Praxis II: Earth Science – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
The study of the Earth, its composition, its history, its place in the universe, and its natural processes
answer
Earth science
question
The spherical solid center of the Earth, composed largely of iron and nickel; about 700-800 miles in diameter
answer
Inner Core
question
A layer of liquid iron and nickel about 1, 400 miles thick
answer
Outer Core
question
A layer of hot, semi-solid rock about 1, 800 miles thick that has currents, causing the plates of crust on top of it to move
answer
Mantle
question
A series of solid plates that cover the Earth's surface, ranging from 5 to 30 miles thick
answer
Crust
question
The crust consists of _______ plates and _______ plates.
answer
Continental and oceanic plates
question
The movement of continental and oceanic plates is known as...
answer
Plate tectonics
question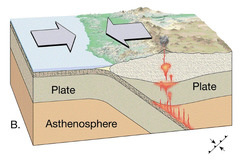
Colliding plates. Forms mountains, ridges, and volcanoes

answer
Convergent plates
question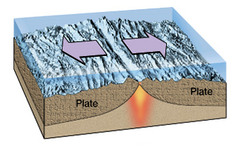
Separating plates. Forms bodies of water and new crust

answer
Divergent plates
question
Rubbing plates. Forms earthquakes.
answer
Transform boundary
question
Name the layers of the atmosphere.
answer
Exosphere, Thermosphere, Mesosphere, Stratosphere, Troposphere
question
Where does the Earth's heat come from?
answer
Radioactivity and solar energy
question
A heat source from the Earth's core, which is responsible for the movement of plates and thus the creation of landforms
answer
Radioactivity
question
Heats the Earth's surface
answer
Solar energy
question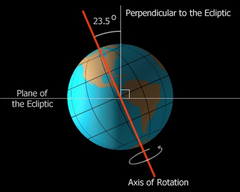
The ________ of the Earth on its _______ determines the amount of direct radiation from the sun at any given point on Earth.

answer
Tilt; axis
question
Responsible for night and day and the gain and loss of heat and sunlight that accompany those times of day
answer
Rotation of the Earth
question
The _________ of the Earth around the sun is responsible for the changing of the seasons.
answer
The revolution of the Earth
question
Type of rock formed through the cooling of magma (ex. granite, obsidian, pumice)
answer
Igneous
question
Type of rock formed when sediments (bits of eroded rock, sand, shells, fossils, etc.) are compressed into hard layers over time. (ex. sandstone, limestone, shale)
answer
Sedimentary
question
Type of rock formed igneous and sedimentary rocks that have morphed due to heat and pressure (ex. marble, quartzite, slate)
answer
Metamorphic
question
The breaking down of rock via natural forces such as water, ice, wind and the sun.
answer
Weathering
question
When pieces of the weathered material are carried away via wind and water.
answer
Erosion
question
Describes how rocks are created, changed, and destroyed.
answer
Rock Cycle
question
Shows how water circulates through the Earth's surface and atmosphere
answer
Water cycle
question
The study of how Earth has developed over time.
answer
Geological history
question
How old is the Earth?
answer
4 to 5 billion years old
question
Helps scientists to learn about different parts of the Earth's history by examining layers of rock.
answer
Geological record
question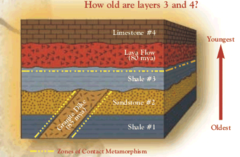
The law that says the oldest rocks are found at the bottom and newer rock are found at the top. This helps scientists to date events and create a timeline of earth's history.

answer
Law of superposition
question
The Earth's history is divided into two major time periods called eons. What are the two major time periods called?
answer
Precambrian and Phanerozoic Eon
question
The time period covering from the beginning of the Earth to the formation of life
answer
Precambrian Eon
question
The time period covering from the formation of life to present day
answer
Phanerozoic Eon
question
The time period approx. 542-251 million years ago. Rise of early life including trilobites, shellfish, corals, sponges, fish, land plants like ferns and trees, insects, amphibians, and reptiles
answer
Palezoic Era
question
The time period approx. 251-65 million years ago. Rise of dinosaurs, mammals, birds, and flowering plants. Also later included the extinction of dinosaurs.
answer
Mesozoic Era
question
The time period approx. 65 million years ago to present day. Rise of primates, including hominids and eventually modern humans
answer
Cenozoic Era
question
The study of fossils. These scientists can study the origins and history of life by looking at the fossils contained within the layers of rock that compose the Earth.
answer
Paleontology
question
States that the universe was created when a large collection of matter exploded, sending pieces of it that would become the planets, stars and other bodes expanding outward.
answer
The Big Bang Theory
question
A system of stars
answer
Galaxies
question
What galaxy does the Earth belong to?
answer
The Milky Way Galaxy
question
Astronomers (scientists who study celestial bodies) keep track of stars by organizing them into....
answer
Constellations
question
Within galaxies are __________, which consists of planets and other bodies orbiting a star.
answer
Solar system
question
Name the eight planets in order.

answer
Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
question
How long does it take the Moon to revolve around the Earth?
answer
28 days
question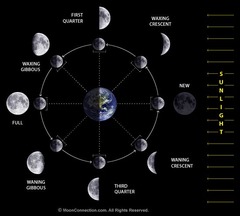
Depending on the position of the Moon and the Earth in relationship to the sun, the Moon looks different from Earth at different times of the month. These are called....

answer
Phases of the Moon
question
Special events in which the sun, Moon and Earth all line up in a direct path.
answer
Eclipses
question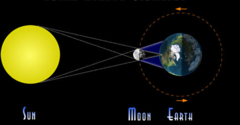
The Moon is directly between the sun and the Earth and casts a shadow on the Earth's surface

answer
Solar Eclipse
question
The Earth is directly between the sun and the Moon, blocking light from hitting the Moon
answer
Lunar Eclipse
question
Large rocky objects in space. There is a large ________ belt between Mars and Jupiter
answer
Asteroids
question
Smaller or metallic objects traveling through space

answer
Meteoroids
question
Meteoroids that enter Earth's atmosphere
answer
Meteorites
question
Streaks of light that trail behind meteorites as they burn in Earth's atmosphere

answer
Meteors
question
Icy bodies that form tails as they near the sun
answer
Comets
question
Scientists speculate that the continents were once all connected in a large land mass and they have separated over time to create out modern continents. What was this land mass called?
answer
Pangaea
question
What are long term changes the Earth has gradually gone through?
answer
- Plate tectonics which has resulted in significant changes to both the composition and the location of Earth's landforms. - Evolution of life forms from the simplest life to the rise of modern humans
question
Name the short term changes, patterns, and cycles.
answer
Water cycle, weather, seasons
question
The circulation of water through the Earth's surface and atmosphere
answer
Water Cycle
question
The state of the atmosphere at a particular time and place, including temperature, air movement, precipitation, and humidity
answer
Weather
question
Four phases of the caused by the Earth's revolution around the sun, marked by differences in weather patterns
answer
Seasons
question
Name some possible careers in the science field.
answer
Medicine, engineering, environmental science, astronomy, geology, computer science, science education, meteorology, biochemistry, etc.
question
List the steps of scientific methods.
answer
- Ask a question - Research a topic - Form a hypothesis - Experiment - Collect and analyze data - Draw conclusions
question
A group of related parts that are organized to create a unified whole, serving a common purpose.
answer
System (ex. ecosystems, body systems, solar systems, and mechanical systems)
question
A system that does NOT interact with other systems. It does not allow certain types of transfers in or out of the system.
answer
Closed System (ex. Earth is a closed system)
question
A system that continuously interacts with its surroundings.
answer
Open System
question
A way of describing behavior using statistics.
answer
Order (ex. probability)
question
Refers to ways of putting data into structures.
answer
Organization (ex. periodic table and the taxonomy for organism classification)



