
Miller and Levine Biology
1st Edition
Joseph S. Levine, Kenneth R. Miller
ISBN: 9780328925124
Textbook solutions
Chapter 1: The Science of Biology
Page 14: Review
Page 21: Science in Context
Page 29: Review
Page 36: Assessment
Page 39: Test Practice
Chapter 2: The Chemistry of Life
Page 46: Review
Page 51: Review
Page 57: Review
Page 61: Review
Page 68: Assessment
Page 71: Test Practice
Chapter 3: The Biosphere
Page 84: Review
Page 91: Review
Page 97: Analyzing Data
Page 101: Review
Page 108: Assessment
Page 111: Test Practice
Chapter 4: Ecosystems
Page 117: Review
Page 122: Review
Page 131: Review
Page 138: Assessment
Page 141: Test Practice
Chapter 5: Populations
Page 151: Review
Page 155: Analyzing Data
Page 157: Review
Page 161: Review
Page 168: Assessment
Page 171: Test Practice
Chapter 6: Communities and Ecosystem Dynamics
Page 179: Analyzing Data
Page 181: Review
Page 185: Review
Page 189: Review
Page 196: Assessment
Page 199: Test Practice
Chapter 7: Humans and Global Change
Page 205: Review
Page 217: Review
Page 221: Analyzing Data
Page 222: Review
Page 225: Review
Page 232: Assessment
Page 235: Test Practice
Chapter 8: Cell Structure and Function
Page 247: Review
Page 257: Review
Page 265: Review
Page 269: Review
Page 276: Assessment
Page 279: Test Practice
Chapter 9: Photosynthesis
Page 285: Review
Page 290: Review
Page 297: Review
Page 304: Assessment
Page 307: Test Practice
Chapter 10: Cellular Respiration
Page 313: Review
Page 320: Review
Page 325: Review
Page 332: Assessment
Page 335: Test Practice
Chapter 11: Cell Growth and Division
Page 342: Review
Page 348: Review
Page 354: Review
Page 361: Review
Page 368: Assessment
Page 371: Test Practice
Chapter 12: Introduction to Genetics
Page 382: Review
Page 388: Review
Page 391: Analyzing Data
Page 392: Review
Page 399: Review
Page 406: Assessment
Page 409: Test Practice
Chapter 13: DNA
Page 417: Review
Page 423: Review
Page 427: Review
Page 434: Assessment
Page 437: Test Practice
Chapter 14: RNA and Protein Synthesis
Page 444: Review
Page 447: Analyzing Data
Page 450: Review
Page 456: Review
Page 461: Review
Page 468: Assessment
Page 471: Test Practice
Chapter 15: The Human Genome
Page 479: Review
Page 484: Review
Page 493: Review
Page 500: Assessment
Page 503: Test Practice
Chapter 16: Biotechnology
Page 508: Review
Page 515: Review
Page 523: Review
Page 527: Review
Page 534: Assessment
Page 537: Test Practice
Chapter 17: Darwin’s Theory of Evolution
Page 545: Analyzing Data
Page 548: Review
Page 554: Review
Page 559: Review
Page 567: Review
Page 574: Assessment
Page 577: Test Practice
Chapter 18: Evolution of Populations
Page 584: Review
Page 591: Review
Page 595: Review
Page 599: Review
Page 606: Assessment
Page 608: Assessment
Page 609: Test Practice
Chapter 19: Biodiversity and Classification
Page 618: Review
Page 628: Review
Page 636: Assessment
Page 639: Test Practice
Chapter 20: History of Life
Page 651: Review
Page 658: Review
Page 665: Review
Page 672: Assessment
Page 675: Test Practice
Chapter 21: Viruses, Prokaryotes, Protists, and Fungi
Page 688: Review
Page 697: Review
Page 703: Review
Page 709: Review
Page 716: Assessment
Page 719: Test Practice
Chapter 22: Plants
Page 726: Review
Page 736: Review
Page 749: Review
Page 756: Assessment
Page 759: Test Practice
Chapter 23: Plant Structure and Function
Page 775: Review
Page 783: Review
Page 787: Review
Page 794: Assessment
Page 797: Test Practice
Chapter 24: Animal Evolution, Diversity, and Behavior
Page 805: Review
Page 815: Review
Page 821: Review
Page 827: Review
Page 834: Assessment
Page 836: Assessment
Page 837: Test Practice
Chapter 25: Animal Systems I
Page 844: Review
Page 848: Review
Page 852: Review
Page 857: Review
Page 864: Assessment
Page 867: Test Practice
Chapter 26: Animal Systems II
Page 875: Review
Page 879: Review
Page 887: Review
Page 891: Review
Page 898: Assessment
Page 901: Test Practice
Chapter 27: The Human Body
Page 909: Review
Page 922: Review
Page 936: Review
Page 943: Review
Page 950: Assessment
Page 953: Test Practice
All Solutions
Page 775: Review
Exercise 1
Result
1 of 1
The three plant tissue systems are the following:
a. Dermal tissue – outer covering that protects the plant
b. Vascular tissue – supports the body of the plant and transports water and nutrients in the plant
c. Ground tissue – responsible for photosynthesis, stores nutrients, and provides additional physical support of the plant
a. Dermal tissue – outer covering that protects the plant
b. Vascular tissue – supports the body of the plant and transports water and nutrients in the plant
c. Ground tissue – responsible for photosynthesis, stores nutrients, and provides additional physical support of the plant
Exercise 2
Result
1 of 1
Roots are hair-like structures that are formed in vascular plants. They anchor the body of the plants to the soil and help absorb the water and nutrients.
Exercise 3
Result
1 of 1
Stems are the structural axes found in plants. Here are the three functions of stems:
1. They serve as the plant’s support by holding up the leaves to the sun.
2. They are the plant’s transport system that delivers the water and nutrients into the different parts of the plant.
3. They form the branches, the leaves, and the flowers.
1. They serve as the plant’s support by holding up the leaves to the sun.
2. They are the plant’s transport system that delivers the water and nutrients into the different parts of the plant.
3. They form the branches, the leaves, and the flowers.
Exercise 4
Result
1 of 1
Leaves are the broad and flat surfaces found in plants that are used in photosynthesis. It protects the plant from water loss by retaining the water and letting the exchange of gases take place.
Exercise 5
Step 1
1 of 2
The combined forces of active transport, root pressure, capillary action, and transpiration aid in the movement of water molecules throughout the entire plant.
a. Root pressure and active transport are the driving forces that cause the fluids and substances to move upward from the soil into the roots.
b. Capillary action is the movement of the water molecules across the surface of plant tissues caused by the adhesion between the two.
c. Transpiration is the evaporation of water from the leaves.
Due to the forces acting between the water and the plant’s transport tissues, the water molecules and nutrients flow in an upward manner. This is important because the pressure coming from the roots allows the molecules to go up instead of accumulating inside the root system. If this happens, the roots will begin to expand as they fill up with water and nutrients.
Result
2 of 2
The combined forces of active transport, root pressure, capillary action, and transpiration aid in the movement of water molecules throughout the entire plant. Due to the forces acting between the water and the plant’s transport tissues, the water molecules and nutrients flow in an upward manner. This is important because the pressure coming from the roots allows the molecules to go up instead of accumulating inside the root system. If this happens, the roots will begin to expand as they fill up with water and nutrients.
Exercise 6
Result
1 of 1
The tree sapling exhibits primary growth in the apical meristems, which are responsible for the increase in its length or height. However, it does not show secondary growth, which happens in the vascular cambium. In this case, the vascular cambium does not produce enough tissues that make the stems thicker over time.
Exercise 7
Result
1 of 1
The rest of the water is lost in the atmosphere in the form of water vapor through a process called transpiration, which is the evaporation of water from the leaves. This process helps the leaves to remain cool during the dry and hot days.
Exercise 8
Step 1
1 of 2
The diagram below shows how materials and substances are transferred in and out of the plant, as well as between the roots, the stems, and the leaves.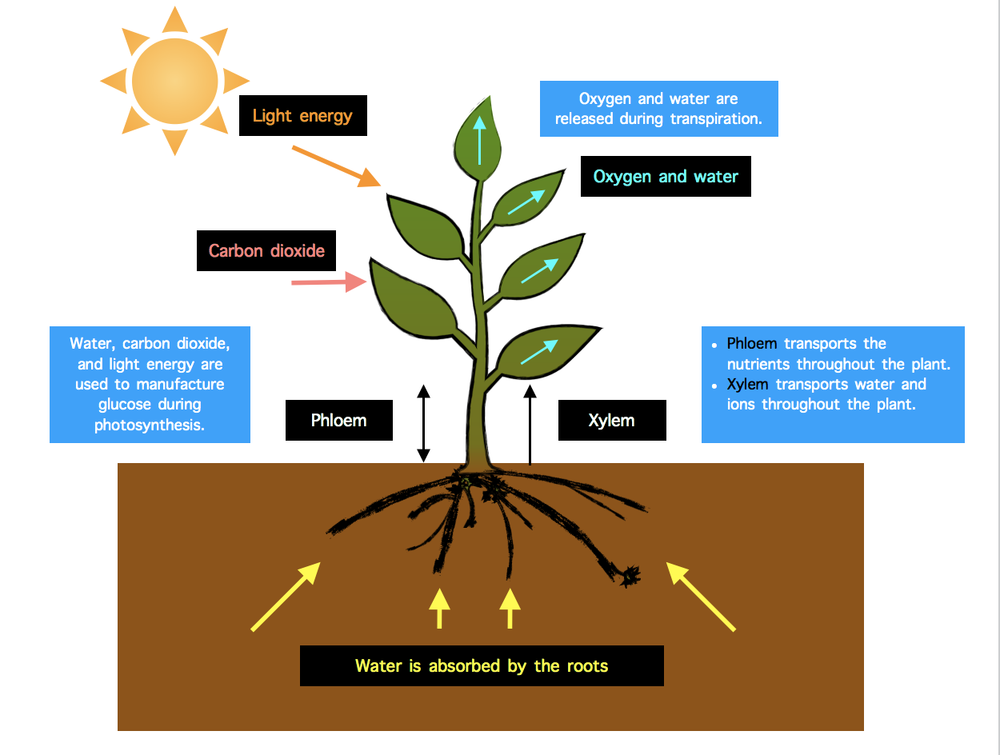

Result
2 of 2
The diagram below shows how materials and substances are transferred in and out of the plant, as well as between the roots, the stems, and the leaves. (Click to see the diagram)
Haven't found what you were looking for?
Search for samples, answers to your questions and flashcards

unlock
