Kaplan Fundamentals A and B (final) – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Describe an airborne precautions room
answer
private room with monitored negative air pressure with 6 to 12 changes per hour, keep door closed and client in room, can place client with another but only if same organism, place mask on client if being transported
question
Name diseases that would require airborne precautions (4)
answer
measles, varicella, tuberculosis, and shingles until the lesions are crusted over.
question
What does nurse wear into an airborne precautions room?
answer
Use respiratory protection, like a protective mask, that is fit-tested. Do not share with other providers.
question
describe droplet precautions
answer
-used with pathogens transmitted by infectious droplets, involves contact of conjunctiva or mucous membranes of nose and mouth -happens during coughing, sneezing, talking, or during procedures such as suctioning or bronchoscopy
question
Describe droplet precautions room
answer
-private room or cohort with client with same infection but no other infection -maintain spatial separation of 3 feer between infected client and visitors or other clients -door may remain open -place mask on client if being transported
question
Name diseases that would require droplet precautions (4)
answer
streptococcal pharnygitis, pneumonia, meningitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae type B, mumps
question
What does nurse wear into a droplet precautions room?
answer
everything.
question
neutropenic precautions
answer
-used for clients at increased risk for infection, such as immunosuppressed with neutrophil count under 5000
question
interventions for neutropenic precautions
answer
-private scrupulously cleaned -meticulous handwashing and use of personal protective equipment by all -restriction of visitors -no fresh fruit of vegetables -avoid invasive procedures, such as catheterization, unless essential
question
How do you ambulate with a cane?
answer
Cane should be held in hand opposite affected extremity. Advance cane and affected leg, about 4 to 12 inches. To go upstairs, step up with good extremity and then place cane and affected extremity on step. Reverse when going downstairs.
question
cane lenght
answer
should be equal to the distance between the greater trochanter and the floor;
question
straight leg cane
answer
-used to support and balance a patient with decreased leg strength (keep on strong side of the body) -walk placing cane 15-25cm forward, keeping weight on both legs
question
quad cane
answer
-provides most support -used when there is partial or complete leg paralysis or some hemiplegia
question
walkers
answer
-must be waist high -patient must be able to lift the walk unless they have been fitted with wheels or short runners
question
4 point crutch walk
answer
-used when weight-bearing is allowed for both legs -slow, safe -right crutch, left foot, left crutch, right foot
question
2 point crutch walk
answer
-used when weight-bearing is allowed for both legs; less support than 4-point -faster, safe -right crutch and left foot advance together, then left crutch and right foot advance together
question
3 point crutch walk
answer
-used when weight-bearing is allowed on one leg -faster gait, safe -advance weaker leg and both crutches simultaneously, then advance strong leg
question
swing-to-swing thru crutch walk
answer
-used when partial weight-bearing is allowed on both legs; requires coordination -fast gait but requires more strength and balance -advance both crutches then both legs
question
Before ambulation, what should you assess?
answer
Activity tolerance of the patient, strength, mobility status, mental status, degree of personnel and equipment assistance needed. Assess safety of environment and adequacy of clothing, including nonslip shoes.
question
Before ambulation, what should you talk to the patient about?
answer
Inform patient of rationale and specific goals for walking. Tell them to report any dizziness, weakness, or shortness of breath.
question
Describe how to ambulate in progressive stages
answer
First sit on the bed and dangle, then stand to side of bed, then progressively walking. Nurse can use gait belt to support patient. If patient is dizzy or unsteady, return patient to close bed, chair, or gently lower to the floor.
question
Name some ambulatory assistance devices
answer
Gait belt, crutches, walker, cane
question
Purpose of ambulation
answer
Allows for muscle movement and joint flexibility. Improves respiratory and GI function. Rules risk of complications of immobility.
question
Describe how to use a walker from the bed
answer
Set walker in front of seated patient. Have patient stand with assistance as needed. Have patient hold walker's handgrips firmly. Stand slightly behind patient, on one side. Have patient move walker forward 6 to 8 inches and set it down, making sure all feet on the floor. Tell patient to step forward with either foot into the walker, support self. Follow through with other leg. Continue pattern.
question
Describe proper position of crutches
answer
Hold crutches 6 inches in front of and 6 inches to the side of each foot. Should be 1.5 to 2 inches below armpits. Elbows are flexed at a 15 degree angle
question
Purpose of anti embolism stockings
answer
Reduces risk of DVT and pulmonary embolism. Helps prevent phlebitis.
question
how do aniembolism stockings work?
answer
Exert external pressure on lower extremity muscles and superficial leg veins, thus preventing stasis and promoting venous return in lower extremities by maintaining external pressure.
question
When should anti embolism stockings not be worn?
answer
Do not apply if skin lesions or gangrene present.
question
When should anti embolism stockings be put on?
answer
In the morning before patient out of bed
question
Teach patient to recognize possible indicators of DVT or phlebitis, such as:
answer
-redness, tenderness, -pain on dorsiflexion (postiive Homans sign) -calf pain -localized edema of one extremity -possible warm skin over the affected leg -possible fever, chills, and perspiration
question
When patient in on anti embolism stocking, when would they notify provider? What are abnormal symptoms?
answer
skin irritation and breakdown, abnormal color, warm or cool temperature, unusual sensations, swelling, changes in movement
question
Can patient wear anti embolism stockings with nonskid socks?
answer
Yes, but skid resistant socks on patient prior to ambulation
question
Apical pulse is the best site location in which instances?
answer
best pulse site in infants and young children and if patient is taking a medication that affects the heart rate
question
Pulse deficit: how is it calculated?
answer
Compare radial and apical heart rates. Normally are the same. If radial is slower there is a perfusion issue.
question
PMI
answer
point of maximal impulse, the apical pulse, which is where the impulse of the left ventricle is felt more strongly; 5th intercostal space at the mid clavicular line on the left side
question
2 types of aseptic technique
answer
medial asepsis is clean technique and surgical asepsis
question
Describe medical asepsis, or clean technique
answer
Focuses on reducing number of microorganisms and preventing them from spreading
question
Surgical asepsis
answer
Sterile technique and focuses on eliminating the microorganisms from an area; including sterile objects and rules therein; prevents introduction or spread of pathogens from environment to patient
question
Surgical asepsis principles
answer
Sterile object touched by nonsterile is contaminated Only sterile objects on the sterile field Out of range of vision or below waist is contaminated long exposure to air is contaminated in contact with wet ifs contamined
question
Primary cause of falsely elevated reading of blood pressure
answer
Cuff is too narrow
question
How do you get false-high readings with blood pressure cuffs?
answer
Cuff too small, cuff wrapped too loosely, cuff deflated too slowly, ensure going 2 mm Hg
question
Cuffs come in how many standard sizes?
answer
6; ranging from newborn to extra-large adult
question
Normal adult BP values
answer
systolic 90 to 140 and diastolic 60-90
question
If you have trouble hearing the sound as it is low and indistinct, what can you do?
answer
raise patient's arm over her head with cuff intact to cause blood to enter the lower arm. Hold position for 15 seconds before rechecking pressure. Infalte the cuff while arm is elevated. Support arm while it is beign lowered.
question
Nursing proper body mechanics to prevent injury
answer
Bed to proper working height Lower side rail on side of patient contact Bend knees when lifting Assess weight before lifting Determine if assistance needed Hold lifted object close to body Don't twist Push rather than pull Low center of gravity Wide base of support
question
Is informed consent required for bone marrow biopsy?
answer
yes
question
What does bone marrow biopsy examine?
answer
number, size, and shape of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelet precursors in the bone marrow
question
Where are bone marrow biopsy specimens obtained?
answer
iliac crest and sternum
question
Nursing responsibilities with bone marrow biopsy
answer
Cleanse site with alcohol to remove povidone iodine, apply pressure with sterile gauze pad for several minutes to control bleeding, apply STERILE pressure dressing by having patient lie on back, continually assess for bleeding and drainage, give an analgesic as necessary
question
Life threatening complications of bone marrow biopsy
answer
Infection and bleeding
question
What is bone marrow biopsy used to diagnose?
answer
multiple myeloma, all types of leukemia, some lymphomas, some solid tumors
question
What can you do to enhance patient comfort and cooperation before a bone marrow biopsy?
answer
Explain the test: takes 5-10 minutes, taken from iliac crest, get consent, tell which bone will be sampled, small incision, provide a sedative as ordered
question
bone marrow biopsy (other info)
answer
- fever, yellow drainage=osteomyletis; -no sports 48 hours. -Ileac older than 2. 1 year old use tibia. no sternum or scapula.
question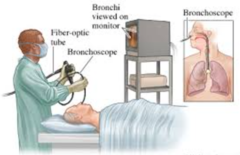
Bronchoscopy procedure

answer
Bronchoscopy is a procedure that allows your doctor to look at your airway through a thin viewing instrument called a bronchoscope. During a bronchoscopy , your doctor will examine your throat, larynx , trachea , and lower airways. Can get a specifimen collection, do biopsy, suction mucous plugs and remove foreign objects. can diagnose lung issues;
question
Things to do before bronchoscopy
answer
Instruct patient to be on NPO status 6-12 hours before the procedure. Obtain signed permit. Give sedative if ordered. Inspect mouth for infection, remove dentures, prepare client for sore throat afterwards
question
Things to do after bronchoscopy
answer
Keep patient NPO until gag reflex returns. Monitor for recovery from sedation. Blood-tinged mucous is normal. Monitor for hemorrhage and pneumothroax if biopsy was done. Instruct patient to sit or lie on side afterwards. Observe respirations carefully.
question
Change dressings when
answer
They become wet
question
How can you promote healing with any wound?
answer
Keep it moist, clean, and free from debris
question
dressing change
answer
-know type of dressing, placement of drains, and equipment needed -prepare patient for a dressing change: evaluate pain, describe procedure steps, gather supplies, recognize normal signs of healing, answer questions about the procedure or wound -perform hand hygiene and don appropriate gloves -change gloves between dirty and clean steps of the procedure -assess the wound and peri-wound (measure if required per agency protocol)
question
Tips for removing an old dressing
answer
Wear gown, face shield, and gloves Loosen by holding patient's skin and pulling dressing toward the wound Slowly remove Loosen with sterile normal saline Observe dressing for drainage color, odor, etc Discard dressing and gloves in waterprofoof trash
question
Caring for a wound
answer
Sterile procedure if fresh wound or open wound Saturate sterile gauze pads with cleaning agent Wipe incision closest to open wound and then away to least clean area Check for signs of infection, like heat, redness, swelling, odor Irrigate as ordered Pack the wound if ordered
question
wound irrigation
answer
flushing of an open wound using a medicated solution, water, sterile saline. they are ordered to clean the area of pathogens and other debris and to promote wound healing., Done just before applying new dressing, Best used when granulation tissue has formed, should be done gently to prevent disturbing healthy cells
question
Open wounds
answer
exposed to environmental factors, potential injury, and infection; more likely to heal at slower pace
question
Who might be on a clear liquid diet
answer
Surgical clients, those with acute vomiting or diarrhea, used to empty GI tract to prevent aspiration, maintain fluid balance; Not for calories, GI stim., or nutrients.
question
Clear liquid diet includes
answer
Gelatin, popsicles, tea, ginger ale, fruit juice without pulp, bouillon. Milk and juice with pulp are prohibited.
question
Progression of diets from clear liquid diet
answer
Clear liquid diet, then full liquid diet, soft diet, and then normal or modified
question
What do contact lenses correct
answer
refractive errors of the eye or abnormalities in the shape of the cornea
question
Why must all contact lenses be removed periodically?
answer
to prevent infection and corneal ulcers or abrasions
question
What indicates contact lens overwear?
answer
Pain, tearing, discomfort, and redness of the conjunctivae
question
Encourage contact lens wearing patient to remember the acronym RSVP
answer
redness, sesnitivity, vision problems, and pain. Remove contact lenses immediately if any of these problems.
question
Things to keep in mind with documentation
answer
do not leave blank lines, draw horizontal lines so nothing can be added do not use correction fluid, cross out and write error legal document document everything appropriately reflect only what saw or told, not interpretation or opinion
question
SOAP system of documentation
answer
subjective, objective, assessment, plan
question
When is EKG a standard of care?
answer
during general anesthesia and strongly encouraged during deep sedation
question
What makes the P wave on an EKG?
answer
right and left atria
question
What makes the QRS complex on an EKG?
answer
ventricles make QRS complex.
question
What makes the T wave on an EKG?
answer
electrical recovery or return to a resting state for the ventricles, or ventricle repolarization
question
To determine the heart rate from a rhythm strip what do you do?
answer
Obtain a 6 second strip, count the complexes, multiply by 10, this is for regular rhythms. So if 14 complexes on a strip, it is 140 beats per minute.
question
PR interval
answer
passage through AV node
question
What should a patient not do 24 hours before EKG?
answer
drink, or smoke, or caffeine
question
What to tell patient about EKG?
answer
Do not drink caffeine or smoke 24 hours before test Only takes about 10 minutes No discomofrt Lie still, relax, breathe normally Helps with treatment
question
EEG
answer
asleep some, may be sleep deprived prior, flickering lights
question
Hyperthermia
answer
Core body temp elevate above normal range
question
Causes of hyperthermia
answer
hyperthyroidism, thyroid storm, central nervous system disorders, heat stroke, infections
question
Nursing considerations for hyperthermia
answer
cool environment with tepid baths, hypothermia blankets, antipyretics, increase fluid intake, oral hygiene, cough and deep breathe if immbiolity exists, avoid shivering as will increase temperature
question
Signs of hyperthermia
answer
increased pulse, decreased blood pressure, disorientation
question
Hyperthermia treatment
answer
fluid replacement
question
Enema
answer
introduction of a Solution into the rectum and sigmoid colon for cleaning or therapeutic purposes
question
Types of enemas
answer
Oil retention, soapsuds, tap water, barium enema for xrays
question
Nursing responsibilities with enemas
answer
Position patient on left side use tepid solution hold irrigation set no more than 18 inches above rectum insert tube no more than 4 inches instruct client as to how long to retain solution
question
When should you NOT give an enema?
answer
in presense of abdominal pain, anausea, vomiting, or suspected appendicitis
question
Purposes for enemas
answer
Stimulates peristalsis, lubricates and softens stool, expels flatus, cleans colon, used for medicaton administration
question
Food temperature for enteral tube feedings
answer
room temperature or warmed in a basin of water = diarrhea if food too cold, too much; to-do = elevate HOB, check residual, flush, feed, flush.
question
Nursing considerations for epilepsy and seizures
answer
Document type and progress and behavior, oxygen and suction at bedside, position on back with head turned to side or position on side to prevent aspiration and promote drainage of secretions. highest incidence for younger than 10, older than 65. falls is main concern.
question
Impaction
answer
accumulation of hardened feces wedged in rectum or sigmoid colon
question
Inidcations of impaction
answer
no bowel movement for several days despite urge, diarrhea of liquid part goes through, loss of appetite, distended and cramping abdomen, rectal pain, urinary incontinence from pressure on baladder
question
Risk factors for fecal impaction
answer
Long periods of bed rest, dehydration, nutritional depletion, confusion, unconcious, medications with constipation effects, barium xrays
question
Interventions for impactions
answer
Oil and cleansing enemas, using a gloved finger to digitally remove
question
Things to consider when feeding a patient
answer
maximize independence support dignity encourage social aspects offer toilet before provide hygiene Choose own foods risk for aspiration and impaired swallowing
question
Femoral angiogram (for PAD)
answer
peripheral vessel blood flow is assessed by injecting contrast media into the appropriate arteries and veins. Can see atherosclerotic plaques, occlusion, aneurysms, venous abnormalities, or traumatic injury. - get written consent; - NPO after mindnight
question
Nursing interventions for femoral angiogram
answer
Check for allergy to contrast media, give milk sedative if ordered, check extremity with puncture site for pulsation, warmth, color, and motion after procedure inspect insertion site for bleeding or swelling, observe patient for allergic reactions. Be sure to assess pulses. pt will have to keep the leg straight for at least 6 hrs after the procedure to prevent bleeding from the femoral artery;
question
Allergic reaction signs from contrast media from femoral angiogram
answer
dyspnea, nasuea, vomiting, sweating, tachycardia, numbness of extremities
question
Treatment for femoral angiogram contrast media allergy
answer
epinephrine, antihistamines, steriods
question
PAD foot care
answer
warm water, dry, lotion, wear clean socks.
question
PVD
answer
cool, brown skin. edema, decreased pulses. -- BEDREST, ELEVATE LEGS, WARM/MOIST PACKS, ELASTIC HOSE (6-8 WEEKS), AMBULATE, ANTICOAGS.
question
Semi Fowler's
answer
30 to 45 degrees; promotes lung expansion especially with ventilator, used when patients receive gastric feedings to reduce regurgitation and risk of aspiration
question
Fowler's
answer
45 to 60 degrees; use while patient is eating, during NG tube insertion and tracheal suction, promotes lung expansion, eases breathing
question
What do hazards of immobility include?
answer
contracture, pressure ulcers, osteoporosis, hypercalcemia, negative nitrogen balance, increased cardiac workload, orthostatic hypotension, statsis of respiratory secretions, urinary stasis, constipation, thrombus, boredom, depression
question
Nursing considerations for hazards of immobility
answer
-contracture = frequent position changes/ ROM exercises; -pressure ulcers = turn, clean, dry, ambulate, diet (protein, vitamin, carbs), air matress, moving bed, watch for low albumin; -osteoporosis = weight bearing, diet; - hypercalcemia = - negative nitrogen balance - increased cardiac workload = don't hold breath, no Valsalva, rise slowly; - orthostatic hypotension = rise from bed slowly; - statsis of respiratory secretions = turn, cough and deep breathe; postural drainage, incentive spirometer - urinary stasis =void normal, increase fluids, low calcium diet, watch I&O; - constipation = ambulate, increase fluids, privacy, stool softeners; - thrombus = leg exercises, ambulate, turn, avoid gatching bed, use TED hose; -boredom, depression = tv, visitors; Turn frequently, provide good skin care, given high-protein diet with small frequent feedings,,
question
What is hemoptysis?
answer
Expectoration or coughing up of blood from respiratory tract, including larynx, trachea, bronchi, or lungs.
question
Disorders related to hemoptysis?
answer
bacterial pneumonia, bronchitis, TB, lung abscess, lung cancer, pulmonary emboli
question
Nursing considerations with hemoptysis?
answer
determine where it is from--respiratory tract or GI tract; may pH test to help tell where it is from; hemoptysis will be alkaline where stomach will be acidic; describe hemoptysis according to amount and color and wehter mixed with sputum
question
Some hypoxia causes
answer
decreased hemoglobin level, high altititude, cyanide poisoning, pneumonia, poor tissue perfusion, impaired ventilation
question
Signs and symptoms of hypoxia
answer
apprehension, restless, decreased LOC, dizzy, behavioral changes, cant lie flat, increased pulse, increased rate and depth of respirations, blood pressure elevated early on, cyanosis and respiratory decline are late stages
question
Nursing intervention for hypoxia
answer
2 L oxygen per nasal cannula if O2 less than 95%, call provider then
question
To obtain urine sample from indwelling foley catheter
answer
Apply calamp to drainage tube distal to injection port, clean port with antiseptic, insert sterile needle and syringe into the port, aspirate quanity or urine needed, inject urine in sterile specimen container, remove clamp
question
What must be explained before giving informed consent?
answer
Explanation of risks, benefits, expectations, and alternatives to procedure; can be withdrawn at any time
question
Intake and output should be within _____ to ____ milli liters of each other
answer
200 to 300 ml
question
I&O
answer
measured each shift, 24 hrs., and hourly in ICU. output=urine, liquid stool, vomit, fluids from suction, drainage. input=oral, semisolid, ice, parenteral, enteral fedings, irrigations.
question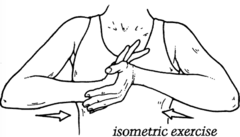
Isometric exercises

answer
performed by patient; alternate contraction and relaxation of muscle without moving join; maintains strength when joint immoblized, such as with a cast; can also do resistive isometric exercises with patient pushes or pulls like pushing hands together or pushing against a wall
question
Purpose of isometric exercises
answer
increases muscle mass, tone, and strength in bedridden patients, and increases circulation to the exercised body part
question
Criteria for TPN (total parental nutrition)
answer
inability to absorb nutrients from the GI tract for more than 10 days Illness for more than 2 weeks; loss of 10% or more of preillness weight Albumin level less than 3.5 grams Excessive nitrogen loss from wound infection Kidney or liver failure nonfunction of GI tract for 5-7 days
question
Some things to know with TPN
answer
- lipds are administered through separte tubing; - Consistent rate (start at 50ml/hr to 100-125ml/hr); -Change every 24 hours; -Vital signs every 4 hours; -Monitor glucose every 6 hours; -Assess electrolytes; -No meds through this; -USE: large vessel, RAPID dilution, watch for infection, hyperglycemia and fluid overload. -monitor weight, labs, I&O
question
TPN
answer
peripheral=supplements oral, less than 2 weeks central=into subclav vein, ~4 weeks, can be PICC, percutaneous, single or triple lumen.
question
What should patient do during TPN tubing and cap changes
answer
use the valsalva maneuver
question
Low-residue diet description
answer
Minimizes intestinal irritation and activity by reducing fiber and cellulose; for those with temporary GI elimination problems such as a lower bowel surgery and for diverticulitis, crohn's disease
question
Low-residue diet foods
answer
foods need to be easily digested. Foods are high in carbs. roast lamb, buttered rice, sponge cake, bananas, cooked vegetables and fruit, lean tender meats, white breads, canned fruits and veggies, cereal, pasta; NO nuts; seeds, skin on fruit (high fiber), dairy, whole wheat, bran.
question
Low-residue diet foods prohibited
answer
whole wheat, corn, bran, raw fruits and vegetables, seeds
question
Low fat diet description
answer
Reduces calories from fat and minimizes cholesterol intake; used for conditions such as atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease, obesity, cystic fibrosis; liver & gallbladder diseases.
question
Sample menu items for low fat diet
answer
Fruit, vegetables, cereals, lean meat
question
Sample prohibited foods for the low fat diet
answer
marbled meats, avocados, whole milk, bacon, egg yolks, butter
question
Good fats to choose
answer
fish, nuts, vegetable oils
question
Fat and vitamins
answer
Fats are necessary for absorption of A, D, E, K vitamens so strict followers of low fat diet can be deficient in these vitamins
question
Describe lumbar puncture
answer
Insertion of needle into subarachnoid space to obtain specimen of cerebral spinal fluid; relieve pressure, inject dye or medications
question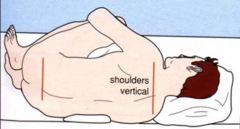
Preparation for lumbar puncture

answer
Explain procedure Informed consent Position client in lateral recumbent fetal position at edge of bed
question
Postprocedure care for lumbar puncture
answer
neurological assessment every 15 to 30 minutes until stable; position flat for 4-12 hours with first laying prone 2-3 hours to prevent CSF leakage then side for 2-3 hours and then supine for 6 hours, encourage oral fluids to 3,000 ml, observe sterile dressing at insertion site for bleeding or drainage, headache is biggest issue after lumbar puncture so lay flat to reduce CSF and therefore headache
question
MRI
answer
magnetic resonance imaging. A diagnostic radiography using electromagnetic energy
question
Nursing care for MRI
answer
Explain procedure, assessing client for claustrophobia, removing all metal jewelry and metal, asking if patient has metal implanted in body; tell pt they have to lie still.
question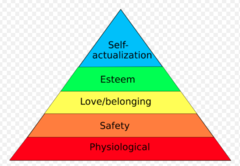
Maslow's 5 levels of need

answer
physiological, safety or security, love and belonging, esteem, and self-actualization; -basic physiological needs (oxygen, water, food, temperature, elimination, sexuality, physical activity, and rest) -safety and security needs (effective handwashing and sterile technique, proper use of electrical equipment, proper administration of medications, effective transfer techniques) -love and belonging needs (family and friends, trusting nurse-patient relationship, special support groups) -self-esteem needs (respect his or her values, setting reasonable goals, support from family and friends) -self-actualization needs-highest level of the hierarchy (to achieve full potential, focus on patient's strengths rather than on his weaknesses)
question
Most common reason for insertion of a NG tube in a postop client diagnosed with a duodenal ulcer includes which reason?
answer
decompress the stomach
question
Would irrigation procedure
answer
warm solution, position patient for gravity drainage, use sterile filed, allow a slow, steady stream of solution with a syringe and sterile catheter, solution must flow away from wound, continue until solution is clear, and try to time with doctor visit she he can inspect at the same time
question
Wound healing diet
answer
high in protein, fat, and carbs. High in vitamins A, C, and E. High in zinc. -sample menu items: 30 grams powdered skim milk and one egg in 100ml water or roast beef sandwich and skim milk -common medical problems: burns, infection, hyperthyroidism -to reestablish anabolism to raise albumin levels
question
Minimal urine output per hour
answer
30 ml
question
Minimal urine output per 24 hours
answer
800 ml
question
Normal urine output per day
answer
1,500 ml
question
Normal urine pH
answer
4.6 to 8.0
question
Normal specific gravity of urine
answer
1.010 to 1.030
question
Oliguria is less than _____ ml per 24 hours
answer
400
question
Oliguria is caused by
answer
dehydration, acute kidney injury, increased ADH secretion
question
Thoracentesis
answer
Aspiration of intrapleural fluid for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes; This is when a needle is inserted in the thoracic cavity (between ribs) into the pleural space to remove fluid or air.
question
Patient position for thoracentesis
answer
patient sits on edge of bed and leans forward over a bedside table.
question
Pre-procedure prep for thoracentesis
answer
take vital signs, shave area around needle insertion site, position patient sitting with arms on pillow or over bed table or lying on side in bed, teach patient to expect stinging sensation with injection of local anesthetic and feeling of pressure when needle inseted
question
Nursing responsibilities after thoracentesis procedure
answer
auscultate breath sounds frequently, monitor vital signs frequently, check for leakage of fluid, location of puncture site, client tolerance, secure a sterile dressing on the puncture site after procedure Look out for respiratory distress; Check for Crepitis (air under tissue) when assessing patient.
question
Therapeutic communication
answer
active listening site facing client observe open posture lean toward client establish and maintain eye contact share observations, empathy, hope, humor, feelings, use touch, use silence, provide information, clarify, focus, paraphrase, ask questions, summarize
question
Risk factors for pressure ulcer development
answer
impaired sensory perception, impaired mobility, altered level of consciousness, shear, friction, moisture
question
Presbycusis
answer
age-related hearing loss; do not hear high pitches anymore; damage to hair cells of the organ of corti; be sensitive to these patients and communicating with them
question
Postural drainage
answer
Uses gravity to facilitate removal of bronchial secretions; client placed in variety of positions to facilitate drainage into larger airways, basically from lungs and bronchi into trachea; secretions may be removed by coughing or suctioning; prevents complication of statsis of respiratory secretions
question
Postural drainage positions
answer
various positions; normally head down position; chosen position maintained for about 5 minutes during percussion and vibration; commonly done 2-4 times a day; 1 hour before meals and 3 hours post meals
question
What is normally done before postural drainage?
answer
aerosolized bronchodilators and hydration therapy, as well as percussion and vibration
question
Preoperative care
answer
Ensuring informed consent signed and attached to chart, all lab tests, chest xray and EKG have been completed, perform skin and bowel prep, NPO, administer pre-op meds such as sedation and antibiotics, removing dentures, jewelry, and nail polish
question
Preoperative exercises
answer
deep reathing, coughing, leg exercises, how to move in bed, how to use an incentive spirometer
question
incentive spirometer
answer
pts. with atelectasis, pnuemonia, had abdominal/chest/pelvic surgery, prolonged bedrest, hx of lungs probs.
question
The nurse understands that psoriasis is
answer
A chronic autoimmune reaction.
question
fears of surgery by age:
answer
Toddler fear - separation Preschool fear - mutilation - allow them to play with a model and encourage questions; School age - losing control Adolescent - losing independence
question
The nurse knows that serum albumin is used as an indicator of malnutrition because
answer
Serum albumin is easy to measure, and can indicate a protein deficiency that may not be detected on physical examination.
question
The nurse is caring for a patient beginning intermittent heparin therapy. The nurse knows which of the following lab tests are used to monitor the effectiveness of heparin?
answer
Partial thromboplastin time. Anticoagulant is working if PTT is 1.5-2 times the control. PTT must be measured at least once a week.
question
The nurse understands that which of these common foods are most likely to cause eczema and should be eliminated form the diet?
answer
Milk, wheat, egg whites.
question
position changes prevent...
answer
-to prevent contractures -to promote circulation -to promote pulmonary function -to promote pulmonary drainage -to relieve pressure on body parts
question
supine
answer
minimize hip flexion
question
sims
answer
drain oral secretions. good for enema, perineal care.
question
fowlers
answer
increase venous return, allow lung expansion. good for heart and lungs. normal = 45-60 semi=30 high=90
question
head and knees elevated
answer
venous return, pressure off lumbar-sacral
question
lithotomy
answer
gyno
question
prone
answer
promote extension of hip joint. allows mouth to drain. use for unconscious.
question
transfering pt
answer
basics: move pt. toward stronger side, use large muscles, use drawsheet, have assistance
question
heat and cold therapy
answer
-heat causes vasodilation when you want inflammation to begin healing. -Cold causes vasoconstriction to limit bleeding. Use cold within first 48 hours. -Must apply heat and cold every 20 minutes
question
incontinence
answer
Inability to control bladder and/or bowels. -urge-strong, sudden urge -stress-sneeze -overflow-constant dribbling -reflex-large amt. urine retained. CNS disease
question
good samaritan law
answer
This law deals with the rendering of first aid by health care professionals at the scene of an accident or sudden injury. It encourages health care professionals to provide medical care within the scope of their training without fear of being sued for negligence
question
paracentesis
answer
is a procedure for withdrawing fluid from the abdominal cavity. Generally done when fluids are crowding the lungs
question
suctioning
answer
wear eyewear, hyperoxygenate, semi fowlers. do not apply suction in and intermittently out.
question
elastic stockings
answer
-to prevent postural hypotension -assess the skin before applying -tape measurer to assess size needed -do not massage the legs -check for wrinkles, rolls, and binding -remove once per shift -assess toes for circulation -can be delegated to NAP
question
protein sources
answer
-meat, fish, nuts, cheese, protein powder, and peanut butter, whole wheat bread, rice, red beans, spaghetti and meat sauce
question
drain purpose
answer
-placed to provide an exit route for air, blood, or other material following surgery -keeps tissues close together so that healing can occur
question
nursing considerations for drains
answer
-monitoring characteristics and volume of drainage and recording in output records -preventing skin contact -securing placement -monitoring for infection



