
All Solutions
Section 5-5: Solving Rational Inequalities
#### (a)
$dfrac{x+5}{x-1} leq 4$
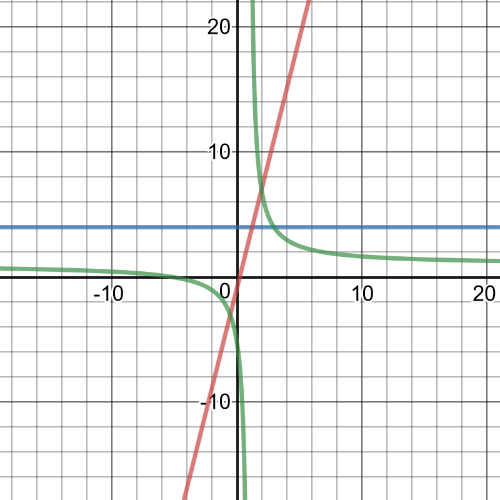
Examine the graph to determine when $dfrac{x+5}{x-1} leq 4$,
determine the green curve is below the blue line.
$textbf{This is true on the intervals}$ $(infty, 1)$ and $(3, infty)$.
#### (b)
$4x-1 geq dfrac{x+5}{x-1}$
Examine the graph. To determine when $4x-1 geq dfrac{x+5}{x-1}$, determine when the red line is above the green curve.
$textbf{This is true on the intervals}$ $(-0.5, 1)$ and $(2,infty)$.
Solve the inequality for $x$.
$dfrac{6x}{x+3} leq 4$
$dfrac{6x}{x+3}-4 leq 0$
$dfrac{6x}{x+3}-4 dfrac{x+3}{x+3}leq 0$
$dfrac{6x-4x-12}{x+3} leq 0$
$dfrac{2x-12}{x+3}leq 0$
$dfrac{2(x-6)}{x+3}leq 0$
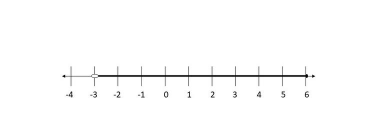
$$
textbf{The solution is $(-3, 6)$.}
$$
$x+2 > dfrac{15}{x}$
$x+2-dfrac{15}{x}>0$
$dfrac{x^2}{x}+dfrac{2x}{x}-dfrac{15}{x}>0$
$dfrac{x^2+2x-15}{x}>0$
$dfrac{(x+5)(x-3)}{x}>0$
$textbf{The equation is negative on $x < -5$}$ and $0 < x < 3$ and $textbf{positive on $-5 < x 3$}$.
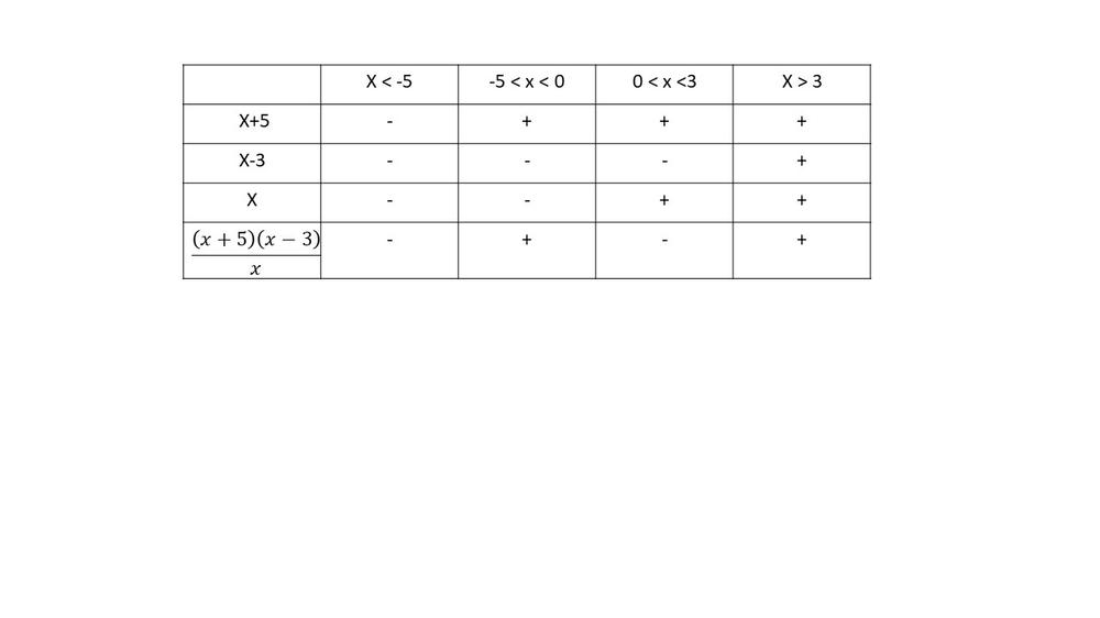
$textbf{The solution to the equation is}$ $left{ xinBbb{R}| x > -5right}$
This can also be written as $( -5, infty )$.
$dfrac{(x+5)(x-3)}{x}>0$
#### (b)
negative on $x < -5$ and $0 < x < 3$ positive on $-5 < x 3$
#### (c)
$left{ xinBbb{R}| x > -5right}$
$dfrac{1}{x+5} >2$
$dfrac{1}{x+5}-2 > 0$
$dfrac{1}{x+5}-2(dfrac{x+5}{x+5}) > 0$
$dfrac{1}{x+5}+dfrac{-2x-10}{x+5} > 0$
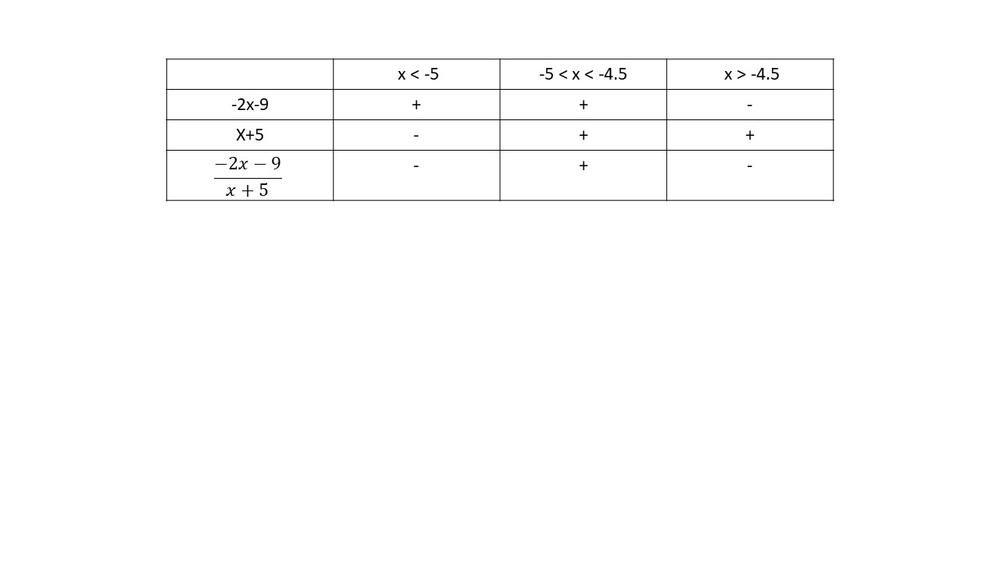
$dfrac{-2x-9}{x+5}> 0$
$textbf{The inequality is true on $-5<x<-4.5$}$.
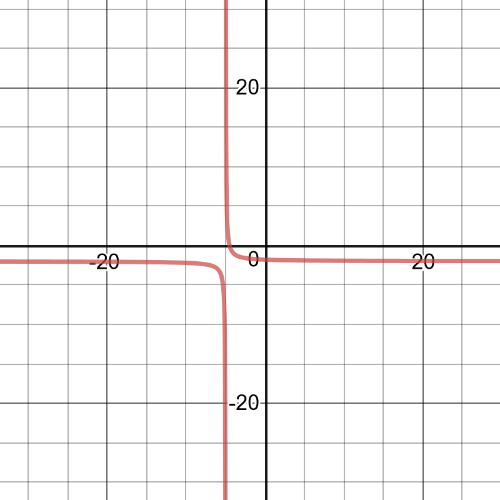
$dfrac{1}{2x+10}<dfrac{1}{x+3}$
$dfrac{1}{x+5}-dfrac{1}{x+3}<0$
$(dfrac{x+3}{x+3})dfrac{1}{x+5}-dfrac{1}{x+3}(dfrac{x+5}{x+5})<0$
$dfrac{x+3}{(x+5)(x+3)}+dfrac{-2x-10}{(x+3)(x+5)}<0$
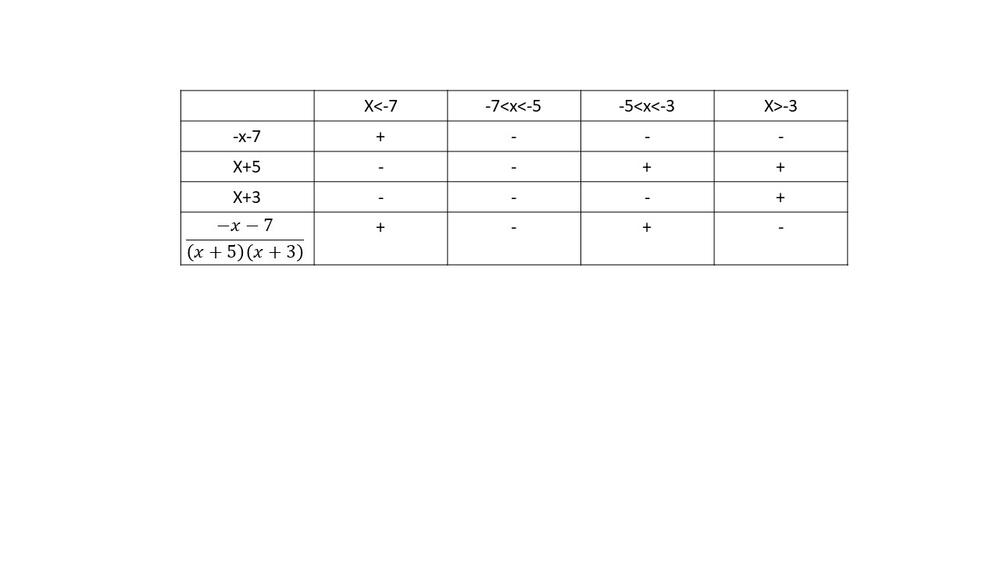
$dfrac{-x-7}{(x+5)(x+3)}<0$
$textbf{The inequality is true on $-7<x-3$}$.
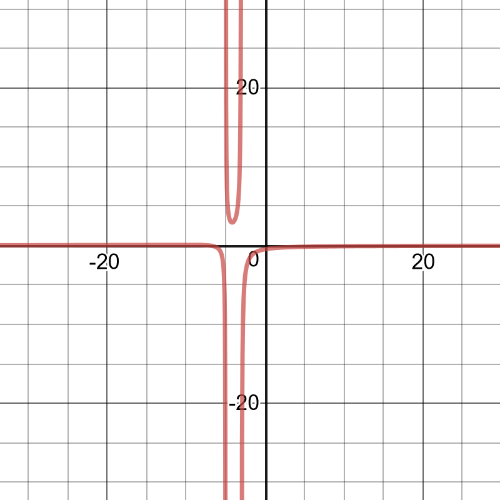
$dfrac{3}{x-2}<dfrac{4}{x}$
$dfrac{3}{x-2}-dfrac{4}{x}<0$
$(dfrac{x}{x})dfrac{3}{x-2}-dfrac{4}{x}(dfrac{x-2}{x-2})<0$
$dfrac{3x}{x(x-2)}+dfrac{-4x+8}{x(x-2)}<0$
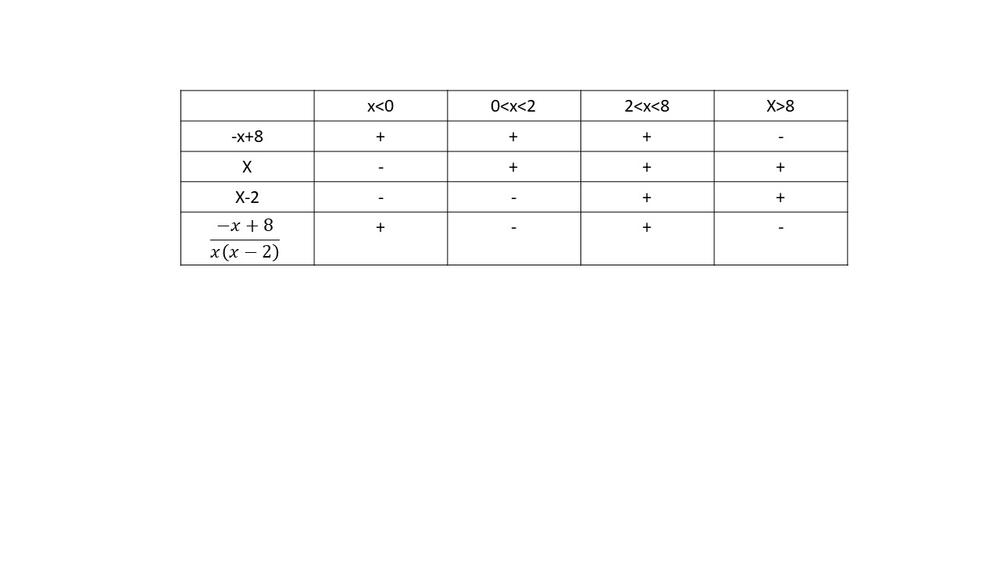
$dfrac{-x+8}{x(x-2)}<0$
$textbf{The inequality is true on $0<x8$}$.
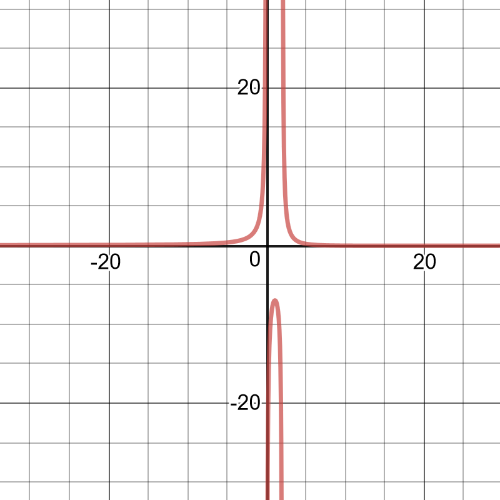
$dfrac{7}{x-3}geq dfrac{2}{x+4}$
$dfrac{7}{x-3}-dfrac{2}{x+4}geq 0$
$(dfrac{x+4}{x+4})dfrac{7}{x-3}-dfrac{2}{x+4}(dfrac{x-3}{x-3})geq 0$
$dfrac{7x+28}{(x+4)(x-3)}+dfrac{-2x+6}{(x+4)(x-3)}geq 0$
$dfrac{5x+34}{(x+4)(x-3)}geq 0$
$textbf{The inequality is true on $-6.8leq x3$}$.
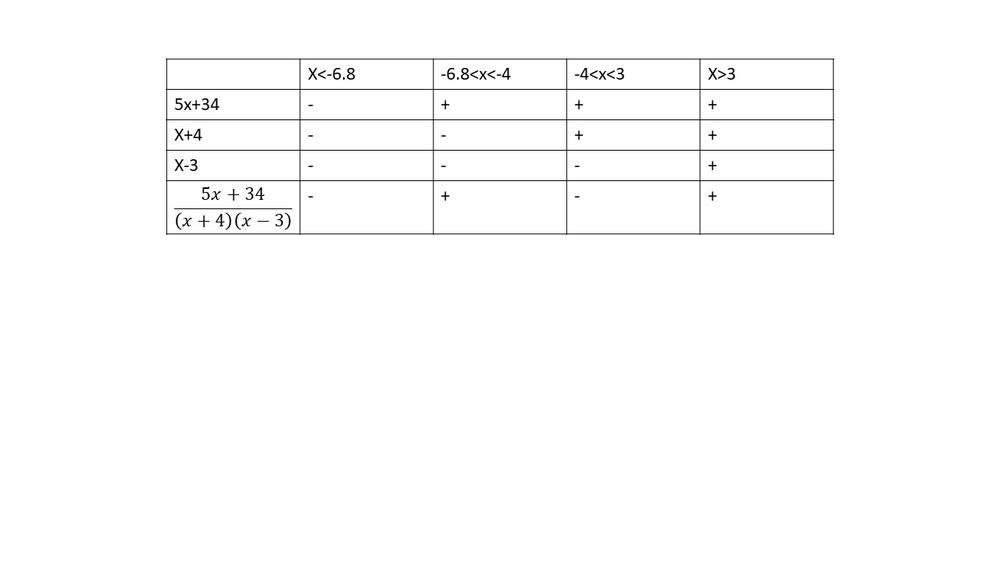
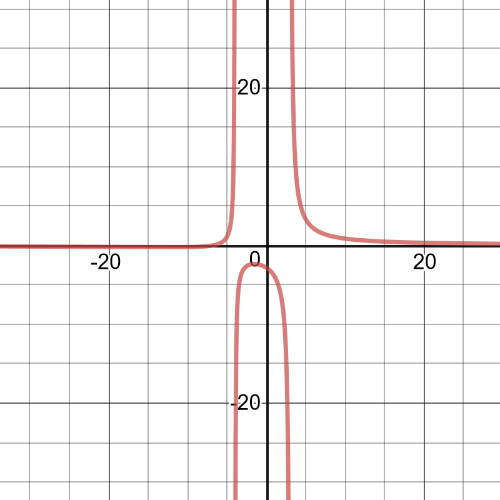
$dfrac{-6}{x+1}>dfrac{1}{x}$
$dfrac{-6}{x+1}-dfrac{1}{x}>0$
$(dfrac{x}{x})dfrac{-6}{x+1}-dfrac{1}{x}(dfrac{x+1}{x+1})>0$
$dfrac{-6x}{x(x+1)}+dfrac{-x-1}{x(x+1)}>0$
$dfrac{-7x-1}{x(x+1)}>0$
$textbf{The inequality is true on $x<-1$ and $-dfrac{1}{7} < x < 0$}$.
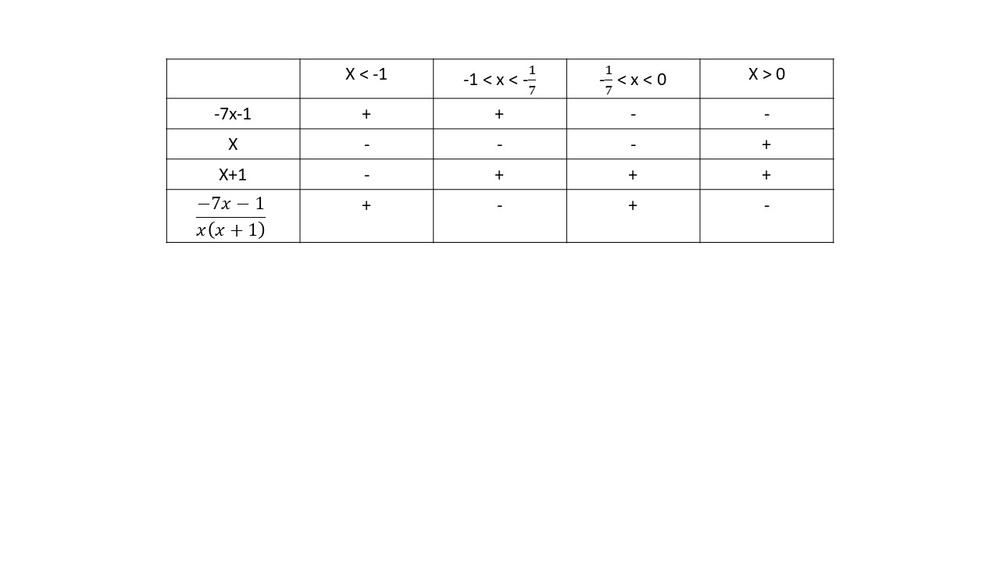
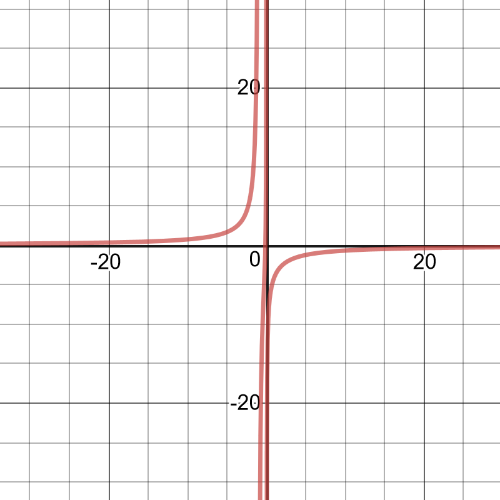
$dfrac{-5}{x-4}<dfrac{3}{x+1}$
$dfrac{-5}{x-4}-dfrac{3}{x+1}<0$
$(dfrac{x+1}{x+1})dfrac{-5}{x-4}-dfrac{3}{x+1}(dfrac{x-4}{x-4})<0$
$dfrac{-5x-5}{(x+1)(x-4)}+dfrac{-3x+12}{(x+1)(x-4)} < 0$
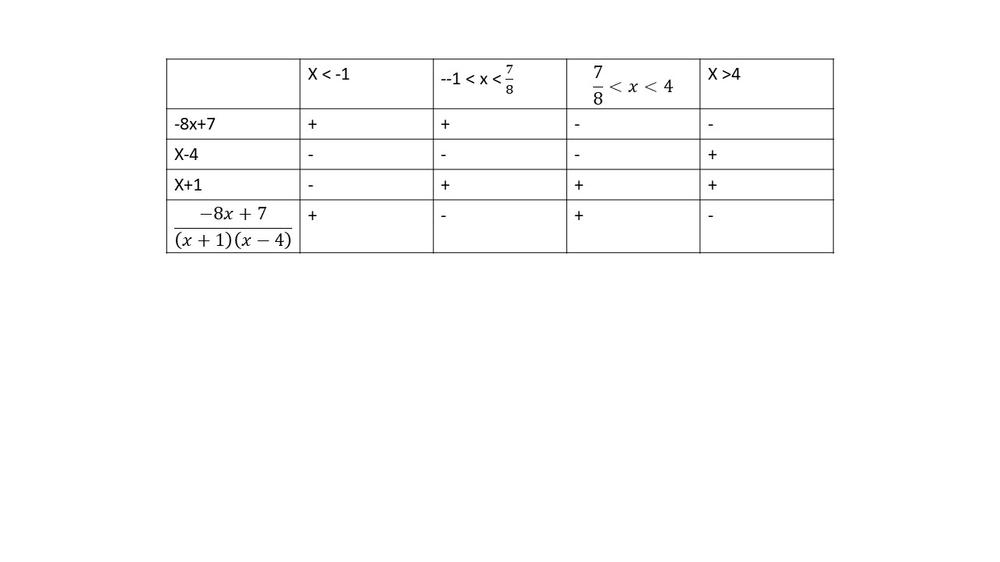
$dfrac{-8x+7}{(x+1)(x-4)} < 0$
$$
textbf{The inequality is true on $-1 < x < dfrac{7}{8}$ and $x < 4$.}
$$
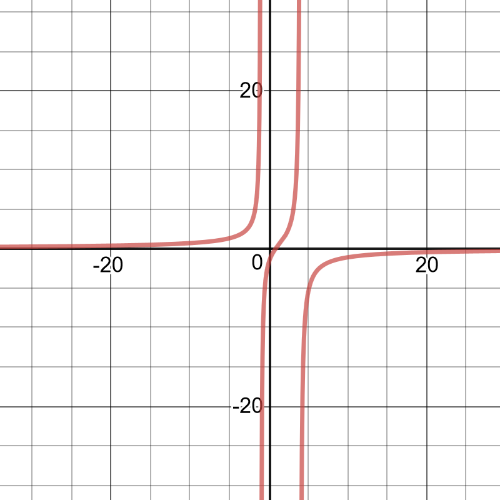
(b) $-7<x-3$
(c) $0<x8$
(d) $-6.8leq x3$
(e) $x<-1$ and $-dfrac{1}{7} < x < 0$
(f) $-1 < x < dfrac{7}{8}$ and $x < 4$
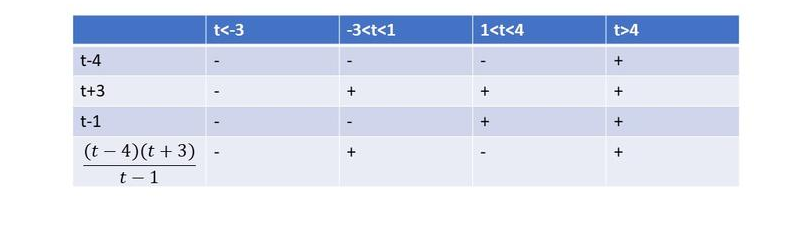
$dfrac{t^2-t-12}{t-1}<0$
$dfrac{t^2-t-12}{t-1}=dfrac{(t-4)(t+3)}{t-1}$
From the following table, we can cocnlude that $textbf{this inequality is true on}$ $tleq-3$ or $1<t<4$.
$dfrac{t^2+t-6}{t-4}geq0$
$dfrac{(t+3)(t-2)}{t-4}geq0$
From the following table, we can cocnlude that $textbf{this inequality is true on}$ $-3leq{t}leq-3$ and $t>4$.
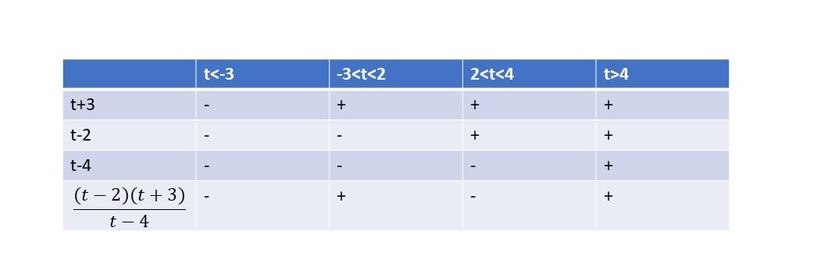
$dfrac{6t^2-5t+1}{2t+1}>0$
$dfrac{(3t-1)(2t-1)}{2t-1}>0$
From the following table, we can cocnlude that $textbf{this inequality is true on}$ $-dfrac{1}{2}leq{t}leqdfrac{1}{3}$ and $t>dfrac{1}{2}$.
$t-1<dfrac{30}{5t}$
$dfrac{5t}{5t}t-dfrac{5t}{5t}1-dfrac{30}{5t}<0$
$dfrac{5t^2}{5t}-dfrac{5t}{5t}-dfrac{30}{5t}<0$
$dfrac{5t^2-5t-30}{5t}<0$
$dfrac{5(t^2-t-6)}{5t}<0$
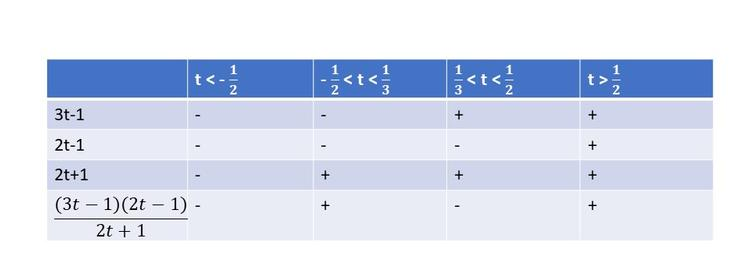
$dfrac{(t-3)(t+2)}{t}<0$
From the following table, we can cocnlude that $textbf{this inequality is true on}$ $t<-2$ and $0<t<3$.
$dfrac{2t-10}{t}>t+5$
$dfrac{2t-10}{t}-t-5>0$
$dfrac{2t-10}{t}-tdfrac{t}{t}-5dfrac{t}{t}>0$
$dfrac{2t-10-t^2-5t}{t}>0$
$dfrac{-t^2-7t-10}{t}>0$
$dfrac{t^2+7t+10}{t}<0$
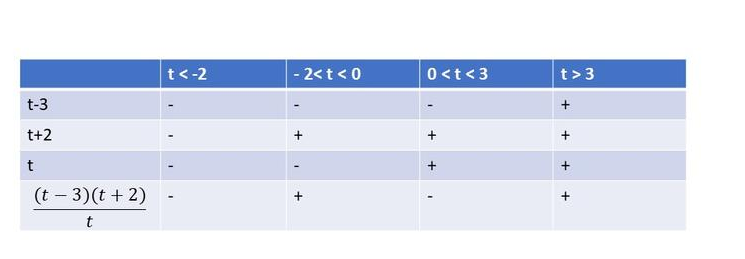
$dfrac{(t+5)(t+2)}{t}<0$
From the following table, we can cocnlude that $textbf{this inequality is true on}$ $t<-5$ or $-2<t<10$.
$dfrac{-t}{4t-1}geqdfrac{2}{t-9}$
$dfrac{-t}{4t-1}-dfrac{2}{t-9}geq0$
$(dfrac{t-9}{t-9})dfrac{-t}{4t-1}-dfrac{2}{t-9}(dfrac{4t-1}{4t-1})geq0$
$dfrac{-t^2+9t}{(4t-1)(t-9)}+dfrac{-8t+2}{(4t-1)(t-9)}geq0$
$dfrac{-t^2+t+2}{(4t-1)(t-9)}geq0$
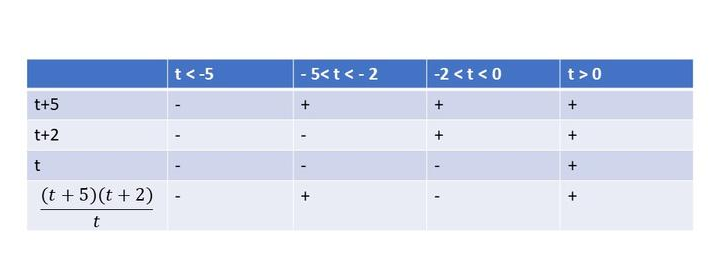
$dfrac{(-t+2)(t+1)}{(4t-1)(t-9)}geq0$
From the following table, we can cocnlude that $textbf{this inequality is true on}$ $-1leq{t}<0.25$ and $2leq{t}<9$.
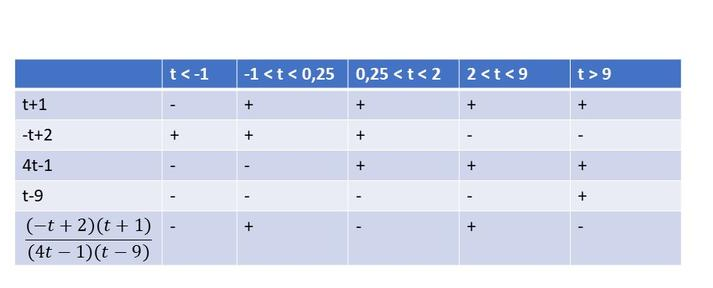
(c) $-dfrac{1}{2}<tdfrac{1}{2}$; (d) $t<-2$ and $0<t<3$;
(e) $t<-5$ and $-2<t<0$; (f) $-1leq{t}<0.25$ and $2leq{t}<9$
#### (a)
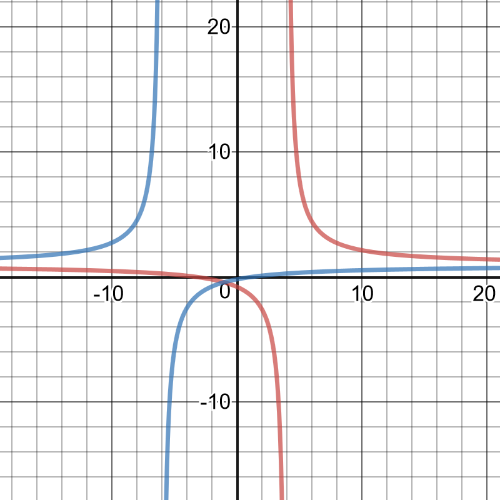
$dfrac{x+3}{x-4} geq dfrac{x-1}{x+6}$
The two graphs intersect at $(-1, -0.4)$.The asymptotes are at $x=4$ and $x=-6$.The graph of $y=dfrac{x+3}{x-4}$ is above $y=dfrac{x-1}{x+6}$ on $x < -6$ and on $-1 < x <4$.
$x+5 3$}
$$
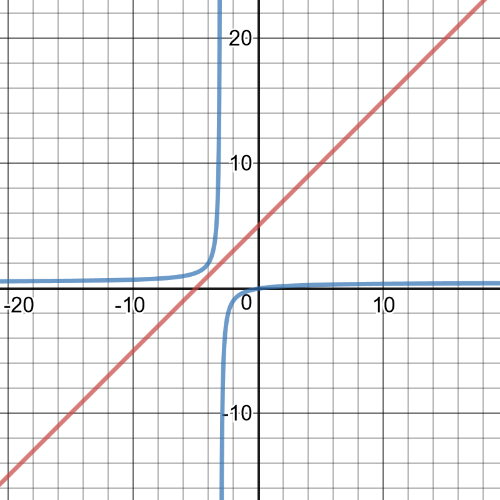
$dfrac{x}{x+4}leq dfrac{1}{x+1}$
Graph each expression to determine when the inequality is true.
The graphs intersect at $(-2,-1)$ and $(2,dfrac{1}{3})$.
The graph of $y=dfrac{x}{x+4}$ is below the other graph on $(-4, 2)$ and $(-1, 2)$.
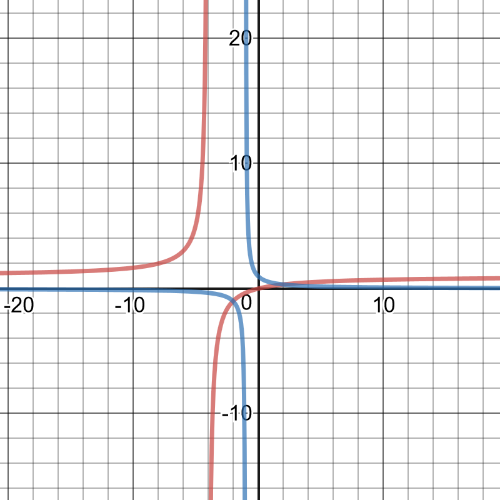
$dfrac{x}{x+9}geq dfrac{1}{x+1}$
Graph each expression to determine when the inequality is true.
The graphs intersect at $(-3, -0.5)$ and $(3, 0.25)$.
Because the inequality is $geq$, the intervals that make inequality true will include the points od intersection. The graph of $y=dfrac{x}{x+9}$ is above or intersecting with the other graph on $(- infty, -9)$, $left[-3, -1 right)$, and $left[3, infty right)$.
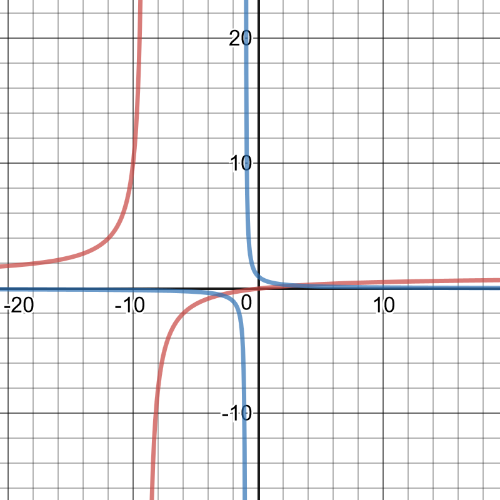
$dfrac{x-8}{x} > 3-x$
Graph each expression to determine when the inequality is true.
The two graph intersect at $(-2, 5)$ and $(4, -1)$.
The graph of $y=dfrac{x-8}{x}$ is above the other graph on $(-2, 0)$ and $(4, infty)$.
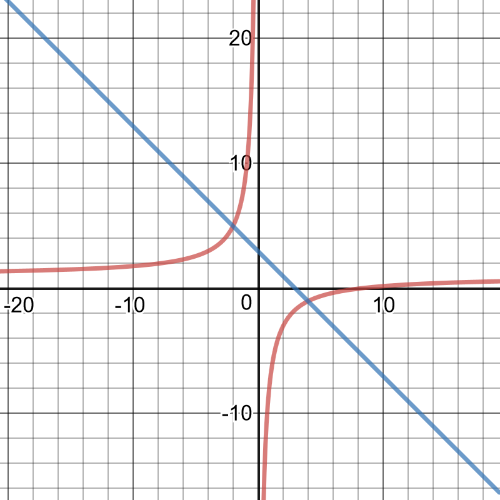
$$
dfrac{x^2-16}{(x-1)^2}geq 0
$$
Graph the expression and determine when the graph is above the $x$-axis.
The graph intersects the $x$-axis at $(-4, 0)$ and $(4, 0)$. The graph of $y=dfrac{x^2-16}{(x-1)^2}$ is above the $x$-axis on$(-infty, -4)$ and $(4, infty)$
(c) $(-4, 2)$ and $(-1, 2)$
(d) $(-4, 2)$ and $(-1, 2)$
(e) $(-2, 0)$ and $(4, infty)$
(f) $(-infty, -4)$ and $(4, infty)$
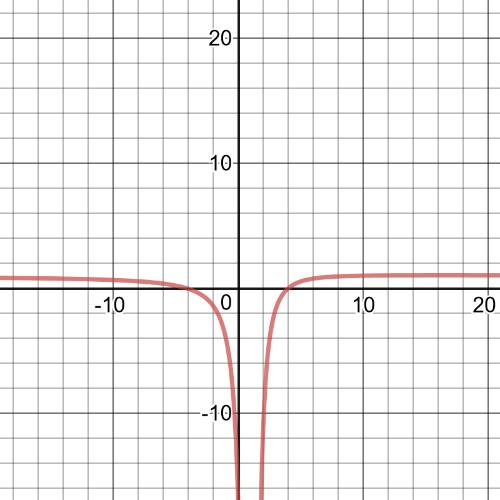
$dfrac{3x-8}{2x-1}>dfrac{x-4}{x+1}$
$dfrac{3x-8}{2x+1}-dfrac{x-4}{x+1}>0$
$(dfrac{x+1}{x+1})dfrac{3x-8}{2x+1}-dfrac{x-4}{x+1}(dfrac{2x-1}{2x-1})>0$
$dfrac{3x^2-8x+3x-8}{(x+1)(2x-1)}+dfrac{2x^2-x-8x+4}{(x+1)(2x-1)}>0$
$dfrac{5x^2-14x-4}{(x+1)(2x-1)}>0$
$dfrac{(x-3.065)(x+0.2614)}{(x+1)(2x-1)}>0$
From the following table we can see that $textbf{the inequality is true on}$ $x<-1$, $-0.2614<x3.065$.
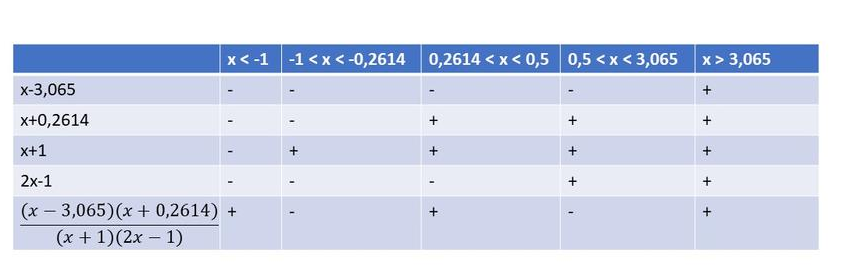
$(-infty,-1)$, $(-0.2614,0.5)$, $(3.065,infty)$
$textbf{Set notation}$:
$left{xinBbb{R}|x<-1, -0.2614<x3.065 right}$
On the following picture is $textbf{solution on number line}$:
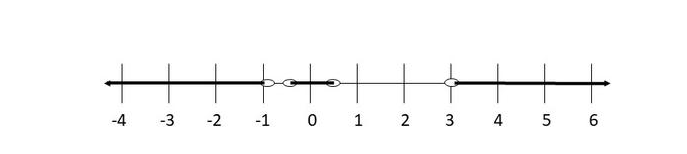
(b) $(-infty,-1)$, $(-0.2614,0.5)$, $(3.065,infty)$; $left{xinBbb{R}| x>-1, -0.2614<x3.065 right}$
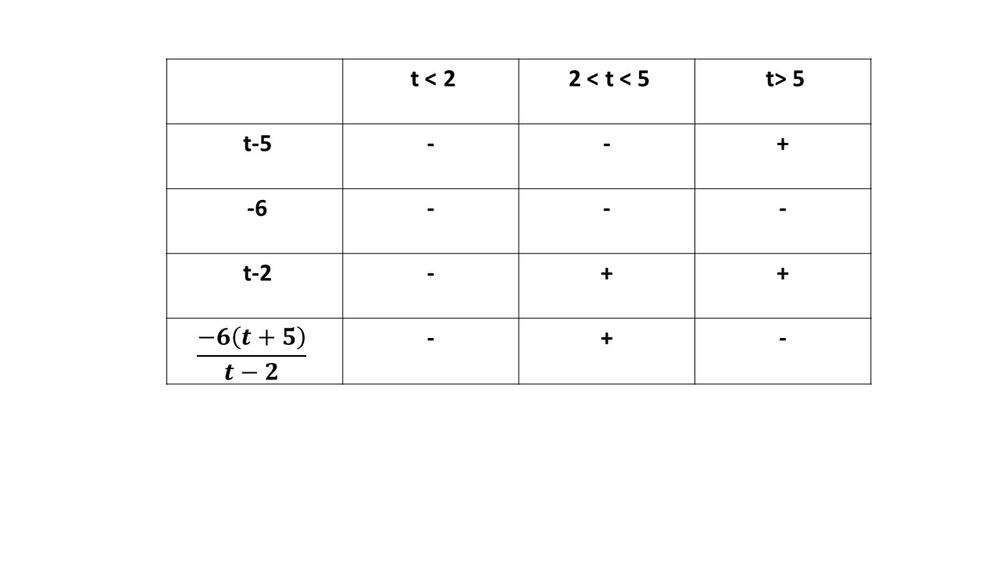
$dfrac{-6t}{t-2} < dfrac{-30}{t-2}$
$dfrac{-6t}{t-2}-dfrac{-30}{t-2}< 0$
$dfrac{-6t+30}{t-2}<0$
$dfrac{-6(t-5)}{t-2}<0$
$textbf{The inequality is true on $t<2$ and $t<5$}$.
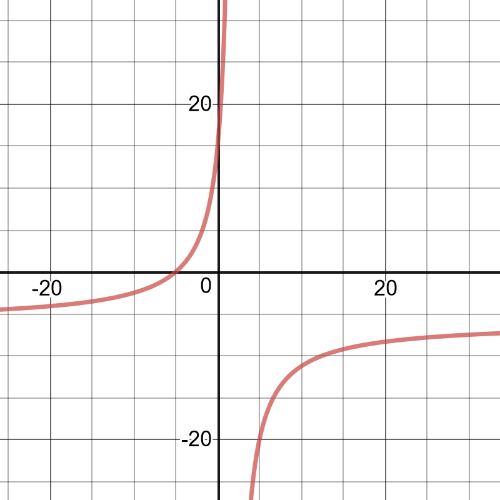
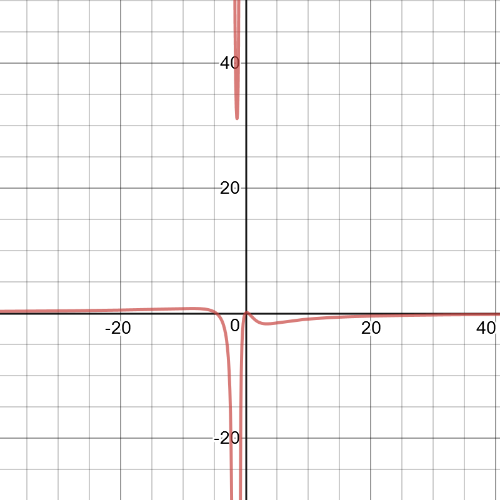
It would be difficult to find a situation that could be represented by these rational expressions because very few positive values of $x$ yield a positive value of $y$.
The equation that gives the bacteria count for the pond water time is $g(t)=dfrac{15t}{t^2+9}$.
To see if the bacteria count in the tap water will ever exceed that of the pond water, set up the inequality $dfrac{5t}{t^2+3t+2}>dfrac{15t}{t^2+9}$.
Solve this ineqaulity graphically.
Graph the expression $y=dfrac{5t}{t^2+3t+2}-dfrac{15t}{t^2+9}$ and determine when iti is greater than $0$ to find the solution to the inequality.
Notice that the only values that make the expression greater than $0$ are negative.$textbf{Because the values og $t$ have to be positive, the bacteria count in the tap water will never be greater than that of the pond water}$.
$0.5x -2 < dfrac{5}{2x}$
$0.5x-2-dfrac{5}{2x}<0$
$(dfrac{2x}{2x})0.5x-(dfrac{2x}{2x})2-dfrac{5}{2x}<0$
$dfrac{x^2-4x-5}{2x}<0$
$dfrac{(x-5)(x+1)}{2x}<0$
The inequality is true for $x< -1$ and $0< x <5$.
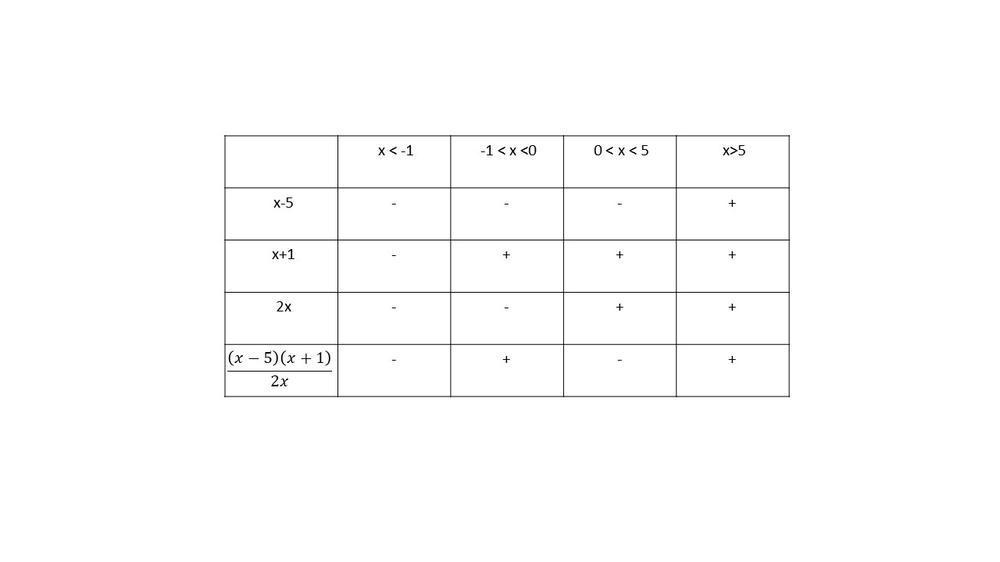
(b) $x< -1$ and $0< x <5$
$P(x)= -x^2 + 10x – (4x+5)$
$=-x^2+6x-5$
$x^2-6x+5$
$(x-1)(x-5)$
Divide this by $x$ to get the average profit.
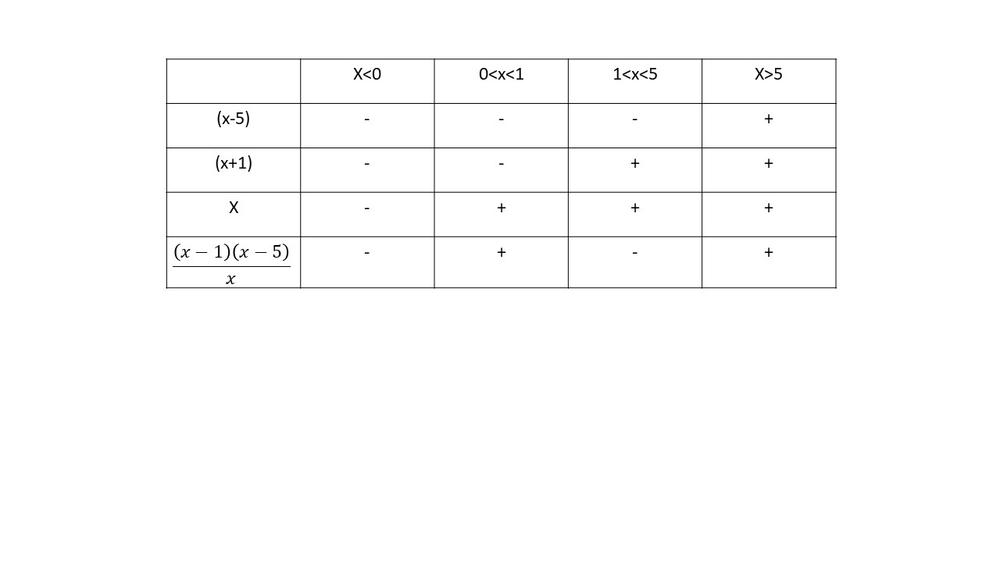
$AP(x)=dfrac{(x-1)(x-5)}{x}$
Substitute the factors of this equation into a table to determine when
$AP(x) > dfrac{(x-1)(x-5)}{(x)}$
From the table, it can be determined that the average profit per snowboard is positive between $0 < x < 1$ and $x 5$}$.
The first inequality can be manipulated algebraically to produce the second inequality.
You could graph the equation $y=dfrac{x+1}{x-1}-dfrac{x+3}{x+2}$ and determine when it is negative.
The values that make the factors of the second inequality zero are $-5$,$-2$, and 1. Determine the sign of each factor in the intervals corresponding to the zeros. Determine when the entire expression is negative by examining the signs of the factors.
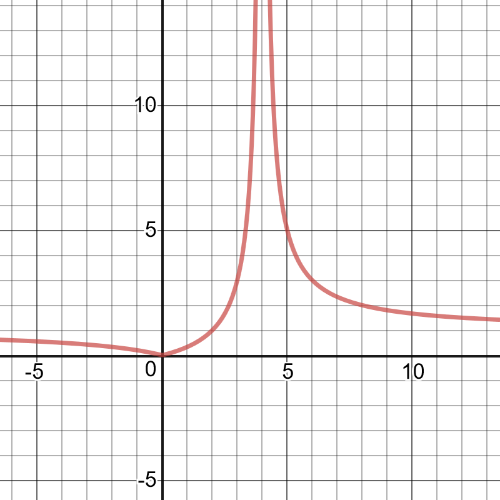
Notice that $textbf{the function is greater than $1$ on $[2, 4)$ and $(4, infty)$}$.We can see that from the following $textbf{graph}$.
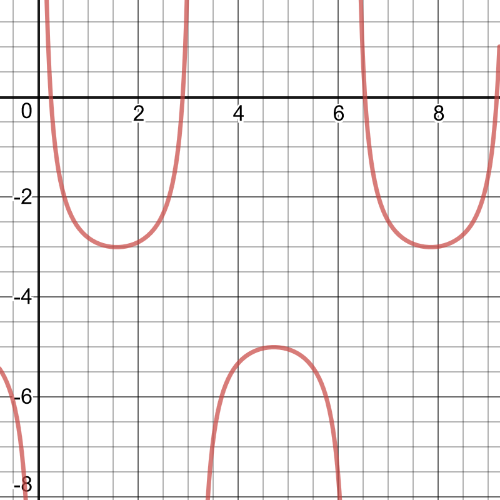
$dfrac{1}{sin{x}}-4<0$
$textbf{The graph is negative}$ on $14.48<x<165.2$ and $180<x<360$, we can see that from the following graph on which is inequality $dfrac{1}{sin{x}}-4<0$
.
$cos{x}>0.5$
$x=0$ would be the asymptote in the case, but values greater than $0$ could satisfy the inequality.
$cos1>0.5$
$0.999>0.5$
$cos{x}$ because less than $0.5x$ after about $2$.
$cos2<1$
$0.99<1$
So, $textbf{the inequality is true on}$ $0<x<2$.

