SAT II Biology – Biochemistry – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion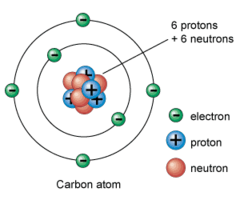
Atom

answer
Consists of: Protons (positively charged) and Neutrons (no charge) in the nucleus, electrons (negatively charged) outside the nucleus.
question
ground state
answer
electrons in the lowest available energy level
question
isotopes
answer
Atoms of one element that vary in the number of neutrons. Example: Carbon-12 and Carbon-14 are isotopes
question
radioisotopes
answer
radioactive isotopes
question
half-life
answer
the rate at which radioisotopes decay
question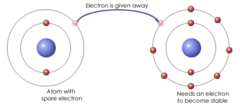
ionic bonds

answer
bonds that form when electrons are transferred.
question
anion
answer
an atom that gains electrons
question
cation
answer
an atom that loses electrons
question
molecule
answer
a group of two or more atoms held together by chemical bonds.
question
covalent bond
answer
bonds that form when electrons are shared
question
polarity
answer
the unequal distribution of charges on a molecule
question
nonpolar covalent bonds
answer
Bonds where electrons are shared equally. They are formed between any two atoms that are alike.
question
polar covalent bonds
answer
Bonds where electrons are shared unequally. They are formed between any two atoms that are unalike.
question
hydrogen bonds
answer
Weak bondsbetween the negative side of the water molecule oxygen and the positive side that the hydrogens create; bonds that hold water molecules together and result in high specific heat; good solvent properties and cohesion that results in surface tension. Keeps strands of DNA bonded together forming the double helix
question
Nonpolar molecules
answer
weak attractions such as Van der Waals. Carbon Dioxide is a nonpolar molecule
question
hydrophobic
answer
"water hating" Nonpolar molecules are hydrophobic and do not dissolve in water.
question
hydrophilic
answer
"water loving" polar molecules are hydrophilic and dissolve in water.
question
Characteristics of Water
answer
1. Water has a high specific heat 2. water has a high heat of vaporization 3. water has high adhesion properties 4. Water is the universal solvent 5. Water has strong cohesion tension (transpirational pull) 6. Ice floats because it is less dense than water
question
adhesion
answer
the clinging of one substance to another
question
cohesion tension
answer
molecules of water tend to stick to each other
question
capillary action
answer
the force of water rising in a thin tube due to cohesion and adhesion
question
mixture
answer
a material that is composed of two or more substances that are physically combined
question
heterogeneous mixture
answer
the different substances can be seen and separated out
question
homogenous mixture
answer
the different substances are evenly mixed and cannot be separated easily
question
solution
answer
is a homogenous mixture that appears to be a single substance but is composed of particles of two or more substances that are distributed evenly amongst each other.
question
solute
answer
the substance that is dissolved
question
solvent
answer
the substance in which the solute is dissolved
question
pH
answer
a measure of acidity and alkalinity (basic) of a solution
question
buffers
answer
substances that resist change in pH
question
acidic
answer
a solution that has a greater amount of H+ than OH- ions
question
basic
answer
a solution that has a greater amount of OH- than H+
question
macromolecules
answer
Four main classes of large biological molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids) made up of many smaller molecules and atoms.
question
monomers
answer
small chemical units that can join together with other small units to form larger units called polymers
question
polymers
answer
Large compounds formed from combinations of many monomers.
question
organic compounds
answer
Compounds that contain carbon atoms and are found in living things.
question
inorganic compounds
answer
Compounds that do not contain carbon; many are also essential to life.
question
isomers
answer
compounds with the same molecular formula, but with different structures. Example: glucose, galactose, fructose
question
monosaccharides
answer
monomer of carbohydrates Have chemical formula of C6H12O6. Examples: glucose, galactose, fructose.
question
disaccharides
answer
All have the chemical forumla C12H22O11. They consist of 2 monosaccharides joined by a process known as the Dehydration synthesis
question
maltose
answer
Glucose + Glucose
question
lactose
answer
Glucose + Galactose
question
sucrose
answer
Glucose + Fructose
question
hydrolysis
answer
opposite of dehydration synthesis, the breakdown of a compound with the addition of water
question
polysaccharides
answer
polymers of carbohydrates Examples: cellulose, chitin, starch, glycogen
question
cellulose
answer
polysaccharide that makes up plant cell walls
question
starch
answer
the way plants store carbohydrates
question
chitin
answer
polysaccharide that makes the exoskeleton in arthropods and the cell walls of mushrooms
question
glycogen
answer
the way animals store starch. Stored in humans in the liver and skeletal muscle.
question
lipids
answer
class of organic compounds that include fats, oils, and waxes. usually made up of one glycerol and three fatty acids
question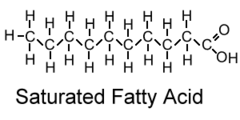
saturated fatty acids

answer
Contain only single bonds between carbon atoms. Come from animals, solid at room temperature, linked to heart disease.
question
unsaturated fatty acids
answer
Have at least one double bond between carbon atoms and the hydrocarbon chain. Are extracted from plants, are liquid at room temperature.
question
Lipid Functions
answer
1. energy storage 2. phospholipids make up cell membrane 3. some lipids are endocrine hormones
question
Steroids
answer
Fashioned on a backbone of four linked carbon rings and include cholesterol and hormones (testosterone, estrogen).
question
proteins
answer
macromolecules containing carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen; proteins are considered the building blocks of tissue
question
amino acids
answer
building blocks (monomers) of proteins; twenty kinds
question
Amino group
answer
-NH2
question
Carboxyl group
answer
-COOH
question
R-group
answer
used to represent one of 20 possible side chains found in amino acids of living systems, "variable group"
question
polypeptides
answer
repeating units of amino acids
question
peptide bonds
answer
bonds between amino acids, form polypeptides
question
dipeptide
answer
two amino acids combined
question
Primary structure proteins
answer
the order of amino acids in a protein
question
Secondary structure proteins
answer
the three dimensional shape that results from the hydrogen bonding between the amino and carboxyl groups of adjacent amino acids
question
tertiary structure proteins
answer
additional three dimensional shaping of a protein that dominates the structure of globular proteins
question
Quaternary structure proteins
answer
The particular shape of a complex protein, defined by the characteristic three-dimensional arrangement of its constituent subunits, each a polypeptide.
question
enzymes
answer
a chemical that speeds up chemical reactions within a living cell
question
coenzyme
answer
a small molecule (not a protein but sometimes a vitamin) essential for the activity of some enzymes
question
cofactor
answer
Any organic or inorganic substance that is needed for the operation of an enzyme.
question
energy of activation
answer
the amount of energy needed to begin a reaction
question
substrate
answer
the chemical that an enzyme works on
question
induced-fit model
answer
describes how enzymes work, As the substrate enters the active site, it induces the enzyme to alter its shape slightly so the substrate fits better
question
denaturation
answer
when proteins lose their natural shape due to change in temperature or pH
question
prions
answer
A misfolded, infectious protein that are normally found in the brains of mammals and cause several brain diseases. (Mad Cow)
question
nucleic acids
answer
macromolecules containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon and phosphorus and are associated with organism's genetic code
question
nucleotides
answer
building blocks (monomers) of nucleic acids
question
DNA
answer
Deoxyribonucleic Acid. Double stranded chain. Deoxygenated (deoxyribose) 5 carbon sugar.
question
RNA
answer
Ribonucleic Acid. Single stranded chain. Oxygenated (ribose), 5 carbon sugar.
question
biochemistry
answer
Chemistry of life, the study of chemical substances and reactions within living organisms.
question
alpha helix
answer
A spiral shape constituting one form of the secondary structure of proteins, arising from a specific hydrogen-bonding structure.
question
beta sheet
answer
secondary structure of proteins with a pleated, ribbonlike shape



