Pharm Test unit 2 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Integumentary system
answer
The skin. We have covered this in med surge already. It is the body's largest organ, and the first line of defense against pathogens. Injuries to the skin provide opening for infection.
question
Integumentary disorders are classified as
answer
-Infectious -Inflammatory -Cancerous
question
Medications prescribed for the integumentary system depends on
answer
Classification. They can be topical -creams- (mild acne, psoriasis, cold sores) or systemic -pills- (Severe Acne, Infection)
question
Acne
answer
Bacterial skin disorder affecting sebaceous glands. Skin produces bumps called pustules.
question
In adolescents, acne is commonly caused by
answer
Hormones
question
In adults, acne is commonly caused by
answer
bacteria (commonly Propionibacterium acnes, which grows inside the sebaceous glands and makes an irritating, acidic substance).
question
Black Heads (Medically known as Comedos)
answer
oil glands plugged with melanin granules
question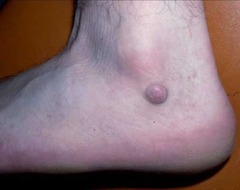
Nodules

answer
Inflammation deep below the skin. Can cause pain, deformity, and scarring.
question
Topical meds
answer
Creams, Gels, lotions
question
benzoyl peroxide
answer
Over the counter. inhibits bacterial growth
question
benzoyl peroxide side effects
answer
peeling,erythema,edema.
question
Contraindication for all of these meds
answer
Hypersensitivity (allergic reaction)
question
Retinoids
answer
Contain vitamin A which increases the body's resistance to infection (acne) by reducing the oil production that clogs pores. Also reduces keratinization
question
examples of retinoids
answer
tretinoin,tazarotene
question
retinoids side effects
answer
photosensitivity (just means sensitivity to light), Local reactions (topical)
question
retinoids contraindications
answer
pregnancy. retinoids are class C meaning that the potential risks of taking it during pregnancy should be outweighed by the benefits
question
Oral contraceptives
answer
Have been shown to be effective in treating acne. Can help stop acne from forming by reducing androgen production.
question
Severe acne
answer
Treatments - Sulfur (removes infected skin) -antibiotics (Tetracyclines. Not to be taken with dairy products, which can inhibit absorption.) -Keratolytics (removes infected skin)
question
Keratolytics
answer
Examples: salicylic acid, ammonium lactate
question
Keratolytic Side effects
answer
burning irritation tinnitus (ringing or buzzing in ears) dizziness ototoxicity (toxic to the ear) headaches (oral)
question
Keratolytic contraindications
answer
prolonged use irritated skin moles birthmarks warts with hair growth mucous membranes
question
Rosacea
answer
Bacterial skin disorder- small bumps and reddened skin irritation without pus. aggravated by sunlight, stress, hot temperatures, alcohol, spicy food, hot beverages. The treatment is same as acne. So think of this as just acne without the pust
question
Rosacea appearance
answer
flushed, especially on the nose and cheek.
question
Impetigo
answer
Common in children after URI where child excessively wipes their nose causing a break in skin for bacteria entry.
question
Impetigo Treatment
answer
Antibiotics- topically, with severe cases requiring the systemic route. corticosteroids (topical) with examples being hydrocortisone and dexamethasone -side effects are burning, itching, and irritation. -Contraindicated in pregnancy
question
Scabies
answer
Parasitic Infestation of the human itch mite that burrows into skin and lay eggs ›Treated with scabicides(topical) - permethrin
question
Pediculosis
answer
Parasitic infestation caused by lice. Nits: lice eggs- need to be combed out and may need retreatment after hatched if not removed ›Treated with pediculicides (topical) - lindane -A neurotoxin
question
Scabicides and pediculocide side effects
answer
rash, redness, itching, and burning -Contraindication: hypersensitivity
question
Viruses
answer
Smaller than bacteria and depends on host cell to grow and reproduce. This makes it hard to kill
question
Human papillomavirus (HPV)
answer
Responsible for most of cervical cancer in women and venereal warts in men and women
question
HPV treatment
answer
cryosurgery (liquid nitrogen) to freeze warts, salicylic acid to shed skin or HPV vaccine to prevent virus
question
HSV-1
answer
Causes cold sores or fever blisters on lips and mouth. This is above the waist
question
HSV-2
answer
Sexually transmitted virus › Affects genital mucosa. This is below the waist.
question
Herpes zoster (Shingles)
answer
Reactivation of chickenpox virus
question
OTC antivirals for HSV-1
answer
Reduces duration of episodes › Examples: docosanol (Abreva) -Side effects: acne, itching, rash -Contraindications: Hypersensitivity
question
Fungi- include Tinea and candidiasis
answer
-Dermatophytes invade keratin and can infect hair, nails and skin -Topical antifungals may be used when the infection is present on the trunk, extremities, groin, or feet -If infection is on scalp, oral agents may be needed
question
Examples of antifungals
answer
clotrimazole, terbinafine -Side effects: Burning, stinging, pruritus (severe itching), erythema -Contraindication: Hypersensitivity
question
Candidal Infections
answer
Caused by Candida Albicans ›Associated with pruritic red rash that may be painful ›If it occurs in the mouth it is called thrush -White plaques are present in mouth ›Treatment - Nystatin (topicalor oral)
question
Burns
answer
- Damage skin by removing water causing it to blister or removing skin entirely - Classified as 1st, 2nd, or 3rd degree
question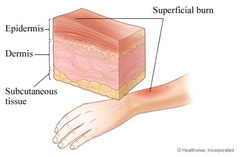
1st degree burn

answer
Epidermis › Most common is sunburn › Skin becomes red and painful to touch › Treatment: - Non pharmalogicalapplication of cool water for 20 minutes and aloe vera - Pharmalogical - lidocaine
question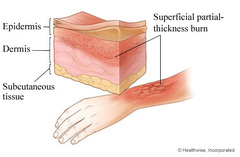
2nd degree burn

answer
Epidermis and dermis ›Blister forms over burn and yellow in appearance ›Treatment -Cover with sterile dressing -silver sulfADIAZINE
question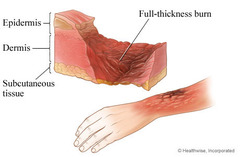
3rd degree burn

answer
affects all layers of skin plus subcutaneous tissue and possible muscle and bone -Great risk for infection and fluid loss
question
3rd degree burn treatment
answer
›Maintaining airway, administering IV fluids ›Antibiotics to prevent infection ›Medication to debride wound and cover with sterile non-adhering dressing -Examples - collagenase ›Medication to stimulate new tissue granulation -Examples- becaplermin
question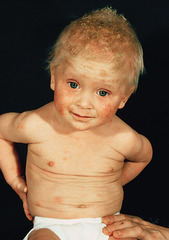
Atopic dermatitis: Eczema

answer
-Allergic disorder causing cutaneous inflammation -Extremely dry, itchy patches of skin -Treatment ›Avoidance of allergens and maintaining hydration ›corticosteroids (topical) -Examples- hydrocortisone acetate Side effects: Burning, itching, irritation Contraindications: Hypersensitivity, pregnanc
question
Immunomodulators
answer
Modify skins immune reactions -Examples - pimecrolimus, tacrolimus Side effects: Burning, pruritus Contraindications: Hypersensitivity, pregnancy, breastfeeding
question
Oral antihistamines
answer
Examples - diphenhydramine Side effects: drowsiness, dizziness, blurred vision, photosensitivity, chest tightness, wheezing ›Contraindications: Hypersensitivity, Acute attacks of asthma, Lactation;
question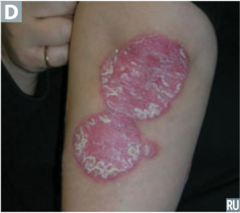
Psoriasis

answer
Chronic inflammatory skin disease Life cycle of skin shortened, thus dead cells cannot be shed quickly enough causing build-up of skin cells on surface. -Flaky white appearance atop a reddened plaque
question
Psoriasis Treatment
answer
Corticosteroids (topical) - Low-dose antihistamines - Salicylic acid -Phototherapy: UV light - Antipsoriatic agents › Examples - Coal tar, calcipotrine, methotrexate (used for severe disease) injectable or oral -Side effects : irritation to surrounding skin; discoloration of skin, hair, or fabrics -Contraindications: Hypersensitivity, use on the face, renal disease, pregnancy, breastfeeding, hypercalcemia (calcipotriene)
question
Cancerous skin disorders
answer
Warning signs: if a nevus (mole) changes colors, grows, or its borders become irregular Good prognosis with early detection
question
Basal Cell Carcinoma
answer
- Most common form - Rarely metastasizes - Treatment › Surgery: Liquid nitrogen › Topical preparations - fluorouracil (5-FU- affects rapidly dividing cancer cells - imiquimod- stimulates the immune system
question
Squamous cell carcinoma
answer
-Malignant keratinocytes -Can metastasize -Treatment ›Surgical removal (Treatment of choice) ›Radiation therapy possible
question
Malignant melanoma
answer
-Unpredictable cancer -Spreads through the lymphatic system and blood -Treatment ›Surgery ›Radiation ›Chemotherapy
question
Nursing Assessment
answer
Assess for allergies. › Assess for pain. › Inspect skin for open areas, inflammation, swelling, drainage, itching, rash. - In dark-skinned patients, inflammation may not be visible; palpate skin for warmth. › Measure length and width of affected area. - Include depth in wounds.
question
Ointments
answer
are more occlusive and preferred for dry, scaly lesions.
question
Creams
answer
should be used on oozing wounds, or skin areas that rub together (axilla, thighs, nares, skinfolds of breasts, etc.).
question
Gels, aerosols, lotions
answer
are useful in hairy areas. - Separate hair and apply a small amount to affected area; rub in gently.
question
Patient teaching with topicals
answer
Wash hands before and after drug application. › Skin should be clean and dry before applying medication. › Avoid exposure to sunlight during drug therapy (for photosensivity) › Notify physician of any skin reactions to the medication. › If ordered, apply dressing after application of drug. › Teach patient the proper disposal of contaminated dressings. › Women of childbearing age should be warned of the possible birth defect risks regarding certain integumentary drugs.
question
Minerals that bone store
answer
calcium, magnesium, and potassium. Endocrine system controls these minerals and must be healthy
question
Thyroid Gland
answer
Produces calcitonin
question
Parathyroid Gland
answer
Secretes parathyroid hormone. Whats the point of this even being on here duhhhh
question
Medications used for musculoskeletal disorders can be placed into two categories:
answer
- Those to treat muscular disorders - Those to treat bone disorders Hell that's what musculoskeletal even stands for is muscle and bone
question
Ailments that orginate in the brain
answer
- Cerebral palsy - Stroke - Multiple sclerosis
question
Ailments that originate in muscle tissue itself
answer
- Muscle injuries - Muscular dystrophy Again it's in the name, whats the point
question
Muscular Symptoms
answer
- Muscle spasms - Dystonia: abnormal tension
question
Treatments for them muscular symptoms
answer
- Muscle relaxants and Antispasmotics › Both classifications work to inhibit neurological activity that causes muscle spasms or rigidity Examples - baclofen, cyclobenzaprine, dantrolene, metaxalone -Side effects - dizziness ,drowsiness, confusion, dry mouth, GI disturbances, and weakness -Contraindication -Asthma, muscular dystrophy, myasthenia gravis, pregnancy and breast feeding diazepam may be given to maximize effectiveness of above medications duloxetine decreases stress felt with chronic pain
question
Antispasmotics
answer
Work on muscle itself botulinum toxin type A- a toxic substance that causes food poisoning; lower doses act by paralyzing muscle - Used to treat › Chronic migraines › Limb spasticity › Abnormal head position › Neck pain - Must be repeated every 3-6 months - Usually administered with local anesthetic because toxin causes pain
question
Myasthenia gravis
answer
- Progressive, autoimmune disease with skeletal muscle fatigue and weakness and loss of acetylcholine receptors, causing a breakdown in communication between nerves and muscles - Treatment: cholinesterase inhibitors to facilitate acetylcholine accumulation - No cure, but treatment can reduce symptoms
question
Example of Myasthenia gravis treatment
answer
- neostigmine -Side Effect - increased saliva, weakness, muscle cramps, diarrhea, frequent urination -Contraindications - Hypersensitivity, peritonitis, mechanical intestinal or urinary obstruction
question
Fibromyalgia
answer
A difficult to manage chronic disorder of pain in muscles and soft tissue surrounding joints - Treatment › Decreasing contributory factors (lack of exercise, etc.) › Physical therapy › Antidepressants - duloxetine, milnacipram ›Antiepileptic - pregabalin (LYRICA) › Anti-inflammatory medications - ibuprofen ›Analgesics - acetaminophen Remember Lyrica
question
Skeletal system
answer
› Comprises 206 bones › Repository for minerals such as calcium, potassium, and magnesium › Calcium needed for nerves, bones, and muscles to function properly
question
Endocrine System
answer
Controls deposit of minerals - Thyroid produces calcitonin: allows calcium to remain in bone - Parathyroid gland: produces parathyroid hormone, which increases calcium in the blood (loss of calcium in bones) - Both work together to keep balance - If either gland fails, musculoskeletal disorders result
question
Risk Factors for hypocalcemia
answer
- Smoking - Lack of exercise - High alcohol consumption (Nursing school ayyyy lmao) - Anorexia nervosa - Estrogen or testosterone deficiency - Poor nutrition - Obesity
question
Osteomalacia in adults and rickets in children
answer
Calcium levels are low, it is not stored in bones, leading to soft, brittle deformed bones
question
Osteoporosis
answer
Occurs with a lack of calcium - Holes are created in bones leading to a sponge-like appearance - Bones break easily
question
Abnormal Calcium levels
answer
Treatment: - Calcium supplements - Vitamin D (assist in absorption of calcium) - calcitonin - Available in nasal spray or injectable form. It is naturally produced by thyroid to deposit calcium into bones
question
calcitonin salmon
answer
Weird name - Side effects - Rhinitis, nasal irritation (nasal spray); hypertension, dizziness, injection site reactions, nausea, vomiting - Contraindication - hypersensitivity, pregnancy, and breastfeeding
question
Estrogen Replacement Therapy
answer
- inhibit bone resorption of calcium › Examples- estradiol - Side effects - breast and uterine cancer, blood clots - Contraindications- history of breast or uterine cancer, pregnancy, thromboembolic disease
question
Bisphosphonate
answer
Similar to estrogen, with fewer side effects › Examples- teriparatideacetate - Side effects -Headache, abdominal pain, bone pain -Contraindications- Hypersensitivity, hypocalcemia, esophageal stricture or achalasia
question
Paget's Disease
answer
Weak and abnormally formed bones from excessive breakdown and formation of bone tissue. Pain, fractures and deformity is the result of the disease. - Treatment › Calcitonin and bisphosphonates › Calcium and vitamin D supplements as needed › NSAIDS › Exercise is encouraged to maintain bone health and joint mobility
question
Osteoarthritis
answer
erosion of bone where bones meet at the joint
question
Rheumatoid Arthritis
answer
chronic, autoimmune, progressive, systemic inflammatory disease that destroys synovial joints and other connective tissue, including major organs - Autoimmune condition
question
Treatment For Arthritis
answer
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) › Examples- aspirin, diclofenac with misoprostol, ibuprofen, naproxen › Side effects - GI ulcers and bleeding, GI upset, headache, tinnitus and hearing loss from toxicity, vision disturbances › Contraindication-Anemia, asthma, children with viral infections (aspirin), clotting disorders, disorders of the CV and GI systems , GERD, lactation, liver and kidney failure, pregnancy, sulfonamide hypersensitivity, thyroid disorders
question
Gout
answer
Form of arthritis caused by build-up of URIC ACID in the joints. Uric acid is the byproduct of food metabolism and is excreted via the kidneys. Too much uric acid produced or not enough secreted causes this condition. - Sudden, severe attack of pain, inflammation and joint tenderness (usually joint of big toe) - Primarily affects men middle aged or older (Amat)
question
Gout Treatment
answer
During acute attack - NSAIDs in high doses to halt attack and lower doses to prevent future attacks - For those unable to take NSAIDs: colchine is utilized for the pain of gout (Remember this and why they can't take nsaids) - Glucocorticoids › After acute attack ended - NSAIDS in lower doses to prevent future attacks - Anti-gout medications are given to lower uric acid levels in body - Examples - allopurinol, febuxostat - Side effects: Acute gouty attacks ,headache, GI symptoms - Contraindications-Hypersensitivity, uric acid kidney stones ,blood dyscrasias (disease/disorder), active peptic ulcer
question
NSAIDS
answer
› Reduce inflammation in gout, osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis › Concerns - Increased GI bleeding - Renal and cardiac damage with long-term use › Take only as ordered › Long-term use monitored closely › Aspirin and other analgesics used topically and orally for pain - Topical medications containing medications such as menthol, salicylate and tromaline: Absorbine, Ben-Gay, Icy Hot, and capsaicin
question
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) Inhibitors
answer
› Decrease the production of prostaglandins that cause pain and inflammation › Generally NSAIDs block both COX-1 & COX-2 enxymes › COX-2 inhibitors only block the COX-2 enzymes allowing the COX-1 enzyme to continue to be produced. COX-1 enzymes provide protection to the stomach and intestines reducing the risk of ulceration and GI bleed.
question
celecoxib
answer
Example of a COX-2 inhibitor. Notice it has cox in the name - Side effects-Headache, insomnia, rash, abdominal pain, diarrhea, dyspepsia, upper respiratory infection - Contraindications- Hypersensitivity to sulfonamides Taking this May increase risk of heart problems. Remember that -Contraindications - Sulfa drug allergy. Remember that too
question
Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)
answer
› Used in rheumatoid arthritis when other drugs ineffective › Suppresses the autoimmune response › Also suppresses immunity systemically › May slow down joint destruction although not a cure
question
gold aurothioglucose (Solganal)
answer
A DMARD. Given by injection or orally. - Works best in early stages of disease - Rarely used because newer drugs more effective
question
Rheumatrex (methotrexate), Neoral (cyclosporine), and Azulfidine (sulfasalazine)
answer
Newer, more effective DMARDs - Side effect- Hepatotoxicity, bone marrow suppression, GI disturbances, blood dyscrasias, pruritus ,rashes - Contraindications- Hepatic or renal impairment, pregnancy, breastfeeding, active infection, immunosuppression, known hypersensitivity, lupus, pulmonary fibrosis
question
Drugs that DMARDS interact with
answer
Vaccines, NSAIDs, probenecid, corticosteroids Remember this, I bet you anything it will be on the test.
question
Corticosteroids
answer
Mimic cortisol produced by adrenal gland to reduce inflammation › Used short-term due to decreased ability to fight infection during use › Examples - Decadron (dexamethasone) - Medrol (methylprednisolone)
question
Phantom Limb Pain
answer
Impulse originating in brain and spinal cord does not recognize absence of limb › Some pts report pain diminishes over time others experience a lifetime of pain
question
Phantom limb pain treament
answer
- Tricyclic antidepressants: alter chemical messengers and help with sleep › Elavil (amitriptyline) › Pamelor (nortriptyline) Notice those end with lines - Anticonvulsants: quiet damaged nerves to prevent or slow pain signals › Tegretol (carbamazepine) - Narcotics: dull pain perception center of brain › Roxanol (morphine)
question
Musculoskeletal things to assess
answer
› Assess drug allergies. › Assess use of OTC drugs, herbs, etc. › Assess factors that interfere with activities of daily living (ADLs). › Assess pain and inflammation in joints. - Location, onset, intensity, duration › Inspect joints for immobility, deformities, limits of movement, swelling, and inflammation. Assess labs; renal, hepatic, and hematological functioning prior to NSAIDs, DMARDs, and anti-gout drugs.
question
NSAID nursing implications
answer
- May cause GI bleeding, renal and cardiac damage with long-term use › Monitor CBC, BUN, sedimentation rates, and liver enzymes › Monitor for blood in stool and emesis - Monitor for adverse effects and toxicity - Therapeutic effects may take 3 to 4 weeks
question
DMARD nursing implications
answer
- Suppress the immune system › Assess labs: CBC, hematocrit/hemoglobin, platelets - Assess for toxicity of DMARDs. › Monitor for elevation of liver function tests. - Assess for toxicity of gold products. › Decreased Hgb level, WBC level <4,000/mm³, platelets <150,000/mm ³ › Hematuria, proteinuria, itching, severe diarrhea
question
Cox-2 Inhibitor Nursing Implications
answer
- Assess patients for allergy to sulfonamides, aspirin, or NSAIDs. - Assess patients for skin rash frequently during therapy. › Discontinue immediately at first sign of rash; may be life-threatening; Stevens Johnson syndrome may develop
question
Anti-gout nursing implications
answer
- Monitor joint pain and swelling. - Monitor serum and urine uric acid levels. - Monitor hematological, renal and liver function. › May ↓CBC, platelets › May ↑BUN, serum creatinine, and Cr may indicate nephrotoxicity › May ↑serum alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin, AST, ALT levels
question
Bisphosphonates nursing implications
answer
- Assess serum calcium levels before and periodically during therapy. - In Paget's disease, monitor alkaline phosphatase before and during therapy. - In osteoporosis, assess for low bone mass before and during therapy
question
Patient Teaching
answer
› Advise patient to not crush or chew sustained-release or enteric-coated tablets. › Instruct patient about adverse effects of aspirin, such as GI upset, GI bleeding, heartburn, flushing of face, bruising, rash. - Black tarry stools, gum bleeding, petechiae, or rash should be reported to health-care professional immediately. Physician may discontinue NSAIDs and aspirin several days before surgery (including dental surgery)
question
How to reduce GI irritation caused by NSAIDS
answer
Take with food, milk, or antacids to decrease GI irritation.
question
DMARD patient teaching
answer
Advise patient taking DMARDs to notify health-care professional if the following occur: - Skin rash, sore throat, fever, mouth sores, unusual bleeding or bruising, wheezing, hives › Instruct patient to report adverse effects of gold injections. - Headache, lethargy, pain at injection site
question
Anti Gout patient teaching
answer
Advise patient taking anti-gout medications to increase fluid intake, and an alkaline diet may be ordered. - Fruits, except cranberries, prunes, plums - Vegetables, except corn - Milk - Nuts (almonds, chestnuts)
question
bisphosphonates patient teaching
answer
- On the importance of taking these medications exactly as directed. - To eat a balanced diet and consult with health - care professional about the need for calcium and vitamin D supplements. - To discontinue medication and notify healthcare provider of pain or difficulty swallowing, new/worsening heartburn, retrosternal pain.
question
The Nervous System
answer
› Divided into *Central nervous system (CNS) › Brain and spinal cord - neurons *Peripheral nervous system (PNS) › Include autonomic nervous system
question
Nervous system medications
answer
› Used to treat - Pain - Anxiety - Depression - Mania - Insomnia - Convulsions - Schizophrenia › Act on CNS and peripheral nervous system › Most act at synapse to adjust message by neurotransmitters › Most cross blood-brain barrier - Serious side effects result
question
Peripheral Nervous System
answer
› Somatic nervous system: voluntary - Muscles we have conscious control over › Autonomic nervous system: involuntary - Controls internal organs - Broken down into › Sympathetic nervous system: controls "fight or flight response" › Parasympathetic nervous system: helps body to rest and relax - Acetylcholine and norepinephrine are the two main neurotransmitters that affect the autonomic nervous systems
question
Adrenergic
answer
a nerve cell that releases epinephrine or norepinephrine, which excites the body
question
Cholinergic
answer
a nerve cell that releases acetylcholine which relaxes the body
question
Adrenergic & Cholinergic
answer
› Both are naturally occurring substances - If not adequate to meet the body's needs, artificial equivalents are provided through medication
question
Autonomic Drugs
answer
stimulate the sympathetic nervous system (excite) - Drugs are called Sympathomimetics or adrenergic antagonist
question
Cholinergic Drugs
answer
stimulate the parasympathetic nervous system (calm) - Drugs are called Parasympathomimetics or cholinergic agonist
question
Sympathomimetics (adrenergic agonists)
answer
- Used when body needs to be excited as they mimic the sympathetic nervous system - Stimulate the "fight or flight response" › Restore heart rhythm during cardiac arrest › Increase blood pressure during shock › Constrict capillaries if patient is bleeding › Dilate bronchioles of asthmatic › Dilate pupils for eye procedure
question
Examples of sympathomimetics
answer
Levophed (norepinephrine), epinephrine › Side effects - Chest pain, fast heartrate, headache, in-crease blood glucose,nervousness, tissue death, tremors › Contraindication - Brain damage, CV and heart problems, glaucoma, hyperthyroidism › Interactions Adrenergic blockers ,CNS drugs - Use cautiously in patients with hypertension, MI, Afib, hypovolemia, children, pregnant and breastfeeding women.
question
Adrenergic Blockers
answer
- Block the action of adrenergics - Have a parasympathetic effect - Used to calm (slow heart rate and relax blood vessels) › Treat cardiac arrhythmias › High blood pressure › Migraine headaches › Chest pain
question
Adrenergic blockers are broken into these two groups based on muscles affected
answer
Alpha blockers and Beta blockers
question
Alpha Blockers
answer
- Affect vascular smooth muscle - Treat hypertension and BPH › Examples - alfuzosin (uroxatral), doxazosin (Cardura), prazosin (minipress), tamsulosin (Flomax), and terazosin (hytrin)
question
Beta Blockers
answer
- Block epinephrine - Slows heart rate and force - Treats: hypertension, migraines, glaucoma › Examples - acebutolol (spectral), atenolol (Tenormin), bisoprolol (zebeta), metoprolol (Lopressor), nadolol (corgard), nebivolol (bystolic), propranolol (Inderal LA)
question
Alpha & Beta Blockers
answer
- Side effects - Confusion, decreased blood pressure, blood glucose, energy, heart rate - Contraindications- Asthma, atrioventricular block (heart block),chronic heart failure, diabetes, low blood pressure - Interactions- Alcohol, digitalis (digoxin), epinephrine, insulin, MAO inhibitors (drugs that inhibit the actions of MAO), theophylline, TCAs
question
Parasympathomimetics (cholinergic agonists)
answer
- Mimic parasympathetic system - Rarely used due to severe decrease in heart rate and constriction of respiratory passages › Examples - Nerve gas - Pilocarpine(Pilopine) › Used to treat open-angle glaucoma › Increases drainage of fluid out of the eye reducing ocular pressure › Must be stopped several weeks before surgical procedures d/t increased risk of intraoperative breathing problems - Side effects-Bronchospasm; decreased heart rate, respirations, blood pressure; increased salivation, tears, and sweating; muscle cramps and weakness -Contraindications-Asthma, benign prostatic hypertrophy, cardiac disease, GI disorders, hyperthyroidism - Interactions Quinidine, procainamide
question
Anticholinergics or cholinergic blockers
answer
- Inhibit parasympathetic nervous system - Promote "fight or flight" symptoms - Dry secretions - Used to treat › Asthma › Motion sickness › Preoperative relaxation › Neuromuscular blocking of spasms › Antidotes for insect stings › Cholinergic crisis - Extreme muscular weakness and respiratory depression - Commonly seen in patients with myasthenia gravis
question
Cholinergic Example- Atro-pen(atropine
answer
› Side effects - Blurred vision, confusion, decreased GI motility, dilation of pupils, drying of secretions, fever, flushing, headache, increased heart rate › Contraindications- Asthma, cardiac arrhythmias, COPD, GI or GU obstruction, glaucoma, hypertension › Interactions - digoxin, nitroglycerin, TCAs
question
Analgesics
answer
Reduce pain without eliminating feeling - Salicylates › Relieve mild-to-moderate pain › Reduce inflammation and fever › Improve CV flow by decreasing inflammation in blood vessels
question
Aspirin
answer
ANALGESIC › Causes GI distress › Not to be used in children (Reyes syndrome- remember this) - Methyl salicylate (BenGay) › Topical anti-inflammatory used to irritate surface of skin which increases blood flow, thus decreases pain › Side effects - Coma, depression, dizziness, headache, drowsiness, increased bleeding time, bruising, GI bleeding, liver and kidney disorders, tinnitus, rash › Contraindications- Asthma, bleeding disorders, lactation, pregnancy, vitamin K deficiency › Interactions- Alcohol, antacids, anticoagulants, heparin, NSAIDs, insulin
question
- acetaminophen (Tylenol
answer
ANALGESIC Decreases pain and fever › NO anti-inflammatory effect › Contained in many combination products such as cold medications › Combined with narcotics to treat moderate to severe pain - Oxycodone with acetaminophen (Percocet) - Side effects-Rash, urticaria (high dosages can cause liver failure) - Contraindications- Alcohol abuse, hypersensitivity, liver disease, malnutrition - Interactions- *Alcohol*, oral contraceptives, phenytoin, loop diuretics (water pill. Example-lasix-)
question
ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil)
answer
ANALGESIC NSAID › Reduce pain, inflammation, and fever › May be combined with narcotics to relieve moderate to severe pain - Oxycodone with ibuprofen (Combunox) - Side effects - Blurred vision, constipation, dizziness, drowsiness, dyspepsia, edema, GI bleeding, headache, hepatitis, irregular heart rate, kidney disorders, prolonged bleeding, psychic disturbances, rash, tinnitus - Contraindications- Active GI bleeding, CV disease, hypersensitivity, liver disease, pregnancy, renal disease, ulcer - Interactions- Corticosteroids, salicylates, cyclosporine, anticoagulants, beta blockers, digoxin. So pretty much every other medicaiton we have been over, lol
question
Narcotics
answer
- Stronger pain relievers - Suppress the central nervous system - Active ingredient in most is opium - Excess can cause › Decreased blood pressure, this may lead to risk of falls or death › *Decrease in respiration*
question
Opioid Analgesics
answer
- Strongest pain relievers › Examples - morphine - codeine - fentanyl - Addiction potential with long-term use due to feelings of euphoria - Rarely addictive in patients who take them for relief of acute pain for a short period of time - Severe side effects › Side Effects- Decreased blood pressure, heart rate, and respirations; agitation, blurred vision, confusion, constipation, flushing, headache, over sedation, rash, restlessness, seizures, urinary retention › Contraindications- Lactation and pregnancy, patients with head injury, CNS depression, COPD, hypothyroidism, liver or kidney disease; used with caution in addicted patients, children, elderly patients, hypersensitive patients, suicidal patients › Interactions- Alcohol, antiemetics, antihistamines, antihypertensives, antiarrhythmics, muscle relaxers, psychotropics, sedative-hypnotics
question
Limbic System of brain
answer
Integral to emotions, memory, and level of alertness - If not functioning problems occur with anxiety, insomnia, alertness, or seizure
question
Anxiolytic medications (anxiety meds)
answer
- Reduce intensity of fears, dangers, and/or tension - Calming effect from mild sedation to coma - CNS depressants › Treat anxiety and restlessness
question
Benzodiazapines
answer
- Treat anxiety, seizures, alcohol withdrawal symptoms, and muscle relaxation › Examples - Ativan (lorazepam) - Valium (diazepam) - Xanax (alprazolam) › Side effects - Agitation, amnesia, bizarre behaviors, con-fusion, decreased white blood cell count, depression, drowsiness, hallucinations, headache, lack of coordination, lethargy, over sedation, sensitivity to light, tremors › Contraindications- Not used in children, decreased vital signs, depression, lactation, pregnancy, suicidal ideation; observe for addiction and for evidence that the patient is considering suicide › Interactions - Alcohol, antiemetics, antihistamines, analgesics, CNS depressants, digoxin, *grapefruit juice*, muscle relaxants, phenytoin, psychotropics
question
Insomnia Medications
answer
- Barbiturates: induce sleep by depressing CNS (slowing HR and respirations) - Non-narcotic benzodiazepine hypnotics › Promote sleep with few side effects (do not affect entire CNS) › Possible addiction risk › Examples - Ambien (zolpidem) Lunesta(eszopicolone) › Side effects - Outgoing or aggressive behavior, confusion, agitation, hallucinations, worsening of depression, suicidal thoughts or actions, memory loss, anxiety, sleep activity › Contraindications - Hypersensitivity to ingredients, pregnancy, lactation, children › Interactions - Alcohol, paroxetine, lorazepam, olanzapine
question
› Barbiturates and anti-seizure medications
answer
-- Hydantoins such as phenytoin (Dilantin)-- › Delay sodium from crossing neural membranes, calming cells › Drug of choice for tonic-clonic (grand mal) and partial seizures --- Barbiturates such as phenobarbital-- › Used for tonic-clonic and febrile seizures --Succinimides such as ethosuximide (Zarontin) -- › Delay calcium moving over neurons to relax nerve cells › Drug of choice for absence (petit mal) seizures
question
- Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)
answer
› Naturally occurring neurotransmitter inhibitor, if present will decrease seizure activity › Example of this new drug is vigabatrin (Sabril)
question
- Benzodiazepines such as diazepam (Valium)
answer
Intensifies effect of GABA transmitters in brain
question
Other anti-seizure medication
answer
› Lamictal (lamotrigine) › Gabitril (tiagabine) › Topamax (topiramate) › Tegretol (carbamazepine) › Some medications that reduce seizures manage alcohol withdrawal symptoms by reducing anxiety symptoms. › Side effects - Multiple side effects different for each medication › Contraindications - Dilantin: hypersensitivity, caution in pregnancy, impaired liver function; Luminal: blood disorder porphyria, patients taking GHB; Zarontin: hypersensitivity to succinimides; Sabril: none Lamictal: hypersensitivity; Gabitril: hypersensitivity; Topamax: hypersensitivity, glaucoma; Tegretol: history of bone marrow depresion, hypersensitivity Valium: hypersensitivity, children under 6 months old, myasthenia gravis, severe respiratory or hepatic insufficiency, sleep apnea, acute narrow-angle glaucoma Interactions - Alcohol, salicylates, succinimides, sulfonamides, valproic acid, oral contraceptives, rifampin and many more than possible to list. Imagine that
question
CNS Stimulants
answer
- Attention deficit disorder (ADD) and attention deficit with hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) - Common in both adults and children › Ineffectiveness of impulse control › CNS stimulants such as amphetaminedextroamphetamine (Adderall), pemoline (Cylert), and methylphenidate (Ritalin) have opposite effect of calming patient and increase ability to focus - Works as a stimulant in those without ADD or ADHD
question
Amphetamines such as phentermine (Zantryl)
answer
› Prescribed for obesity › Given 30-60 min before meals to increase metabolism › Side effects - Nervousness, insomnia, irritability, seizures or psychosis; increased heart rate, blood pressure, and irregularity of heart rhythm; dizziness, headache, blurred vision, GI disorders, dependence › Contraindications - Nervousness, insomnia, irritability, seizures, or psychosis; increased heart rate, blood pressure, and irregularity of heart rhythm; dizziness, headache, blurred vision, GI disorders, dependence › Interactions - Antacids, anticoagulants, anticonvulsants, clonidine, TCAs
question
Clinical Depression
answer
- Excess of sleeping and eating, inability to concentrate, avoidance of the companionship, decreased interest in activities, feelings of despair - Usually combination of genetic and environmental factors › When neurotransmitters are depleted, patient does not think clearly and mood is depressed.
question
Anti-Depressants
answer
- Preserve neurotransmitters at the synapse - Three categories › MAOIs - monoamine oxidase inhibitors › TCAs- tricyclic antidepressants › SSRIs- selective reuptake inhibitors
question
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
answer
- Inhibit enzyme that stops action of neurotransmitter - Rarely prescribed - Example: selegiline (Eldepryl) › Side effects - Nervousness, headache, stiff neck, increased heart rate and blood pressure, diarrhea, blurred vision › Contraindications - Known hypersensitivity, heart disease, hepatic or renal impairment, headaches, cerebrovascular disease, pregnancy, lactation › Interactions - Adrenergics, diuretics, antidepressants, CNS depressants, insulin, levodopa, foods containing tyramine, herbs such as St. John'swort - Requires dietary exclusion foods containing tyramine › causes critical HTN
question
Tricyclic Anti Depressants
answer
› Three ring chemical structure that keeps norepinephrine and serotonin at nerve terminals › Drug of choice if patient has insomnia due to sedative side effect › amitriptyline - Many side effects - Drug of choice for severe depression and in-patient treatment - Side effects-Dry mouth, increased appetite, weight gain, blurred vision, drowsiness, dizziness, constipation, urinary retention, postural hypotension, irregular heart rhythms, headache - Contraindications- Pregnancy and lactation; cardiac, kidney, liver, and GI disorders; glaucoma; obesity; seizures - Interactions -Alcohol, CNS drugs, MAO inhibitors
question
- Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs)
answer
› Prevent serotonin from being used up at the synapse › Few side effects, thus usually first choice - Examples › Celexa (citalopram) › Prozac(fluoxetine) › Paxil (paroxetine) › Zoloft (sertraline) - Side effects - Sexual dysfunction, anorexia, diarrhea, sweating, insomnia, anxiety, nervousness, tremor, fatigue, dizziness, drowsiness, headache - Contraindications- Pregnancy and lactation; patients with thoughts of suicide, diabetes, bipolar disorders, eating disorders - Interactions - CNS drugs, MAO inhibitors, anticoagulants, beta blockers, antiarrhythmics
question
Mood stabilizers (antimanic agents)
answer
- Stabilize extreme mood shifts seen in patients with bipolar disorder - Most common: Lithium › Lithium is a salt - Do not become dehydrated - Avoid table salt › Small therapeutic range - Blood levels drawn regularly - Fatal if toxic - Signs of toxicity › Drowsiness, blurred vision, confusion, sensitivity to light, tremors, muscle weakness, cardiovascular collapse, seizures, and coma - Side effects - GI distress, hypotension, cardiac irregularities, polyuria, tremors, thyroid problems - Contraindications- Seizure disorders; Parkinson's disease; CV, kidney, and thyroid diseases; dehydration, pregnancy, lactation - Interactions - NSAIDs, diuretics, ACE inhibitors, sodium salts
question
Psychoses
answer
class of disorders characterized by abnormal thoughts, disorganized communication, and lack of interaction with environment.
question
Frequent symptoms of psychoses
answer
delusions, hallucinations, paranoia, bizarre thoughts and behaviors.
question
Antipsychotic medications (neuroleptics)
answer
› Treat abnormal actions and behaviors or psychoses such as talking and interacting with situation only they can see and hear › Used for other symptoms (nausea, vomiting, spasms, etc.); know why a patient is on this drug - Examples - chlorpromazine, Clozaril(clozapine), Haldol(haloperidol) - Side effects - ECG changes, hypotension, agitation, dizziness, sedation, drowsiness, dystonia, headache, constipation, dry mouth, photosensitivity, nausea - Contraindications -Hypersensitivity, cardiac arrhythmias, seizure disorder, thyroid disease, renal or hepatic impairment - Interactions - Anticholinergics, CNS depressants, alcohol, beta blockers, caffeine, antidepressants, lithium
question
Dementia
answer
- Alzheimer's disease most common cause - Goal of therapy to prevent or slow down further deterioration... NO CURE - Cholinesterase inhibitor showing promise in slowing down progression › Aricept (donepezil HCL
question
Parkinson's Disease
answer
Degenerative disorder of CNS - Neurons that produce dopamine die; muscle movements become disorganized - Lack of dopamine and increase in acetylcholine causes tremors, slow movement, rigid muscles, and balance problems. - Antiparkinsonian drugs focus on keeping dopamine and acetylcholine at the nerve synapse Michael J Fox
question
- Antiparkinsonian drugs
answer
› Dopaminergic (replacing or increasing dopamine) - Eldepryl (selegiline), Requip (ropinirole), Sinemet (carbidopa/levodopa) › Cholinergic agents (those that inhibit the action of acetylcholine) such as biperiden (Akineton) - Side effects - Involuntary movements, loss of appetite, anxiety, confusion, depression, psychosis, decreased blood pressure, dizziness, fainting - Contraindications - Pregnancy and lactation, asthma and emphysema, cardiac disease, decreased blood pressure, peptic ulcer, diabetes, glaucoma - Interactions - Benzodiazepines, pyridoxine, phenothiazines, haloperidol, antihypertensives, phenytoin, vitamin B6, MAO inhibitors - Patients need a combination of drugs to achieve sufficient dopamine levels
question
Drug Holiday
answer
Think Parkinsons. When dose cannot be increased or side effects intolerable, doctor orders drug holiday. Patient stops medications for a week or so and then restarts them at a lower dose with desired effects
question
Anesthesia
answer
loss of sensation
question
Local Anesthesia
answer
Creates a lack of feeling without a loss of consciousness › Creams: Emla (lidocaine/prilocaine) Aerosolspray:Exactacain(Benzocaine/butamben/tetracaine) › Otic: American otic (benzocaine) › Injectable solution: Xylocaine (lidocaine) › Classified as amides or esters - Amides last longer; adverse effects and allergies are rare - Esters have potential severe allergic reactions and thus are limited to topical preparations › Side effects - Heart block, hypotension, bradycardia, arrhythmias, restlessness, anxiety, dizziness, headache, nausea, vomiting › Contraindications - Known hypersensitivity, severe hypertension, shock, hematologic disorders, psychosis › Interactions - Sedatives, sulfonamides
question
General Anasthesia
answer
Creates loss of both feeling and consciousness › IV infusion: midazolam(Versed), propofol(Diprivan) or ketamine (Ketalar) used initially for longer procedures followed by › Inhalation therapy: desflurane (Suprane), isoflurane (Forane), sevoflurane (Ultane) - Volatile; can depress respiratory and cardiovascular function - Use of IV medications allows lower doses of inhalation therapy, thus reduced risk of severe side effects with inhalation therapy - Side effects - Cardiopulmonary depression, confusion, sedation, nausea, vomiting, hypothermia, malignant hyperthermia - Contraindications - Known hypersensitivity, hepatic disorder, malignant hyperthermia, pregnancy, lactation - Interactions - CNS depressants, neuromuscular blockers, catecholamines
question
Alcohol
answer
› CNS depressant - Interacts with many medications › Confusion, peripheral vasodilation, increased heart rate, electrolyte imbalances, decreased motor coordination, unsteady gait, and slurred speech - Prolonged use: damage to CNS and liver › S/S of chronic alcoholism - Irritability, tremors, GI disorders, frequent falling accidents, blackouts, memory loss, confusion, neural and muscular weakness, and conjunctivitis. › Treatments: disulfiram (Antabuse), behavior modification, vitamin B injections, and dietary changes
question
Things To assess
answer
Assess drug allergies. › Assess pain. - Location, onset, intensity, duration › Assess physical and emotional status prior and during psychotropic drug therapy. › Assess neurological function and level of consciousness. › Assess sleep patterns › Assess for suicide tendencies during psychotropic drug therapy. › Assess motor responses. - Agitation, trembling › Assess autonomic responses. - Cold, clammy skin; sweating; pallor › Assess nutritional status. › Assess use of OTC drugs, herbs, etc › Assess activities of daily living (ADLs) and movement in patient taking antiparkinsonian drugs. › Assess patient's history of seizure disorder. - Duration/frequency, seizure activity intensity, precipitating factors › Assess for CNS toxicity in the elderly. - Confusion, hallucinations, excessive sedation › Assess for addiction tendencies. › Assess for sexual dysfunction (erectile dysfunction, decreased libido). › Assess vital signs. › HR, BP, and RR may increase with adrenergics, CNS stimulants . › HR, BP, and RR may decrease with narcotics, barbiturates, cholinergics, adrenergic blockers.
question
Serum drug levels to assess during therapy
answer
-**** Lithium **** - Phenobarbital - Phenytoin (Dilantin) › Lithium: 0.6 to 1.2 mEq/L for long-term control › Phenobarbital: 10 to 40 mcg/mL › Phenytoin: 10 to 20 mcg/mL
question
What to monitor in lithium patients
answer
MONITOR I&O - Patient needs 2,000 to 3,000 mL/day. - Monitor weight every 3 months
question
Patient teaching that isn't common sense
answer
› Advise patient taking MAOIs to avoid foods containing tyramine, which may cause critical hypertension. - Avocados, bananas, chocolate, dairy, hot dogs, wine, yeast, raisins, and others › Advise patient taking anxiolytics to avoid grapefruit juice. - May affect metabolism of drug



