Home Page
Textbooks
Prentice Hall Biology (California)
Section 20.4: Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown, and Green Algae

Prentice Hall Biology (California)
1st Edition
Kenneth R. Miller, Levine
ISBN: 9780132013529
Textbook solutions
Chapter 1: The Science of Biology
Section 1.1: What is Science?
Section 1.2: How Scientists Work
Section 1.3: Studying Life
Section 1.4: Tools and Procedures
Page 31: Chapter 1 Assessment
Page 33: Standards Practice
Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life
Section 2.1: The Nature of Matter
Section 2.2: Properties of Water
Section 2.3: Carbon Compounds
Section 2.4: Chemical Reaction and Enzymes
Page 57: Chapter 2 Assessment
Page 59: Standards Practice
Chapter 3: The Biosphere
Section 3.1: What is Ecology?
Section 3.2: Energy Flow
Section 3.3: Cycles of Matter
Page 83: Chapter 3 Assessment
Page 85: Standards Practice
Chapter 4: Ecosystems and Communities
Section 4.1: The Role of Climate
Section 4.2: What Shapes and Ecosystem?
Section 4.3: Biomes
Section 4.4: Aquatic Ecosystems
Page 115: Chapter 4 Assessment
Page 117: Standards Practice
Chapter 5: Populations
Section 5.1: How Populations Grow
Section 5.2: Limits to Growth
Section 5.3: Human Population Growth
Page 135: Chapter 5 Assessment
Page 137: Standards Practice
Chapter 6: Humans in the Biosphere
Section 6.1: A Changing Landscape
Section 6.2: Renewable and Nonrenewable Resources
Section 6.3: Biodiversity
Section 6.4: Charting a Course for the Future
Page 163: Chapter 6 Assessment
Page 165: Standards Practice
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
Page 173: Section Assessment
Section 7.2: Eukaryotic Cell Structure
Section 7.3: Cell Boundaries
Section 7.4: The Diversity of Cellular Life
Page 197: Chapter 7 Assessment
Page 199: Standards Practice
Chapter 8: Photosynthesis
Section 8.1: Energy and Life
Section 8.2: Photosynthesis: An Overview
Section 8.3: The Reactions of Photosynthesis
Page 217: Chapter 8 Assessment
Page 219: Standards Practice
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration
Section 9.1: Chemical Pathways
Section 9.2: The Krebs Cycle and Electron Transport
Page 237: Chapter 9 Assessment
Page 239: Standards Practice
Chapter 10: Cell Growth and Division
Section 10.1: Cell Growth
Section 10.2: Cell Division
Section 10.3: Regulating the Cell Cycle
Page 257: Chapter 10 Assessment
Page 259: Standards Practice
Chapter 11: Introduction to Genetics
Section 11.1: The Work of Gregor Mendel
Section 11.2: Probability and Punnett Squares
Section 11.3: Exploring Mendelian Genetics
Section 11.4: Meiosis
Section 11.5: Linkage and Gene Maps
Page 283: Chapter 11 Assessment
Page 285: Standards Practice
Chapter 12: DNA and RNA
Section 12.1: DNA
Section 12.2: Chromosomes and DNA Replication
Section 12.3: RNA and Protein Synthesis
Section 12.4: Mutations
Section 12.5: Gene Regulation
Page 315: Chapter 12 Assessment
Page 317: Standards Practice
Chapter 13: Genetic Engineering
Section 13.1: Changing the Living World
Section 13.2: Manipulating DNA
Section 13.3: Cell Transformations
Section 13.4: Applications of Genetic Engineering
Page 337: Chapter 13 Assessment
Page 339: Standards Practice
Chapter 14: The Human Genome
Section 14.1: Human Heredity
Section 14.2: Human Chromosomes
Section 14.3: Human Molecular Genetics
Page 363: Chapter 14 Assessment
Page 365: Standards Practice
Chapter 15: Darwin’s Theory of Evolution
Section 15.1: The Puzzle of Life’s Diversity
Section 15.2: Ideas That Shaped Darwin’s Thinking
Section 15.3: Darwin Presents His Case
Page 389: Chapter 15 Assessment
Page 391: Standards Practice
Chapter 16: Evolution of Populations
Section 16.1: Genes and Variation
Section 16.2: Evolution as Genetic Change
Section 16.3: The Process of Speciation
Page 413: Chapter 16 Assessment
Page 415: Standards Practice
Chapter 17: The History of Life
Section 17.1: The Fossil Record
Section 17.2: Earth’s Early History
Section 17.3: Evolution of Multicellular Life
Section 17.4: Patterns as Evolution
Page 443: Chapter 17 Assessment
Page 445: Standards Practice
Chapter 18: Classification
Section 18.1: Finding Order in Diversity
Section 18.2: Modern Evolutionary Classification
Section 18.3: Kingdoms and Domains
Page 465: Chapter 18 Assessment
Page 467: Standards Practice
Chapter 19: Bacteria and Viruses
Section 19.1: Bacteria
Section 19.2: Viruses
Section 19.3: Diseases Caused By Bacteria and Viruses
Page 493: Chapter 19 Assessment
Page 495: Standards Practice
Chapter 20: Protists
Section 20.1: The Kingdom Protista
Section 20.2: Animal-Like Protists: Protozoans
Section 20.3: Plantlike Protists: Unicellular Algae
Section 20.4: Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown, and Green Algae
Section 20.5: Funguslike Protists
Page 523: Chapter 20 Assessment
Page 525: Standards Practice
Chapter 21: Fungi
Section 21.1: The Kingdom Fungi
Section 21.2: Classification of Fungi
Section 21.3: Ecology of Fungi
Page 545: Chapter 21 Assessment
Page 547: Standards Practice
Chapter 22: Plant Diversity
Section 22.1: Introduction to Plants
Section 22.2: Bryophytes
Section 22.3: Seedless Vascular PLants
Section 22.4: Seed Plants
Section 22.5: Angiosperms–Flowering Plants
Page 575: Chapter 22 Assessment
Page 577: Standards Practice
Chapter 23: Roots, Stems and Leaves
Section 23.1: Specialized Tissues in PLants
Section 23.2: Roots
Section 23.3: Stems
Section 23.4: Leave
Section 23.5: Transport in Plants
Page 605: Chapter 23 Assessment
Page 607: Standards Practice
Chapter 24: Reproduction of Seed Plants
Section 24.1: Reproduction with Cones and Flowers
Section 24.2: Seed Development and Germination
Section 24.3: Plant Propagation and Agriculture
Page 629: Chapter 24 Assessment
Page 631: Standards Practice
Chapter 25: Plant Responses and Adaptations
Section 25.1: Hormones and Plant Growth
Section 25.2: Plant Responses
Section 25.3: Plant Adaptations
Page 651: Chapter 25 Assessment
Page 653: Standards Practice
Chapter 26: Sponges and Cnidarians
Section 26.1: Introduction to the Animal Kingdom
Section 26.2: Sponges
Section 26.3: Cnidarians
Page 679: Chapter 26 Assessment
Page 681: Standards Practice
Chapter 27: Worms and Mollusks
Section 27.1: Flatworms
Section 27.2: Roundworms
Section 27.3: Annelids
Section 27.4: Mollusks
Page 711: Chapter 27 Assessment
Page 713: Standards Practice
Chapter 28: Arthropods and Echinoderms
Section 28.1: Introduction to the Arthropods
Section 28.2: Groups of Arthropods
Section 28.3: Insects
Section 28.4: Echinoderms
Page 741: Chapter 28 Assessment
Page 743: Standards Practice
Chapter 29: Comparing Invertebrates
Section 29.1: Invertebrate Evolution
Section 29.2: Form and Function in Invertebrates
Page 761: Chapter 29 Assessment
Page 763: Standards Practice
Chapter 30: Nonvertebrate Chordates, Fishes and Amphibians
Section 30.1: The Chordates
Section 30.2: Fishes
Section 30.3: Amphibians
Page 793: Chapter 30 Assessment
Page 795: Standards Practice
Chapter 31: Reptiles and Birds
Section 31.1: Reptiles
Section 31.2: Birds
Page 817: Chapter 31 Assessment
Page 819: Standards Practice
Chapter 32: Mammals
Section 32.1: Introduction to the Mammals
Section 32.2: Diversity of Mammals
Section 32.3: Primates and Human Origins
Page 845: Chapter Assessment
Page 847: Standards Practice
Chapter 33: Comparing Chordates
Section 33.1: Chordate Evolution
Section 33.2: Controlling Body Temperature
Section 33.3: Form and Function in Chordates
Page 867: Chapter Assessment
Page 869: Standards Practice
Chapter 34: Animal Behavior
Section 34.1: Elements of Behavior
Section 34.2: Patterns of Behavior
Page 885: Chapter Assessment
Page 887: Standards Practice
Chapter 35: Nervous System
Section 35.1: The Human Body Systems
Section 35.2: The Nervous System
Section 35.3: Divisions of the Nervous System
Section 35.4: The Senses
Section 35.5: Drugs and the Nervous System
Page 917: Chapter Assessment
Page 919: Standards Practice
Chapter 36: Skeletal, Muscular, and Integumentary Systems
Section 36.1: The Skeletal System
Section 36.2: The Muscular System
Section 36.3: The Integumentary System
Page 939: Chapter Assessment
Page 941: Standards Practice
Chapter 37: Circulatory and Respiratory System
Section 37.1: The Circulatory System
Section 37.2: Blood and the Lymphatic System
Section 37.3: The Respiratory System
Page 967: Chapter Assessment
Page 969: Standards Practice
Chapter 38: Digestive and Excretory Systems
Section 38.1: Food and Nutrition
Section 38.2: The Process of Digestion
Section 38.3: The Excretory System
Page 993: Chapter Assessment
Page 995: Standards Practice
Chapter 39: Endocrine and Reproductive System
Section 39.1: The Endocrine System
Section 39.2: Human Endocrine Glands
Section 39.3: The Reproductive System
Section 39.4: Fertilization and Development
Page 1027: Chapter Assessment
Page 1029: Standards Practice
Chapter 40: The Immune System and Disease
Section 40.1: Infectious Disease
Section 40.2: The Immune System
Section 40.3: Immune System Disorders
Section 40.4: The Environment and Your Health
Page 1059: Standards Practice
All Solutions
Section 20.4: Plantlike Protists: Red, Brown, and Green Algae
Exercise 1
Step 1
1 of 2
**Rhodophyta (red algae)** has chlorophyll a and phycobilins. They can live in deep water due to phycobilins. **Phaeophyta (brown algae)** has chlorophyll a and c as well as fucoxanthin. **Chlorophyta (green algae)** has a carbohydrate cell wall and photosynthetic pigments that are similar to plants such as chlorophyll a.
Result
2 of 2
See explanation.
Exercise 2
Step 1
1 of 2
In plants, alternation of generations mean switching between haploid and diploid forms by using mitosis and meiosis processes throughout their lives. This is how they grow and reproduce.
Result
2 of 2
See explanation.
Exercise 3
Step 1
1 of 2
Multicellular algae can perform photosynthesis to make organic food sources and oxygen. Oxygen is released into the environment where it is used up by various organisms, such as us. The organic food source is consumed by many organisms, such as small fish. Without algae, many organisms will die.
Result
2 of 2
See explanation.
Exercise 4
Step 1
1 of 2
In their cells, red algae have phycobilin pigment that has the ability to obtain blue light. They are able to live in deep water because blue light can penetrate deep water.
Result
2 of 2
See explanation.
Exercise 5
Step 1
1 of 1
The diagram below shows the life cycle of a unicellular green alga called Chlamydomonas. It can reproduce through an asexual propagation of zoospores and it can reproduce sexually through a fusion called syngamy.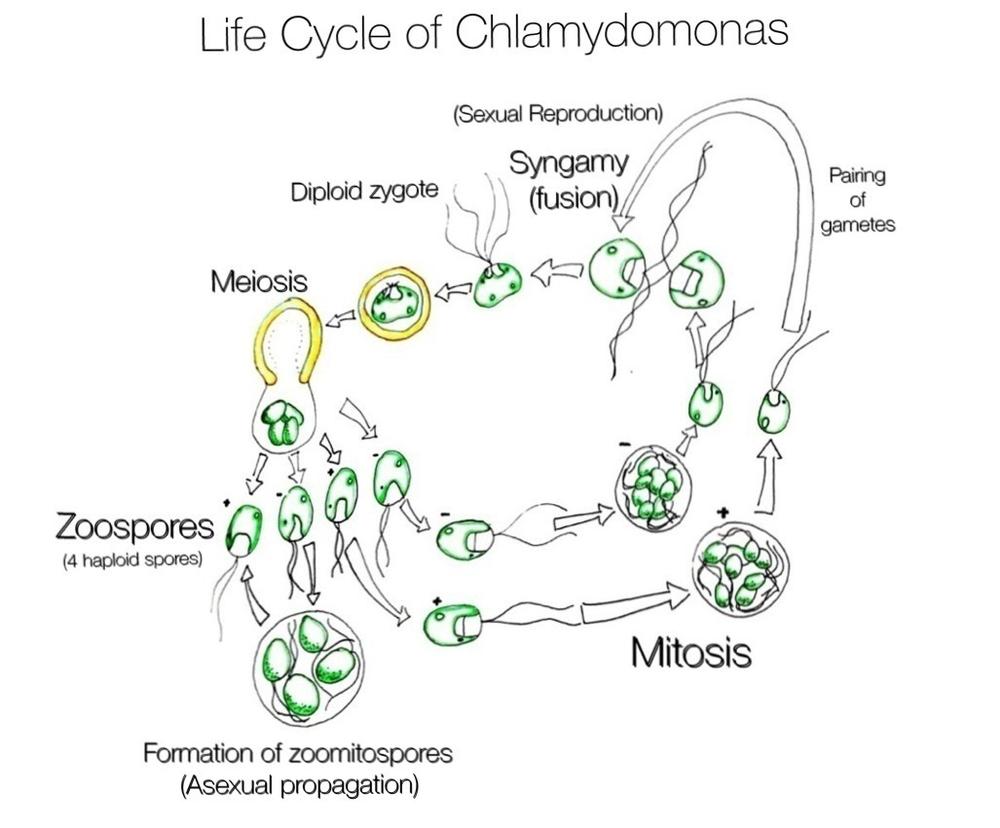

Haven't found what you were looking for?
Search for samples, answers to your questions and flashcards

unlock
