CM Cervical Disorders – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion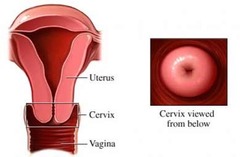
normal cervix

answer
differences in nulliparous and parous (os never completely goes back to smaller diameter)
question
acute cervicititis
answer
brillant redness of cervix redness friable (speculum touches and causes bleeding) tend to be infectious causes
question
chronic cervicitis
answer
clear mucusou/watery discharge granular redness scarring cervical stenosis tend to be non-infectious causes
question
cervicitis due to infection
answer
purulent discharge etiology: gonorrhea chlymydia HPV trichomonas micoplasma genitalian (BV) cytomegalovirus BV
question
noninfectious cervicitis
answer
Mechanical irritation Chemical irritation/allergic response Trauma (intercourse, surgery) Systemic inflammatory disease Radiation
question
cervicitis Sx
answer
spotting discharge pain irritation dysuria is os open or not? complications scarring abnormal bleeding cancer could spread tx underlying cause
question
nabothian cysts - glands that have not completely opened up;' normal physical finding
answer
Dx: colposcope (magnify lens looking at cervix)
question
endocervical polyps usually benign
answer
bleed w/ interDx: ect Dx bx to r/o cancer Tx ring forcep, twist off silver nitrate cauterate for hemostasis removal about 90% curative
question
cervical cancer
answer
asypmtomatic vaccine to 100% prevent it Third most common gyn cancer Leading cause of cancer death in medically underserved countries 75% decrease in incidence due to screening
question
leading cause of cancer death in medically underserved countries
answer
cerivial cancer less in US because of pap smears/screening
question
site most common for cervical cancer
answer
normal metaplastic transformation zone (from columnar to squamous cells)
question
Pap terminology results KNOW MEANING
answer
normal atypical squamous cell of ... ASC-US ASC-H = atypical squamous cell LSIL (low grade) HSIL (high grade; moderate, severe) Cancer
question
histology pap terminology (bx results) insert pic slide 21
answer
CIN 1 Low grade dysplasia 10% progress to CIN 2,3 CIN 2 High grade dysplasia 5% progress to cancer if untreated CIN 3 High grade dysplasia 12-40% progress to cancer if untreated CIS Invasive carcinoma
question
HPV and cervical cancer 80% of women infected with HPV by age 50 Incidence of cervical cancer rises after age 40 Average age of diagnosis of cancer 48 yrs in US
answer
risk factor have intercourse at young age because kertinazaion of transitional zone underdeveloped
question
HPV risk factors
answer
Multiple sexual partners High risk sexual partner Young age (3 live births) Early age at first birth (<20 yr) Younger age at first full-term pregnancy Genetic?
question
cervical cancer development
answer
Oncogenic HPV infection at transformation zone (Squamo-Columnar Junction) Persistence of HPV infection
question
natural history of HPV
answer
skin disease slide 23 normal cervix HPV infection (asymptomatic) persistent/clearance progression/regression pre-cancer (want to rid cells, can't rid virus) cancer Time from initial infection to cancer about 15 years. Transient infections are usually cleared within 6-18 months Greater chance of regressing in younger women
question
role of HPV
answer
More than 100 subtypes of HPV Subtype 6,11 cause warts Most frequent oncogenic types: 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52, 58 Subtypes 16 and 18 are found in >70% of cervical cancers HPV present in 99.7% of all invasive cancers
question
HPV subtypes that cause genital warts
answer
6 11
question
HPV subtypes that cause cervical cancers
answer
16 (squamous cell carcinoma) 18 (adenocarinoma from columnar glandular cells; most common < 35)
question
types of cervical cancer
answer
Squamous cell carcinoma 70-75% Adenocarcinoma 20-25% Adenosquamous carcinoma 3-5% Undifferentiated carcinoma Neuroendocrine carcinoma
question
screening guidelines
answer
start screening age 21 Do not colpo until age 25 (unless HSIL Pap) Do not do HPV testing under age 30 30 yo (after 3 consecutive negative) Pap q 3 years OR Pap + HPV every 5 years Stop screening >65 yo if 3 negative, but if new partner... Immunocompromised or history of cervical dysplasia continue annual screening
question
cervical cancer Sx
answer
asymptomatic (early) abnormal vaginal bleeding vaginal discharge pain systemic symptoms -anemia -weight loss cervical lesion on speculum exam or palpated on bimanual exam
question
cervical cancer Dx
answer
pap test colposcopically guided bx bx anything suspicious endocervical curettage conization of the cervix clinical exam and imaging for staging LEEP= electrocautery conization
question
cervical cancer staging just FYI, no test
answer
I: carcinoma confined to the cervix II: invades beyond the uterus, but not to the pelvic wall or lower third of vagina III: tumor extends to the pelvic wall and/or involves lower third of the vagina and/or causes hydronephrosis IV: carcinoma has extended beyond the true pelvis or involves the mucosa of the bladder or rectum
question
cervical cancer Tx
answer
surgery chemotherapy radiation Preinvasive/Microinvasive LEEP, CKC, simple hysterectomy Early stage (IA2-IIA) Radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy Primary radiation with concurrent chemotherapy Locally advanced (IIB-IVA) Primary radiation with concurrent chemotherapy Metastatic, persistent or recurrent Chemotherapy Palliative radiation Central pelvic recurrence Total pelvic exenteration
question
cervical cancer factors affecting prognosis
answer
Stage Histologic cell type and grade Depth of invasion Lymph node involvement Recurrence
question
cervical cancer prognosis
answer
Untreated/fails to respond to treatment 2 yr 5% Stage IB 5yr 80% IIA,B 5yr 58-63% III 5yr 30% IVA 5yr 16%
question
cervical cancer prevention
answer
HPV vaccine Approved for females (and males) 9-26 yo (insurance won't cover older ones currently) Ideally vaccinate before exposure to HPV (11-12 yrs old...before sexually active) GARDASIL®: Quadrivalent vaccine HPV subtypes: 16, 18 ,6 , 11 (6 and 11 are condyloma) **GARDASIL®9 HPV subtypes: 6, 11, 16, 18, 31, 33, 45, 52, and 58 CERVARIX Bivalent vaccine against HPV subtypes 16,18 Highly immunogenic Some protection against severe disease even in those with prior HPV infection (b/c may not have had all the strains) ~100% time if not exposed ~50% time if exposed not a live vaccine 3 shots over 6 mo period effective in cervical, vulvar, vaginal, rectal HPV cancers



