All Solutions
Page 592: Closure Activity
$$
(x-x_1)^2+(y-y_1)^2=r^2
$$
a.The circle has center
$(0,3)$ and radius 6.
$$
(x^2-8x+16)+(y^2+2y+1)=16
$$
Factorize the perfect square trinomial ($a^2pm 2ab+b^2=(apm b)^2$):
$$
(x-4)^2+(y+1)^2=4^2
$$
Thus the circle has center $(4,-1)$ and radius 4.
$$
(x^2)+(y^2+20y+100)=100
$$
Factorize the perfect square trinomial ($a^2pm 2ab+b^2=(apm b)^2$):
$$
x^2+(y+10)^2=10^2
$$
Thus the circle has center $(0,-10)$ and radius 10.
b. $(-1,-2)$, $sqrt{8}approx 2.8$
c. $(4,-1)$, 4
d. $(0,-10)$, 10
$$
(x-x_1)^2+(y-y_1)^2=r^2
$$
The circle has center
$(4,-2)$ and radius 4, thus the equation is:
$$
(x-4)^2+(y+2)^2=4^2
$$
(x-4)^2+(y+2)^2=4^2
$$
$$
r=dfrac{4}{sin{60text{textdegree}}}approx 4.62in
$$
The diameter is twice the radius:
$$
D=2(4.62)=9.24in
$$
$$
mangle C=dfrac{90text{textdegree}}{2}=45text{textdegree}
$$
Alternate interior angles of parallel sides are congruent:
$$
moverarc{CD}=mangle E=mangle C=45text{textdegree}
$$
$$
mangle A=dfrac{112text{textdegree}}{2}=56text{textdegree}
$$
The sum of all angles in a triangle is 180$text{textdegree}$:
$$
moverarc{AB}=2mangle C=2(180text{textdegree}-65text{textdegree}-56text{textdegree})=2(59text{textdegree})=118text{textdegree}
$$
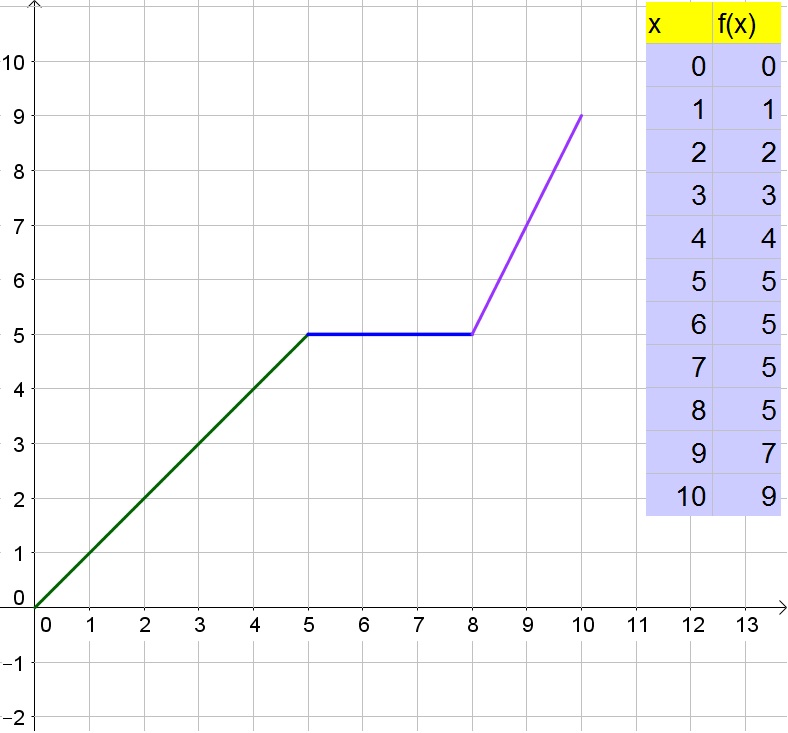
b. 118$text{textdegree}$
$$
y=-2x+9
$$
Interchange $x$ and $y$:
$$
x=-2y+9
$$
Solve the equation to $y$ by subtract 9 from both sides of the equation:
$$
x-9=-2y
$$
Divide both sides of the equation by $-2$:
$$
-dfrac{1}{2}(x-9)=y
$$
Finally replace $y$ with $f^{-1}(x)$ and interchange the left and right side of the equation:
$$
f^{-1}(x)=-dfrac{1}{2}(x-9)
$$
$$
y=3(x+5)
$$
Interchange $x$ and $y$:
$$
x=3(y+5)
$$
Solve the equation to $y$ by dividing both sides of the equation by 3:
$$
dfrac{1}{3}x=y+5
$$
Subtract 5 from both sides of the equation:
$$
dfrac{1}{3}x-5=y
$$
Finally replace $y$ with $g^{-1}(x)$ and interchange the left and right side of the equation:
$$
g^{-1}(x)=dfrac{1}{3}x-5
$$
b. $g^{-1}(x)=dfrac{1}{3}x-5$
$$
0=x^2+2x-3
$$
Factorize:
$$
0=(x+3)(x-1)
$$
Zero product property:
$$
x+3=0text{ or }x-1=0
$$
Solve each equation to $x$:
$$
x=-3text{ or }x=1
$$
Determine $y$:
$$
y=-5x-7=-5(-3)-7=15-7=8
$$
$$
y=-5x-7=-5(1)-7=-5-7=-12
$$
Thus the solutions are $(-3,8)$ and $(1,-12)$.
$$
0=x^2+8x+12
$$
Factorize:
$$
0=(x+6)(x+2)
$$
Zero product property:
$$
x+6=0text{ or }x+2=0
$$
Solve each equation to $x$:
$$
x=-6text{ or }x=-2
$$
$$
x-4=0text{ or }x+2=0
$$
Solve each equation to $x$:
$$
x=4text{ or }x=-2
$$
$$
x^2-6x+9=18
$$
Factorize the perfect square trinomial ($a^2pm 2ab+b^2=(apm b)^2$):
$$
(x-3)^2=18
$$
Take the square root of both sides of the equation:
$$
x-3=pm sqrt{18}=pm 3sqrt{2}
$$
Add 3 to both sides of the equation:
$$
x=3pm 3sqrt{2}
$$
$$
x=dfrac{-1pmsqrt{1^2-4(1)(5)}}{2(1)}=-dfrac{1}{2}pm dfrac{sqrt{19}}{2}i
$$
b. $x=4$ or $x=-2$
c. $x=3pm 3sqrt{2}$
d. $x=-frac{1}{2}pm frac{sqrt{19}}{2}i$
Thus the vertex is $(1,-4)$.
$$
0=(x-1)^2-4
$$
Add 4 to both sides of the equation:
$$
4=(x-1)^2
$$
Takle the square root of both sides of the equation:
$$
pm 2 = x-1
$$
Add 1 to both sides of the equation:
$$
3text{ or }-1=1pm 2=x
$$
Thus the $x$-intercepts are $x=3$ and $x=-1$.
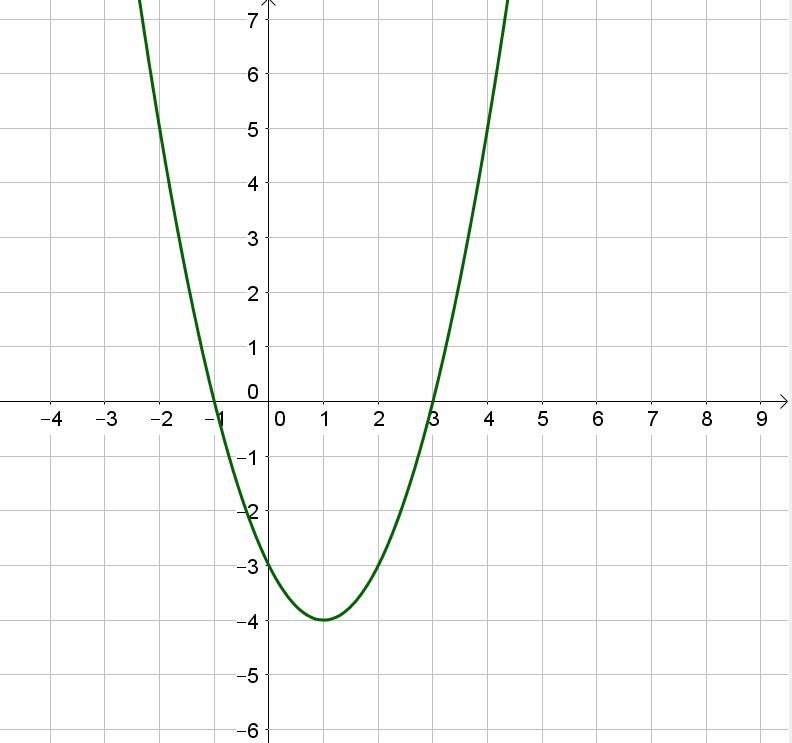
b. $x=3$ and $x=-1$
c. Graph