AQA Physical Chemistry and Practical – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
What is enthalpy of formation?
answer
The enthalpy change when one mole of a compound is formed from its constituent elements in their standard states under standard conditions.
question
What is the enthalpy of combustion?
answer
Enthalpy change when 1 mole of a substance undergoes complete combustion in an excess of oxygen with all elements in their standard states under standard conditions.
question
What is the enthalpy of neutralisation?
answer
Enthalpy change when one mole of water is produced from a reaction between an acid and alkali with all substances in their standard states under standard conditions.
question
What is the first ionisation energy?
answer
Enthalpy change when each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms loses one electron to form 1 mole of gaseous 1+ ions
question
What is meant by the term first electron affinity?
answer
The enthalpy change when each atom in one mole of gaseous atoms gains one electron, becoming one mole of gaseous 1- ions.
question
What is meant by the term enthalpy of atomisation?
answer
Enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous atoms is formed from an element in its standard states under standard conditions.
question
What is hydration enthalpy?
answer
Enthalpy change when one mole of gaseous ions become hydrated.
question
What is enthalpy of solution?
answer
Enthalpy change when one mole of an ionic solid dissolves in an amount of water large enough so that the dissolved ions are well separated and do not interact with each other.
question
What is bond dissociation enthalpy?
answer
Enthalpy change when one mole of covalent bonds is broken in the gaseous state.
question
What is lattice enthalpy of formation?
answer
Enthalpy change when one mole of a solid ionic compound is formed from its constituent ions in the gas phase.
question
What is lattice enthalpy of dissociation?
answer
Enthalpy change when one mole of a solid ionic compound is broken up into its constituent ions in the gas phase.
question
What is enthalpy of vapourisation?
answer
Enthalpy change when one mole of a liquid is turned into a gas.
question
What is enthalpy of fusion?
answer
Enthalpy change when one mole of a solid turned into a liquid.
question
In a Born Haber cycle how is enthalpy of formation calculated?
answer
It is the sum of all the other enthalpy values.
question
In a Born Haber cycle which direction does the arrow for lattice enthalpy of formation point?
answer
Down
question
In a Born Haber cycle which direction does the arrow for lattice enthalpy of dissociation point?
answer
Up
question
Why do some ions show covalent character?
answer
There may be distortion (they are polarised), meaning they aren't perfectly spherical.
question
Why might the lattice enthalpy be different in theory to the experimental value?
answer
covalent character
question
What is entropy measured in?
answer
J/mol/K
question
What state do substances have the most entropy in?
answer
Gases because particles move more rapidly and randomly.
question
What is the 2nd law of thermodynamics?
answer
Over time entropy will naturally increase.
question
How is °C converted into K?
answer
+273
question
How would you carry out a titration?
answer
Rinse out conical flask with distilled water Rinse burette with reagent (known conc.) Run solution to fill tap Rough titration to estimate end-point Reading should be 2 d.p. end in 0 or 5 Average titre of concordant results Conical flask on white tiles
question
How would you test for a carboxylic acid
answer
Add solid sodium carbonate +ve test fizzes and gives off gas that turns cloudy when bubbled through limewater
question
How would you test for alkenes?
answer
Add bromine water Shake Turns orange to colourless
question
How would you carry out a flame test for calcium?
answer
Dip nichrome wire loop in conc. HCl, dip into unknown compound, hold over flame, +ve test will give brick red flame
question
What colour flame would strontium give in a flame test?
answer
Red
question
What colour flame would barium give in a flame test
answer
Pale green
question
How would you test for ammonium ions?
answer
Add dilute NaOH solution Heat Ammonia given off (turns damp red litmus blue)
question
How would you test for sulfate ions?
answer
Add dilute HCl Add barium chloride +ve forms white precipitate
question
How would you test for hydroxide ions?
answer
Red litmus paper into solution turns blue
question
How would you test for the halide ions?
answer
Add dilute nitric acid Add silver nitrate solution Bromide ions form cream ppt. (dissolves in conc. ammonia) Chloride ions form white ppt.(dissolves in dilute ammonia) Iodide ions form yellow ppt.(won't dissolve in conc. ammonia)
question
How would you test for carbonate ions?
answer
Add dilute HCl +ve will fizz
question
When is a dynamic equilibrium reached in a reversible reaction?
answer
When the conc. of reactants and products are constant, and the forward and backward reactions are going at the same rate.
question
What requirements are needed for a dynamic equilibrium to form?
answer
Reaction must be reversible Must be in a closed system Constant temperature
question
What is le Chateliers principle?
answer
If a reaction at equilibrium is subjected to a change in pressure, temperature or concentration, the position of equilibrium will move to counteract the change.
question
Give an equation for Kc
answer
Kc= [D]^d x [C]^c/[A]^a x [B]^b Where lower case is the number of moles
question
Describe how Rutherford determined his model of the atom?
answer
Alpha particles are fired at an atom, most pass through empty space, some are deflected very strongly by the nucleus.
question
What is the general trend in 1st IE down a group?
answer
Decrease
question
What is the general trend for atomic radius across a row?
answer
Decrease
question
Which elements deviate from the atomic radius trend across the row from lithium to boron?
answer
Boron because it goes from a 2s orbital to a 2p orbital which has a higher energy level.
question
Why is the melting point of carbon high?
answer
Macromolecular Many covalent bonds Covalent bonds are very strong
question
What increases van der waal forces?
answer
Greater Mr Greater size Greater electron cloud
question
What is the trend in melting point of the group 2 elements?
answer
Decrease because ionic radius becomes greater
question
Why does aluminium not folllow the general trend of 1st IE?
answer
lowers because it goes from a 3s to a 3p orbital and the 3p is shielded by the 3s orbital
question
What is the trend in m.p of the period 3 metals?
answer
Increases because there is a higher charge density, so stonger attraction between +ve ions and -ve electrons.
question
What are the axis on a mass spectrometre?
answer
% abundance on Y axis mass/charge on X axis
question
How do you calculate relative atomic massof an element from a mass spectrometre?
answer
Multiply the abundance of each peak with the mass/charge Add the totals Divide by 100
question
What is the relative mass of an electron?
answer
0.0005
question
What is the mass number?
answer
The number of protons and neutrons bound within the nucleus
question
What is the atomic number?
answer
Number of protons bound within the nucleus
question
What is an isotope?
answer
Atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons.
question
Why do istopes have the same chemical properties?
answer
They have the same electron configuration
question
Why do isotopes have different physical properties?
answer
Relative masses are different
question
Why is the mass number of carbon 12.00000?
answer
By definition
question
What is the relative atomic mass?
answer
The weighted mean mass of an atom of an element compared to 1/12 the mass of a 12C atom. Always given to 1 d.p
question
What is relative isotopic mass?
answer
The actual mass of an atom of an isotope of an element compared to 1/12 the mass of a carbon atom. Always an integer value.
question
What are the stages in a mass spectrometry?
answer
Vaporisation Ionisation- Sample dissolved in a polar solvent and pushed through a small nozzle at high pressure. A high voltage is applied so each atom loses an electron. Acceleration- Ions pass through an electric field, given an equal acceleration. Lighter ions accelerate more. Time measurement- drift with a constant speed Detection- smaller ions hit detector first and times are recorded to calculate mass/charge.
question
What are the isotopes of bromine?
answer
79Br and 81Br
question
What is an orbital?
answer
A region of space in which we find electrons
question
What is Avogadro's constant?
answer
6.02 x10^23
question
How would you calculate the number of particles in a substance?
answer
No. of moles x Avogadro's constant
question
What is the ideal gas equation?
answer
PV=nRT P is in Pa Volume is in m³ R is gas constant 8.31 J/K/mol Temperature is in K
question
What is atom economy?
answer
Atom economy is a measure of the proportion of reactants that become useful products
question
How is atom economy calculated?
answer
relative atomic mass of desired product/total relative atomic mass of reactants x100
question
Why is a high atom economy important?
answer
Shows how many atoms are 'wasted' Shows which processes are efficient
question
What is empirical formula?
answer
The empirical formula of a compound shows the simplest/smallest whole number ratio of atoms of each different element in the molecule.
question
What is the bond angle in a tetrahedral molecule?
answer
109.5?
question
What is the structure type for diamond, graphite and silicon dioxide?
answer
Macromolecular crystal type
question
What is electronegativity?
answer
The ability of an atom in a covalent bond to attract the bonding pair of electrons towards itself.
question
What three factors affect electronegativity?
answer
Proton number Amount of shielding Atomic radius
question
What are intermolecular forces?
answer
Weak forces of attraction acting between adjacent molecules
question
What is the structure of a pyramidal molecule?
answer
bond angle is 107
question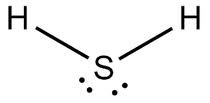
What is the structure of a bent molecule?

answer
bond angle is 104.5
question
What is the structure of a square planar molecule?
answer
b.a is 90
question
State the trends in melting point across period 3 and which elements deviate from this
answer
Increases then decreases after silicon Al and s deviate
question
What are the four types of crystal types?
answer
Ionic Simple molecular Giant covalent (macromolecular) Metallic
question
Are simple molecular substances soluble?
answer
Polar simple molecular substances dissolve in polar solvents Non-polar simple molecular substances dissolve in non-polar solvents
question
What equation would you use to calculate enthalpy?
answer
Q=mc?t
question
What is Hess's law?
answer
Enthalpy change for a reaction is independent of the route taken.
question
How would you calculate overall enthalpy change when given the enthalpy values for the products/reactants?
answer
making-breaking
question
When calculating enthalpy of a neutralisation reaction, what mass should be used?
answer
The mass of the water
question
What does the maxwell-boltzmann graph look like?
answer
no. of particles on y axis
question
Give two requirements for a reaction to occur between molecules in the gas phase?
answer
molecules must have EA have to collide with each other
question
Why does the volume need not be known in calculating the value of Kc?
answer
The volumes cancel out because there are equal molar quantities on both sides
question
What is the Gibbs free energy equation?
answer
?G=?H-T?S ?S is entropy
question
Why may a feasible reaction not actually take place?
answer
The activation energy may be too high
question
What value must ?G be for a reaction to e feasible?
answer
Zero or below
question
Why is entropy zero when the temp. is zero Kelvin?
answer
Particles are stationary Perfect order
question
What is the cycle of enthalpy of solution, ionic solid and dissolved ions?
answer
?solH= ?hydrationH-?lattice enthalpy of dissociationH
question
What are the assumptions made when carrying out a clock reaction?
answer
concentration of each reactant doesn't change significantly during reaction Temperature stays constant Reaction hasn't proceeded too far when the endpoint is seen
question
What is the purpose of a clock reaction?
answer
Measure how long it takes for a set amount of product to form and how that varies when you change the conc. of one of the reactants.
question
What is the first part of the iodine clock reaction?
answer
A small amount of sodium thiosulfate solution and starch are added to an excess of hydrogen peroxide and iodide ions in acid solution. H?O?(aq) + 2I¯(aq) + 2H?(aq) ? 2H?O(l) + I?(aq)
question
What is the second part of the iodine clock reaction?
answer
Starch turns blue/black in presence of iodine Sodium thiosulfate reacts with any iodine formed 2S?O?(aq) + I?(aq) ? 2I¯(aq) + S?O?(aq)
question
What is the third part of the iodine clock reaction?
answer
Once all the sodium thiosulfate has reacted, iodine will turn the starch blue/black. This is the end of the clock reaction. Then can vary [iodide] or [hydrogen peroxide]
question
What is meant by the term order of reaction?
answer
The order of reaction with respect to a given reactant is the power to which the concentration of reactant is raised in the rate equation.
question
How is overall order of reaction calculated?
answer
sum of the powers of the concentration terms in the rate equation
question
What affects the rate constant, k?
answer
Temperature (increases)
question
What is the equation for kp?
answer
where p=partial pressure
question
How is partial pressure calculated?
answer
mole fraction x total pressure
question
What units are used for kp?
answer
K Pa
question
Why is kw used instead of kc for the ionic product of water?
answer
Water conc. so high it acts as a constant Equilibrium lies far to the left
question
How can hydrogen ion conc. be calculated from kw?
answer
[H+]=square root of kw
question
Why is water always neutral even if the pH changes with temperature?
answer
[H+]=[OH-]
question
Why does the value of kw increase with temperature?
answer
Dissociation is endothermic Equ. moves right to absorb heat
question
What is a buffer solution?
answer
A buffer solution is one which resists changes in pH when small quantities of an acid or alkali are added to it.
question
What happens when an acid is added to a weak acid buffer solution?
answer
H+ removed by salt, e.g. ethanoate ions to make ethanoic acid
question
What happens when alkali is added to a weak acid buffer?
answer
Will either: OH- react with acid to make salt + water H+ from ionisation of acid combine with OH- to make water
question
What happens when an acid is added to a weak alkali buffer?
answer
H+ reacts with alkali, e.g. NH3 forms NH4+
question
What equilibrium is going on in an ammonia and ammonium chloride buffer solution and where will equ. be?
answer
NH3(aq) + H2O(l) ====; NH4+(aq) + OH-(aq)
question
How can pKa and Ka be used in the same equation?
answer
so Ka = 10^-pKa
question
How would you construct a pH curve?
answer
Measure initial pH of acid Add alkali in small amounts (note vol. added) Stir to equalise pH Record pH to one d.p Add until alkali in excess Calibrate meter by measuring known pH of a buffer solution.
question
What is the rate determining step?
answer
Slowest step in a reaction
question
Describe how an acid reacts with water?
answer
HA(aq) + H?O(l) ? H?O+ + A?(aq)
question
Describe how a base reacts with water?
answer
B(aq) + H?O(l) ? BH+(aq) + OH?(aq)
question
Give an example of a strong acid?
answer
HCl
question
Give an example of a weak acid?
answer
Any carboxylic acid
question
Give an example of a strong base
answer
Anything with hydroxide in it
question
Give an example of a weak base
answer
Ammonia
question
What are the units for kw?
answer
mol²dm¯?
question
What is a diprotic acid?
answer
release two mol of H+ when 1 mole of acid dissociates.
question
What happens to reactivity down a group?
answer
Increases because ionisation energy decreases
question
What happens to a group 2 element when it reacts with water?
answer
M(S) + 2H?O(l) ? M(OH)? (aq) + H?(g)
question
Give a use of barium sulfate?
answer
Barium meals
question
What is used to extract titanium from its ore?
answer
Magnesium which acts as a reducing agent TiCl?(aq) + 2Mg(l) ? Ti(s) + 2MgCl?(aq)
question
How is sulfur dioxide removed from flue gases?
answer
wet scrubbing where slurry (calcium oxide/carbonate and water. Forms calcium sulfite. CaO(s) + 2H?O(l) + SO?(g) ? CaSO?(s) + 2H?O(l) CaCO?(s) + 2H?O(l) + SO?(g) ? CaSO?(s) + 2H?O(l) + CO?(g)
question
What is the trend of boiling points down group 7?
answer
Size and mr increases so van der waal forces are stronger.
question
Which of the group 2 ions is sparingly soluble when bonded to hydroxide ions?
answer
Magnesium
question
Which of the group 2 ions is most soluble when bonded to hydroxide ions?
answer
Barium
question
Which of the group 2 ions is most soluble when bonded to a sulfate ion?
answer
Magnesium
question
Which of the group 2 ions is least soluble when bonded to a sulfate ion?
answer
Barium
question
What is a use of barium sulfate?
answer
Can be used to test for sulfate ions because they'll react with barium chloride to form insoluble barium sulfate.
question
Write an equation to show barium chloride reacting with sulfate ions?
answer
BaCl?(aq) + FeSO?(aq) ? BaSO?(s) +FeCl?(aq)
question
What is a use for calcium hydroxide?
answer
Neutralise acidic soils in agriculture
question
What is a use for magnesium hydroxide?
answer
Neutralise excess stomach acid
question
When will a halogen displace a halide?
answer
If the halide is below it in the periodic table
question
What happens to reactivity down group 7?
answer
Decreases because atoms are bigger so less attraction between electrons and protons. So they are less oxidising down the group.
question
What happens to electronegativity down group 7?
answer
Decreases because more shielding
question
How is bleach made?
answer
2NaOH(aq) + Cl?(g) ? NaClO(aq) + NaCl(aq) + H?O(l) Chlorate(I) ion formed in NaClO and kill bacteria
question
Give a use of chlorine?
answer
Kill bacteria in water
question
What happens to chlorine when it reacts with water?
answer
Undergoes disproportionation Cl?(g) + H?O(g) ? 2H+ + Cl-(aq) + ClO-(aq) In sunlight, it will decompose: Cl?(g) + 2H?O(l) ? 4H+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) + O?(g)
question
What happens to reducing power down group 7?
answer
Increases because more shielding and electrons are further away.
question
What happens when sodium fluoride or sodium chloride reacts with sulfuric acid?
answer
Forms a hydrogen halide and NaHSO?
question
What happens when sodium bromide reacts with sulfuric acid?
answer
HBr and NaHSO?
question
What happens when sodium iodide react with sulfuric acid?
answer
Hydrogen iodide and NaHSO?
question
What happens when hydrogen iodide reacts with sulfuric acid?
answer
Iodine, sulfur dioxide and water
question
What happens when hydrogen iodide reacts with sulfur dioxide?
answer
H?
question
Why does equilibrium shift when temperature increases?
answer
It moves towards the endothermic reaction; to oppose the change (to oppose increase in temp.)
question
With reference to the Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution, explain why an increase in temperature increases the rate of a chemical reaction.
answer
Increase in the number of molecules with greater energy than the activation energy; So more frequent successful collisions
question
Explain how a catalyst increases rate of reaction?
answer
Catalysts provide an alternative reaction pathway; with a lower Ea
question
Suggest why a students value for enthalpy of combustion for methanol is different from that in a Data Book (besides incomplete combustion or heat transfer to the environment)
answer
Data book value came from use of mean bond enthalpy data
question
Explain why a thermometer with an uncertainty of 0.5% is adequate for this experiment?
answer
Error on thermometer is less than other errors in the experiment
question
Explain why a thin layer of a catalyst is spread over a honeycomb ceramic support.
answer
save cost; honeycomb increases surface area
question
Explain why mass spectrometry cannot distinguish between propanal and prop-2-en-1-ol
answer
both have the same molecular formula; both would have the same mr
question
Give one reason why bonds in molecules such as carbon dioxide absorb IR?
answer
IR radiation excite electrons in covalent bonds
question
suggest how anti bumping granules work
answer
provide nucleation points for bubbles to form on
question
why is a conical flask used in titration?
answer
to reduce any loss due to splashing
question
why would you rinse the sides of the conical flask with distilled water near the end point?
answer
to ensure all splashes of acid and alkali are rinsed down and have to chance to react
question
why can the conical flask be rinsed with distilled water?
answer
there is already a measured quantity of moles in conical flask so addition of water does not affect this
question
why must the burette and pipette be rinsed with the correct solutions and not distilled water?
answer
to ensure no dilution of the solution
question
When analysing the purity of aspirin tablets, what is the biggest experimental error?
answer
not all 2-ethanoylhydroxybenzoic acid may be hydrolysed in simmering.



