
All Solutions
Page 303: Unit Review
BaSO$_4$ is a salt. Its positive ion is Ba$^+$ which implies that the base used was Ba(OH)$_2$ and its negative ion is SO$_4^{-2}$ which implies that the acid used was H$_2$SO$_4$. Equation of the reaction becomes:
$$
mathrm{Ba(OH)_{2(aq)} + H_2SO_{4(aq)} longrightarrow BaSO_{4(aq)} + 2H_2O_{(l)}}
$$
KCl is a salt. Its positive ion is K$^+$ which implies that the base used was KOH and its negative ion is Cl$^{-}$ which implies that the acid used was HCl. Equation of the reaction becomes:
$$
mathrm{KOH_{(aq)} + HCl_{(aq)} longrightarrow KCl_{(aq)} + H_2O_{(l)}}
$$
$$
mathrm{2Cu_{(s)} + O_{2(g)} longrightarrow 2CuO_{(s)}}
$$
$$
mathrm{CaO_{(s)} + H_2O_{(l)} longrightarrow Ca(OH)_{2(aq)} }
$$
$$
mathrm{Ca(OH)_{2(aq)} + H_2SO_{4(aq)} longrightarrow CaSO_{4(aq)} + 2H_2O_{(l)}}
$$
Ca, calcium lies in group II of the Periodic table. This implies that it is a metal with 2 valence electrons in its outermost orbit and it is easier for it to lose these 2 electrons rather than gain $8-2=6$ electrons to achieve a stable electronic configuration. Therefore, it will form a positive ion with an ionic charge of $+2$ on it by losing its 2 valence electrons.
S, sulfur lies in group VI of the Periodic table. This implies that it is a non-metal with 6 valence electrons in its outermost orbit and it is easier for it to gain 2 electrons rather than to lose $8-2=6$ electrons to achieve a stable electronic configuration. Therefore, it will form a negative ion with an ionic charge of $-2$ on it by gaining 2 electrons.
K,potassium lies in group I of the Periodic table. This implies that it is a metal with 1 valence electron in its outermost orbit and it is easier for it to lose this 1 electron rather than gain $8-1=7$ electrons to achieve a stable electronic configuration. Therefore, it will form a positive ion with an ionic charge of $+1$ on it by losing its 1 valence electron.
Al, aluminum lies in group III of the Periodic table. This implies that it is a metal with 3 valence electrons in its outermost orbit and it is easier for it to lose these 3 electrons rather than gain $8-3=5$ electrons to achieve a stable electronic configuration. Therefore, it will form a positive ion with an ionic charge of $+3$ on it by losing its 3 valence electrons.
$text{4Fe + 3O$_2$ + 6H$_2$O $rightarrow$ 4Fe (OH)$_3$}$
Since three reactants are joining to produce one product we consider that a synthesis reaction.
textbf{Synthesis reaction}
$$
$$
mathrm{2C_2H_{2(g)} + 5O_{2(g)} longrightarrow 4CO_{2(g)} + 2H_2O_{(g)}}
$$
mathrm{2C_2H_{2(g)} + 5O_{2(g)} longrightarrow 4CO_{2(g)} + 2H_2O_{(g)}}
$$
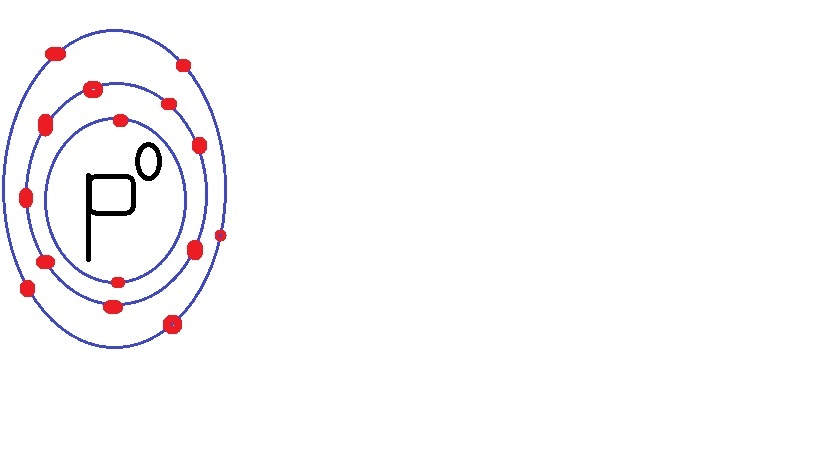
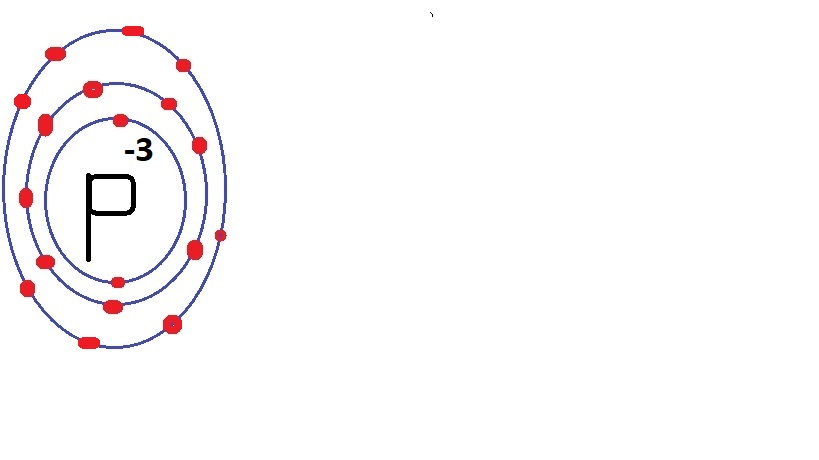
Magnesium chloride is MgCl$_2$.
Aluminum sulfide is Al$_2$S$_3$.
Tin(II) sulfate is SnSO$_4$.
Iron(III) oxide is Fe$_2$O$_3$.
Lead(II) nitrate is Pb(NO$_3$)$_2$.
Silver phosphate is AgPO$_4$.
Sulfuric acid is H$_2$SO$_4$.
Hydrocholoric acid is HCl.
Chlorine dioxide is ClO$_2$.
Dinitrogen monoxide N$_2$O.
K$_2$O is potassium oxide.
CuS is copper(II) sulfide.
Na$_3$PO$_4$ is sodium phosphate.
Pb(OH)$_2$ is lead(II) hydroxide.
HNO$_3$ nitric acid.
CO is carbon monoxide.
NO is nitrogen oxide.
ammonia + sulfuric acid $longrightarrow$ ammonium sulfate
This is a synthesis reaction as 2 reactants combine to form one product.
aluminum + copper(II) chloride $longrightarrow$ aluminum chloride + copper
This is a single displacement reaction as copper is replaced by aluminum in this reaction.
phosphoric acid + sodium hydroxide$longrightarrow$ sodium phosphate + water
This is a neutralization reaction as acid and base here react together to form salt and water.
aluminum sulfate $longrightarrow$ aluminum oxide + sulfur trioxide
This is a decomposition reaction because one reactant is breaking down to yield 2 products.
ethene + oxygen $longrightarrow$ carbon dioxide + water
This is a combustion reaction as a hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water.
ammonia + sulfuric acid $longrightarrow$ ammonium sulfate
Balanced chemical equation:
$$
mathrm{2NH_{3(g)} + H_2SO_{4(aq)} longrightarrow (NH_4)_2SO_{4(aq)}}
$$
aluminum + copper(II) chloride $longrightarrow$ aluminum chloride + copper
Balanced chemical equation:
$$
mathrm{2Al_{(s)} + 3CuCl_{2(aq)} longrightarrow 2AlCl_{3(aq)}+3Cu_{(s)}}
$$
phosphoric acid + sodium hydroxide$longrightarrow$ sodium phosphate + water
Balanced chemical equation:
$$
mathrm{H_3PO_{4(aq)} + 3NaOH_{(aq)} longrightarrow Na_3PO_{4(aq)}+3H_2O_{(l)}}
$$
aluminum sulfate $longrightarrow$ aluminum oxide + sulfur trioxide
Balanced chemical equation:
$$
mathrm{Al_2(SO_4)_{3(s)} longrightarrow Al_2O_{3(s)}+3SO_{3(g)}}
$$
ethene + oxygen $longrightarrow$ carbon dioxide + water
$$
mathrm{2C_2H_{6(g)} + 7O_{2(g)} longrightarrow 4CO_{2(g)} + 6H_2O_{(g)}}
$$
iron(III) oxide + carbon $longrightarrow$ iron + carbon dioxide
Balanced chemical equation:
$$
mathrm{2Fe_2O_{3(l)} + 3C_{(l)} longrightarrow 4Fe_{(l)}+3CO_{2(g)}}
$$
This reaction can be classified as a single displacement reaction (or reduction) where carbon displaces iron from its oxide to form carbon dioxide.
Excess of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere can adversely affect the environment. Carbon dioxide can dissolve in water to form carbonic acid. This can cause atmospheric air to become acidic as it carries water vapors saturated with carbonic acid. These vapors then form clouds and precipitation which falls back to earth as acid precipitation polluting our land and oceans. This can reduce the pH of oceans.
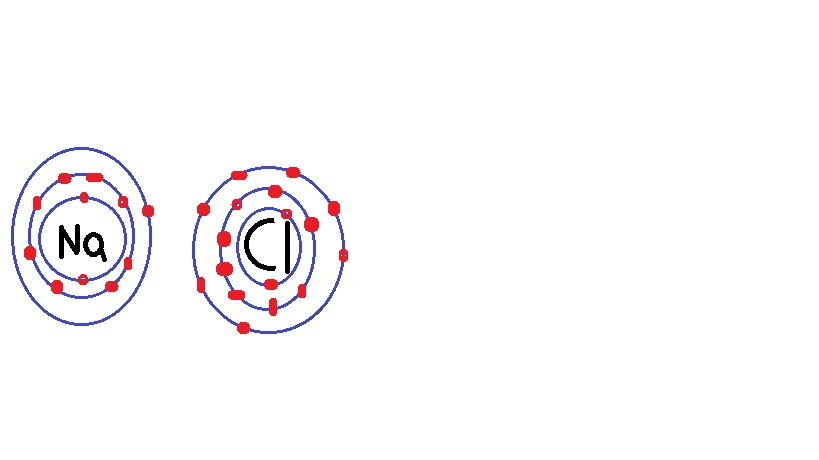
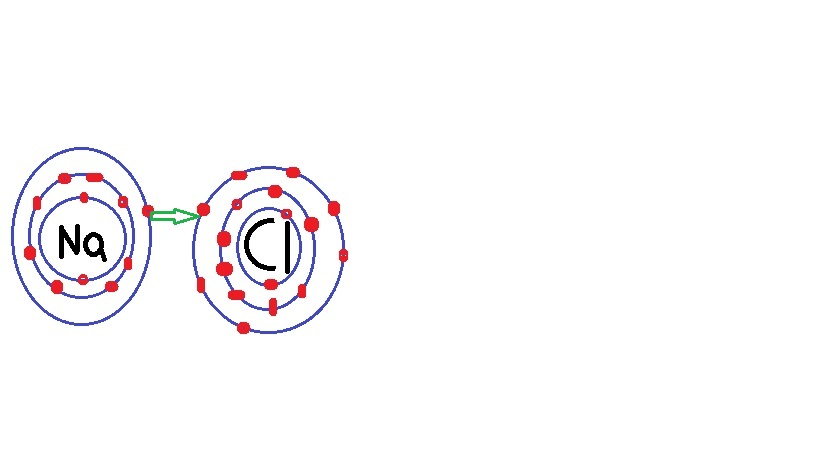
K$_2$S is potassium sulfide.
CBr$_4$ is tetra-bromo methane.
FeO is iron(II) oxide.
CuSO$_4$ is copper(II) sulfate.
AgNO$_3$ is silver nitrate.
PbO$_2$ is lead(IV) oxide or lead dioxide.
N$_2$O is dinitrogen monoxide.
item iron(III) chloride= FeCl$_3$
item tin(II) chloride= SnCl$_2$
item iron(II) chloride= FeCl$_2$
item tin(IV) chloride= SnCl$_4$
end{enumerate}
$text{SnCl$_2$ + FeCl$_3$ $rightarrow$ FeCl$_2$ + SnCl$_4$}$
The number of chloride atoms in the reactant side is not the same as the number on the product side (5:6), therefore I multiplied the FeCl$_3$ in the reactant by two and the FeCl$_2$ in the product side by two also.
The final formula will be: $text{SnCl$_2$ + 2FeCl$_3$ $rightarrow$ 2FeCl$_2$ + SnCl$_4$}$
Now the number of atoms of each element in the reactant side is equal to the number of atoms of each element on the product side.
text{SnCl$_2$ + 2FeCl$_3$ $rightarrow$ 2FeCl$_2$ + SnCl$_4$}
$$
begin{enumerate}
item The poor growth of trees affected the wood products industry and the loss was valued by billions of dollars.
item The reduction in fish stocks was valued by multi-billions of dollars.
end{enumerate}
The combustion of hydrocarbons can be a complete or incomplete reaction depending on the availability of oxygen gas, if the reaction was complete the products will be carbon dioxide and water, and if the reaction was incomplete it will produce carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, carbon as soot and water.
begin{enumerate}
item carbon emissions: natural gas emits almost 50% less CO2 than coal.
item efficiency of burning: Natural gas is more efficient than coal.
item price-wise: coal prices are between 60 and 143 USD, while the price of natural gas is between 41 and 74 USD.
end{enumerate}
begin{enumerate}
item carbon emissions: natural gas 5, coal 1
item efficiency of burning: Natural gas 4, coal 2
item price-wise: Natural gas 5, coal 2
end{enumerate}
Finally, the summation will be Natural gas is 14 while coal is 5.\

