
All Solutions
Page 237: Chapter 9 Assessment
All organisms must get energy from the chemical energy of food, regardless of whether they created the food themselves or took it from the environment, hence all perform cellular respiration.
oxygen + glucose $rightarrow$ carbon dioxide + water + energy
6O$_{2}$ + C$_{6}$H$_{12}$O$_{6}$ $rightarrow$ 6CO$_{2}$ + 6H$_{2}$O + energy
oxygen + glucose $rightarrow$ carbon dioxide + water + energy
6O$_{2}$ + C$_{6}$H$_{12}$O$_{6}$ $rightarrow$ 6CO$_{2}$ + 6H$_{2}$O + energy
Alcoholic Fermentation:
pyruvic acid + NADH $rightarrow$ alcohol + carbon dioxide + NAD$^{+}$
Lactic Acid Fermentation:
pyruvic acid + NADH $rightarrow$ lactic acid + NAD$^{+}$
The equation for cellular respiration is shown below.
oxygen + glucose $rightarrow$ carbon dioxide + water + energy
The equation for alcoholic fermentation and lactic acid fermentation are shown below.
Alcoholic Fermentation:
pyruvic acid + NADH $rightarrow$ alcohol + carbon dioxide + NAD$^{+}$
Lactic Acid Fermentation:
pyruvic acid + NADH $rightarrow$ lactic acid + NAD$^{+}$
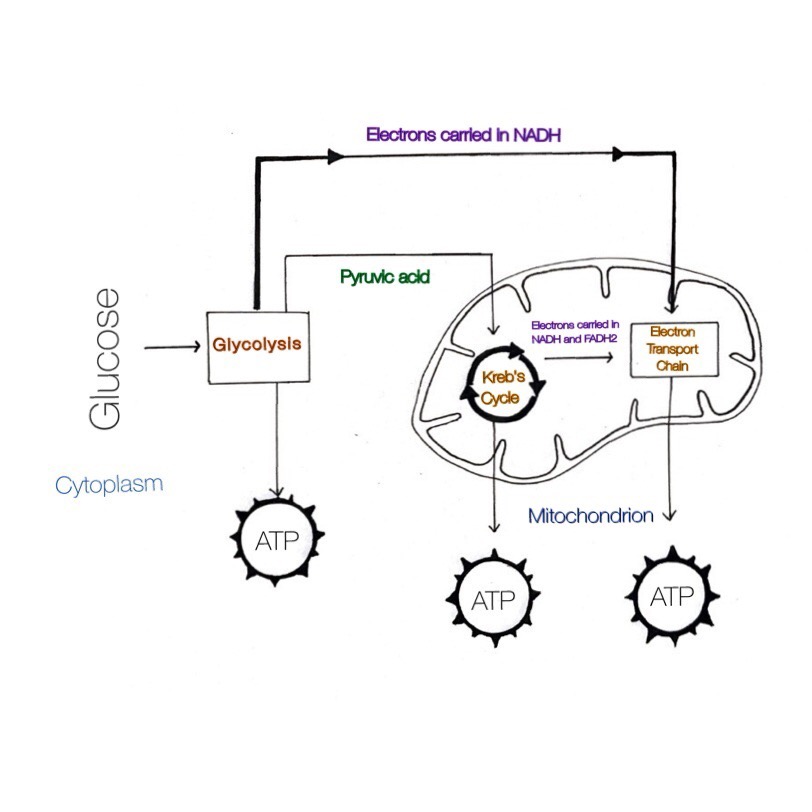
In cellular respiration, the process starts with oxygen and glucose (6-carbon molecule) to produce ATP. Cellular respiration is aerobic since oxygen is required for releasing the energy from the glucose.
On the other hand, fermentation starts with pyruvic acid (3-carbon molecule) and NADH. The end products of fermentation can either be an alcohol and carbon dioxide, or lactic acid. This process releases energy from the glucose molecules in the absence of oxygen; hence, it is anaerobic.
Photosynthesis uses light energy by converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. This process takes place in the chloroplast.
2. Cellular respiration
In cellular respiration, the process starts with oxygen and glucose (6-carbon molecule) to produce ATP. This process takes place in the mitochondria.
2 – Cellular respiration
To test, ask two persons to participate in this experiment. The first person (person A) must be asked to do a jogging exercise for ten days straight, while the second person (person B) must refrain from doing any exercises for ten days straight. On the eleventh day, ask them to ride a bicycle. They must keep cycling for thirty minutes with no rest. Once done, ask them if they feel any muscle discomfort, nausea, or weakness. If person B experiences muscle discomfort that is more painful that what person A felt, this means that there is more lactic build up in person B than person A.

