
All Solutions
Section 13-1: Writing a Critical Analysis
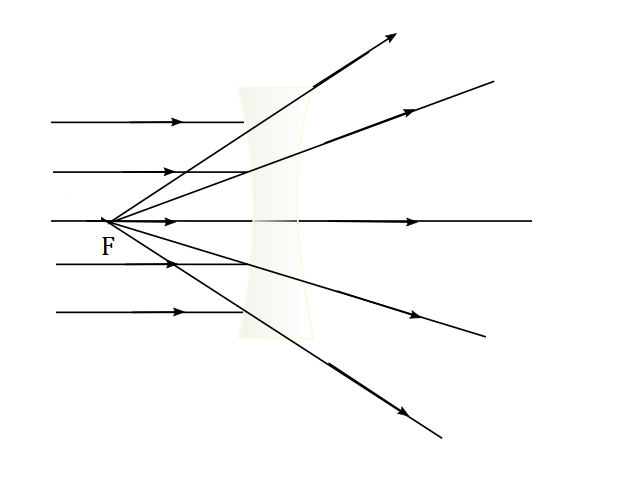
$textit{b.}$, Diverging lens spreads parallel beam of light on one of its surface and rays diverge on the other side of the lens in the point of the focus on the incident side of the lens.
First it refracts towards the normal while it enters optically denser medium which is glass of the lens and the location is entrance into the lens, second one occurs when light ray exits the glass and enters less dense medium which is the air, the location is exit of the denser medium.
$textit{b.}$, Since Ray diagrams are easier to draw and to understand behaviour of light, number of refraction is reduced to one.
.
$textit{b.}$, Number of refraction is reduced to one since the Ray diagrams are easier to draw and understand behaviour of light.
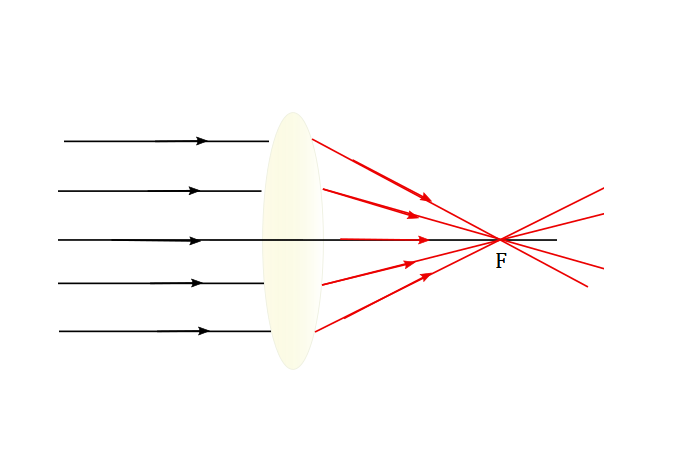
Converging lens can have more than one focus depending on where the object is and focuses have to have same distance from the centre.
Their distance from the centre is equal on the both sides.
Parallel incident ray of light on the left side will converge into the focus on the right side and vice versa.
$textit{b.}$, Principal focus of a diverging lens is located on the both sides of the converging lens.
Distance from the centre is equal on the both sides.
Parallel incident ray of light on the left side will diverge into the focus on the left side and vice versa.
$textit{c.}$, Diverging lens differ from converging lens because of the image which is formed and because diverging lens spreads a beam of light and converging one focuses them.
$textit{b.}$, It is placed on the both sides of the diverging lens.
$textit{c.}$, Images which are formed are different and converging lens focuses beam of light, while diverging spreads them.

