
All Solutions
Page 304: Assessment
Carbon dioxide + Water $longrightarrow$ Sugars + Oxygen
Water shortage can decrease the rate of photosynthesis, or in worst cases, stop it.
The intensity of light affects the rate of photosynthesis. If a plant has increased exposure to sunlight, the rate of photosynthesis will increase.
On the other hand, the enzymes involved in photosynthesis work best at a temperature between 0 to 35 degrees Celsius. If the temperature will go above or below the ideal temperature, it will affect the rate of photosynthesis.
Water shortage can decrease the rate of photosynthesis, or in worst cases, stop it.
The intensity of light affects the rate of photosynthesis. If a plant has increased exposure to sunlight, the rate of photosynthesis will increase.
On the other hand, the enzymes involved in photosynthesis work best at a temperature between 0 to 35 degrees Celsius. If the temperature will go above or below the ideal temperature, it would affect the rate of photosynthesis.
carbon dioxide + water $rightarrow$ glucose + oxygen
6CO$_{2}$ + 6H$_{2}$O $rightarrow$ C$_{6}$H$_{12}$O$_{6}$ + 6O$_{2}$
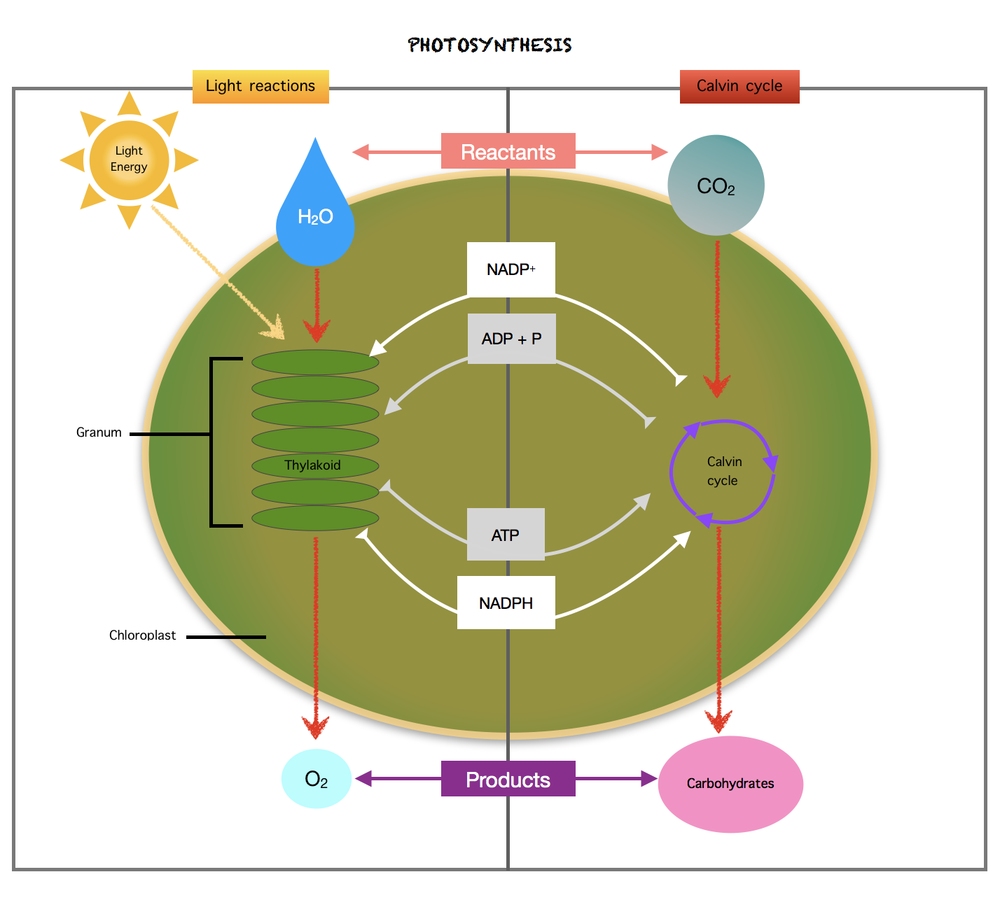
In photosystem I, the same electrons from photosystem II are reenergized. Once NADP$^{+}$ picks up the high-energy electrons and H$^{+}$ ions, NADPH is formed. On the other hand, ATP synthase binds ADP and phosphate to produce ATP. Since the inside of the thylakoid membranes are filled with positively charged hydrogen ions, the outside of the thylakoid membranes becomes negatively charged. The difference in the charges creates an energy that is used to combine a phosphate group to ADP in order to form ATP.
During photosynthesis, plants use the energy from the sun by converting carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. The sources of glucose are from the carbon atoms in carbon dioxide and hydrogen atoms in water. The sugars and high-energy molecules, such as ATP, that are produced by the plants are transferred to primary consumers when they eat them. In return, the consumers use this sugars to produce their own cellular energy or ATP to do their work.
By losing one phosphate group, it gives off energy. Once energy is released, it becomes ADP.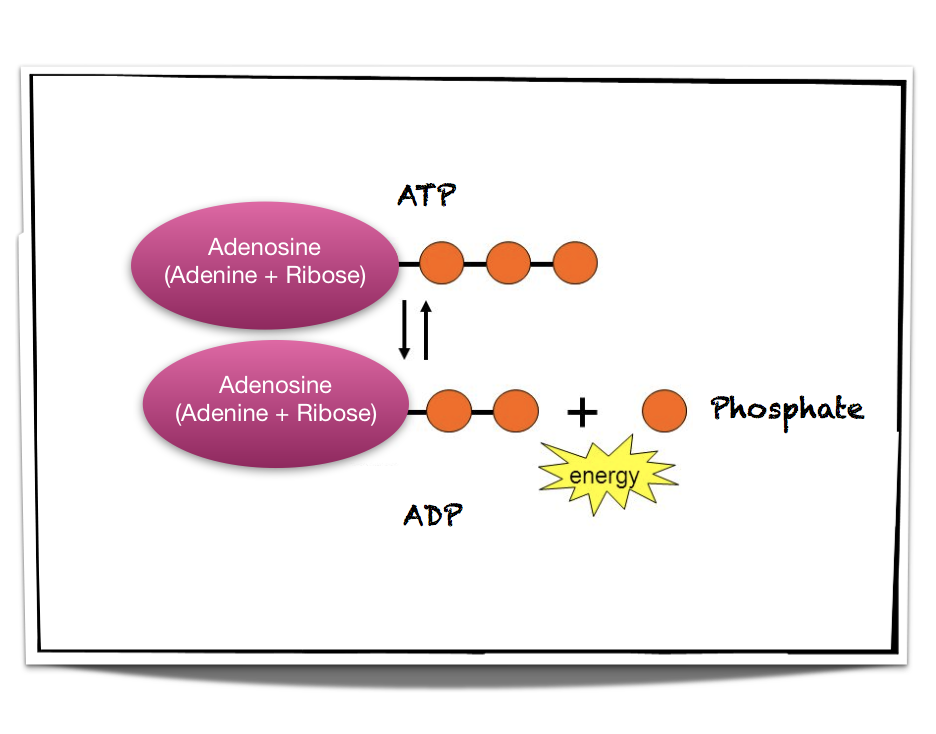
By losing one phosphate group, it gives off energy. Once energy is released, it becomes ADP. (Click to see the diagram)
If autotrophs are going to be wiped out from the Earth, then heterotrophs would not survive. Moreover, if heterotrophs are no longer around, there would be less supply of carbon dioxide. This event would slow down or hinder the process of photosynthesis in plants.
1. What are the parts found in algae?
2. What is the role of algae in the ecosystem found in the aquarium?
3. Do the algae use the process of photosynthesis?
4. How does the photosynthesis in aquatic organisms differ in the autotrophs that live on land?
5. Do the algae grow well if they are exposed to long periods of sunlight?
6. Do the algae grow well in a warm or a cold environment?
Since the inside of the thylakoid membranes are filled with positively charged hydrogen ions, the outside of the thylakoid membranes becomes negatively charged. The difference in the charges creates an energy that is used to convert ADP into ATP. ATP and NADPH are used for producing high-energy sugars during the next stage of photosynthesis, which is the Calvin cycle.
In the first stage of this cycle, carbon fixation happens, wherein carbon molecules combine with a five-carbon molecule called RuBP.
In the next stage, the organic molecule is reduced and it becomes a simple sugar. NADPH donates electrons to molecules to make the sugar.
The third step is the regeneration which requires ATP. The regeneration happens when sugar molecules proceed to make glucose and the other molecules are recycled to regenerate RuBP compound, which in turn would accept new carbon molecules.
b. One glucose molecule is produced when six carbon atoms enter the cycle. The carbon atoms usually come from the atmosphere.
c. The reason for this event is because the light-independent reactions rely on ATP and NADPH, which was produced from light-dependent reactions, to assemble energy-rich sugars.
b. One glucose molecule is produced when six carbon atoms enter the cycle. The carbon atoms usually come from the atmosphere.
c. The reason for this event is because the light-independent reactions rely on ATP and NADPH, which was produced from light-dependent reactions, to assemble energy-rich sugars.
This model, which only shows a part of photosynthesis, can be improved if it would be integrated with the processes that take place when the electrons are carried to photosystems II and I. This would allow a better understanding of the role of the transport system in the entire process of photosynthesis.
For example, the light energy is absorbed by the leaves of the plants during photosynthesis. In this case, the light was transformed into chemical energy in the form of sugars and molecules. However, these sugars can never be recycled back to light energy since the process is irreversible. It just goes on and on until the energy is lost in the atmosphere in the form of heat energy. Also, when plants take in water and carbon dioxide, they undergo processes that continuously break and re-assemble their molecules.
The cycling of matter in the environment usually occurs as the elements are transferred from one step in the food chain into the next; for example, the carbon in plants is transferred to herbivores, then to the carnivores. Once the top-level consumer dies, carbon goes back to the environment and gets to be absorbed again by plants as nutrients for photosynthesis.
A. If the light source is 5 cm away, then the bubbles produced per minute is 43.5.
y = -0.8x + 39.8
5 = -0.8x + 39.8
0.8x = 39.8 – 5
$dfrac{text{0.8x = 34.8}}{text0.8}$
x = 43.5
B. If the light source is 25 cm away, then the bubbles produced per minute is 18.5.
y = -0.8x + 39.8
25 = -0.8x + 39.8
0.8x = 39.8 – 25
$dfrac{text{0.8x = 14.8}}{text0.8}$
x = 18.5
C. If the light source is 50 cm away, then the bubbles produced per minute is -12. 75.
y = -0.8x + 39.8
50 = -0.8x + 39.8
0.8x = 39.8 – 50
$dfrac{text{0.8x = -10.2}}{text0.8}$
x = -12.75
If the light source is 5 cm away, then the bubbles produced per minute is 43.5.
If the light source is 25 cm away, then the bubbles produced per minute is 18.5.
If the light source is 50 cm away, then the bubbles produced per minute is -12.75.
Using this information, we can conclude that when the aquatic plant is placed far from light, it gets less sun exposure. This affects the rate of photosynthesis, including its by-products. When the rate of photosynthesis is slow, the oxygen produced as a waste product is also low.
On the other hand, the light-independent reaction, which is also known as the Calvin cycle, takes place in the stroma of the chloroplasts. It uses carbon dioxide, ATP and NADPH to produce high-energy molecules, such as glucose. This cycle does not require the presence of light.
On the other hand, the ATP and NADPH, which contain chemical energy, are used to convert carbon dioxide from the atmosphere into high-energy sugars during light-independent reactions. In turn, the sugars are used by the plant for its growth and development. The sugars are also stored as nutrients, which are later transferred to consumers once they eat the plant.
1. During light-dependent reactions:
a. Photosystem II involves light absorption.
b. Light energy breaks down water into hydrogen ions (H$^{+}$), oxygen, and energized electrons.
c. High-energy electrons are transported to photosystem I.
d. NADP$^{+}$ picks up the high-energy electrons and H$^{+}$ ions, NADPH is formed.
e. Phosphate combines with ADP. ATP is formed.
2. During light-independent reactions:
a. ATP and NADPH are used for producing high-energy sugars.
b. Carbon fixation: Carbon molecules combine with a five-carbon molecule called RuBP to form an organic molecule.
c. Reduction: The organic molecule is reduced and it becomes a simple sugar.
d. NADPH donates electrons to the molecules in order to make the sugar.
e. Regeneration: ATP is used to make glucose, while other molecules are recycled to regenerate RuBP.
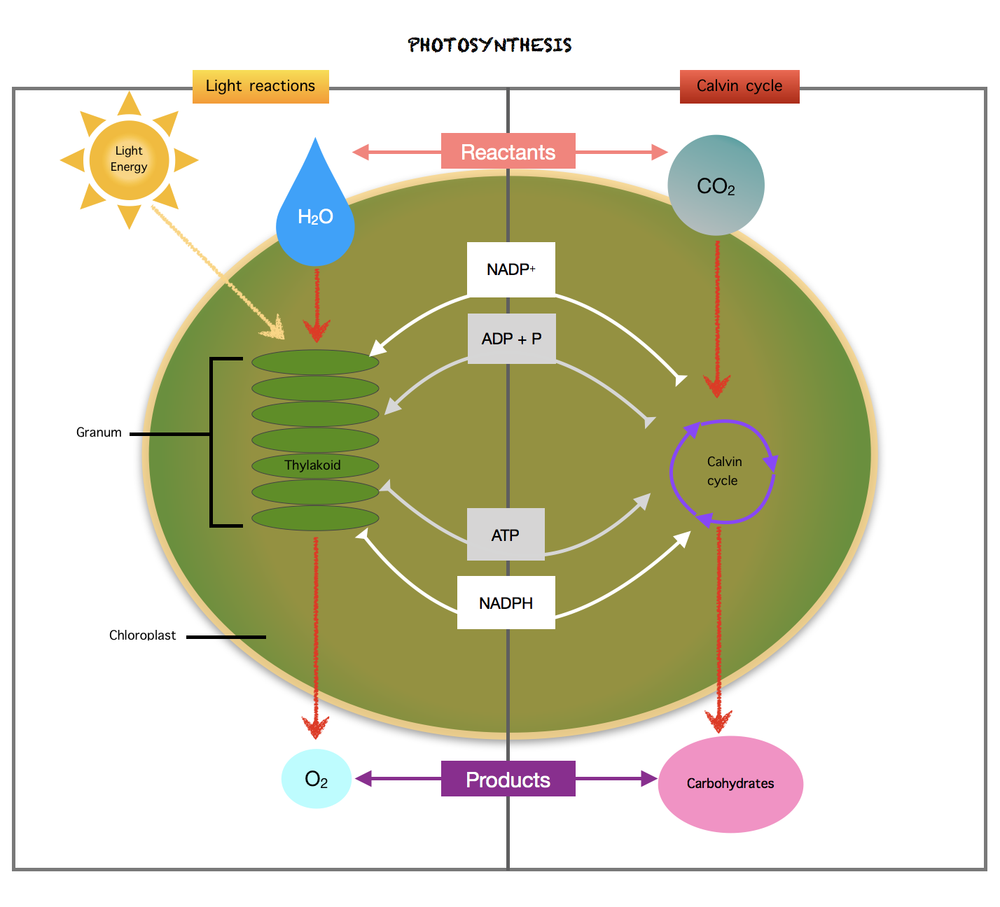
The photosystem II and photosystem I are the two reaction centers in the chlorophyll during light-dependent reactions. In photosystem II, light absorption takes place and the breakdown of water molecules. Next, the high-energy electrons are transported to photosystem I. This is where NADP$^{+}$ picks up the high-energy electrons and H$^{+}$ ions to form NADPH, while one phosphate group combines with ADP to form ATP.
In turn, the products of light-dependent reactions: ATP and NADPH are used for producing high-energy sugars on the next stage of photosynthesis, which is the light-independent reactions.

