
All Solutions
Page 196: Assessment
On the other hand, the term niche is defined as the role of an organism in the ecosystem. It can be compared to a person’s occupation. In an organism’s habitat, abiotic factors, biotic factors, and food web are all included in determining the role of a species in the ecosystem.
B is incorrect because climax species refer to the species that remain stable in a habitat that is undisturbed.
C is incorrect. Primary producers or autotrophs harness energy to perform either photosynthesis or chemosynthesis in order to make their own food.
D is correct. The first species to occupy a barren area that has no existing community due to volcanic explosions and retreating glaciers are called pioneer species.
On the other hand, if an area contains a disturbed or damaged habitat that was caused by a natural disturbance or human activities, a secondary succession will take place. Examples of this succession occur in a forest cleared by a fire, and a wheat field that was destroyed by a hurricane. Oftentimes, once the plant and animal life in this area is restored, a climax community is formed.
1. Primary Succession: Primary succession refers to the process of taking over a barren or undeveloped land that was exposed to volcanic explosions and retreating glaciers. This succession is similar to a situation when a person buys an empty lot.
2. Secondary Succession: This succession refers to the process of taking over a land where the residues from the previous ecosystem are still seen. This succession is similar to a situation when a person buys an old house.
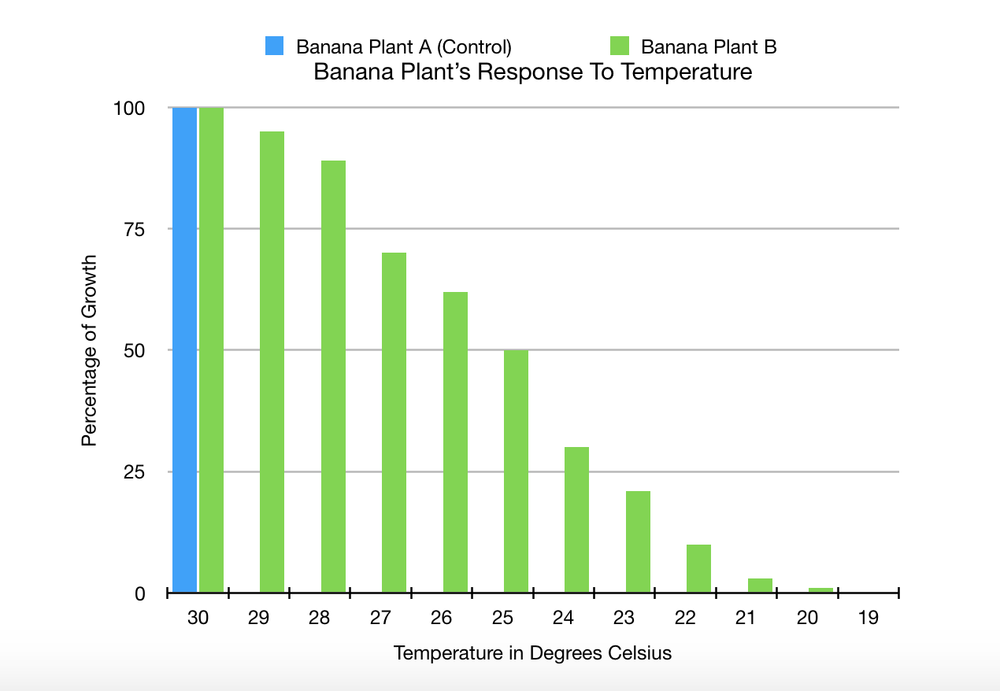
1. Observe the peanut plant for 10 days. Does the peanut plant, along with the presence of the bacteria, wither after a few days?
2. Check the appearance and the color of the leaves. Does the peanut plant, along with the presence of the bacteria, show signs of healthiness?
3. Check the soil condition including the nutrient levels in it.
The peanut plant contains nitrogen-fixing rhizobium bacteria in its roots, which help convert nitrogen gas into ammonia. The bacteria allows the plant to absorb nitrogen from the soil and reduce their dependence to nitrogen-rich fertilizers. The symbiosis between the peanut plant and the rhizobium bacteria indicates a mutualistic relationship.
As a solution, farmers should refrain from using pesticides. Instead, they should employ alternative non-toxic methods such as crop rotation. In this way, the infestation of pests would be reduced. In addition, planting trap crops are helpful in attracting the pests so that they would not infest the valuable crops.
One particular example of a wetland is a salt marsh. It houses a wide range of species such as herbs, grasses, shrubs, fishes, amphibians, mammals, and birds. It is also the shelter of migratory birds when they feed, breed, and nest during their breeding cycles. The interaction between the plant and animal species in this ecosystem allows it to deliver nutrients to its surrounding marine environment, and build climate resilience and coastal protection.
On the other hand, zebras are more active during the day. Their diet consists of a variety of grasses. Unlike wildebeests, zebras can consume shrubs, herbs, twigs and tree barks when the supplies of green grasses are low. They are usually seen in the open woodlands of Africa. They are also a reliable food source of lions, leopards, wild dogs, hyenas, cheetahs, and crocodiles.
In addition, both species have the same predators. If predators only consume the one type of species, their population would decline and there is a possibility of them getting extinct. Therefore, it makes sense if predators have different food sources in the grassy plains and the open woodlands.
On the other hand, zebras consume a variety of grasses, herbs, and shrubs, including twigs and tree barks. This is the reason why they are likely seen in the open woodlands.
The predators of zebras and wildebeests also live in the same habitat. This makes sense because they ensure that the food sources of those herbivores do not diminish completely. Overall, their ecological roles are important in maintaining the health of their ecosystem.
a. Hunting – The demand for wildlife products continue to lessen the population of most animal and plant species. Hunting has caused endangerment of wild animals, and in worst cases, the extinction of species.
b. Altered habitats – This causes the habitat fragmentation. Habitat fragmentation means breaking or dividing the ecosystem into several pieces due to the developments happening in the environment.
c. Invasive species – These are the species that are introduced into a new environment in which their population can grow very quickly. This event causes the native species to be out-competed by the new species.
e. Pollution – It causes disruption in ecosystems and may eventually lead to death in most organisms and life forms. This factor also contributes to global warming and climate change.
Biodiversity can be recovered by eradicating the cause of the disappearance of plant and animal species in a particular area. Prohibiting the hunting of wild animals and illegal logging, restoring wetlands, planting more trees and plants and reducing the use of chemicals and plastics are some of the things that we can do to promote the recovery of biodiversity. Once the conditions of habitats are restored, reintroducing the plant or animal species into areas from which they are wiped out can be done.
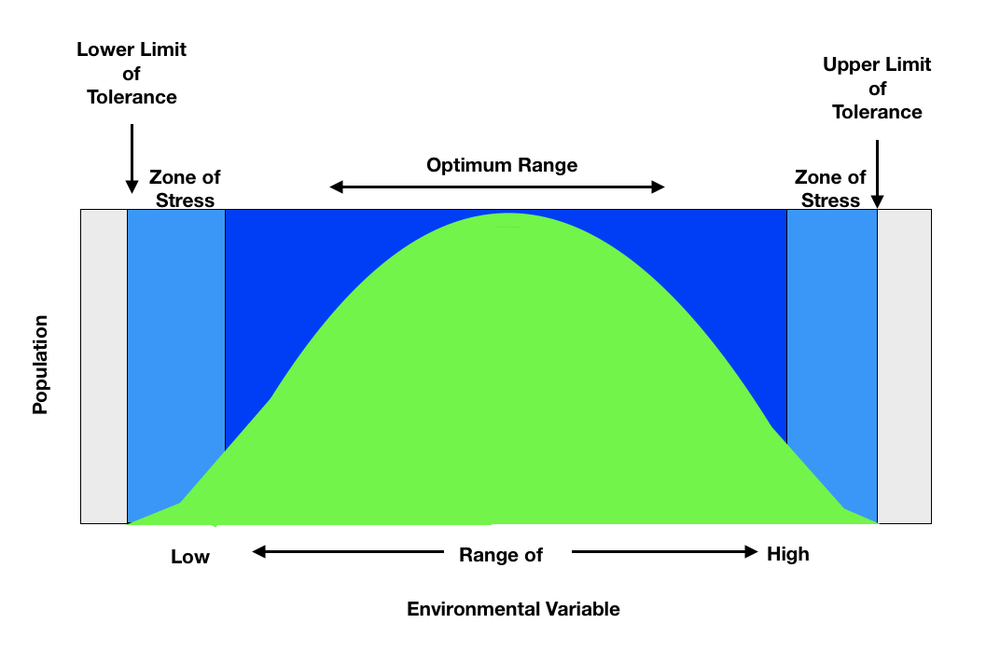
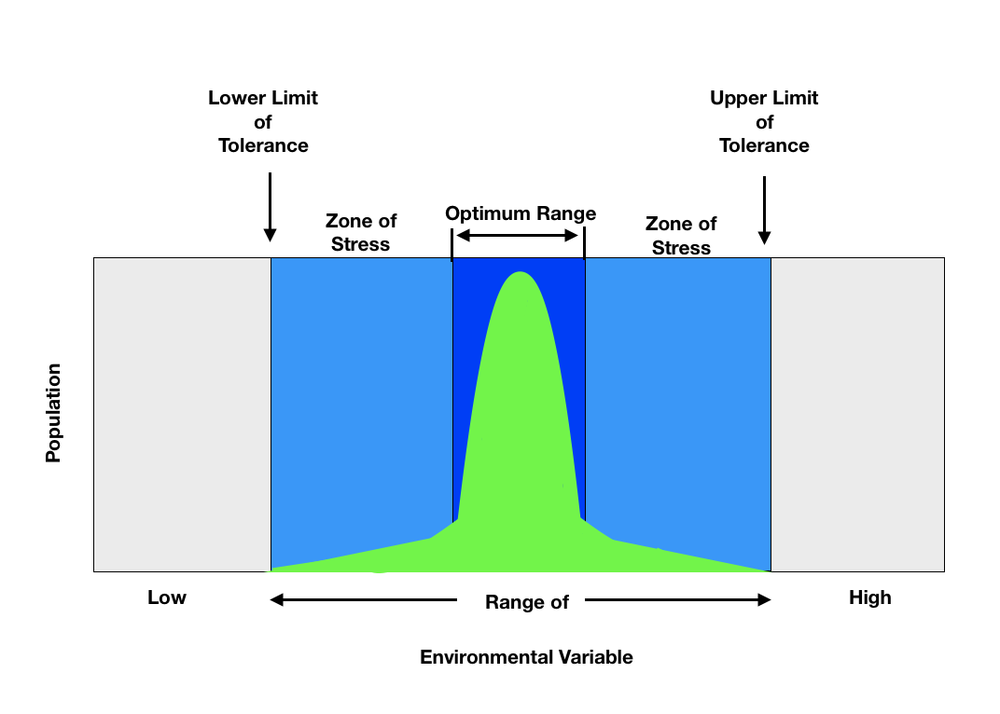
Eventually, the mosses cause the rocks to break and organic matter slowly accumulates. After this event, mosses are replaced by living plants like grasses. When the soil condition starts to normalize, a healthy plant and soil life will happen. In this stage, shrubs and trees will begin to grow. After several years, the softwood trees mature into hardwood trees. The ecosystem is likely to remain stable until a natural disturbance takes place.
1. Observe the feeding behavior of the bird. What does the pheasant eat? How do they obtain their food?
2. Observe the physical structure of the bird. What is the most distinguishable feature of the bird?
3. Observe the environment where the pheasants live. Do they live with other bird species?
4. Which organism feeds on pheasants?
Let us take the biodiversity found in the wetlands as an example. Wetlands are considered as productive ecosystems due to its numerous benefits that include supporting diverse life-forms, preventing floods, improving the water quality by filtering waste and pollutants, and providing a source of livelihood for people that live near the area. Without the different life-forms that dwell in the wetlands, its ecosystem would not work efficiently. Without the microbes and plants, nutrient cycling and filtrating of waste and pollutants would not occur. If there are no animals, there would be no balance in the food web and in the entire ecosystem. Without biodiversity, the towns near the coast would have no access to clean water and food. They would have no protection against flooding and coastal erosion.

