
All Solutions
Page 108: Assessment
a. Observing/Observation – This is the process of obtaining significant information using the senses. It helps answer questions by simply looking around for evidence.
b. Experimenting/Experimentation – This is the process of testing the hypothesis by setting up a controlled environment in a laboratory.
c. Modeling – This is the process of using models, such as mathematical models, to show how a certain event or phenomenon occurs with the aim to answer questions.
a. All the global systems are identified.
b. The processes that operate within the global systems are explained.
c. The ways the global systems, ecological events, and processes interact with each other are illustrated.
Similarities:
a. Both ecosystems share a wide range of biodiversity and different trophic levels.
b. There is a presence of mutual interdependence of species that belong in these two ecosystems.
Differences:
a. Sunlight is usually available in most terrestrial environments. On the other hand, light doesn’t reach the deepest parts of an aquatic ecosystem.
b. Water is readily available in an aquatic ecosystem, while water supply in a terrestrial ecosystem depends on the amount of rainfall and groundwater.
c. An aquatic ecosystem is less prone to fluctuations in temperature and other variables. Unlike an aquatic ecosystem, a terrestrial ecosystem experiences more changes in the temperature and other factors.
Materials:
a. 12 lettuce seeds
b. 2 identical seedbeds
c. shovel
d. water
e. fume hood
f. aluminum pan
g. 2 plastic bags
h. damp soil
Method:
a. There should be 6 burned seeds and 6 unburned seeds to be used in this experiment. In this case, put 6 lettuce seeds in an aluminum pan and heat it under the fume hood at 140 degrees Fahrenheit for 15 minutes.
b. Stratify all the seeds at 33 degrees Fahrenheit for 3 weeks to break seed dormancy. To stratify the seeds, put damp soil and all the unburned seeds in a plastic bag. Label it with Seeds A. On the other hand, put the burned seeds and the damp soil in a separate plastic bag. Label it with Seeds B. Store the bags in a place with a cold temperature of about 33 degrees Fahrenheit.
c. Plant the 6 unburned seeds in a seedbed. Label it with Seedbed A.
d. Plant the 6 burned seeds in another bed. Label it with Seedbed B.
e. Expose the seeds to 15 hours of sunlight every day.
f. Using equal amounts of water, the seeds must be watered twice a day until the soil is moist.
g. Check the germination or seed growth each day for 14 days.
h. Determine which set of plants are able to germinate at a faster rate.
For example, plants and animals living in a tundra biome are adapted to survive in a cold environment. Animals go through hibernation during the winters or they are covered with thick fur which can help them withstand the cold weather. Plants in this biome have a stunted growth since the soil is usually frozen most of the time.
On the other hand, plants and animals living in the desert are adapted to an extremely hot and dry environment. Plants in this environment, such as cacti, have spines and thick cuticle which prevent water loss.
Overall, both biotic and abiotic factors are equally important in our ecosystem. Both factors are important when it comes to the complex processes that continuously shape our biosphere. They are both related in terms of the viability of our planet. However, based on the examples given above, abiotic factors become more important because they directly affect how organisms would survive in a particular region.
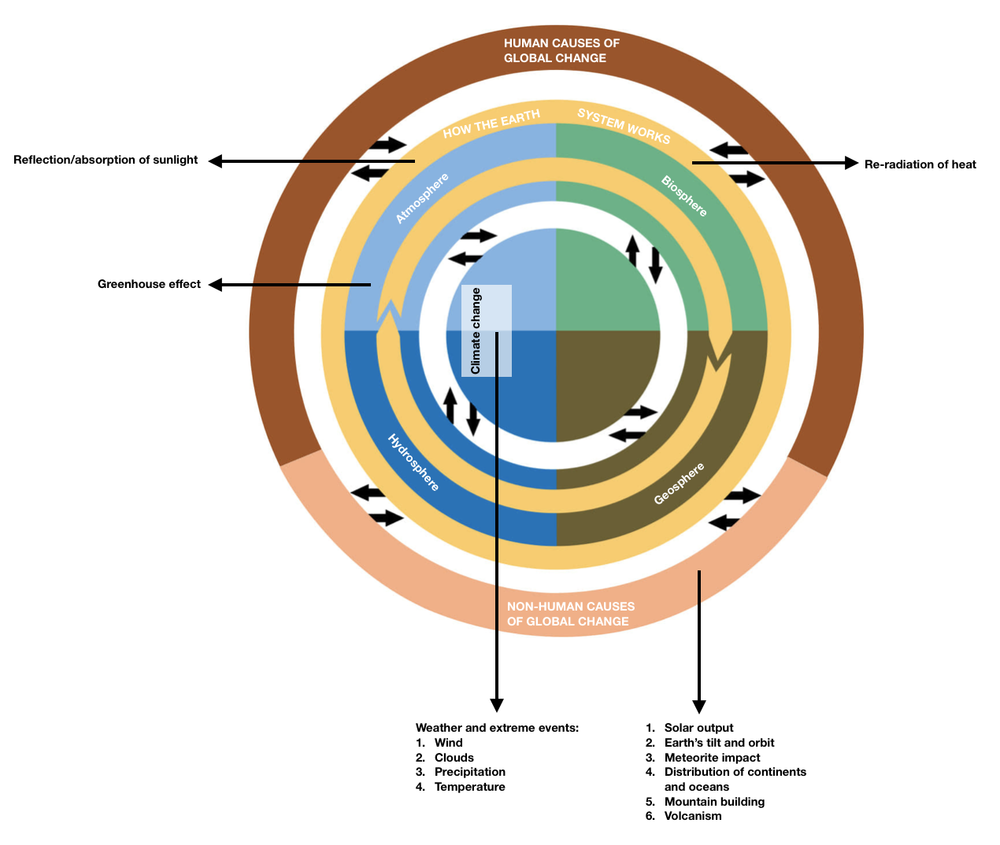
B. Greenhouse effect – This event takes place within the Earth’s atmosphere.
C. Wind, Clouds, Precipitation, Temperature – These icons are involved in the weather/extreme events that are associated with climate change. The atmosphere and the hydrosphere are the Earth systems that are affected by climate change.
D. Solar output, Earth’s tilt and orbit, meteorite impact, distribution of continents and oceans, mountain building, volcanism – These icons are placed under the non-human causes of global change.

Volume = Area $times$ Height
Given:
Area = 100 km$^{2}$
Height = 30 cm
Volume = ?
Before solving, convert 30 cm to km in order to get all the values in the same unit. Therefore, 30 cm is equivalent to 0.0003 km.
Solve:
Volume = 100 km$^{2}$ $times$ 0.0003 km
Volume = 0.03 km$^{3}$
Therefore, a volume of 0.03 km$^{3}$ was lost.
Because of its extremely cold climate, there is a low biodiversity in this region. Plant and animal species that are able to survive harsh winters can adapt to this kind of environment. Moreover, a frozen soil layer called permafrost exists in this region. This is the reason why the active soil layer in the tundra biome is very thin. It could not support tall trees to grow in this condition. Instead, plants that thrive in this environment have shallow root systems. These plants can carry out photosynthesis under low temperature and low light intensity. Examples of these plants are lichens, mosses, liverworts, grasses, shrubs, and other low growing plants. On the other hand, tundra animals, such as polar bears, wolves, arctic foxes, snowy owls, and reindeers, usually breed during the short summers. During winters, some animals migrate. while the others hibernate during winters. Overall, all the biotic factors, such as plant and animals species, are specifically adapted to the abiotic factors, which include the limited amount of sunlight and cold temperature, that are present in this region.
On the other hand, the ocean’s current is described as the movement of water from one place to another. Currents are mainly driven by the winds. In turn, the current affects the climate of the land that is near the ocean. In general, warm currents from the tropical zone are blown toward the poles, whereas the cold currents from the poles are brought into the equator. For an instance, when the wind blows across warm water currents on a cold region, it brings a mild, rainy weather in the land near the coast. On the other hand, if the wind blows a cold water current into a warm region, it brings a cool, dry weather into the coast. Therefore, the wind and the current are important factors that drive the climate of a region. Other driving factors include the topography, altitude, vegetation, and the land’s nearness to the water.

