
All Solutions
Section 11-9: Images in Curved Mirrors
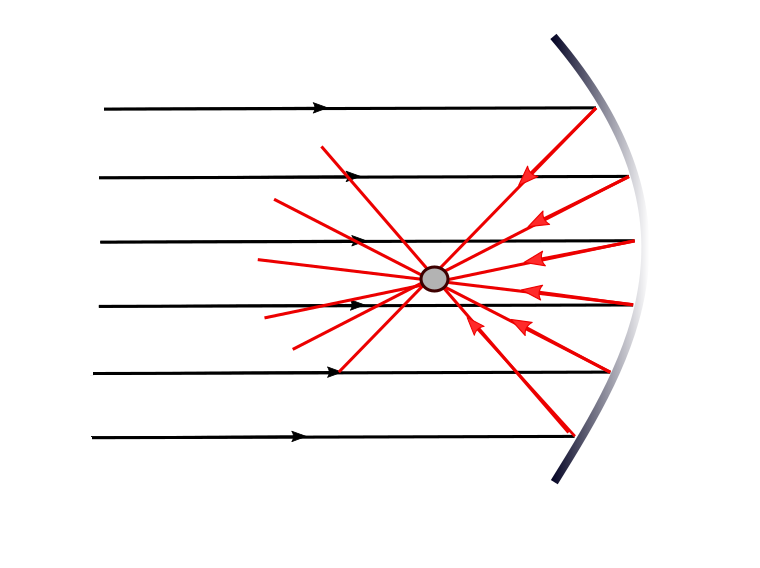
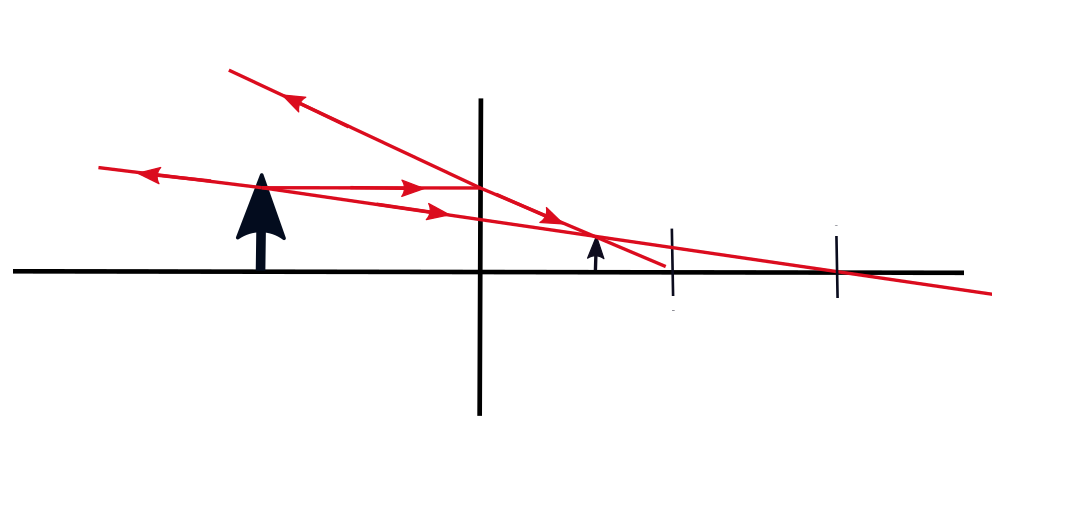
1., Ray of light which is parallel to the principal axis will always be reflected towards the focus of the mirror on reflection.
2., Ray of light which is passing through the focus of the mirror will always be reflected parallel to the principal axis on the reflection.
In order to make image of an object we have to draw two lines from the top of the objects while one of them will be parallel to the principal axis which passes through the focus of the lens and the other which is passing through the focus which reflects parallel to the principal axis and that point of intersection will be the location of the top of the image of that object.
1. A ray of light parallel to the principal axis is always reflected towards the focus of the mirror on reflection.
2. A ray of light passing through the focus of the mirror is always reflected parallel to the principal axis on reflection.
Therefore, in order to make the image of an object in front of a concave mirror 2 lines are drawn from the top of the object 1 parallel to the principal axis which passes through the focus of the lens on reflection and the other passing through the focus which reflects parallel to the principal axis. These 2 reflected rays intersect at a point. This point of intersection is the location of the top of the image of the object. The image can then be drawn.
They are used because if the face is positioned at the right distance from the mirror, image will be upright and magnified, and that location is within the focal length.
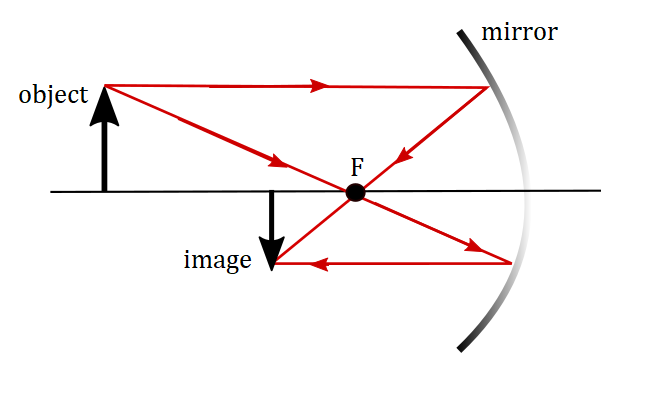
$textit{b.}$, Image is placed behind the mirror.
$textit{c.}$, Image is virtual, upright and smaller than the object.
$textit{b.}$, behind the mirror
$textit{c.}$, virtual, upright and smaller than the object.
c. Virtual, upright and smaller in size than the object and is
b. located behind the mirror.
Such images are only produced by convex mirrors so this must me a convex mirror.
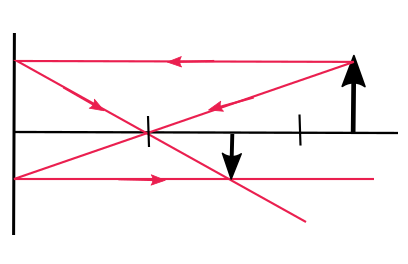
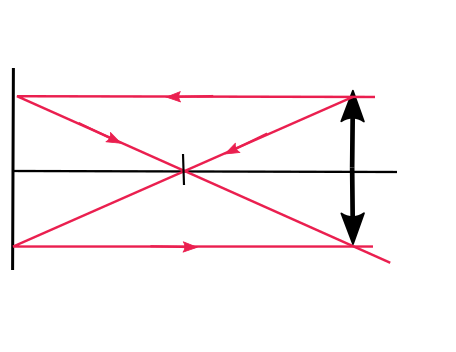
$textit{b.}$, Image is real, inverted and same size as the object.
$textit{b.}$, They are used when the are no surveillance cameras in order to keep different zones under observation.
$textit{b.}$, They are used when the are no surveillance cameras in order to keep different zones under observation.
Convex mirrors, because of their virtual focus always create images that are virtual in nature and upright in attitude but smaller in size, therefore these mirrors offer a wide field of view and therefore used on turns in parking garages to give drivers a view of any approaching vehicle(s) on turns.

