
All Solutions
Page 197: Chapter 7 Assessment

a. Nuclear envelope: It is a double-membrane structure that serves as the outermost layer of the nucleus
b. Nucleoplasm: It is a fluid found inside the nucleus where the chromatin and nucleolus are found
c. Chromatin: It is the genetic material which consists of DNA and proteins. The threadlike chromatins condense to form chromosomes.
d. Nucleolus: It is the dark stained area in the nucleus which helps synthesize the ribosomes.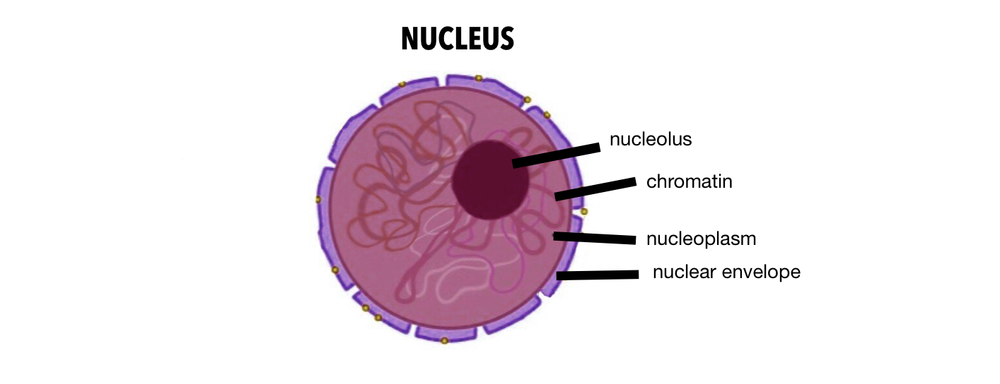
microfilaments
$$
microtubule
$$
Formula:
Concentration = mass of the solute (g) / volume of the solution (L)
= 2 g / 4 L
= 0.5 g/L
**Diffusion** is where the substances move from a higher concentration area to a lower concentration in a given solution.
Hence, in osmosis, only water can move in the setup.
Here are some examples:
a. muscle cells, muscle tissues, muscular system
b. nerve cells, nerve tissues, nervous system
c. bone cells, bone tissues, skeletal system
Given:
Mass of solute = 18 grams of salt
Volume of solution = 6 liters of water.
Formula:
Concentration = mass of solute (g) / volume of solution (L)
Solve:
= 18 g / 6 L
= 3 g/L
Given:
Mass of solute = 24 grams of salt
Volume of solution = 12 liters of water.
Formula:
Concentration = mass of solute (g) / volume of solution (L)
Solve:
= 24 g / 12 L
= 2 g/L
Since diffusion is caused by the movement of ions or molecules from an area of higher concentration to a lower concentration, adding heat to it can increase the motion of these molecules. As a result, the rate of diffusion happens faster if there is an increase in temperature.
Hypothesis: The presence of a high temperature will make the rate of diffusion faster.
In this experiment, we will determine the effect of a hot temperature on the rate of diffusion.
Materials needed:
a. 3 beakers
b. vegetable coloring in three different colors (blue, red, yellow)
c. 100 mL of hot water
d. 100 mL of cold water
e. 100 mL of room temperature water
f. dropper
g. timer
Steps:
1. Prepare the food coloring and the beakers. Label the beakers with A, B, and C. Beaker A will serve as the controlled group.
2. Beaker A must be poured with 100 mL of room temperature water.
3. Place one drop of the yellow color into beaker A.
4. Use the timer and see how much time it takes until the water gets a consistent yellow color. Record the time in seconds.
5. Pour the cold water in beaker B and place one drop of blue color in it. Record the time until the water gets a consistent blue color.
6. Pour the hot water in beaker C and place one drop of red color in it. Record the time until the water gets a consistent red color.
7. Compare the results and determine which beaker has the lowest time.
A cell is compared to a restaurant.
1. The cell membrane is like the restaurant doors. It controls what gets in and gets out of the cell, which is just like how the restaurant doors control who goes in and goes out of the restaurant.
2. The cytoplasm is compared to the restaurant floor. It holds the organelles together in place, which is just like the restaurant floor that holds all the tables, chairs and other equipment.
3. The nucleus controls the cell’s activities, just like a restaurant manager who oversees what happens inside the restaurant.
4. Ribosomes produce the proteins, which is similar to the work of the chef who cooks the food.
5. Mitochondria serve as the powerhouse of the cell. It stores energy obtained from the food which is going to be used by the other organelles. It is similar to the function of the refrigerator which stores the food until it is needed to be cooked.
6. The endoplasmic reticulum is the place where proteins and other compounds are produced. This is similar to the function of the kitchen wherein all the foods are prepared and cooked.
7. The Golgi apparatus prepares, modifies, and sorts proteins from the endoplasmic reticulum, which is similar to a waiter. The waiter ensures that all orders are sorted and served to the hungry customers.

