All Solutions
Section 11-7: Images in Plane Mirrors
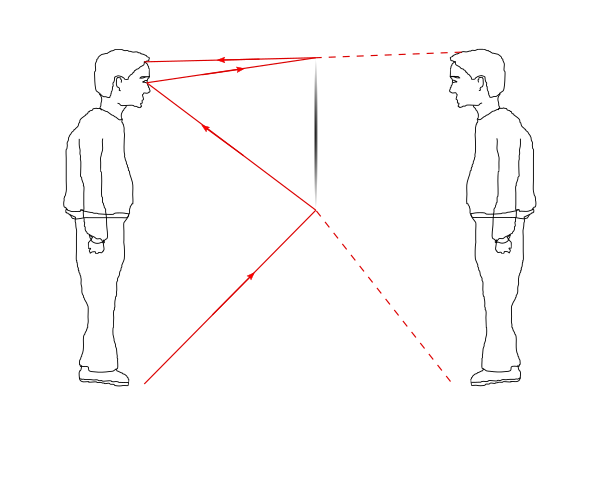
They differ from real images since they are not formed from the actual rays of light but from their extensions.
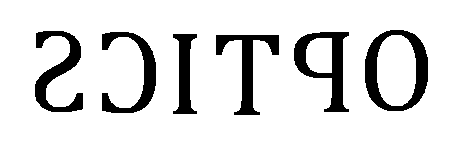
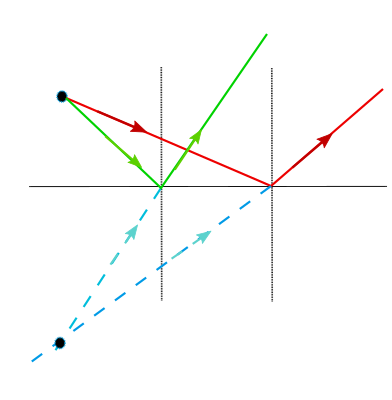
Each line perpendicular to the reflective surface is normal.
Incident rays and reflected rays are in green and red color and ther extensions are blue, the converge and form image.
S – size of the image with respect to the object
A – attitude of the image with respect to the object
L – location of the image with respect to the object
T – type of the image
S – size of the image with respect to the object
A – attitude of the image with respect to the object
L – location of the image with respect to the object
T – type of the image
This is used so that the drivers which are driving in front of the emergency vehicles would see the words correctly in the rearview mirror.
Rays of light are travelling from the human eye to the ends of the mirror where it is been reflected and extensions of incoming rays are converging and forming image.