All Solutions
Page 1027: Chapter Assessment
Zygote.
– Site : Ampulla of the Fallopian tube.
– the optimum time for Fertilization is day 13 – 15 of
the normal menstrual cycle.
– the ovum can retain the capacity to be fertilized for
one day, while the sperms retain their power to
fertilize ova for 2 days.
– the sperm spends 10 hours in the Female tract to be
capable of Fertilization ( sperm capacitation ).
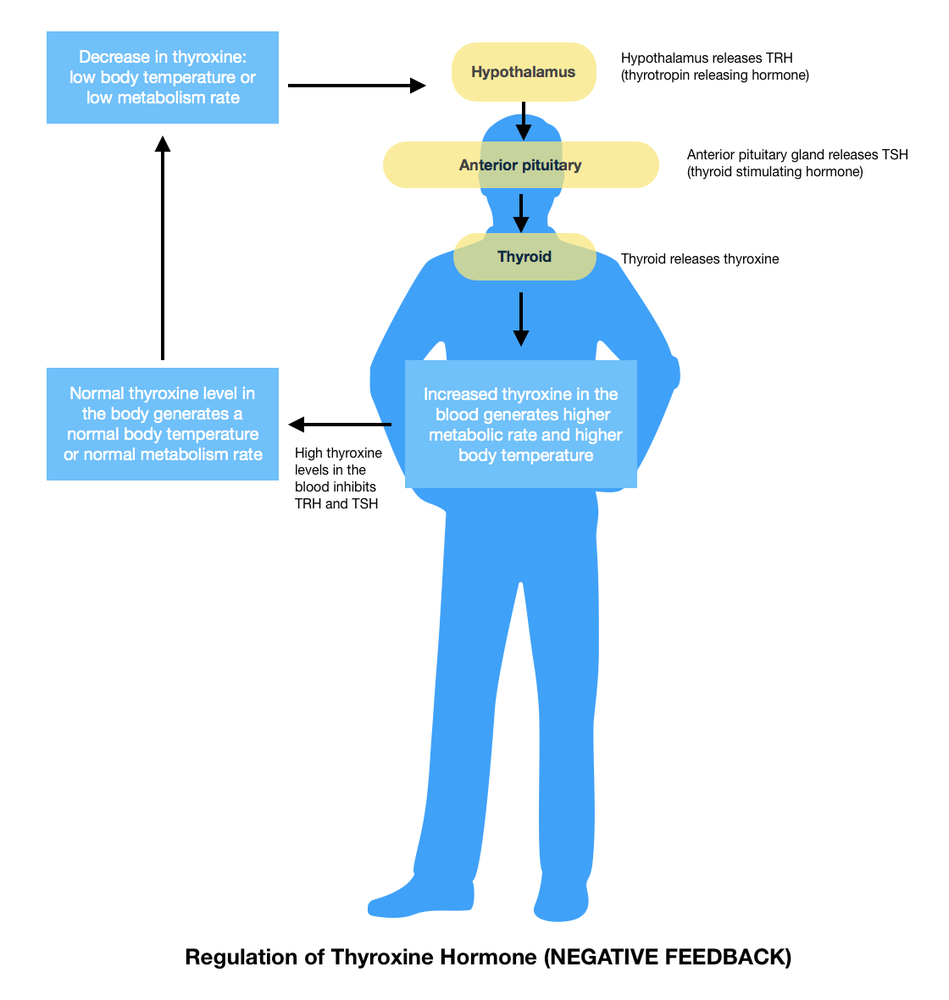
For example, if the body has detected a stimulus, which in this case is a high blood sugar level in the body, the endocrine system gives a signal to the pancreas to produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone that regulates the blood sugar level in the body.
1. Follicular phase – The hypothalamus creates a response and stimulates the anterior pituitary gland to release FSH and LH in the blood in order for the follicles to develop to maturity.
2. Ovulation phase – This is the shortest among the phases, as it only lasts for three to four days. In this phase, the matured egg is released into one of the Fallopian tubes, ready for fertilization.
4. Menstruation – This is the phase after the egg was not fertilized. In this phase, the lining of the uterus will shred and detach along with the blood and unfertilized egg, and it will be discharged outside through the vagina. Menstruation lasts for an average of 3-5 days, and a new cycle will begin after this phase.