Gynecologic Malignancies – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
3 most common gynecologic malignancies
answer
1. adenomocarcinoma of the endometrium 2. Epithelial ovarian cancer 3. Squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix
question
Type I endometrial cancer
answer
-*Estrogen related* -younger perimenopausal patients -*heavier patients* -low grade
question
Type II endometrial cancer
answer
-*Unrelated to estrogen* -*older patients* -thinner patients -*aggressive* -Potential genetic basis: Lynch Syndrome (but can be associated with either type, more commonly II)
question
Most common sites for cancers of the female reproductive tract
answer
-Uterine corpus not including the cervix -ovaries -uterine cervix
question
Less common sites for cancers of the female reproductive tract
answer
-Fallopian tubes -vagina -Vulva/perineum -placenta
question
Most common type of cancer in the female reproductive tract
answer
Carcinomas
question
Most common site for sarcomas in the female reproductive tract
answer
Uterine corpus
question
Other types of cancers that occur in the female reproductive tract
answer
Melanomas and lymphomas
question
Ovarian cancer risk
answer
1 in 70
question
Uterine cancer risk
answer
1 in 40
question
Cervical cancer risk
answer
One in 140
question
Breast cancer risk
answer
One in 8
question
Risk factors for type I endometrial cancer
answer
-Obesity ? >50 lbs overweight = 10X relative risk -extended reproductive life -nulliparous -late menopause -hypertension -diabetes type I and type II -Exogenous estrogen (unopposed) *think more years of ? estrogen, and HTN and DM*
question
Percent of endometrial carcinomas that are type I
answer
80%
question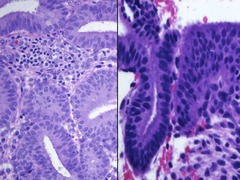
Atypical hyperplasia

answer
in-situ Phase that precedes type I endometrial carcinoma -characterized by increased* gland to stroma ratio* -histologically there are enlarged in round nuclei, loss of cell polarity, and prominent nucleoli
question
atypical hyperplasia rate of progression to carcinoma
answer
8 to 25% or higher
question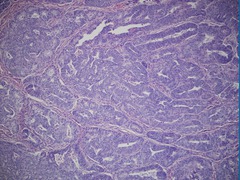
Endometrial endometriod carcinoma

answer
Characterized by confluent glands or solid sheets of tumors *type I*
question
Percent of type I endometrial carcinomas that have mutations in the *PTEN tumor suppressor gene*
answer
80%
question
Percent of endometrial hyperplasia is that have a *PTEN mutation*
answer
20%, which supports the theory that It is a precursor lesion
question
Risk factors for type II endometrial adenocarcinoma
answer
-lean women -African-American
question
Percent of endometrial carcinoma is better type II
answer
15%
question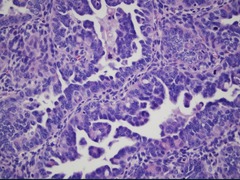
Type II endometrial carcinoma histology

answer
*serous* -Cells with very high nuclear to cytoplasmic ratios -numerous, atypical mitoses
question
Percent of patients with type II serous endometrial carcinomas that have mutations in the p53 tumor suppressor gene
answer
>90%
question
Presentation of endometrial cancer
answer
-Most common presenting complaint is postmenopausal or abnormal perimenopausal bleeding
question
true or false: bleeding after menopause is NEVER normal
answer
True
question
Only life-threatening cause of postmenopausal bleeding
answer
Cancer
question
Percent of postmenopausal bleeding that is accounted for by cancer
answer
20%
question
Who Needs an Endometrial Biopsy?
answer
1. Abnormal bleeding -*Postmenopausal bleeding* - Perimenopausal intermenstrual bleeding - Bleeding with history of anovulation 2. Postmenopausal women with endometrial cells on Pap test 3. Thickened endometrial stripe via sonography - Especially an *endometrial thickness of >5 mm in a postmenopausal woman*
question
Staging Endometrial/Uterine and Ovarian Cancer
answer
-Staging is* surgical/pathologic* -performing a predefined operation and assigning stage based on pathological evaluation of tissues removed
question
Goals of endometrial cancer staging
answer
- define the extent of the disease - minimize both over and under use of adjuvant treatment - decrease both patient risks and costs associated with treatment - allow for optimal comparison of outcomes
question
Components of endometrial cancer staging
answer
-Abdominal exploration -peritoneal cytology -total abdominal hysterectomy -bilateral salpingo-oopherectomy -bilateral pelvic and aortic lymph node dissection
question
Stage I
answer
Confined to uterus: A) endometrium only or 1/2 myometrium
question
Stage II
answer
Cervix involvement A: glands only B: stromal invasion
question
Stage III
answer
Uterine serosal adnexal disease positive cytology vaginal mets pelvic or aortic node involvement
question
Stage IV
answer
Bladder or bowel invasion inguinal nodes involved other distant metastases *not curable*
question
Survival rates of surgical stage one disease
answer
-In the absence of pathologic porpoise factors, surgery can be therapeutic with survival rates = 90-98%
question
Pathologic risk factors for recurrence of disease
answer
-High histologic *grade* (2 or 3) -depth of *myometrial invasion* -tumor* size* (>2 cm) -presence of* lymph-vascular* space invasion -*aggressive histologic cell type* (serous or clear cell cancer) the presence of 2 or more of these risk factors increases the recurrence rate to as high as 30% and justifies the use of postoperative adjuvant therapy
question
Stages II-IV
answer
Requires adjuvant therapy -generally pelvic radiation therapy with vaginal cuff boost -chemo therapy for cases with adnexal, nodal, or distant metastases
question
Percent of all endometrial cancers that are stage I
answer
70%
question
Percent of all endometrial cancers that are staged II
answer
18%
question
Percent of all endometrial cancers that are stage III
answer
8%
question
Percent of all endometrial cancers that are staged IV
answer
4%
question
Overall survival rate of stage I endometrial cancer
answer
76%
question
Overall survival rate of stage II endometrial cancer
answer
60%
question
Overall survival rate of stage III endometrial cancer
answer
30%
question
Overall survival rate of stage for endometrial cancer
answer
10%
question
Recurrent disease
answer
-Generally considered incurable -exception is isolated vaginal cuff recurrence and a woman who has not received adjuvant radiation
question
management of recurrent disease
answer
platinum-based chemotherapy participation in clinical trials is encouraged
question
Endometrial Cancer: Adjuvant Postoperative Therapy
answer
Whole Pelvic Radiation and Vaginal Cuff Boost Most common indications - cervical spread (stage II) - nodal involvement (stage IIIC) Can reduce recurrence rate by up to 50% Estimated cost 5,040 cGy PRT: $20,000 Treatment duration: 25 to 30 days Chemotherapy
question
Ovarian Cancer
answer
- Second most common gynecologic malignancy in the US - Responsible for 25,000 cases annually - 14,500 deaths annually - *Most lethal gynecologic malignancy * - 70% of patients present with advanced disease - no effective screening
question
Most common source of malignant ovarian tumors
answer
Surface epithelium
question
Risk factors for ovarian cancer
answer
-Age/postmenopausal -family history/genetics -infertility/low parity or other factor resulting in uninterrupted ovulation -personal cancer history (most commonly breast cancer) *has to do with ovulation, increased # of ovulations, means more repair to the ovaries = ? risk*
question
Factors that reduce the risk for ovarian cancer
answer
-Oral contraceptive use -pregnancy -tubal ligation -breast-feeding
question
Most common presenting templates for ovarian cancer
answer
-Abdominal bloating -early satiety -small or large bowel obstruction -many women do seek medical attention earlier in the disease process but symptoms are overlooked as minor gastrointestinal or genitourinary conditions such as *irritable bowel or UTI*
question
Definitive diagnostic modality for ovarian cancer
answer
Surgical exploration/pathology
question
Most common histologic subtype of epithelial ovarian cancer
answer
Serous carcinoma
question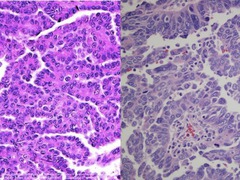
2 categories of serous carcinoma of the ovary

answer
-Low grade -high-grade
question
Mutations commonly seen with low-grade serous cancers of the ovary
answer
- KRAS - BRAF - PTEN - B-catenin
question
Type of serous ovarian cancer with better purposes
answer
Low grade
question
Mutations associated with high-grade serious cancers of the ovary
answer
p53
question
The vast majority of epithelial covariant cancers are of which grade?
answer
High grade serous
question
Reason why the serum tumor marker CA125 and pelvic ultrasound are not reliable screening tests for ovarian cancer?
answer
-Lack the sensitivity (too many false negatives) -lack the specificity (too many false positives)
question
Management of ovarian cancer
answer
-Involves both surgery and systemic adjuvant, platinum and taxane paste chemotherapy
question
2 major surgical concepts of important in ovarian cancer
answer
-Complete surgical staging of disease that clinically appears to be confined to the ovaries -cytoreductive surgery or debulking
question
Complete staging of ovarian cancer
answer
-Peritoneal cytology -TAH/BSO -omentectomy -peritoneal biopsies from pelvis, mid abdomen, and diaphragmatic surfaces -pelvic and aortic node dissections
question
Ovarian Cancer: CA125 Testing
answer
- Elevated in > 80% of advanced EOCs and functions well as a tumor marker in majority of these cases - Elevated in 25-50% of Stage I cancers ? POOR SENSITIVITY - Elevated by many non-malignant conditions especially in premenopausal women ? POOR SPECIFICITY - NOT a screening test for the general population
question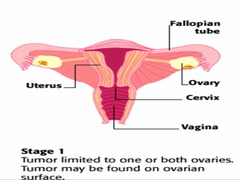
Stage I ovarian cancer

answer
*Confined to the ovaries* A ? one ovary B ? both ovaries C ? one or both with surface disease or positive cytology
question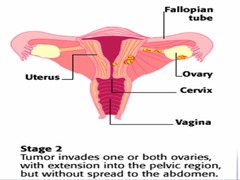
Stage II ovarian cancer

answer
*Confined to the Pelvic Organs*
question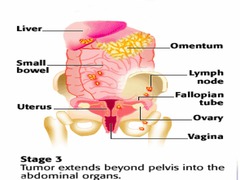
Stage III ovarian cancer

answer
*Spread to the Upper Abdomen* (lymph nodes) A ? microscopic disease only B ? Largest lesion 2cm ( most common overall stage)
question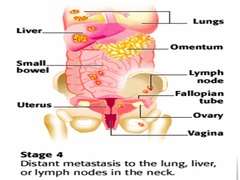
Stage IV ovarian cancer

answer
*Malignant pleural effusion or liver mets*
question
Percent of ovarian cancers that appear confined to the ovary (stage I) in which there is microscopic spread upstaging to stage IIIC
answer
30%
question
Key to a good outcome of ovarian cancers that have spread beyond the ovaries
answer
Tumor mass reduction and debulking -the more tumor removed, the better chance for survival
question
Optimal surgical debulking
answer
*leaving no tumor nodule >0.5 cm *
question
Post operative edge event chemotherapy for ovarian cancer
answer
Required in all cases other than stage IA grade 1 lesions
question
most common drug combinations used in Ovarian cancer chemotherapy
answer
-IV carboplatin and Taxol -intraperitoneal cisplatin and Taxol
question
Percent of women that will have good response to chemotherapy and will be in remission after 6 to 8 cycles of therapy
answer
70-80%
question
Percent of women who reach remission that will have a recurrence within the 1st 3 years after completing treatment
answer
>50%
question
Therapy for ovarian cancer recurrence
answer
-Reoperation for debulking -pretreatment with chemotherapy
question
Cure rate of recurrent ovarian cancer
answer
0%; considered incurable
question
percent of ovarian cancers that are diagnosed as stage I
answer
24%
question
Percent of ovarian cancers that are diagnosed in stage II
answer
6%
question
Percent of ovarian cancers that are diagnosed in stage III
answer
55%
question
Percent of ovarian cancers that are diagnosed as stage IV
answer
15%
question
Percent survival of stage I ovarian cancer
answer
95%
question
Percent survival of stage II ovarian cancer
answer
65%
question
Percent survival of stage III ovarian cancer
answer
15-30%
question
Percent survival of stage IV ovarian cancer
answer
0-20%
question
Overall survival rates of ovarian cancer
answer
50%
question
Surgical Rx for Early Stage ovarian cancer Disease
answer
*TAH BSO + staging * Infracolic omentectomy Peritoneal samples pelvis, gutters, diaphragm Pelvic and aortic lymph node dissection -In younger women, reproductive conservation may be appropriate -Approximately 30% will have histologic evidence of metastatic disease when clinically disease appears confined to the ovary
question
Surgical Treatment for Advanced ovarian cancer Disease
answer
Significant survival advantage for women optimally cytoreduced Procedures may include: En bloc resection of uterus, ovaries and pelvic tumor Omentectomy Bowel resection Removal of diaphragmatic and peritoneal implants Splenectomy, appendectomy
question
Ovarian Cancer Chemotherapy
answer
- All patients should receive a taxane and a platinum - 73% response rate, however more than half of these women will experience recurrence of the disease - Median survival: 38 months for Stage III/IV - Many new agents being tested - Encourage clinical trial participation
question
Ovarian Cancer Follow-up
answer
-Recto-Vaginal pelvic exam and CA125 q 3-4 mo x 2 years, q 6 mo for years 3-5 - CT scan for symptoms - General health maintenance (mammography, Pap smear, bone density, colon-rectal screening, cholesterol, etc.) - Discuss HRT, diet, exercise
question
Cervical Cancer Incidence
answer
American Cancer Society Estimates 12-13,000 cases of invasive cervical cancer/year 4600 of these women die International estimates Approximately 500,000 deaths/year! Number 1 or 2 cancer killer of women worldwide
question
Cervical Cancer Risk Factors
answer
-Early age of intercourse -Number of sexual partners -Smoking -Lower socioeconomic status -High-risk male partner -Other sexually transmitted diseases -Up to 50% of the U.S. population is infected with HPV
question
Percent of cervical cancers worldwide contain Human Papilloma Virus DNA
answer
*99.7%*
question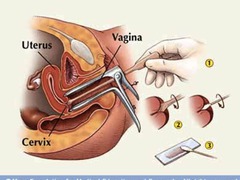
Cervical cancer screening

answer
Pap test
question
Percent of cervical cancers accounted for by type 16 HPV
answer
60%
question
Percent of cervical cancers accounted for by type 18 HPV
answer
10%
question
HPV infections locations
answer
-Basal cells of the squamous epithelium, usually at the squamocolumnar junction of the cervix
question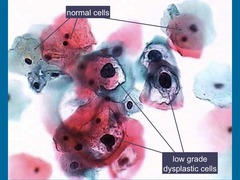
koilocytosis

answer
Squamous cell with a dark, irregular nucleus and a sharply defined perinuclear halo which is characteristic of HPV infection
question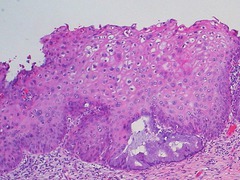
Low-grade or mild dysplasia

answer
Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia grade 1
question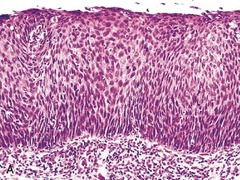
high grade or severe dysplasia

answer
Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia grade 3"
question
Why does the Pap test work?
answer
- cervix can be sampled relatively non-invasively - natural history of cervical cancer is slowly progressive - dysplastic (pre-invasive) changes can be recognized microscopically - dysplastic (pre-invasive) changes can be treated and prevented from progressing to invasive cancer - test is relatively inexpensive - HPV testing is integrated into screening in patients over 29 years of age (extends interval)
question
Cervical Cancer Prevention
answer
*HPV vaccination* available in US since 2006 recommended to males and females age 9-26 years 3 dose schedule
question
Where HPV viral particles are found in epithelial cells
answer
-Halo area
question
Treatment of cervical squamous cell dysplasia
answer
conization Cryotherapy
question
Oncogenesis from HPV
answer
Occurs when the virus becomes integrated into the host DNA and viral E6 and E7 proteins bind to retinoblastoma tumor suppressor genes and to the p53 tumor suppressor gene
question
mild cervical squamous cell dysplasia definition
answer
Abnormal cells confined to the lower 1/3 of the epithelium
question
Moderate cervical squamous cell dysplasia definition
answer
Abnormal cells extend into the middle 1/3
question
Severe dysplasia definition
answer
Abnormal cells are present in the superficial 1/3 of the epithelium
question
Signs and Symptoms of Invasive Cervical cancer
answer
May be silent until advanced disease develops *Post-coital bleeding* *Foul vaginal discharge* *Abnormal bleeding* Pelvic pain Unilateral leg swelling or pain Pelvic mass Gross cervical lesion
question
Most common presenting complaints for women with invasive squamous cell carcinoma
answer
Painless postcoital bleeding
question
Clinical staging of cervical squamous cell carcinoma
answer
-General physical exam -rectovaginal bimanual pelvic exam -plain film chest x-ray -cytoscopy and/or proctoscopy -intravenous pyelogeram
question
Type of staging used for cervical cancer
answer
-Unlike the other 2, it is *staged by clinical criteria* rather than surgical/pathologic staging
question
Type of staging used for ovarian cancer
answer
Surgical/pathologic staging
question
Type of staging used for uterine cancer
answer
Surgical/pathologic staging
question
Rationale for clinical staging of cervical cancer
answer
-The majority of squamous cell carcinoma affects women in the underdeveloped world where access to diagnostic modalities are limited or unavailable -continued clinical staging allows for comparison across every different geographic and socioeconomic population
question
Stage I cervical cancer
answer
*Confined to cervix* - A < 5mm invasion or 7mm lateral spread - B any lesion larger than IA microscopic or any visible lesion
question
Stage II cervical cancer
answer
*Vaginal and/or Parametria involved* A ? Upper 2/3 vagina B ? Parametria but not to the pelvic sidewall
question
Stage III cervical cancer
answer
*Extensive Vaginal or Parametria* A ? Lower 1/3 vagina B ? Parametria to the sidewall or any lesion causing hydronephrosis
question
Stage IV cervical cancer
answer
Distant Disease A ? Bladder or Rectal mucosa invasion B ? Distant mets
question
Treating Early Cervical Cancer
answer
1. Conization or simple hysterectomy - microinvasive cancer 2. Radical hysterectomy - removal of the uterus with its associated connective tissues, the upper vagina, and pelvic lymph nodes. Ovarian preservation is possible. 3. Chemoradiation therapy
question
Cervical Cancer Treating Advanced Cervical Cancer
answer
*Chemoradiation is the mainstay of treatment* - 4-5 weeks of external radiation - Two or more implants (brachytherapy) - Concurrent Cisplatin-based chemotherapy significantly improves the chances of survival - Radiation treats the primary tumor and adjacent tissues and lymph nodes - Chemotherapy acts as a radiation sensitizer and may also control distant disease
question
Cervical Cancer recurrence management
answer
Palliative chemotherapy Pelvic exenteration (if central recurrence) 50% cure rate
question
Five-year survival of stage I cervical cancer after treatment with radical hysterectomy
answer
85-98%
question
Five-year survival of stage I cervical cancer after treatment with chemo and radiation therapy
answer
85-95%
question
Five-year survival of stage II cervical cancer after treatment with chemo and radiation therapy
answer
70-80%
question
Five-year survival of stage III cervical cancer after treatment with chemo and radiation therapy
answer
50-65%
question
Five-year survival of stage IV cervical cancer after treatment with chemo and radiation therapy
answer
20-30% (IVA) <10% (IVB)
question
endometriod
answer
Type I endometrial carcinoma
question
serous
answer
Type II endometrial carcinoma
question
BRCA 1 or BRCA2 germline mutation
answer
35-65% lifetime risk of ovarian cancer
question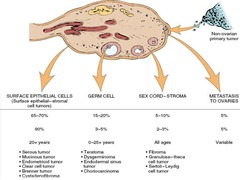
types of ovarian cancer

answer
>90% are surface epithelial cancers (serous)
question
postcoital bleeding
answer
rule out cervical cancer
question
postmenopausal bleeding
answer
rule out uterine (endometrial) cancer



