
All Solutions
Section 5-4: Patterns and the Periodic Table
Metals:
All metals are solid at room temperature. The only exception is mercury which is a liquid.
Non-Metals:
All non-metals are either liquids or gases at room temperature. The only exception is carbon which is a solid.
Metals:
All metals are good conductors of electricity.
Non-metals:
All non-metals are bad conductors of electricity. The only exception is graphite(carbon) which is an electrical conductor.
Metals:
All metals have a shiny appearance.
Non-Metals:
All non-metals have a dull appearance.
Metals:
All metals have either 1, 2 or 3 electrons in their outermost orbit.
Non-Metals:
All non-metals have 4 or more electrons in their outermost orbit.
Halogens are group VII elements. The halogen in the second period is Flourine.
Alkaline earth metals are group II elements. The alkaline earth metal in the fifth period is Stronium.
The noble gas with the smallest atomic number is Helium with an atomic number of 2.
The non-metal in the fifth period with seven outer most electrons must lie in group VII and is Iodine.
Alkali metals are group I elements. The alkali metal in the fourth period is Potassium.
The metal in the third period with three outer most electrons must lie in group III and is Aluminium.
The unreactive gas of the second period is the nobel gas Neon in group VIII.
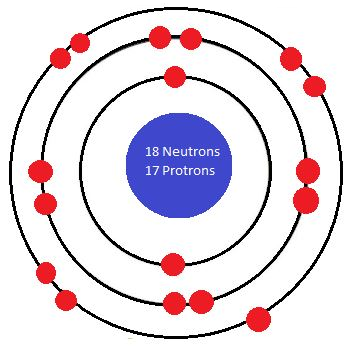
Note that the sizes of the electrons shown here vary. This is because the diagrams are not drawn to scale.
Study the Periodic Table. The element having the atomic number 118 lies in group VIII. This implies that an element with an atomic number of 119 will lie in the next group after group VIII and since group VIII is the last of the $8$ groups, the new element must lie in group I. This element will therefore be a member of the family of alkali metals.
Since it is established that this element will lie in group I, it can be further concluded that it will have $1$ electron in its outermost shell
The new element lies in group I of the Periodic table, it can be deduced that it will have properties similar to that of alkali metals. A physical property of this element will be that it will be soft in texture. It will react violently with water to form its metallic hydroxide and release hydrogen gas according to the equation:
$$
mathrm{2X_{(s)} + 2H_2O_{(l)} longrightarrow 2XOH_{(aq)} + H_2{(g)}}
$$
, where X is the symbol of the new element.
$$
mathrm{K_{(s)} + H_2O_{(g)} longrightarrow KOH_{(aq)} + H_2{(g)}}\
$$
The hydrogen gas formed is also very combustible. Because of this property of potassium, it is stored under paraffin oil.

