
All Solutions
Page 486: Check Your Understanding
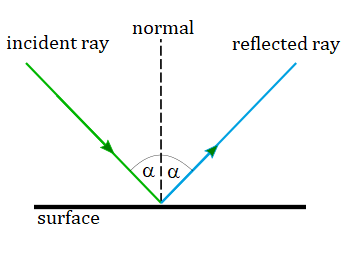
We can also see that incident ray, reflected ray and normal always lay in the same plane.
1., Angle of incidence and angle of reflection are always equal.
2., The incident ray, the reflected ray and normal lie in the same plane.
2., The incident ray, the reflected ray and normal lie in the same plane.
1. The angle of incidence and the angle of reflection are always equal.
2. The incident ray, the normal and the reflected ray, all lie in the same plane (that is on the same side of the object and the 3 meet at the same point of incidence/reflection).
After the specular reflection incident rays of light are reflected in the same direction they fell on the surface and it seems like the whole beam is reflected.
Diffuse reflection is reflection on the rough surfaces where the beam of light is being diffused since every ray hits different point on the rough surface.
$textit{b.}$, Examples:
Specular reflection is reflection of sunlight from the metallic surface of the car and diffuse reflection is reflection from the paper.
$textit{b.}$, Specular reflection: reflection of sunlight from the metallic surface of the car.
Diffuse reflection: reflection of light from the paper.
$textit{b.}$, Matt paint should be used since it will give dull appearance to the walls which will help in diffuse reflection.
$textit{b.}$, Matt paint should be used since it will give dull appearance to the walls which will help in diffuse reflection.
b. $47text{textdegree}$
c. $50text{textdegree}$
It can be used as an extra lightning and enhances brightness in the kitchen, bathroom or bedroom.
On the other hand diffuse reflection is reflection on the rough surfaces which are walls in these rooms diffuse lights that are too much bright.
And diffuse reflection diffuse lights that are too bright, and main role in this have walls.

