
All Solutions
Page 283: Chapter 11 Assessment
a. Principle of Dominance
This states that some alleles are dominant, and some alleles are recessive. Dominant alleles exhibit their effect in the form of a trait in an organism. On the other hand, recessive allele is masked by the dominant allele. It would only show if it is teamed up with another recessive allele.
b. Principle of Segregation
This explains how genes are separated during meiosis. During the formation of gametes in an organism, the pair of alleles segregate from each other in order for each gamete to carry one of the two alleles. In this way, an offspring acquires one allele from each parent.
c. Biological Inheritance
Biological inheritance is influenced by chemical factors that determine the traits which are passed to the next generation. This chemical factor is called genes. Genes produce the characteristics of an organism’s trait in two contrasting forms called alleles.
d. Principle of Independent Assortment
Independent assortment happens when a pair of genes separates independently during metaphase I in meiosis. In this stage, there are random combinations of genes that are formed. Genetic variation was made possible because of this principle.
Y = yellow seeds (dominant)
y = green seeds (recessive)
If two heterozygous parents with a genotype of Yy are crossed, the possible combination of genotypes in their offspring would be YY, Yy, Yy, and yy. This can be shown in the Punnett square diagram below.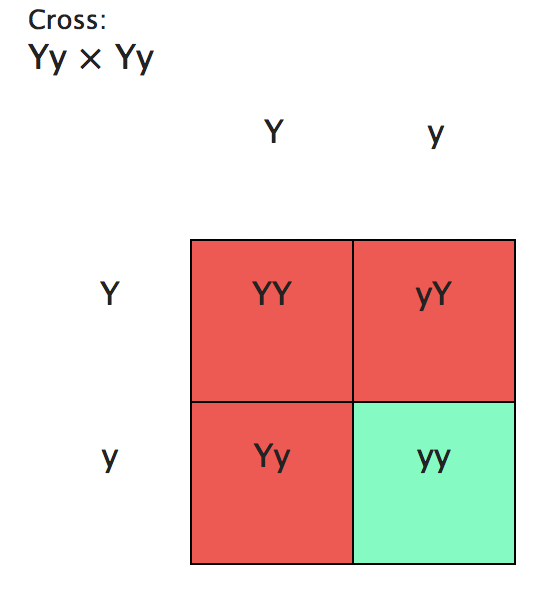
3 possible genotypes
a. YY = 25%
b. Yy = 50%
c. yy = 25%
Therefore, the genotypic ratio of the offspring produced is 1:2:1.
On the contrary, a polygenic trait occurs when a trait is controlled by two or more genes. For example, the wide range of skin color is caused by more than four different genes that control this trait. If a person who has a medium skin complexion has a genotype of AaBbCc, this means that there are 3 dominant genes and 3 recessive genes that are involved in this trait.
To get the number of chromosomes of the organism’s gametes, we have to divide the equation 2N = 8 by 2.
$dfrac{2N}{2}$ = $dfrac{8}{2}$
$$
N = 4
$$
Based on the computation, the number of chromosomes in the organism’s gametes is 4.
In meiosis II, there is no chromosome replication that is involved because the chromosomes are no longer identical due to the assortment in meiosis I. These chromosomes are further separated which results to 4 haploid cells. Each haploid cell has 2 chromatids.
To determine the probability of an offspring having a particular genotype, we can use a Punnett square diagram.

AA = short hair
Aa = short hair
Aa = short hair
aa = long hair
a. Aa $times$ Aa = AA, Aa, Aa, aa (3 tall plants and 1 short plant)
b. Aa $times$ aa = Aa, Aa, aa, and aa (2 tall plants and 2 short plants)
On the other hand, these genotypes could not have been present in the cross:
a. AA $times$ aa = Aa (all tall plants)
b. aa $times$ aa = aa (all short plants)
c. AA $times$ AA = AA (all tall plants)
This trait is formed due to an interplay of both genetics and environment. The way a gene is expressed can be affected by environmental factors such as temperature, light, food, drugs, or toxins.

