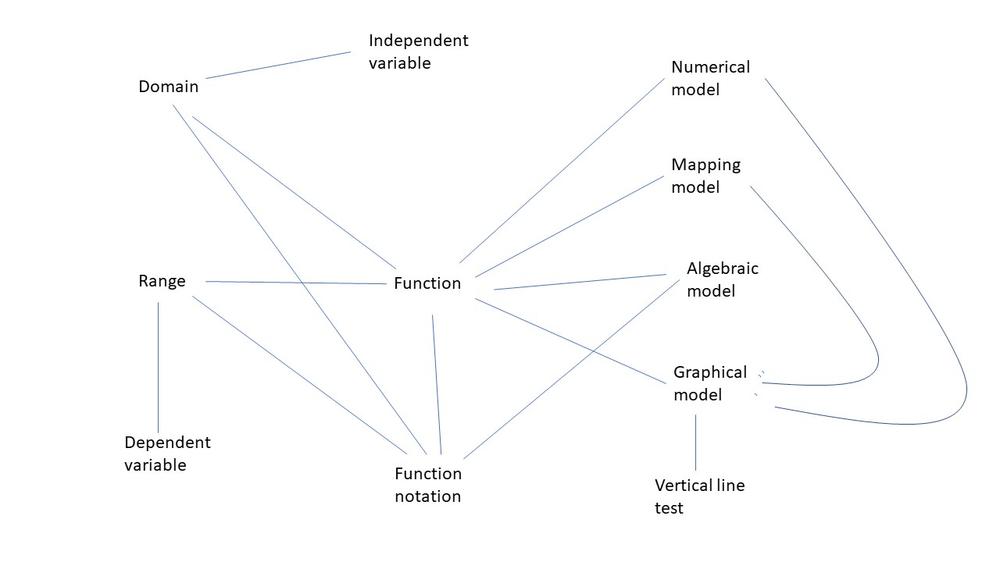
All Solutions
Section 1-1: Functions
Domain is $textbf{R}$ and the range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left[-2,-4 right]
end{equation*}
$$
This relation is a function according to vertical line test.
#### (b)
The domain is
$$
begin{equation*}
left[-1,+infty right]
end{equation*}
$$
and the range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left[1,+infty right]
end{equation*}
$$
This is a function according to vertical line test
#### (c)
The domain is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{1,2,3,4 right}
end{equation*}
$$
the range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{-5,4,7,9,11 right}
end{equation*}
$$
This is not a function according to diagram.Actually,1 is mapped into more than one element, in 4 and 9.
#### (d)
The domain and the range is $textbf{R}$ and this is the function because from creating the table of values we can see that each point is mapped to exactly one point.
#### (e)
The domain is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{-4,-3,1,2 right}
end{equation*}
$$
the range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{-0,1,2,3 right}
end{equation*}
$$
And this is function, we can see that from diagram.
The domain is $textbf{R}$ and the range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left(-infty,0 right]
end{equation*}
$$
and this is the function, we can conclude that making a table of value.
Domain: $textbf{R}$,
Range:
$$
begin{equation*}
left[-2,-4 right]
end{equation*}
$$
It is the function
#### (b)
Domain:
$$
begin{equation*}
left[-1,+infty right]
end{equation*}
$$
Range:
$$
begin{equation*}
left[1,+infty right]
end{equation*}
$$
#### (c)
Domain:
$$
begin{equation*}
left{1,2,3,4 right}
end{equation*}
$$
Range:
$$
begin{equation*}
left{-5,4,7,9,11 right}
end{equation*}
$$
It is not function.
#### (d)
Domain and range are $textbf{R}$ and it is the function.
#### (e)
Domain:
$$
begin{equation*}
left{-4,-3,1,2 right}
end{equation*}
$$
Range:
$$
begin{equation*}
left{0,1,2,3 right}
end{equation*}
$$
It is the function
#### (f)
Domain is $textbf{R}$, range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left(-infty,0 right]
end{equation*}
$$
It is the function
Domain and the range is $textbf{R}$
This relation is a function, we can see that by creating the table of values.
#### (b)
The domain is $textbf{R}$ without -3 and the range is $textbf{R}$
This is a function according to table of values.
#### (c)
The domain is $textbf{R}$, the range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left(0,1 right]
end{equation*}
$$
We can check that this is the function by vertical line test.
#### (d)
The domain is $textbf{R}$ and the range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left[0,2 right]
end{equation*}
$$
Again, this is the function according to vertical line test.
#### (e)
The domain is
$$
begin{equation*}
left[-3,3 right]
end{equation*}
$$
the range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left[-3,3 right]
end{equation*}
$$
And this is function, we can see that apply vertical line test.
#### (f)
The domain is $textbf{R}$ and the range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left[-2,2 right]
end{equation*}
$$
and this is the function, we can check that by creating a table of values.
Domain and the range is $textbf{R}$
This relation is a function.
#### (b)
The domain is $textbf{R}$ without -3 and the range is $textbf{R}$
This is a function.
#### (c)
The domain is $textbf{R}$, the range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left(0,1 right]
end{equation*}
$$
|This is the function.
#### (d)
The domain is $textbf{R}$ and the range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left[0,2 right]
end{equation*}
$$
This is the function.
#### (e)
The domain is
$$
begin{equation*}
left[-3,3 right]
end{equation*}
$$
the range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left[-3,3 right]
end{equation*}
$$
This is function.
#### (f)
The domain is $textbf{R}$ and the range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left[-2,2 right]
end{equation*}
$$
This is the function
Domain is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{1,3,5,7 right}
end{equation*}
$$
The range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{2,4,6 right}
end{equation*}
$$
This is the function.
#### (b)
The domain is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{0,1,2,5right}
end{equation*}
$$
The range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{-1,3,6right}
end{equation*}
$$
This is a function.
#### (c)
The domain is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{0,1,2,3 right}
end{equation*}
$$
The range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{2,4 right}
end{equation*}
$$
This is the function.
#### (d)
The domain is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{2,6,8 right}
end{equation*}
$$
The range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{1,3,5,7 right}
end{equation*}
$$
This is not the function.
#### (e)
The domain is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{1,10,100 right}
end{equation*}
$$
the range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{0,1,2,3 right}
end{equation*}
$$
This is not function.
Domain is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{1,3,5,7 right}
end{equation*}
$$
The range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{2,4,6 right}
end{equation*}
$$
This is the function.
#### (b)
The domain is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{0,1,2,5right}
end{equation*}
$$
The range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{-1,3,6right}
end{equation*}
$$
This is a function.
#### (c)
The domain is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{0,1,2,3 right}
end{equation*}
$$
The range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{2,4 right}
end{equation*}
$$
This is the function.
#### (d)
The domain is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{2,6,8 right}
end{equation*}
$$
The range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{1,3,5,7 right}
end{equation*}
$$
This is not the function.
#### (e)
The domain is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{1,10,100 right}
end{equation*}
$$
the range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left{0,1,2,3 right}
end{equation*}
$$
This is not function.
$$
f colon left{1,3,5,7 right} to left{2,4,6 right}
$$
This is the function.
#### (b)
$$
f colon left{0,1,2,5 right} to left{-1,3,6 right}
$$
This is a function.
#### (c)
$$
f colon left{0,1,2,3 right} to left{2,4right}
$$
This is the function.
#### (d)
$$
f colon left{2,6,8 right} to left{1,3,5,7 right}
$$
This is not the function.
#### (e)
$$
f colon left{1,10,100 right} to left{0,1,2,3 right}
$$
This is not function.
#### (f)
$$
f colon left{1,2,3,4right} to left{1,2,3,4right}
$$
This is the function
Domain and range is $textbf{R}$ and it is the function.
#### (b)
It is not the function
#### (c)
We have that
$$
begin{equation*}
y=dfrac{x^2}{2}-1
end{equation*}
$$
And this is the function, where $x$ is dependent variable.
#### (d)
Here we have that
$$
begin{equation*}
y=pmsqrt{x}
end{equation*}
$$
and this is not the function.
#### (e)
The domain is $textbf{R}$ without 0, the range is $textbf{R}$ and it is the function.
#### (f)
The domain and the range is $textbf{R}$ and this is the function.
Domain and range is $textbf{R}$ and it is the function.
#### (b)
It is not the function
#### (c)
This is the function,.
#### (d)
This is not the function.
#### (e)
The domain is $textbf{R}$ without 0, the range is $textbf{R}$ and it is the function.
#### (f)
The domain and the range is $textbf{R}$ and this is the function.
Here we have that $x$=3-$y$, or $y$=3+$x$.
#### (b)
Here is $y$=5-2$x$
#### (c)
(2+$x$)3=$y$, or $y$=3$x$+6
#### (d)
$x$+$y$=5, or $y$=5-$x$
$y$=3+$x$.
#### (b)
$y$=5-2$x$
#### (c)
$y$=3$x$+6
#### (d)
$y$=5-$x$
From the text of the task we have information that the length of the closet, $l$, is twice the size of its width, which is $w$, and we conclude that it is
$$
l=2w
$$
#### (b)
We have that $f(l)=w+l$ and from the task $l=2w$, so we have that $w=dfrac{l}{2}$, and finally, the equation for $f(l)$ is:
$$
begin{equation*}
f(l)=w+l=dfrac{l}{2}+l=dfrac{3}{2}l
end{equation*}
$$
#### (d)
We have, all from task that the $w+l=12$ and $l=2w$, so, when we replace $l$ in the first equation, we get:
$w+2w=12$
$3w=12$
$w=4$ and we get $l=12-4=8$
#### (c)
Here we have graph of $f(l)=dfrac{3}{2}l$
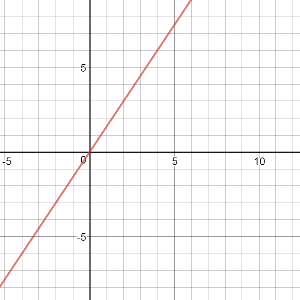
From the text of the task $l=2w$
#### (b)
$$
begin{equation*}
f(l)=w+l=dfrac{l}{2}+l=dfrac{3}{2}l
end{equation*}
$$
#### (c)
$w=4$, $l=8$
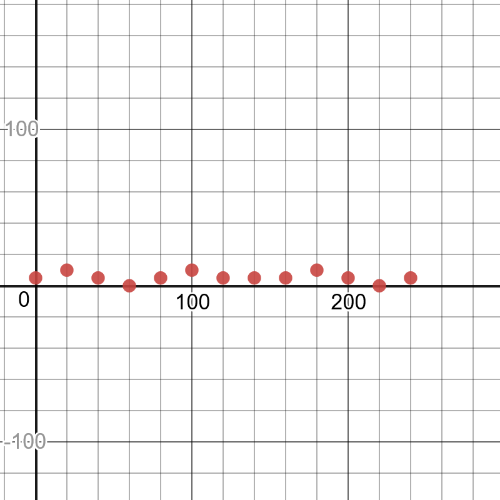
$$
D=left{0,20,40,60,80,100,120,140,160,180,200,220,240 right}
$$
#### (c)
$$
R=left{0,5,10 right}
$$
#### (d)
$textbf{It is a function}$ because it passes the vertical line test.
#### (e)
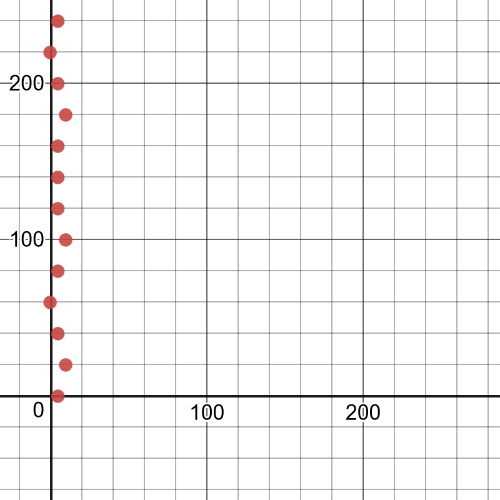
$textbf{It is not a function}$ because for example $(5,0)$ and $(5,40)$ are both in relation.
(c) $R=left{0,5,10 right}$;
(d) $textbf{It is a function}$;
(f) $textbf{It is not a function}$
The next mapping is a function:
$$
begin{equation*}
left{left(1,3 right),left(2,2 right),left(3,1 right) right}
end{equation*}
$$
When we replace the coordinates we get a mapping which is still a function:
$$
begin{equation*}
left{left(3,1 right),left(2,2 right),left(1,3 right) right}
end{equation*}
$$
#### (b)
The next mapping is a function:
$$
begin{equation*}
left{left(1,1 right),left(2,1 right),left(3,2 right) right}
end{equation*}
$$
But when we replace the coordinates, we get a mapping that is no longer a function:
$$
begin{equation*}
left{left(1,1 right),left(1,2 right),left(2,3 right) right}
end{equation*}
$$
#### (c)
The next mapping is not a function:
$$
begin{equation*}
left{left(1,1 right),left(1,2 right) right}
end{equation*}
$$
When we replace the coordinates we get a mapping which is a function:
$$
begin{equation*}
left{left(1,1 right),left(2,1 right) right}
end{equation*}
$$
$d=sqrt{(4-0)^2+(3-0)^2}=sqrt{4^2+3^2}=sqrt{25}=5$
$textbf{Yes}$, because the distance from $(4,3)$ to $(0,0)$ is $5$.
#### (b)
$d=sqrt{(1-0)^2+(5-0)^2}=sqrt{1^2+5^2}=sqrt{26}ne5$
$textbf{No}$, because the distance from $(1,5)$ to $(0,0)$ is not $5$.
#### (c)
$textbf{No}$, because $(4,3)$ and $(4,-3)$ are both in the relation.
Based on the values for x and y from the table, we create the equation of the right through two points, that is, the required function.Let’s take $x_1=0, x_2=1, y_1=3, y_2=4$, so we have:
$y-y_1=dfrac{y_2-y_1}{x_2-x_1}(x-x_1)$
$y-4=dfrac{4-3}{1-0}(x-0)$
$$
y=x+4
$$
#### (b)
From the table, we have:
$g(3)-g(2)=12-7=5$
$g(3-2)=g(1)=4$
We get
$$
begin{equation*} 5ne4 end{equation*}
$$
so we conclude that
$$
begin{equation*} g(3)-g(2)ne{g(3-2)} end{equation*}
$$
$$
y=x+4
$$
#### (b)
$$
begin{equation*} g(3)-g(2)ne{g(3-2)}
end{equation*}
$$
The factors of 6 are 1, 2, 3 and 6.
$f(6)=1+2+3+6=12$
The factors of 7 are 1 and 7.
$f(7)=1+7=8$
The factors of 8 are 1, 2,4 and 8.
$f(8)=1+2+4+8=15$
#### (b)
The factors of 3 are 1 and 3.
$f(3)=1+3=4$
The factors of 5 are 1 and 5.
$f(5)=1+5=6$
The factors of 3 are 1 and 3.
$f(3)=1+3=4$
The factors of 15 are 1, 3, 5 and 15.
$f(15)=1+3+5+15=24$
And we have that:
$$
begin{equation*}
f(3)times{f(5)}=4times6=24
end{equation*}
$$
So, the coclusion is:
$$
begin{equation*}
f(3)times{f(5)}=f(15)
end{equation*}
$$
.The factors of 4 are 1, 2 and 4.
$f(4)=1+2+4=7$
The factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3 ,4, 6 and 12.
$f(12)=1+2+3+4+6+12=28$
And we have that:
$$
begin{equation*}
f(3)times{f(4)}=4times7=28
end{equation*}
$$
So, the coclusion is:
$$
begin{equation*}
f(3)times{f(4)}=f(12)
end{equation*}
$$
#### (c)
Yes, the sigma function of a number is a product of the sigma function of any two numbers contained in it, and which in the product give this number. In the general case, it is valid:
$$
begin{equation*}
{atimes{b}=c}Rightarrow{f(a)times{f(b)}=f(c)}
end{equation*}
$$
$$
begin{equation*}
left[-5,5 right]
end{equation*}
$$
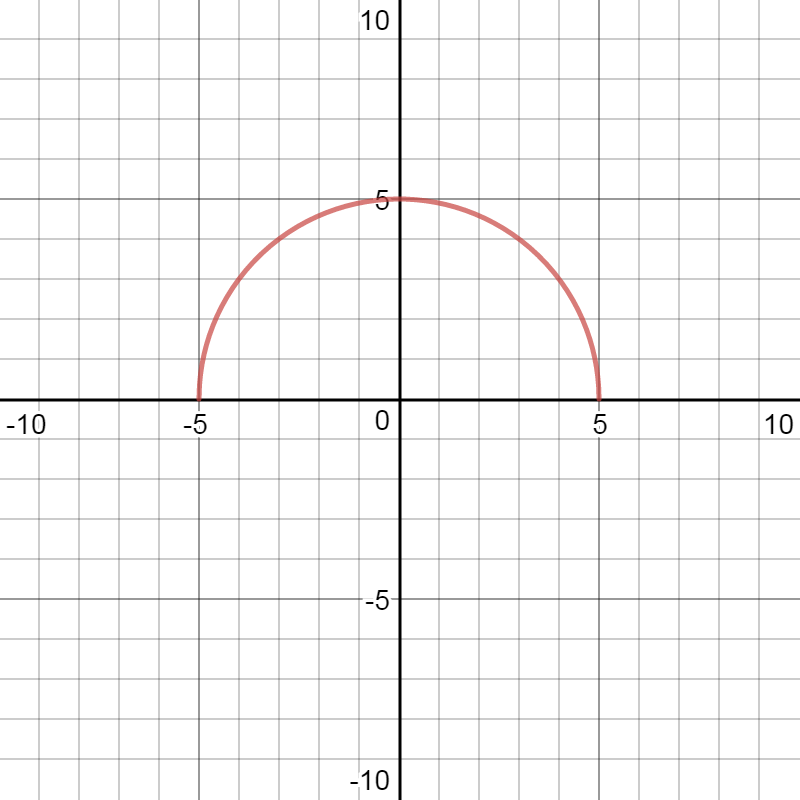
Here we have graph of this function:
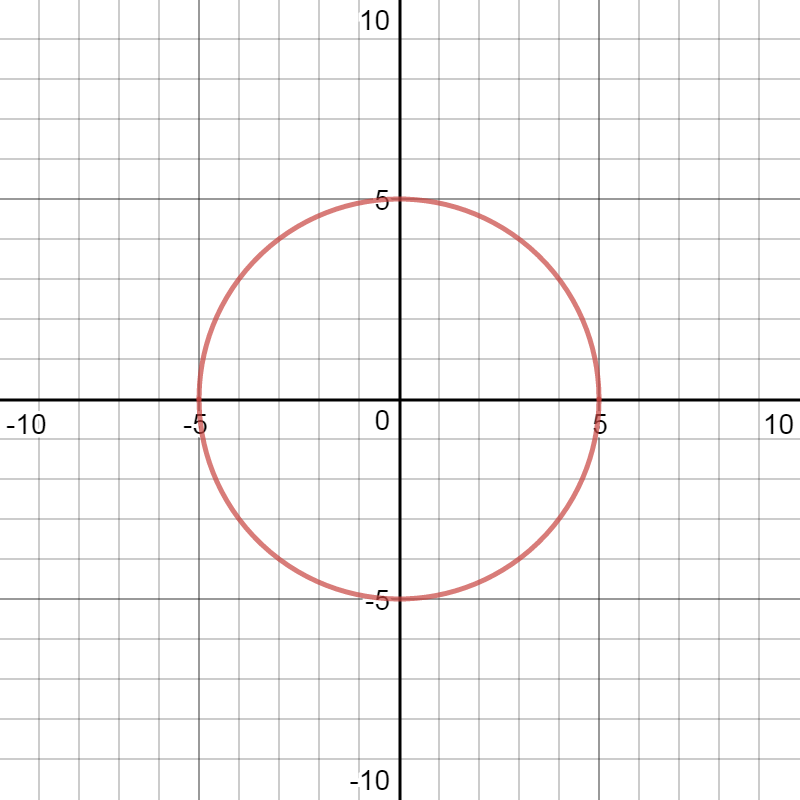
begin{equation*}
textcolor{#c34632}{y=sqrt{25-x^2}}
end{equation*}
$$
This is the function, we can see that from the graph of this function, applying test of vertical lines.The domain of this function is
$$
begin{equation*}
left[-5,5 right]
end{equation*}
$$
and the range is
$$
begin{equation*}
left[0,5 right]
end{equation*}
$$
Here we have graph of this function: