
All Solutions
Page 138: Assessment
B: A bear is an omnivore. Omnivores eat plants and other animals.
C: A cow is a herbivore. Herbivores are animals that feed on plants.
D: A snail is an omnivore. Aside from plants and other animals, other omnivores can also feed on other food sources, such as algae and fungi.
E: An owl is a carnivore. Carnivores feed on flesh.
F: A human is an omnivore. Omnivores eat plants and other animals.
B: omnivore
C: herbivore
D: omnivore
E: carnivore
F: omnivore
Therefore, C is the correct answer.
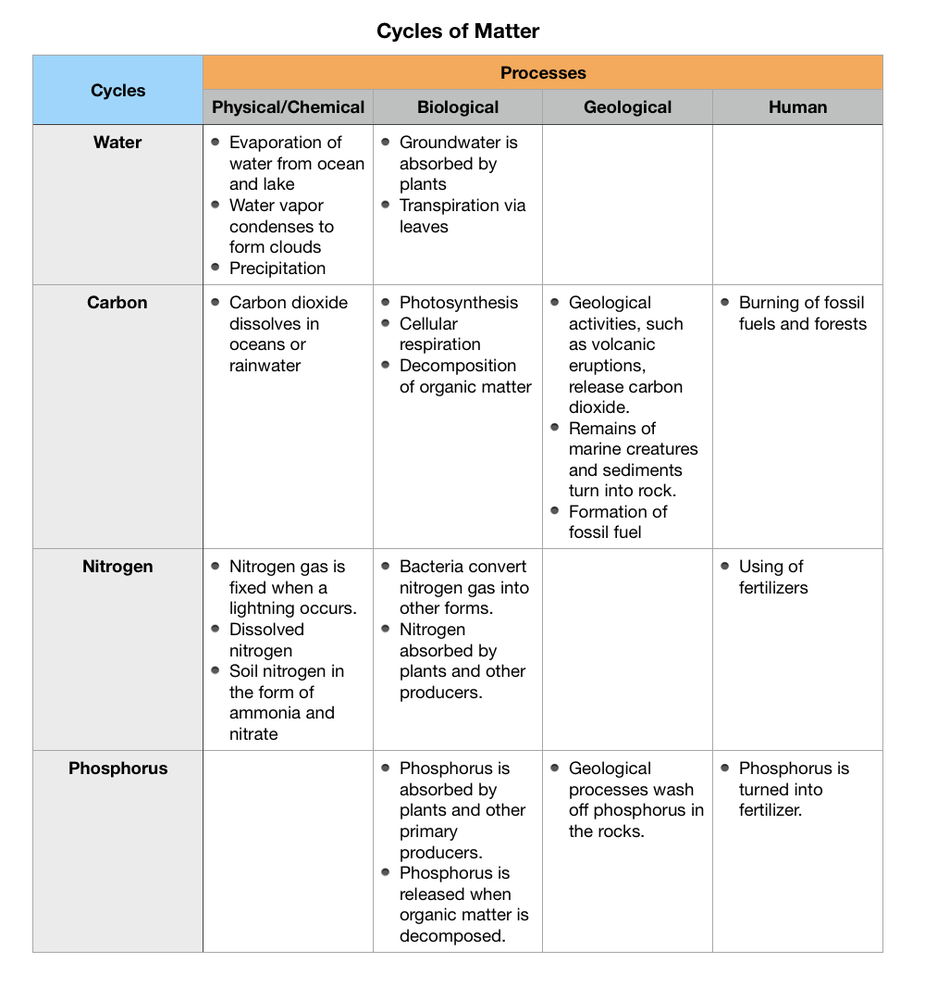
a. Carbon is present in the atmosphere in the form of carbon dioxide gas.
b. A supply of carbon is present in a decaying matter and waste.
c. There is an amount of carbon in the organic matter in soils.
d. Carbon is present in fossil fuels in the form of coal and oil that are found in rock layers within the Earth’s crust.
e. Carbon is present in the oceans in the form of dissolved carbon dioxide and calcium carbonate in the shells of marine organisms.
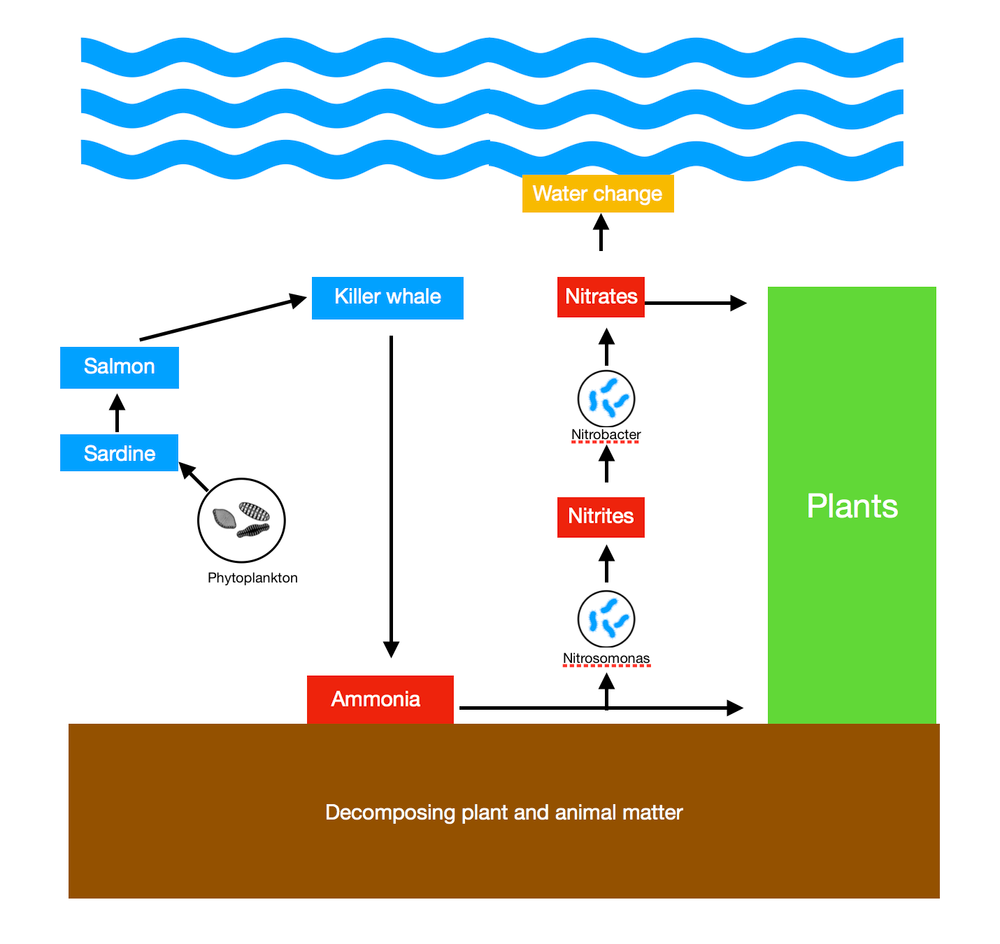
a. What condition causes the green algae to grow rapidly?
b. What is the primary source of nitrogen and phosphorus in the water?
c. Is there a farm, factory, or sewage near the pond?
d. How fast can the green algae grow?
e. Is the excessive algae growth dangerous for aquatic animals?
f. How do you get rid of the green algae?
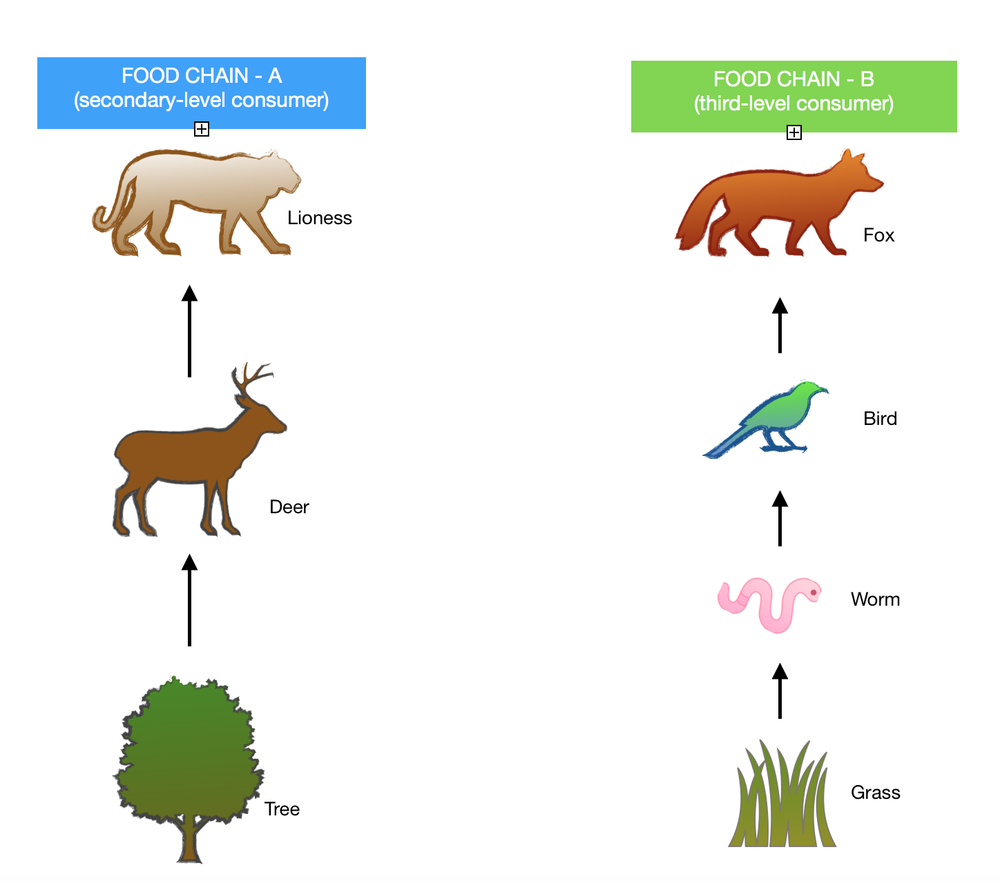
b. Insects, such as flies and beetles, slugs, and snails are the decomposers that can be added to the food web. They are the organisms that consume the energy from waste and remains of plants and animals.
c. Please see the diagram below.
d. If the primary producers on both food chains have 100% chemical energy, second-level consumers would get 1% chemical energy. On the other hand, third-level consumers get 0.1% energy.

1. The water sample contains a high concentration of phosphorus and nitrogen.
2. There is an algal bloom in the stream.
3. The level of dissolved oxygen in the water is very low, which resulted in the death of many fishes due to hypoxia.
The carbon cycle occurs in the atmosphere and in the hydrosphere. Terrestrial producers use carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and aquatic producers get carbon dioxide from water to generate chemical energy (glucose) and oxygen, which are both needed by consumers to sustain life. In turn, once consumers eat the plants, they get the stored energy and return carbon dioxide in the atmosphere through respiration. Eventually, when plants and animals die, decomposers consume the organic matter and release carbon dioxide during respiration.
Decomposition, pressure, and heat allow the compaction of the dead matter and return carbon as underground deposits or fossil fuels. When fossil fuels are burned to generate energy, carbon dioxide is released in the atmosphere.
Decomposition, pressure, and heat allow the compaction of the dead matter and return carbon as underground deposits or fossil fuels. When fossil fuels are burned to generate energy, carbon dioxide is released in the atmosphere.
On the other hand, human activities that affect the cycles involve mining, burning of fossil fuels, burning forests, clearing land for building and farming, and using fertilizers. These activities, which lie in the outermost ring of the model, are the human causes of global change because their interference with the natural processes causes the entire global systems to become unbalanced.
Answer: Aquaponic farming is a form of agriculture that integrates and combines the raising of fishes (aquaculture) and the soil-less growing of plants (hydroponics). In this integrated system, the excretion of the fishes is broken down by nitrifying bacteria and utilized by the plants as nutrients. Once the water is filtered by the plants, it goes back to the aquaculture system. This mechanism saves a lot of water since it gets recycled or circulated in the whole system.
This type of farming is not only considered economical and productive, but it is environment-friendly. It does not employ the use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides, which are the chemicals that are known to harm or disrupt the ecosystem. Therefore, it prevents the effects of fertilizer runoff, which occurs from traditional farming.
First, the plankton or the tiny drifting producers, harness the sun’s energy to produce chemical energy through photosynthesis. In turn, the sardine gets this stored energy when they feed on the plankton. Then, when the salmon feeds on the sardine, the energy gets transferred to the second-level consumer. Once the salmon gets caught for human consumption, the stored energy in the salmon is transferred to the humans (third-level consumers).
On the other hand, the lemon tree and the broccoli plant are both primary producers. They harness solar energy during photosynthesis to produce chemical energy. When the lemon and broccoli are consumed by a human, the stored chemical energy is transferred. In turn, the cells in the human body use this energy to carry out their function and other life processes.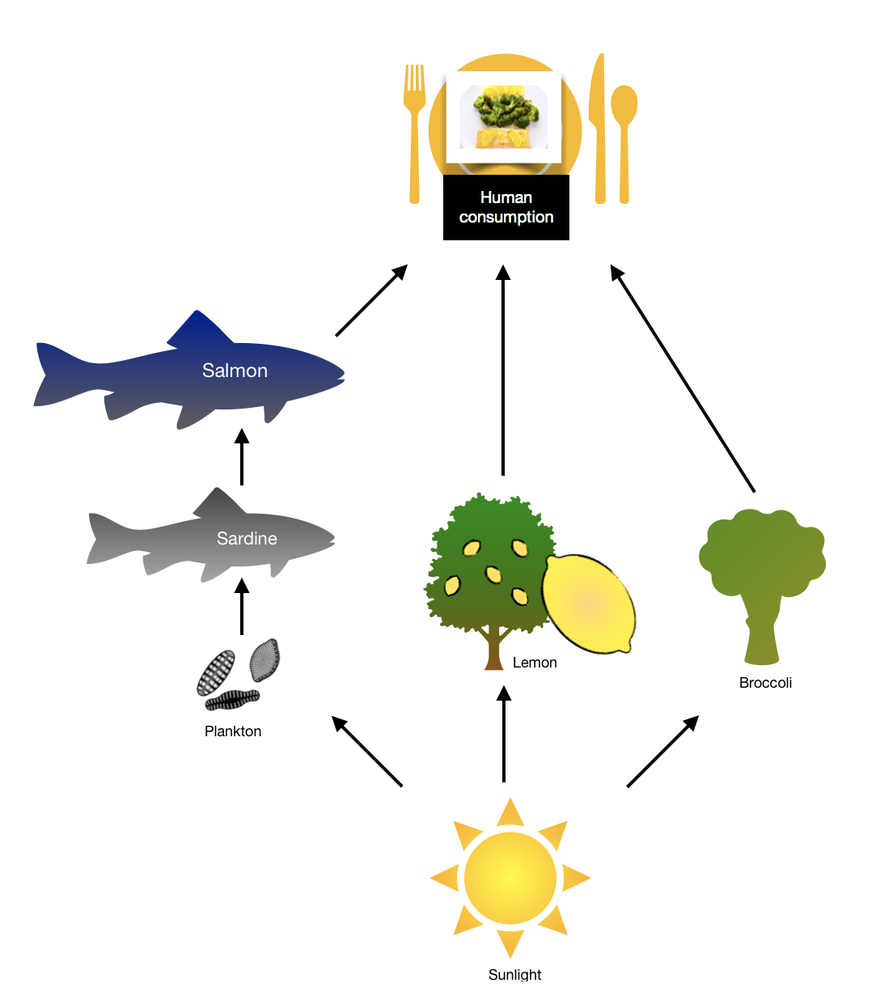
For example, the plants that conduct photosynthesis harness sunlight and use carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and water to produce chemical energy. In turn, they release oxygen, which is a gas needed by consumers for respiration. Once the consumers feed on the plants, they get to use the stored chemical energy to perform or carry out their life processes. In turn, they release carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, which is again taken by the plants for photosynthesis.

