All Solutions
Page 363: Closure Activity
$$
x^2+x-30=(x+6)(x-5)
$$
$$
-3x^3+23x^2-14x=-x(3x^2-23x+14)
$$
Factorize further:
$$
-3x^3+23x^2-14x=-x(x-7)(3x-2)
$$
$$
6x^3+10x^2-24x=2x(3x^2+5x-12)
$$
Factorize further:
$$
6x^3+10x^2-24x=2x(x+3)(3x-4)
$$
b. $-x(x-7)(3x-2)$
c. Not possible to factorize
d. $2x(x+3)(3x-4)$
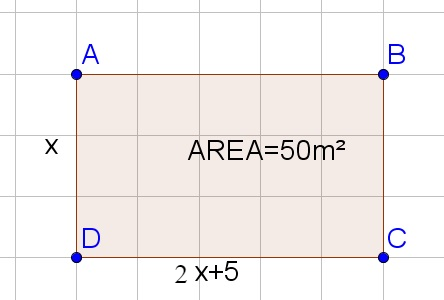
$$
x(2x+5)=50
$$
c. Subtract 50 from both sides of the equation:
$$
2x^2+5x-50=0
$$
Determine the roots using the quadratic formula $x=frac{-bpm sqrt{b^2-4ac}}{2a}$ for a quadratic equation of the form $ax^2+bx+c=0$.
$$
begin{align*}
x&=frac{-5pm sqrt{5^2-4(2)(-50)}}{2(2)}
\ &=frac{-5pm sqrt{425} }{4}
\ &=frac{-5pm 5sqrt{17} }{4}
\ &approx -6.4039text{ or }3.9039
end{align*}
$$
Since the width has to be positive, the width is approximately 3.9039m and the length is $2cdot 3.9039+5=$12.8078m.
b. $x2(x+5)=50$
c. Width $3.9039$ m and length 12.8078 m.
The legs of a 45$text{textdegree}$-45$text{textdegree}$-90$text{textdegree}$ are equal and the hypotenuse can be determined using the Pythagorean theorem, moreover the legs are half the hypotenuse multiplied by $sqrt{2}$.
If two lengths of the right triangle are given, determine the third using the Pythagorean theorem.
$$
a^2+b^2=c^2
$$
The sum of all angles is in a triangle should be a 180$text{textdegree}$.
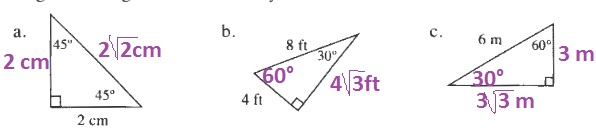
b. 60$text{textdegree}$, $4sqrt{3}$ ft
c. 30$text{textdegree}$, 3m, $3sqrt{3}$ m
$$
a^2+b^2=c^2
$$
a.
$$
x=sqrt{15^2-12^2}=sqrt{81}=9
$$
b.
$$
x=sqrt{24^2+10^2}=sqrt{676}=26
$$
b. 26
a.
$$
8^{1/3}=sqrt[3]{8}=sqrt[3]{2^3}=2
$$
b.
$$
32^{2/5}=(sqrt[5]{32})^2=(sqrt[5]{2^5})^2=2^2=4
$$
c.
$$
125^{4/3}=(sqrt[3]{125})^4=(sqrt[3]{5^3})^4=5^4=625
$$
b. 4
c. 625
$$
x=dfrac{-4pm sqrt{4^2-4(3)(-7)}}{2(3)}=dfrac{-4pm 10}{6}=1text{ or }-dfrac{7}{3}
$$
$$
(x-6)(x+3)=0
$$
Zero product property:
$$
x-6=0text{ or }x+3=0
$$
Solve each equation to $x$:
$$
x=6text{ or }x=-3
$$
$$
x^2+4x+4=3
$$
Factorize:
$$
(x+2)^2=3
$$
Take the square root of both sides of the equation:
$$
x+2=pm sqrt{3}
$$
Subtract 2 from both sides of the equation:
$$
x=-2pm sqrt{3}
$$
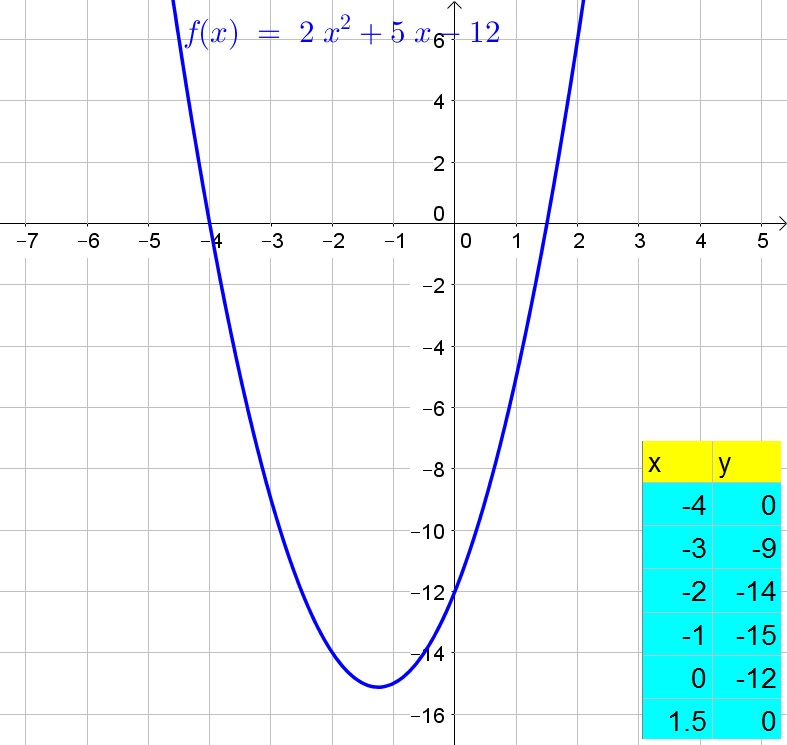
b. $x=6$ or $x=-3$
c. $x=-2pm sqrt{3}$
d. $x=-4$ or $x=1.5$
a.
$$
(3+4i)+(7-2i)=(3+7)+(4i-2i)=10+2i
$$
b.
$$
(3+5i)^2=9+30i+25i^2=9+30i-25=-16+30i
$$
c.
$$
(7+i)(7-i)=49-i^2=49+1=50
$$
d.
$$
(3i)(2i)^2=(3i)(4i^2)=(3i)(-4)=-12i
$$
b. $-16+30i$
c. 50
d. $-12i$
$$
sqrt{8^2-5^2}=sqrt{39}
$$
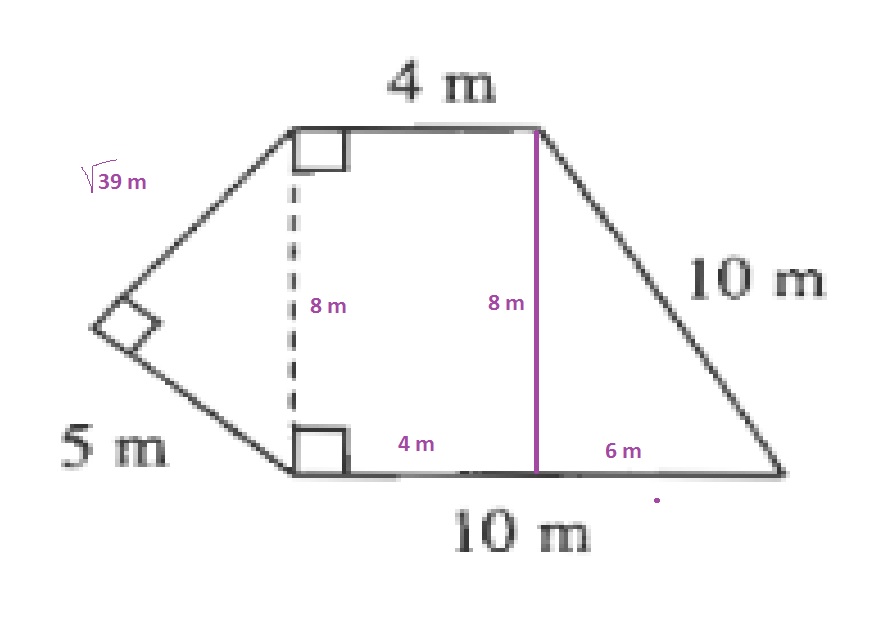
$$
PERIMETER=4+10+10+5+sqrt{39}=29+sqrt{39}mapprox 35.24m
$$
The area of a trapezium is the sum of the bases, multiplied by the height divided by 2. The area of a rectangle is the product of the base and the height divided by 2.
$$
AREA=dfrac{(4+10)8}{2}+dfrac{5sqrt{39}}{2}=56+dfrac{5sqrt{39}}{2}m^2approx 71.61m^2
$$
Area $71.61$ m$^2$
$$
P(pool)=P(1,5)+P(3,5)+P(1,7)=dfrac{3}{4}cdot dfrac{1}{3}+ dfrac{1}{4}cdot dfrac{1}{3}+ dfrac{3}{4}cdot dfrac{1}{3}=dfrac{7}{12}approx 0.5833=58.33%
$$
b. The probability of the event is the sum of the probabilities of the possibilities that are part of the event. The probability of each spin is equal.
$$
P(pool)=P(2,4)+P(2,5)+P(2,6)+P(3,4)+P(3,5)+P(3,6)+P(4,4)+P(4,5)+P(5,4)
$$
$$
=9P(2,4)=9cdot dfrac{1}{4}cdot dfrac{1}{3}=dfrac{3}{4}=0.75=75%
$$
b. 75%

