
Nelson Science Perspectives 10
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780176355289
Textbook solutions
All Solutions
Page 66: Self-Quiz
Exercise 11
Result
1 of 1
In mitosis the total number of chromosomes are transferred to the daughter cell, therefore each new horse cell after mitosis will have 60 chromosomes.
Exercise 12
Step 1
1 of 1
The purpose of chloroplast in plant cell is to trap sunlight from the surroundings and use it to convert carbon dioxide and water to glucose and oxygen. Each unit of chloroplast works exactly the same way and this is how a plant manufactures food primarily for itself and secondarily for all other species that depend on it.
Exercise 13
Step 1
1 of 8
Type of cell
What is the function?
How does the structure suit the function?
Step 2
2 of 8
Red blood cell
Transport oxygen to all parts of the body
Biconcave in shape to easily pass through and across blood vessels. Contain hemoglobin to efficiently absorb oxygen from the lungs.
Step 3
3 of 8
Nerve cell
Transmit a neurosignal to the required part of the body.
Contains nerve endings to provide senses to all parts of the body.
Step 4
4 of 8
Fat cell
Store excess food in living beings as fats
Contain a large food vacuole to provide for the storage required to store fats.
Step 5
5 of 8
Sperm cell
Fertilize the female egg for reproduction to take place
Is composed of a long tail to propel itself towards the egg.
Step 6
6 of 8
Epidermal cell of a plant
Protects the plant from its envirnoment
Waxy surface to provide the required barrier between the environment and the plant. Regulate water losses.
Step 7
7 of 8
Photosynthetic cell of a plant
Produce glucose by the process of photosynthesis
Contains chloroplast to trap sunlight required for photosynthesis to take place.
Result
8 of 8
Click to see table.
Exercise 14
Step 1
1 of 3
a. The cells with the cycle of 72 hours must have come from the root tip. This is because the roots are underground and therefore grow at a slower speed than the rest of the plant. Note that the root is the first part of the plant to develop and therefore the oldest part of the plant.
Step 2
2 of 3
b. The other cells might belong to the leaves. Leaves are most vulnerable to the environment and can fall off at a heavy gush of wind and therefore have a fast growth cycle so that new leaves can grow in place of old ones.
Result
3 of 3
a. Cells with a 72 hour growth cycle must have come from the root tip.
b. The other sample might have come from the leaves.
Exercise 15
Step 1
1 of 2
Mitosis is a naturally occurring continuous process and therefore it can be concluded that it is occurring in all living beings at all times. Note that its rate varies with age. Children in growing age have a faster rate of mitosis as they grow up. The rate of mitosis reduces with age because once a child has grown up, the size of the resulting adult is no longer changing at the same rate but even then mitosis is required to produce new cells as old ones die out. For example independent of age of an adult, red blood cells in a human being have a maximum life of 4 months and need to be replaced continuously.
Result
2 of 2
Yes mitosis a continuously occurring natural process.
Exercise 16
Step 1
1 of 1
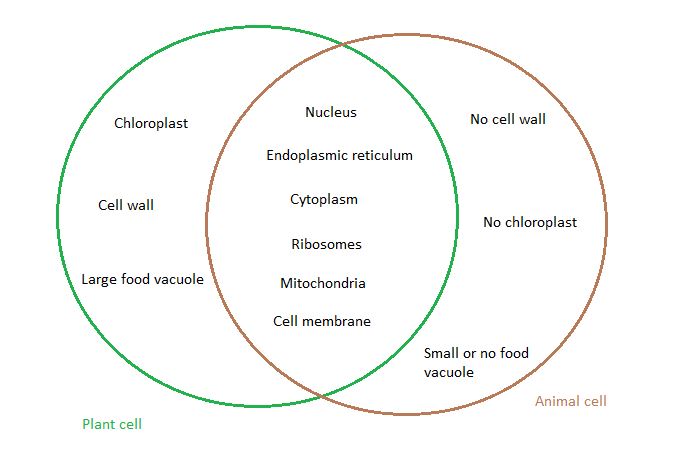
A Venn diagram that shows the similarities and differences between plant and animal cells could be represented as follows:

Exercise 17
Step 1
1 of 2
The dissolving of the nuclear membrane is essential so the the chromosomes after separation to chromatids can travel to opposite ends of the parent cell. The new nucleus membranes than forms around them, enclosing them as two nuclei instead of one.
Result
2 of 2
The dissolving of the nuclear membrane is essential so the the chromosomes after separation to chromatids can travel to opposite ends of the parent cell.
Exercise 18
Step 1
1 of 3
a) Find databases using a web search.
Step 2
2 of 3
b) The research on therapy or solutions to help cancer patients survive or overcome the illness has led to a decrease of infection length while various foods and medical devices may have increased the frequency of cancer occurring in people
Result
3 of 3
a) Find databases using a web search.
Exercise 19
Step 1
1 of 3
a. The antibiotic affects the replication of the DNA of the bacterial cells disturbing it to reduce and eventually stop its growth. The growth of bacteria hence reduces in the body and finally stops. The existing bacterial cells slowly die out and are eliminated from the body. This is how an antibiotic stop a bacterial infection in a body.
Step 2
2 of 3
b. DNA replication of human body cells MUST not be changed by any antibiotic because the growth of human body cells must remain as it is for regular growth and repair.
Result
3 of 3
a. Antibiotics reduce and stop the bacterial cells capability to reproduce.
b. Human body cells must continue to undergo mitosis for growth and repair.
Exercise 20
Step 1
1 of 3
a) Sun exposure, smoking, and chewing tobacco.
Step 2
2 of 3
b) Wear sunscreen, do not smoke, do not chew tobacco
Result
3 of 3
a) Sun exposure, smoking, and chewing tobacco.
Exercise 21
Result
1 of 1
Plant five of the same plant in the same area with equal sunlight. Water them the same amount every day but subject them all to different temperatures and measure their growth differences .
Exercise 22
Step 1
1 of 2
The process of mitosis ensures the survival of living beings by repairing wounds and injuries that might have led to even death if this naturally occurring mechanism was not in place. Human muscle and nerve cells have a very slow rate of mitosis which may even cease if it is not required, therefore it is harder to recover from a muscle or a nerve injury because the damaged cells are harder to repair and/or replace.
Result
2 of 2
Rate of mitosis is slow for muscle and nerve cells and therefore such injuries take a long time to heal.
Exercise 23
Step 1
1 of 2
a. The one question required here is that “Is the mole hurting?”.
Step 2
2 of 2
b. The asymmetry, border, color and diameter of the mole are to be observed. She should be recommended a dermatologist if any one or more of the following is visible:
1. The mole is asymmetrical.
2. The border is not defined/visible.
3. The mole color is varying and not uniform.
4. It is large in size.
Exercise 24
Step 1
1 of 2
a. Asexual reproduction results in offspring(s) that are identical to its only parent. Sexual reproduction results in offspring(s) that take 50$%$ of each their genetic makeup from both of its(their) parent.
Step 2
2 of 2
b. A genetically diverse population is a result of sexual reproduction. According to the saying “Survival of the fittest”. Sexual reproduction ensures, that the best of the genes are passed on.
unlock

