is a leak somewhere in the bronchial tree so you want to have good visualization while intubating)
signs of injury in the setting of penetrating neck trauma. What is your next step?
this
> 0.5 -1L/hr from the tube, you need surgical thoracotomy
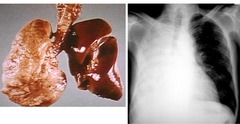
class="flashcard__a_text">cardiac contusion
class="lbl">answer
class="flashcard__a">answer
CXR and ECG are done. Managed appropriately. Stable now, Which additional tests might you consider
pyelopgraphy (it is faster than CT)
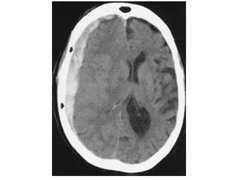
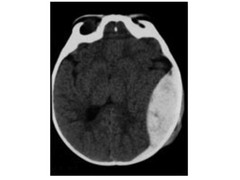
class="flashcard__img">
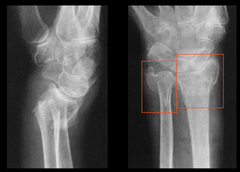
class="single__flashcard">
class="lbl">question
What should be on differential
What should you do if it is negative?
ppx If near vessel --> Dopplers or CT anguo If pt sx (decreased pulses, expanding hematoma, pulsatile bleeding--> go directly to OR!
class="flashcard__a">answer
rehab for burns? What are you trying to prevent?
(which is the saphenous branch of the femoral nerve) and the plantar foot
- John Locke essays
- 9/11 essays
- A Good Teacher essays
- A Healthy Diet essays
- A Modest Proposal essays
- A&P essays
- Academic Achievement essays
- Achievement essays
- Achieving goals essays
- Admission essays
- Advantages And Disadvantages Of Internet essays
- Alcoholic drinks essays
- Ammonia essays
- Analytical essays
- Ancient Olympic Games essays
- APA essays
- Arabian Peninsula essays
- Argument essays
- Argumentative essays
- Art essays
- Atlantic Ocean essays
- Auto-ethnography essays
- Autobiography essays
- Ballad essays
- Batman essays
- Binge Eating essays
- Black Power Movement essays
- Blogger essays
- Body Mass Index essays
- Book I Want a Wife essays
- Boycott essays
- Breastfeeding essays
- Bulimia Nervosa essays
- Business essays
- Business Process essays
- Canterbury essays
- Carbonate essays
- Catalina de Erauso essays
- Cause and Effect essays
- Cesar Chavez essays
- Character Analysis essays
- Chemical Compound essays
- Chemical Element essays
- Chemical Substance essays
- Cherokee essays
- Cherry essays
- Childhood Obesity essays
- Chlorine essays
- Classification essays
- Cognitive Science essays


Unfortunately copying the content is not possible
Tell us your email address and we’ll send this sample there.
By continuing, you agree to our Terms and Conditions.


