All Solutions
Page 575: Chapter 22 Assessment
Rhizomes are a bundle of underground stems that are found in a plant. It forms new shoots and stores protein and starches.
Roots are hair-like structures that are formed in vascular plants like ferns. They have a similar function with rhizoids.

Mosses, which are under the phylum Bryophyta, undergo reproduction using spores, and not by seeds or flowers. During mitosis, gametes or haploid cells fuse together to grow a new diploid cell called sporophyte. In turn, this sporophyte grows on top of the gametophyte part of the plant. Mosses are relatively small due to the fact that they lack a vascular system.
Seedless Vascular Plants: Ferns
In a fern’s life cycle, they reproduce by spores. The dominant phase is the sporophyte in the diploid phase, wherein the sporophyte plant goes through meiosis to produce haploid spores. When the spores fuse together, a heart-shaped gametophyte plant is formed. This part grows independently from the sporophyte. The height of a fern can go as little as 1 inch tall and it can be as high as 80 feet.
Gymnosperms: Conifers
Gymnosperms produce through seeds and not by spores. Conifers produce pollen cones that produce pollen grain. Once the pollen is blown to another cone, fertilization will take place. Some conifers such as giant redwoods can grow up to 100 meters.
Angiosperms: Flowering Plants
Angiosperms have flowers as their reproductive structure. Flowers have ovaries which protect the young seeds and later on, these seeds become a fruit after a successful pollination. When the seeds inside the fruit get dispersed, a new plant will emerge.
The size range of angiosperms is very large. It can go as little as half an inch to a hundred feet.
1) They develop unique reproductive organs known as **flowers**. Flowers are an advantage to bees, and moths, which then transport pollen from flower to flower. Transfer of pollen with animals is much more efficient than wind pollination
Since we usually classify plants based on their appearance and their similarities with other organisms, there are instances that we place them under a group which is not suited to their evolutionary history. An example is a plant called Tmesipteris, which is a fork fern from the fern allies. They are relatives of the ferns but they are not true ferns. They only share similar characteristics in the way they reproduce but they differ in terms of the leaf structure. Because of this, the role of DNA classification has been an effective help in creating a distinction and similarities between the ferns and the fern allies. They were able to determine that the fork ferns closely resembled ferns, which changed the idea that they are actually ferns and not fern allies. By determining the genetic makeup of life-forms, it allowed the scientists to know how they are going to classify organisms.
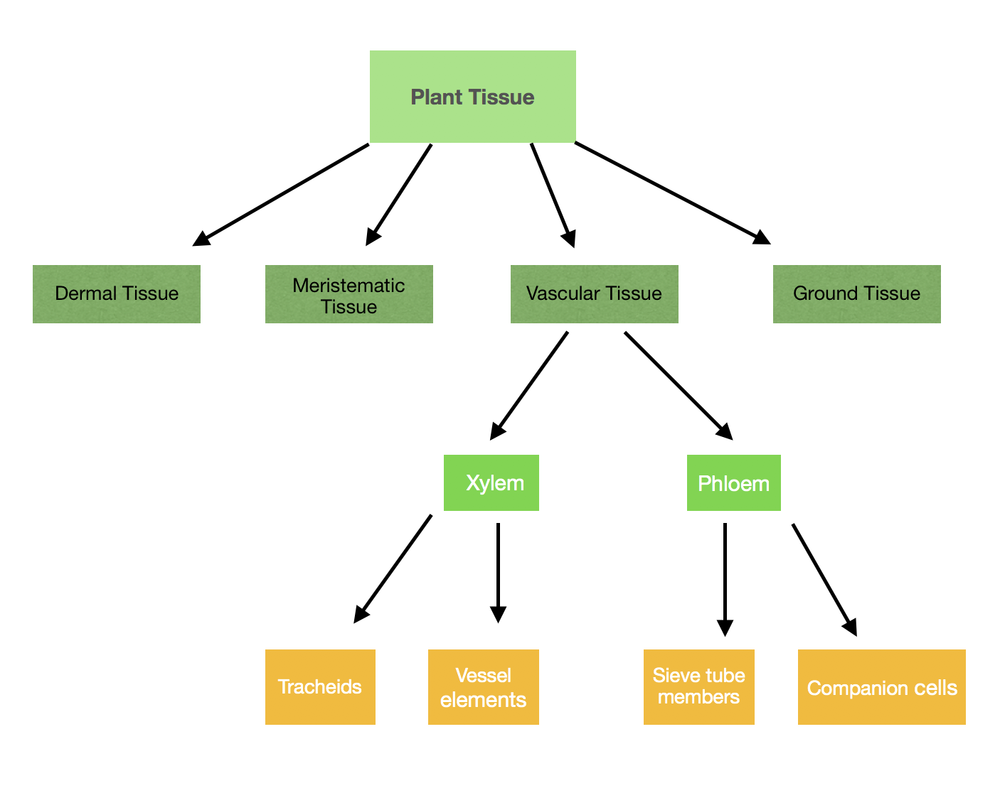
Xylem carries water from the roots going upward to the other parts of the plant. The tracheids are the long cells found in the xylem, while the vessel elements are the shorter and wider cells in the xylem tissue. Both tracheids and vessel elements are involved in the movement of water throughout the plant.
Phloem carries the nutrients and the products of photosynthesis throughout the plant. It has sieve tube elements which are the specialized cells involved in transferring the molecules to the other parts of the plant. The activity of the sieve tube elements is regulated by companion cells.