AP Human Geography: Population and Migration – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
The Birth Rate Formula
answer
Lives Births/ (Population/1000)
question
The Death Rate Formula
answer
Deaths/ (Population/1000)
question
The Natural Rate of Increase (RNI)
answer
(Birth Rate - Death Rate)/10
question
(DINK) double-income-no-kid
answer
a phenomenon that may account for shrinkage (fecundity)
question
Formula for Doubling Time
answer
70/ Rate of Natural Increase
question
The Net Migration Rate Formula
answer
(Number of Immigrants/1000) - (Number of Emigrants/1000)
question
The Demographic Equation
answer
((Birth Rate - Death Rate) + Net Migration Rate)/10 = Percent Population Growth Rate
question
Total Fertility Rate Formula
answer
Number of Children Born/Women Aged 15 to 45
question
The Demographic Transition Model
answer
Provides insight into our past and future, a unifying concept in the Human Geography concept, predictive capacity, divided into four increments: Pre-Agricultural, Agricultural, NIC (newly industrialized countries)'s manufacturing, and services
question
Newly Industrialized Countries (NICs)
answer
Brazil, Mexico, and India fall into this category
question
Stage 1
answer
pre-agricultural society, engaged in subsistence farming and transhumance (seasonal migration for food and resources or owning livestock), birth and death rates fluctuate as the result of factors such as climate, warfare, disease, and ecological factors, but overall both rates are high, the result is little population growth until the death rate begins to decline, RNI is low, or even negative, low life expectancy, examples in today's world are Liberia and Sierra Leone, are many sub-Saharan countries affected by the AIDS epidemic
question
Stage 2
answer
agriculturally based economies, birth rates remain high as death rate decline over time, RNI goes up significantly as birth rates and death rates diverge, children are even more important as a source of labor, infant and childhood mortality is still high, birth rates are still extremely high, the relative increase in food volume, year-round availability, and nutrient quality means that people live longer, decreasing the death rate, Ghana and Nepal are good examples
question
Stage 2.5-ish
answer
Newly Industrialized Countries, transitioning away from agricultural, birth rates begin to decline with urbanization, as families move to cities they find (in comparasion to the rural agricultural lifestyle) that they have less time, less need, and less space for children, child labor is often illegal discrediting that use for children, death rates continue to decline, Mexico and Malaysia are examples
question
Stage 3
answer
During this time these same countries have completed the transition, that is, completing the S-curve and moving into stage four, stage three is what we should expect many NICs to look like as they continue to industrialize, birth rates continue to decrease as a result of increased education for women, availability of contraceptives, etc, decreased death rates as a result of increased health care, nutrition, and sanitation, will eventually bottom out, obviously, China (although their curve is unique due to their one-child policy) and Uruguay are examples
question
Stage 4
answer
Birth and death rates converge to result in limited population growth and even population decline, mostly first world countries with service-based economies (finnace, insurance, real estate, health care, and communications), manufacturing is a dying breed in these countries, birth rates bottom out into the lower teens, when birth rates = death rates, this is when you have a zero population growth, and an RNI of 0.0 percent, Italy, former Communist satellite states, have experienced negative population growth in recent years, however, the population is still increasing due to labor immigration
question
Malthusian Theory
answer
Englishman Thomas Malthus published An Essay on the Principle of Population in 1798, his main idea was that the global population would one day expand to the point where it could not produce enough food to feed everyone. He predicted this would happen before 1900. The Malthusian catastrophe did not happen by 1900 or even by today, but some more recent thinkers (neo-Malthusians) think it still could in the future. made sense, he lived during a time when the UK was shifting from stage 2 to stage 3, seeing rapid migration to the cities and a population explosion, food grew linearly, while the human population grew exponentially, but new technology soon boosted food production (internal combustion engine, artificial fertilizers, pesticides, irrigation pumps, etc)
question
Neo-Malthusian Philosophy
answer
1. Sustainability - when we do reach carrying capacity, we may have a problem feeding 10 billion people long term, global warming may continue to damage the world's current growing areas, 2. Increasing per capita Demand - can the planet provide enough food and other products when all 10 billion of us eat like the First World does today?, 3. Natural Resource Depletion (obvious)
question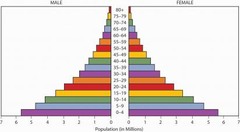
The Perfect Pyramid

answer
Philippines (RNI = 2.1%)
question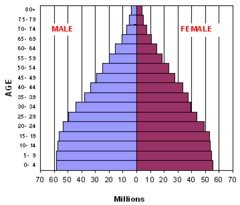
Starting to Slow Pyramid

answer
NIC, like Mexico, (RNI = 1.6%)
question
Column-Shaped Pyramid

answer
United States, (RNI = 0.6%)
question
Reducing Pentagon Pyrmaid
answer
Reducing Pentagon of Germany, RNI = -0.2%
question
ecumene
answer
the living space of humans on the earth's surface
question
Inter-regional and internal migrants
answer
move from one region of the country to another
question
transnational migration
answer
occurs when migrants move from one country to another
question
Step migration
answer
when people move up of hierarchy of locations, with each move to a more advantageous or economically prosperous place
question
Chain migration
answer
occurs when a pioneering individual or group settles in a new place, establishing a new migrant foothold, these people send information back to friends, family, and business contacts, the pioneer provides information on employment opportunities, access to markets or social networks, and encourages other to migrate to the location. Over time, more and more people move in and a growing immigrant community is established
question
periodic movement
answer
migrant workers in Mexico that move with the seasons exercise this kind of movement
question
remittances
answer
transmittals of money sent home by transnational migrants
question
Frostbelt to Sunbelt Shift
answer
With declines in manufacturing employment, especially in the northeastern United States, many people left the colder, more populated regions of the northeastern upper Midwest for new service employment opportunities and better climates in the South and Southwestern United States
question
Push factors
answer
specific things about the rural agricultural landscape and livelihood that force people off the farm
question
pull factors
answer
specific things about the city that draw people to the urban landscape



