
Miller and Levine Biology
1st Edition
ISBN: 9780328925124
Textbook solutions
All Solutions
Page 368: Assessment
Exercise 1
Step 1
1 of 2
The larger the cell is, there are more requirements on its DNA molecule. The need for nutrients is larger as well as the production of waste products, compared to the smaller cells. Since transport of these substances is done through the cell membrane, we describe a ratio of surface area to volume, which practically means that larger cells have also a larger surface of the cell membrane, and vice verca.
Result
2 of 2
d surface area
Exercise 2
Step 1
1 of 2
The cell cycle of eukaryotic organisms consists of following phases – G1, S, G2, and the cell division. The first phase represents the cell growth, while the DNA replication occurs in the S phase. In the G2 phase, the cell prepares itself for the process of division.
Result
2 of 2
a duplicate its genetic information
Exercise 3
Step 1
1 of 2
In sexual reproduction, two parents pass their genetic material to the offspring. This method is more complex, but it creates offspring that is genetically distinct.
Result
2 of 2
b. sexual reproduction
Exercise 4
Result
1 of 1
The larger the cell is, there are more requirements on its DNA molecule. The need for nutrients is larger as well as the production of waste products, compared to the smaller cells. Since transport of these substances is done through the cell membrane, we describe a ratio of surface area to volume. Cell volume is the total amount of the molecules and structures that build a cell. Surface area is the total surface of the cell membrane. When the surface area is divided by the cell volume, we speak about their ratio. This practically means that larger cells have also a larger surface of the cell membrane, and vice verca.
Exercise 5
Result
1 of 1
In asexual reproduction, there is only one parent and the offspring is their clone, which may not be able to survive a change in the environment. In sexual reproduction, two parents pass their genetic material to the offspring. This method is more complex, but it creates offspring that is genetically distinct, which might help the population to persist through the environmental changes.
Exercise 6
Step 1
1 of 2
The centromeres of the chromosomes are regions where the sister chromatids are connected to each other. This is also the place where the chromosomes are attached to the microtubules which allow them to move towards the centrioles during the cell division.
Result
2 of 2
b. centromere
Exercise 7
Step 1
1 of 2
Mitosis consists of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase and cytokinesis. In prophase, each chromosome contains doubled DNA material which is arranged in two sister chromatids. Therefore, at this phase the chromosome number is diploid, but the number of chromatids is doubled. In metaphase, chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell. During anaphase, paired chromatids are divided and they move toward the opposite ends of the cell. Each of the two daughter cells has the same number of chromosomes, but one half of the number of chromatids as the parental cell. In telophase and cytokinesis, this cell divides into two cells. The one diploid cell is divided into two diploid cells.
Result
2 of 2
c. 12
Exercise 8
Step 1
1 of 2
Cytokinesis represents the division of the cytoplasm. It is the final stage of the mitotic division. Plant cells have a rigid wall and a membrane which is not as flexible as the one in animal cells. Thus, the plant cells are characterized by the formation of the cell plate, which is a structure that forms in the place where the division of the cytoplasms should occur. The cell plate gradually develops into cell membranes, around which the cell wall is made.
Result
2 of 2
d. cell plate
Exercise 9
Result
1 of 1
The cell cycle is a sequence of events that a cell goes through as it grows and divides. The cell cycle of eukaryotic organisms consists of following phases – G1, S, G2, and the cell division. The first phase represents the cell growth, while the DNA replication occurs in the S phase. In the G2 phase, the cell prepares itself for the process of division. The DNA material is being tightly packed around histones into nucleosomes, which are packed further into threads which makes chromatin. Right before the beginning of the cell division, duplicated chromatin is being folded and coiled into chromosomes, where each one of them contains two sister chromatids which will be passed on the two daughter cells at the end of the mitotic division.
Exercise 10
Result
1 of 1
The cell cycle is a sequence of events that a cell goes through as it grows and divides. The cell cycle of eukaryotic organisms consists of following phases – G1, S, G2, and the cell division. The first three stages are known as the interphase. The G1 phase represents the cell growth, while the DNA replication occurs in the S phase. In the G2 phase, the cell prepares itself for the process of division.
Exercise 11
Step 1
1 of 3
Mitosis consists of the following phases: Prophae, Metaphase, Anaphase, and Telophase
Step 2
2 of 3
1. Prophase – each chromosome contains doubled DNA material which is arranged in two sister chromatids
2. Metaphase – chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell
3. Anaphase – paired chromatids are divided and they move toward the opposite ends of the cell
4. Telophase – the nucleus divides
Result
3 of 3
See the explanation
Exercise 12
Result
1 of 1
The picture shows metaphase of the mitotic division. In this stage, the chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell. Fibers of the mitotic spindle are attached to the centromeres of chromosomes.
Exercise 13
Step 1
1 of 2
The scientists have discovered the family of proteins which they named cyclins, that regulates the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells. These proteins bind with a certain enzyme and form a mitosis-promoting factor. The experiments showed that the cells in which the cyclins were injected during mitosis, would go through the cell cycle more quickly than the ones that were not injected with cyclins.
Result
2 of 2
c. cyclins
Exercise 14
Step 1
1 of 2
The two types of proteins that control the cell cycle are internal and external regulators. Internal regulators enable the cell cycle to continue only when certain events happen, while external regulators increase or decrease the speed, or even stop of the cell cycle. External regulators respond to events that occur outside of a cell.
Result
2 of 2
a. they respond to the events occurring inside a cell
Exercise 15
Result
1 of 1
Cancer is a disease that is characterized by abnormal cell growth and division.
The similarity between cancer and normal cells is in their structure. Cancer cells have the mutation which affects proliferation and programmed cell death, but they still have all the organelles as the normal cells.
However, cancer cells multiply uncontrollably, which is not characteristic of noncancerous cells. Also, the cancer cells are not programmed to die, while the process of apoptosis is present in normal cells.
The similarity between cancer and normal cells is in their structure. Cancer cells have the mutation which affects proliferation and programmed cell death, but they still have all the organelles as the normal cells.
However, cancer cells multiply uncontrollably, which is not characteristic of noncancerous cells. Also, the cancer cells are not programmed to die, while the process of apoptosis is present in normal cells.
Exercise 16
Result
1 of 1
If we remove cells from the center of the tissue culture, the new cells will restore the tissue. The process of cell division will last until the new cells make contact with other cells. When that happens, the cells will stop dividing.
Exercise 17
Result
1 of 1
The scientists have discovered the family of proteins which they named cyclins, that regulates the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells. These proteins bind with a certain enzyme and form a mitosis-promoting factor. The experiments showed that the cells in which the cyclins were injected during mitosis, would go through the cell cycle more quickly than the ones that were not injected with cyclins.
Exercise 18
Step 1
1 of 2
Stem cells are unspecialized cells from which different kinds of specialized cells can develop. We differ embryonic and adult type. Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent, which means that they have the ability to develop into any cell type in the body. However, adult stem cells are multipotent, which means that they can differentiate into several types of specialized cells. Adult stem cells are found in the bone marrow, hair follicles, while small groups of stem cells are also located in the brain, heart and skeletal muscles.
Result
2 of 2
b. adult stem cells
Exercise 19
Step 1
1 of 2
Cell differentiation is the process in which specialized cells are formed from totipotent cells. Totipotent cells are present in the zygote and they have the ability to develop into any type of cells. They can even differentiate to extra-embryonic membranes and placenta.
Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent, which means that they have the ability to develop into any cell type in the body.
However, adult stem cells are multipotent, which means that they can differentiate into several types of specialized cells. Adult stem cells are found in the bone marrow, hair follicles, while small groups of stem cells are also located in the brain, heart and skeletal muscles.
Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent, which means that they have the ability to develop into any cell type in the body.
However, adult stem cells are multipotent, which means that they can differentiate into several types of specialized cells. Adult stem cells are found in the bone marrow, hair follicles, while small groups of stem cells are also located in the brain, heart and skeletal muscles.
Result
2 of 2
a. totipotent
Exercise 20
Result
1 of 1
The blastocyst represents a stadium of the intrauterine baby development.
The $text{textcolor{#c34632}{zygote}}$ is formed when the oocyte gets fertilized by a sperm cell. This cell divides and enters the stages of $text{textcolor{#c34632}{morula}}$ and blastocyst.
The $text{textcolor{#c34632}{blastocyst}}$ has an inner and outer cell layer. The blastocyst attaches to the endometrium of a uterus in a process called implantation. At this point, the blastocyst becomes a $text{textcolor{#c34632}{embryo}}$. The outer cell layer will be included in forming the placenta. The cells of the inner layer are pluripotent and they will differentiate into specialized cells that make an embryo.
An embryo becomes a $text{textcolor{#c34632}{fetus}}$, after 8 weeks of conception, or about 10 weeks of gestation.
The $text{textcolor{#c34632}{zygote}}$ is formed when the oocyte gets fertilized by a sperm cell. This cell divides and enters the stages of $text{textcolor{#c34632}{morula}}$ and blastocyst.
The $text{textcolor{#c34632}{blastocyst}}$ has an inner and outer cell layer. The blastocyst attaches to the endometrium of a uterus in a process called implantation. At this point, the blastocyst becomes a $text{textcolor{#c34632}{embryo}}$. The outer cell layer will be included in forming the placenta. The cells of the inner layer are pluripotent and they will differentiate into specialized cells that make an embryo.
An embryo becomes a $text{textcolor{#c34632}{fetus}}$, after 8 weeks of conception, or about 10 weeks of gestation.
Exercise 22
Result
1 of 1
Stem cell research was at first done on the embryonic stem cells that were extracted from the embryo, but the procedure led to its destruction. The ethical concerns were controversal. One group found unethical to destruct a living creature, while others thought that the potential results may lead to finding a cure for many illnesses which would save lives, thus, the methods in research shouldn’t have limitations.
The progress in technology could be in harmful extraction of the stem cells from the living embryo.
The other possibility is in inducing adult somatic cells to become pluripotent. These cells are known as induced pluripotent stem cells or shortly iPS cells. The scientists are now able to make specific conditions for the adult cells in which they start the process of reprograming themselves into embryonic stem cells.
The progress in technology could be in harmful extraction of the stem cells from the living embryo.
The other possibility is in inducing adult somatic cells to become pluripotent. These cells are known as induced pluripotent stem cells or shortly iPS cells. The scientists are now able to make specific conditions for the adult cells in which they start the process of reprograming themselves into embryonic stem cells.
Exercise 23
Result
1 of 1
First, we must calculate the surface areas and the volumes for these two figures.
Figure 1:
A = 6 * 9 * 9
A = 486
V = 9 * 9 * 9
V = 729
Ratio of surface area to volume is 486/729, or 1:1.5.
Figure 2:
A = 4 * 36 * 6 + 2 * 6 * 6
A = 936
V = 36 * 6 * 6
V = 1296
Ratio of surface area to volume is 936/1296, or 1:1.4.
The larger the cell is, there are more requirements on its DNA molecule. The need for nutrients is larger as well as the production of waste products, compared to the smaller cells. Since transport of these substances is done through the cell membrane, we describe a ratio of surface area to volume. Nature has solved this problem, larger cells have also a larger surface of the cell membrane, and vice verca. Therefore, the paramecia, which is a large organism, has a flattened structure so the ratio of surface area to volume is not disrupted.
Figure 1:
A = 6 * 9 * 9
A = 486
V = 9 * 9 * 9
V = 729
Ratio of surface area to volume is 486/729, or 1:1.5.
Figure 2:
A = 4 * 36 * 6 + 2 * 6 * 6
A = 936
V = 36 * 6 * 6
V = 1296
Ratio of surface area to volume is 936/1296, or 1:1.4.
The larger the cell is, there are more requirements on its DNA molecule. The need for nutrients is larger as well as the production of waste products, compared to the smaller cells. Since transport of these substances is done through the cell membrane, we describe a ratio of surface area to volume. Nature has solved this problem, larger cells have also a larger surface of the cell membrane, and vice verca. Therefore, the paramecia, which is a large organism, has a flattened structure so the ratio of surface area to volume is not disrupted.
Exercise 24
Result
1 of 1
The apoptosis is programmed cell death. If a cell is damaged but doesn’t enter the process of apoptosis, there is a certain chance to develop into the cancer cell. Our immune system will recognize these cells and it will trigger the external pathway of apoptosis. However, some of these cells manage to survive and develop cancer. Cancer is a disease that is characterized by abnormal cell growth and division. Cancer cells have the mutation which affects proliferation and programmed cell death.
Exercise 25
Result
1 of 1
The answer to this question is – the organisms that reproduce sexually.
In asexual reproduction, there is only one parent and the offspring is their clone, which may not be able to survive a change in the environment.
In sexual reproduction, two parents pass their genetic material to the offspring. This method is more complex, but it creates offspring that is genetically distinct. That is the main advantage of sexual, over asexual reproduction, which might help the population to persist through the environmental changes.
In asexual reproduction, there is only one parent and the offspring is their clone, which may not be able to survive a change in the environment.
In sexual reproduction, two parents pass their genetic material to the offspring. This method is more complex, but it creates offspring that is genetically distinct. That is the main advantage of sexual, over asexual reproduction, which might help the population to persist through the environmental changes.
Exercise 26
Step 1
1 of 2
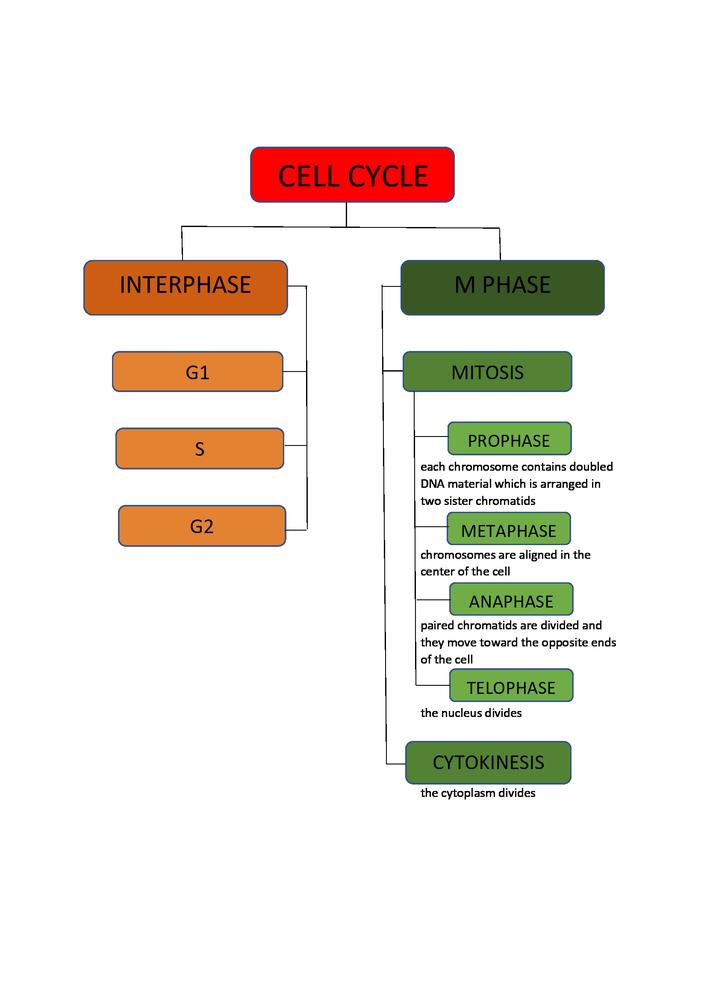
Result
2 of 2
Please click to see the diagram.
Exercise 27
Result
1 of 1
DNA molecule in prokaryotes is usually single and circular, while eukaryotes have up to one thousand more genetic material in their nuclei. Replication process begins in one spot in prokaryotes, while a number of spots can be even several hundred in the DNA of eukaryotes. In both cases, replication is done in two directions. In eukaryotic cells, DNA molecule is wrapped around histones and forms nucleosomes. These structures slow down DNA polymerase, which moves about 50 times slower than in prokaryotes.
Exercise 28
Result
1 of 1
a. The picture shows metaphase of the mitotic division. In this stage, the chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell. Fibers of the mitotic spindle are attached to the centromeres of chromosomes.
Since the centrioles are present, we can conclude that this is a eukaryotic cell.
b. Mitosis consists of four phases (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) after which the cell goes through cytokinesis. In prophase, each chromosome contains doubled DNA material which is arranged in two sister chromatids. Therefore, at this phase the chromosome number is diploid, but the number of chromatids is doubled. In metaphase, chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell. During anaphase, paired chromatids are divided and they move toward the opposite ends of the cell. Each of the two daughter cells has the same number of chromosomes, but one half of the number of chromatids as the parental cell. In telophase and cytokinesis, this cell divides into two cells. The one diploid cell is divided into two diploid cells.
Since the centrioles are present, we can conclude that this is a eukaryotic cell.
b. Mitosis consists of four phases (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) after which the cell goes through cytokinesis. In prophase, each chromosome contains doubled DNA material which is arranged in two sister chromatids. Therefore, at this phase the chromosome number is diploid, but the number of chromatids is doubled. In metaphase, chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell. During anaphase, paired chromatids are divided and they move toward the opposite ends of the cell. Each of the two daughter cells has the same number of chromosomes, but one half of the number of chromatids as the parental cell. In telophase and cytokinesis, this cell divides into two cells. The one diploid cell is divided into two diploid cells.
Exercise 29
Step 1
1 of 2
The cell cycle is a sequence of events that a cell goes through as it grows and divides. The cell cycle of eukaryotic organisms consists of interphase (G1, S, and G2) and the cell division. The G1 phase represents the cell growth, while the DNA replication occurs in the S phase. In the G2 phase, the cell prepares itself for the process of division.
Mitosis consists of four phases (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) after which the cell goes through cytokinesis. In prophase, each chromosome contains doubled DNA material which is arranged in two sister chromatids. In metaphase, chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell. During anaphase, paired chromatids are divided and they move toward the opposite ends of the cell. In telophase and cytokinesis, this cell divides into two cells.
If there are some cells in cell culture that have multiple nuclei, we can presume that these cells have entered mitosis, but that they didn’t go through the telophase and cytokinesis.
Mitosis consists of four phases (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) after which the cell goes through cytokinesis. In prophase, each chromosome contains doubled DNA material which is arranged in two sister chromatids. In metaphase, chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell. During anaphase, paired chromatids are divided and they move toward the opposite ends of the cell. In telophase and cytokinesis, this cell divides into two cells.
If there are some cells in cell culture that have multiple nuclei, we can presume that these cells have entered mitosis, but that they didn’t go through the telophase and cytokinesis.
Result
2 of 2
The cell cycle is a sequence of events that a cell goes through as it grows and divides. The cell cycle of eukaryotic organisms consists of interphase (G1, S, and G2) and the cell division. The G1 phase represents the cell growth, while the DNA replication occurs in the S phase. In the G2 phase, the cell prepares itself for the process of division.
In prophase, each chromosome contains doubled DNA material which is arranged in two sister chromatids. In metaphase, chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell. During anaphase, paired chromatids are divided and they move toward the opposite ends of the cell. In telophase and cytokinesis, this cell divides into two cells.
If there are some cells in cell culture that have multiple nuclei, we can presume that these cells have entered mitosis, but that they didn’t go through the telophase and cytokinesis.
In prophase, each chromosome contains doubled DNA material which is arranged in two sister chromatids. In metaphase, chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell. During anaphase, paired chromatids are divided and they move toward the opposite ends of the cell. In telophase and cytokinesis, this cell divides into two cells.
If there are some cells in cell culture that have multiple nuclei, we can presume that these cells have entered mitosis, but that they didn’t go through the telophase and cytokinesis.
Exercise 31
Result
1 of 1
The ability of the peripheral nerves to undergo mitosis is very important in the healing of the damaged nerve tissue. It takes several months to restore a peripheral nerve cell. However, this process is seldom, which practicaly means that nerve tissue damage won’t fully recover.
Exercise 32
Result
1 of 1
If a cell would grow uncontrolled, at some point its organelles wouldn’t be able to fulfill its needs for survival. The larger a cell becomes, there are more requirements on its DNA molecule. The need for nutrients increases as well as the production of waste products, which causes problems in transporting these substances across the cell membrane. Therefore, at some point, the cell must divide.
The cell is often compared to a factory in order to understand better its function and structure. If organelles are employees, they will have the trouble to complete the job in the large factory, compared with the smaller one. The cell membrane regulates what enters and what molecules leave the cell which is like the shipping/receiving department in the factory model. If this section is overload, the workers won’t be able to accept nor export the packages in time. Ribosomes, endoplasmatic reticulum, and the Golgi apparatus are included in the process of making proteins. They act like employes in the assembly line and the ones in the sorting department. In a large factory, they will make more products than in a smaller factory, but not enough for the factory to work properly. We can compare lysosomes with the maintenance workers, who will not be able to clean up.
The cell is often compared to a factory in order to understand better its function and structure. If organelles are employees, they will have the trouble to complete the job in the large factory, compared with the smaller one. The cell membrane regulates what enters and what molecules leave the cell which is like the shipping/receiving department in the factory model. If this section is overload, the workers won’t be able to accept nor export the packages in time. Ribosomes, endoplasmatic reticulum, and the Golgi apparatus are included in the process of making proteins. They act like employes in the assembly line and the ones in the sorting department. In a large factory, they will make more products than in a smaller factory, but not enough for the factory to work properly. We can compare lysosomes with the maintenance workers, who will not be able to clean up.
Exercise 33
Result
1 of 1
Adult stem cells are multipotent, which means that they can differentiate into several types of specialized cells. Adult stem cells are found in the bone marrow, hair follicles, while small groups of stem cells are also located in the brain, heart and skeletal muscles. The scientists are now able to make stem cells of the skin pluripotent. They are able to produce new heart muscle cells from these pluripotent cells, which will help in the tissue recovery after the heart attack.
Exercise 34
Step 1
1 of 2
As we can conclude from the table, as the temperature decreases, the length of the cell cycle in onion cells takes longer.
Result
2 of 2
b. more that 54.6 hours
Exercise 35
Step 1
1 of 2
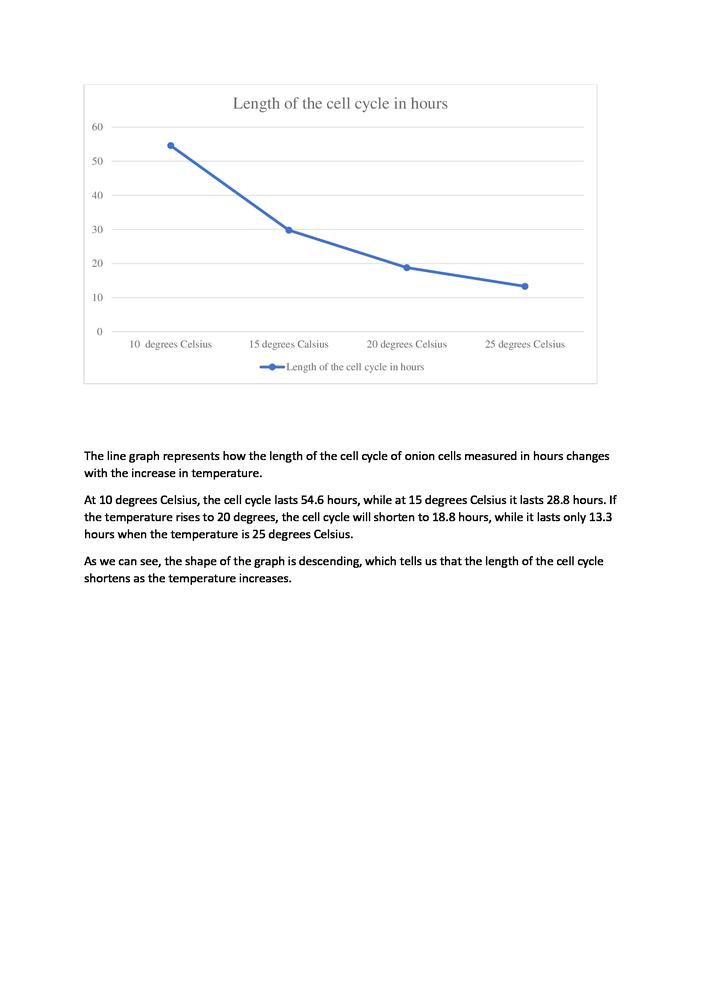
Result
2 of 2
Please click to see the answer.
Exercise 36
Result
1 of 1
We can conclude from the table that the length of the cell cycle in onion cells takes longer as the temperature decreases.
Exercise 37
Result
1 of 1
The cell cycle is a sequence of events that a cell goes through as it grows and divides. The cell cycle of eukaryotic organisms consists of following phases – G1, S, G2, and the cell division. The first phase represents the cell growth, while the DNA replication occurs in the S phase. In the G2 phase, the cell prepares itself for the process of division.
The diagram that represents the cell cycle is circular because the process is continuous. After the division of the parental cell, two daughter cells enter the interphase. The interphase lasts much longer than the cell division, which is shown in the picture.
The diagram that represents the cell cycle is circular because the process is continuous. After the division of the parental cell, two daughter cells enter the interphase. The interphase lasts much longer than the cell division, which is shown in the picture.
Exercise 38
Result
1 of 1
Mitosis consists of the following phases:
1. prophase – each chromosome contains doubled DNA material which is arranged in two sister chromatids
2. metaphase – chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell 3. anaphase – paired chromatids are divided and they move toward the opposite ends of the cell
4. telophase – the nucleus divides
If we want to revise the diagram that represents the cell cycle, the M phase should consist of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis instead of mitosis and cytokinesis.
1. prophase – each chromosome contains doubled DNA material which is arranged in two sister chromatids
2. metaphase – chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell 3. anaphase – paired chromatids are divided and they move toward the opposite ends of the cell
4. telophase – the nucleus divides
If we want to revise the diagram that represents the cell cycle, the M phase should consist of prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis instead of mitosis and cytokinesis.
Exercise 39
Result
1 of 1
At the end of mitosis, one parental cell divides into two daughter cells. After completing the second cell cycle, two cells will give 8, while at the end of the third cycle these 8 cells will divide into 16 daughter cells. Since each of these cells has a diploid number of chromosomes in its nucleus, the total number of chromosomes will be 768 (16 * 48).
Exercise 40
Result
1 of 1
If a cell would grow uncontrolled, at some point its organelles wouldn’t be able to fulfill its needs for survival. The larger a cell becomes, there are more requirements on its DNA molecule. The need for nutrients increases as well as the production of waste products, which causes problems in transporting these substances across the cell membrane. Therefore, at some point, the cell must divide.
The cell cycle is a sequence of events that a cell goes through as it grows and divides. The cell cycle of eukaryotic organisms consists of interphase (G1, S, and G2) and the cell division (mitosis and cytokinesis). The G1 phase represents the cell growth, while the DNA replication occurs in the S phase. In the G2 phase, the cell prepares itself for the process of cell division.
Mitosis consists of four phases (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) after which the cell goes through cytokinesis. In prophase, each chromosome contains doubled DNA material which is arranged in two sister chromatids. Therefore, at this phase the chromosome number is diploid, but the number of chromatids is doubled. In metaphase, chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell. During anaphase, paired chromatids are divided and they move toward the opposite ends of the cell. Each of the two daughter cells has the same number of chromosomes, but one half of the number of chromatids as the parental cell. In telophase and cytokinesis, this cell divides into two cells. The one diploid cell is divided into two diploid cells.
The cell cycle is a sequence of events that a cell goes through as it grows and divides. The cell cycle of eukaryotic organisms consists of interphase (G1, S, and G2) and the cell division (mitosis and cytokinesis). The G1 phase represents the cell growth, while the DNA replication occurs in the S phase. In the G2 phase, the cell prepares itself for the process of cell division.
Mitosis consists of four phases (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) after which the cell goes through cytokinesis. In prophase, each chromosome contains doubled DNA material which is arranged in two sister chromatids. Therefore, at this phase the chromosome number is diploid, but the number of chromatids is doubled. In metaphase, chromosomes are aligned in the center of the cell. During anaphase, paired chromatids are divided and they move toward the opposite ends of the cell. Each of the two daughter cells has the same number of chromosomes, but one half of the number of chromatids as the parental cell. In telophase and cytokinesis, this cell divides into two cells. The one diploid cell is divided into two diploid cells.
Exercise 42
Result
1 of 1
Cell differentiation is the process in which specialized cells are formed from totipotent cells. Totipotent cells are present in the zygote and they have the ability to develop into any type of cells. They can even differentiate to extra-embryonic membranes and placenta.
Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent, which means that they have the ability to develop into any cell type in the body.
However, adult stem cells are multipotent, which means that they can differentiate into several types of specialized cells. Adult stem cells are found in the bone marrow, hair follicles, while small groups of stem cells are also located in the brain, heart and skeletal muscles.
Embryonic stem cells are pluripotent, which means that they have the ability to develop into any cell type in the body.
However, adult stem cells are multipotent, which means that they can differentiate into several types of specialized cells. Adult stem cells are found in the bone marrow, hair follicles, while small groups of stem cells are also located in the brain, heart and skeletal muscles.
Exercise 43
Result
1 of 1
The cell cycle is a sequence of events that a cell goes through as it grows and divides. The cell cycle of eukaryotic organisms consists of interphase (G1, S, and G2) and the cell division. The G1 phase represents the cell growth, while the DNA replication occurs in the S phase. In the G2 phase, the cell prepares itself for the process of division. After the G2 phase, the cell enters process of division.
Mitosis consists of four phases (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) after which the cell goes through cytokinesis.
The headings in the lecture are colored green, while important terms are bolded and marked yellow. This helps in learning about the cell cycle because it makes us easy to understand and remember its phases.
Mitosis consists of four phases (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) after which the cell goes through cytokinesis.
The headings in the lecture are colored green, while important terms are bolded and marked yellow. This helps in learning about the cell cycle because it makes us easy to understand and remember its phases.
unlock

