
All Solutions
Page 294: Review
H$_3$PO$_4$ is phosphoric acid.
HBr is hydrogen bromide.
Fe(OH)$_3$ is iron(III) hydroxide.
H$_2$SO$_4$ is sulfuric acid.
Ca(HCO$_3$)$_2$ is calcium hydrogen carbonate.
KNO$_3$ is nitric acid.
Acids react with metals to form hydrogen gas and a salt of the metal. For example:
$$
mathrm{2HCl_{(aq)} + Mg_{(s)} longrightarrow MgCl_{2(aq)} + H_{2(g)}}
$$
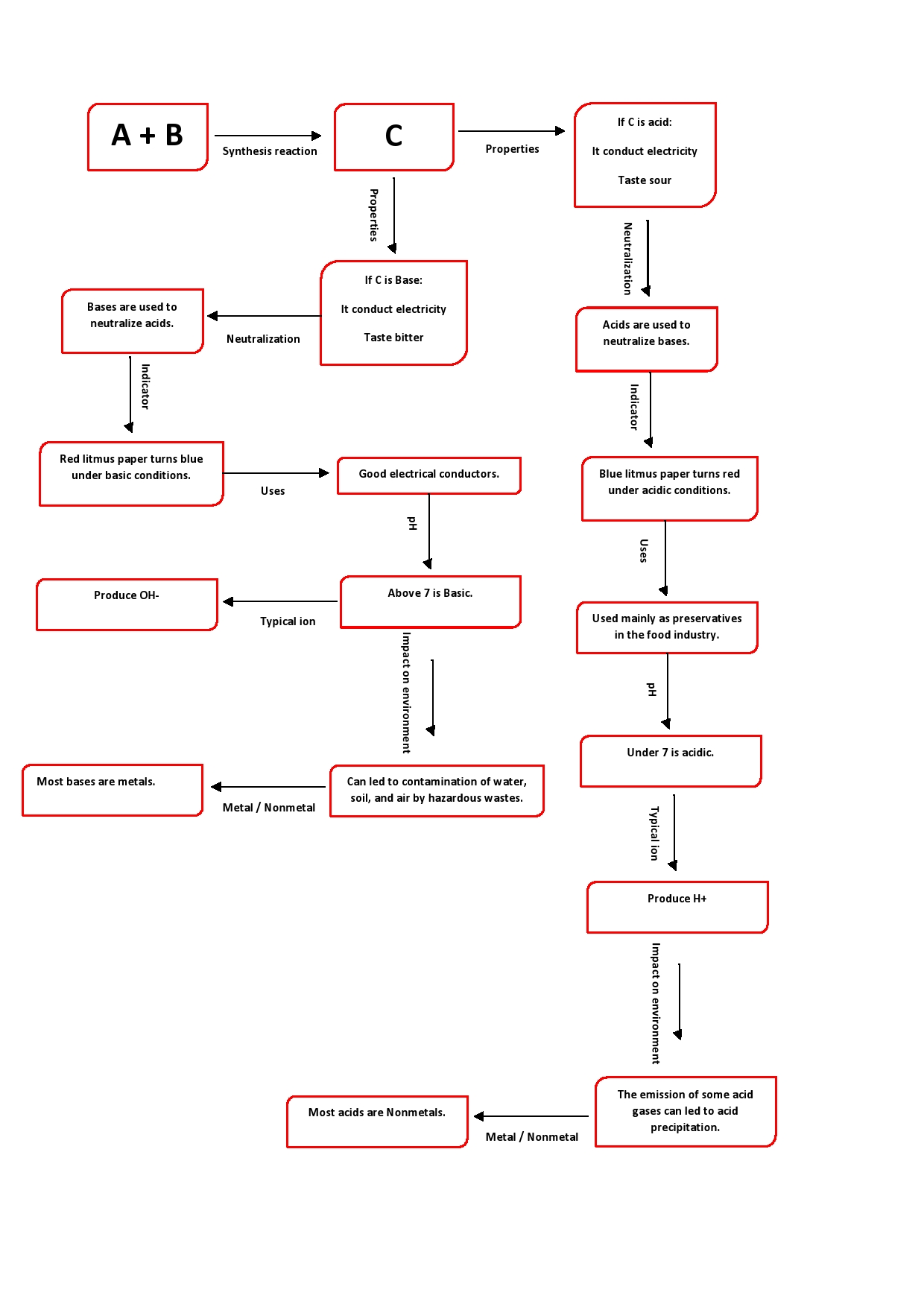
Positive hydrogen ions; H$^+$ are the cause of acidity of acids.
Bromothymol blue indicator gives a yellow color in acids and a blue color in bases.
The product of a neutralization reaction is water; a neutral product formed by the combination of the H$^+$ of the acid and OH$^-$ of the base. The by-product of a neutralization reaction is a salt.
The smaller the value of a pH of a solution the more acidic it is and the greater the value of a pH of a solution the less acidic it is. pH 0 to $<7$ implies an acidic solution.
Atmospheric pollutants sulfur dioxide and oxides of nitrogen released in the atmosphere by the combustion of fossil fuels are responsible for acid precipitation.
Combustion of fossil fuel to facilitate transportation of people and goods and operation of industries and power plants is the source of these pollutants.
Installation of catalytic converters in vehicles can eliminate the emission of oxides of nitrogen to oxygen and nitrogen.
The pH less than 7 will be of solutions of all acids, here they are H$_3$PO$_4$, HBr, and H$_2$SO$_4$.
The pH greater than 7 will be of solutions of all bases, here it is Fe(OH)$_3$.
The pH equal to 7 will be of solutions of salts, here they are KNO$_3$ and Ca(HCO$_3$)$_{2}$.
b. Bleach
Acid precipitation adversely affects aquatic life in lakes. The acid in these precipitation reduces the pH of lakes eliminating certain species that can not survive in low pH environments. One example of this are snails. Snails can only live in water bodies having a pH of 5.5 or greater.
Addition of lime neutralizes the acidic effects of this precipitation as lime is calcium oxide which reacts with these acids to form salt and water. Neutralization of acid means that the pH of the lake will rise to 7, which is a favorable environment for all lake species and can sustain aquatic life.
Hydrochloric acid + potassium hydroxide $longrightarrow$ water + potassium chloride
Sulfuric acid + calcium hydroxide $longrightarrow$ water + calcium sulfate
Phosphoric acid + sodium hydroxide $longrightarrow$ water + sodium phosphate
Balanced chemical equation:
$$
mathrm{HCl_{(aq)} + KOH_{(aq)} longrightarrow H_2O_{(l)} + KCl_{(aq)}}
$$
Balanced chemical equation:
$$
mathrm{H_2SO_{4(aq)} + Ca(OH)_{2(aq)} longrightarrow 2H_2O_{(l)} + CaSO_{4(aq)}}
$$
Balanced chemical equation:
$$
mathrm{H_3PO_{4(aq)} + 3NaOH_{(aq)} longrightarrow 3H_2O_{(l)} + Na_3PO_{4(aq)}}
$$
Word equation:
Calcium hydroxide + nitric acid $longrightarrow$ calcium nitrate + water
Balanced chemical equation:
$$
mathrm{Ca(OH)_{2(aq)} + 2HNO_{3(aq)} longrightarrow Ca(NO_3)_{2(aq)} + 2H_2O_{(l)}}
$$
Combustion of fossil fuels in combustion engines of vehicles raise the temperatures of the engines. At these high temperatures, atmospheric nitrogen in engines combine with oxygen gas to form oxides of nitrogen. These can become dissolve in atmospheric moisture to form an acid which falls to the earth as acid precipitation.
Calcium hydroxide is basic in nature and when dissolved in water form an alkali that has a pH greater than 7 and this is how its addition can increase the pH of soil.
This ability to slowly dissolve in water is an advantage because this prevents the flushing away of calcium hydroxide from the soil at a faster rate, with running water.
begin{enumerate}
item Signal word: it refers to words such as “Danger,” or “Warning,” and it is used to indicate the hazard level.
item Pictograms: a pictogram, or GHS hazard symbol, is a visual representation of hazardous products.
item Hazard statements: they are used to describe the degree of hazard and the nature of the hazardous material.
item Product identification: it describes the chemical`s name.
end{enumerate}
begin{enumerate}
item A plastic container for storage purposes.
item Neutralizing agent for acid spills such as sodium bicarbonate
item Mercury absorbent
end{enumerate}
begin{enumerate}
item The pH of acid is lower than 7 and higher than 7 for a base.
item Acids usually have a sour taste and bases have a bitter taste.
item Both acid and bases are good electrical conductors.
end{enumerate}
item Glycolic Acid
item Lactic Acid
end{enumerate}
* When applying lactic acid on the skin improves firmness and makes it smooth.

