
All Solutions
Page 939: Chapter Assessment
Figure B shows a cardiac muscle.
Figure C shows a smooth muscle.
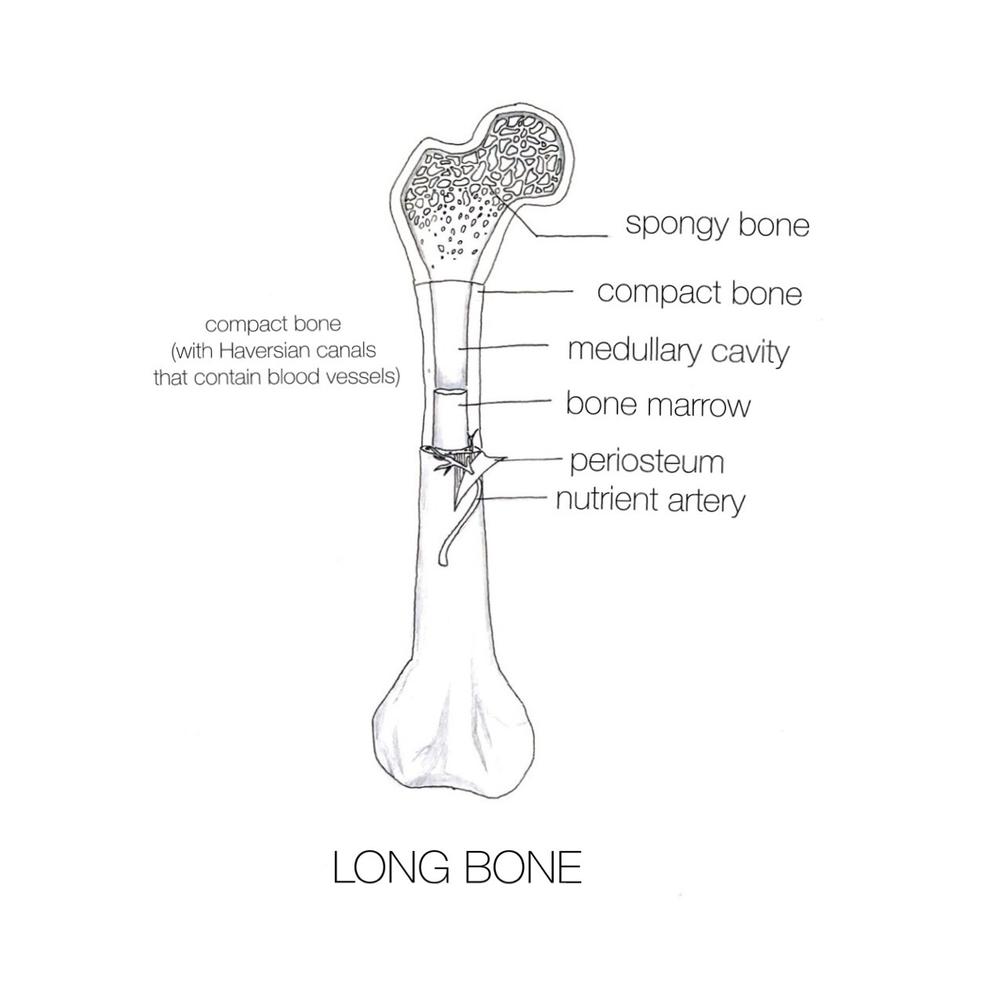
Figure D shows a Haversian canal.
Therefore, figure C is the correct answer.
Both **smooth** and **cardiac muscles** are designed well to facilitate the involuntary contraction and movement of the internal organs including the function of the heart to pump blood and the peristalsis motion of the gastrointestinal tract. On the other hand, **skeletal muscles** regulate voluntary movements which can be consciously controlled by ourselves.
1. The **epidermis** is the outer layer of the skin composed of two layers in which the outer layer is comprised of dead skin cells and the inner layer is comprised of proliferating cells. These cells push the older cells to the surface of the epidermis, and as it moves upward the cells tend to disintegrate and die.
2. The **dermis** is the layer beneath the epidermis. This layer of the skin is composed of collagen fibers, blood vessels, nerve endings, follicles, and smooth muscles. The dermis also contains the two important glands of the skin which are the sebaceous gland and sweat gland.
Although most people have the relative same amount of melanocytes in the skin, the production of the pigment melanin differs, and this result in differences in the skin color among individuals.
1. Joint between the trochlea of humerus and ulna, which is a hinge joint permitting back and forth motion.
2. Joint between capitulum of humerus and radius head, which is also a hinge joint.
3. Upper part of the radius and ulna form a pivot joint. Such a joint allows one bone to rotate over the other bone.
These joints are very essential to replicate the elbow in the robotics arm.
1) Insomnia, depression, fatigue, headache
2) Physical effects include – muscular and skeletal injuries i.e., fractural bones arthritis, etc,
3) Also linked to cellular mutations and cancer as over-exercising can lead to the release of excessive free radicals.
4) It can lead to problems related to heart
In women, it may lead to amenorrhea.

