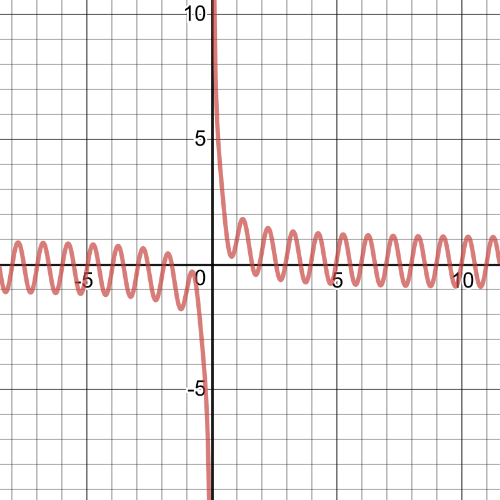
First, we have function $f(x)+g(x)=sin{2pi{x}}+dfrac{1}{x}$
From the graph we can see following:
$textbf{symmetry}$: The function is not symmetric.
$textbf{increasnig/decreasing}$: The function is increasing and decreasing at irregular intervals.
$textbf{zeros}$: The zeros are changing at irregular intervals.
$textbf{maximum/minimum}$:Minimums and maximums are changing at irregular intervals.
$textbf{period}$: N/A
$textbf{domain and range}$: The domain is set of all real numbers except $0$ and range is all real numbers.
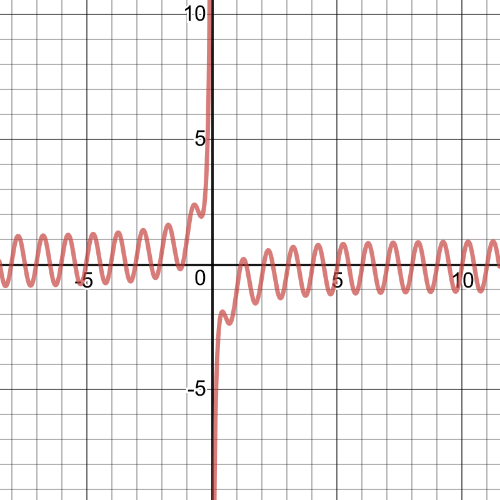
From the graph we can see following:
$textbf{symmetry}$: The function is not symmetric.
$textbf{increasnig/decreasing}$: The function is increasing and decreasing at irregular intervals.
$textbf{zeros}$: The zeros are changing at irregular intervals.
$textbf{maximum/minimum}$:Minimums and maximums are changing at irregular intervals.
$textbf{period}$: N/A
$textbf{domain and range}$: The domain is set of all real numbers except $0$ and range is all real numbers.
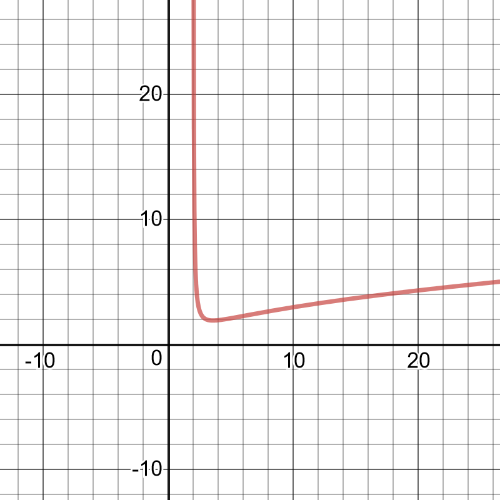
First, we have function $f(x)+g(x)=sqrt{x-2}+dfrac{1}{x-2}$
From the graph we can see following:
$textbf{symmetry}$: The function is not symmetric.
$textbf{increasnig/decreasing}$: The function is increasing on interval $(3.5874,infty)$ and decreasing on interval $(2,3.5874)$.
$textbf{zeros}$: None.
$textbf{maximum/minimum}$:Minimum at $x=3.5874$.
$textbf{period}$: N/A
$textbf{domain and range}$: The domain is set of all real numbers greater than $2$ and range is all real numbers greater than $1.899$.
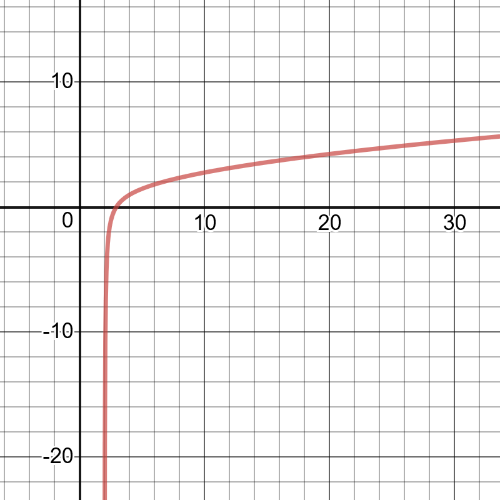
From the graph we can see following:
$textbf{symmetry}$: The function is not symmetric.
$textbf{increasnig/decreasing}$: The function is increasing on interval $(2,infty)$.
$textbf{zeros}$: $x=3$.
$textbf{maximum/minimum}$:None.
$textbf{period}$: N/A
$textbf{domain and range}$: The domain is set of all real numbers greater than $2$ and range is all real numbers.
$textbf{The sum ot two even functions will be even}$ because replacing $x$ with $-x$ will still result in the original function.
#### (b)
$textbf{The sum of two odd functions will be odd function}$ because replacing $x$ with $-x$ will still result in the opposite of the original function.
#### (c)
$textbf{The sum of an even and an odd function will result in neither an even or an odd function}$ because replacing $x$ with $-x$ will not result in the same function or in the opposite of the function.
$R(t)=5000-25t-1000cosleft(dfrac{pi}{6}t right)$;
it is neither odd nor even; it is increasing during the first $6$ months of each year and decreasing during the last $6$ months of each year; it has one zero,which is the point at which the deer popolation has become extinct; it has a maximum value of $3850$ and a minimum value of $0$,so it’s range is $left{R(t)inBbb{R}|0leq R(t)leq3850 right}$.
#### (b)
$R(t)=5000-25t-1000cosleft(dfrac{pi}{6}t right)$
$0=5000-25t-1000cosleft(dfrac{pi}{6}t right)$
Use a graphing calculator to find the zero of the function.
$$
textbf{The deer population is extinct after about $167$ months, or $13$ years and $11$ months.}
$$
If the vehicle is travelling at $90$ km/h, the stopping distance is:
$s(90)=0.006(90)^2+0.21(90)$
$=0.006(8100)+18.9$
$=48.6+18.9$
$=67.5 m$
$$
f(x)=0; g(x)=0
$$
#### (b)
$$
f(x)=x^2; g(x)=x^2
$$
$(f+g)(x)=x^2+x^2=2x^2$
It is a vertical stretch of $2$ from the original function.
#### (c)
$f(x)=dfrac{1}{x-2}$; $g(x)=dfrac{1}{x-2}+2$
So, $(f-g)(x)=dfrac{1}{x-2}-left(dfrac{1}{x-2}+2 right)=-2$
$3=(1+m)(1)^2+(1-n)(1)+2$
$3=1+m+1-n+2$
$3=4+m-n$
$-1=m-n$ EQUATION $1$
$18=(1+m)(-2)^2+(1-n)(-2)+2$
$18=(1+m)(4)-2+2n+2$
$18=4+4m+2n$
$14=4m+2n$ EQUATION $2$
$-1=m-n$
$14=4m+2n$
$2(-1=m-n)$
$14=4m+2n$
$-2=2m-2n$
$14=4m+2n$
$12=6m$
$2=m$
$-1=2-n$
$-3=-n$
$3=n$

