Muscular System Vet. Anatomy and Physiology – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
A collection of tissues that support the body and enable it to move, thermoregulate, and transport materials
answer
Muscle Tissue
question
muscle
answer
Myo-
question
muscle cells
answer
Sarco-
question
a belly, two or more attachment sites
answer
Muscles have
question
Fibrous connective tissue bands that attach skeletal muscles to bones at both ends
answer
Tendons
question
broad sheet of fibrous connective tissue that attaches certain muscles to bones or to other muscles
answer
Aponeuroses
question
white line: runs lengthwise between the muscles of an animal's ventral midline; connects the abdominal muscles from each side together
answer
Linea alba
question
more stable of the attachment sites, does not move much when a muscle contracts, provides stability
answer
Origin of the Muscle
question
more moveable of the attachment sites, when a muscle contracts it exerts traction on ____ and usually produces movement of bone or other structures
answer
Insertion of the Muscle
question
agonist, A muscle or muscle group that directly produces a desired movement
answer
Prime mover
question
A muscle group that directly opposes the action of a prime mover
answer
Antagonist
question
A muscle that contracts at the same time as the prime mover and assists it in carrying out its action
answer
Synergist
question
Stabilize joints to allow other movements to take place
answer
Fixator muscles
question
flex (bend) a joint
answer
Flexor muscles
question
extend (straighten) a joint
answer
Extensor muscles
question
means triangular
answer
Deltoid
question
brachial (upper arm)
answer
Brachii
question
means straight
answer
Rectus
question
In the connective tissue (fascia) just beneath the skin thin, broad, superficial muscles used to twitch the skin
answer
Cutaneous Muscles
question
In the cheek, closes the jaw, chewing muscle
answer
Masseter muscle
question
triangular flat, originates along the dorsal midline, inserts on the spine of the scapula, raises head and neck (3)
answer
Trapezius muscles
question
in the dorsal part of the neck
answer
Splenius muscle
question
large, strap-like muscle that runs from the proximal area of the humerus up to the base of the skull (3), extends the head and neck and pulls the front leg forward

answer
Brachiocephalicus muscle
question
smaller strap-like muscle that extends from the sternum to the base of the skull, lowers head and neck
answer
Sternocephalicus muscle
question
an aponeurosis that extends from the xiphoid process (caudal end) of the sternum to the cranial brim of the pubis (4)
answer
linea alba
question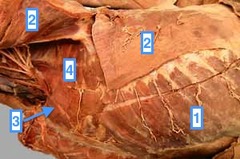
Fibers run in a caudoventral direction (1)

answer
External abdominal oblique
question
Fibers run in a cranioventral direction (1)
answer
Internal abdominal oblique
question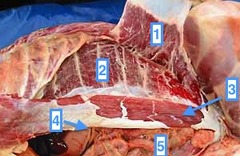
Fibers run directly downward in a ventral direction to insert on the linea alba (2)

answer
Transversus abdominis
question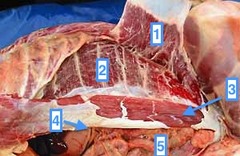
Two strap-like muscles on either side of the linea alba that run from the ribs and sternum back to the brim of the pubis (3)

answer
Rectus abdominis
question
Broad, triangular muscle that extends from the spinal column down to its insertion on the humerus, flexes the shoulder (1)
answer
Latissimus dorsi muscle
question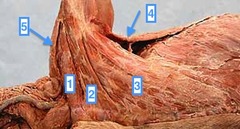
Extend from the sternum to the humerus, Act as adductors (inward movers) of the front leg (1&2)

answer
Pectoral muscles
question
Triangular muscle that extends from the lateral portion of the scapula down to the humerus, abducts (moves outward) and flexes the shoulder joint
answer
Deltoid muscle
question
Extends from the distal end of the scapula to the proximal end of the radius, bends the elbow (8)
answer
Biceps brachii
question
Extends from the distal scapula and proximal humerus down to the olecranon process of the ulna (the point of the elbow), straightens the elbow
answer
Triceps brachii
question
located over the radius, straightens the carpus
answer
Extensor carpii radialis
question
Located beneath some of the other digital flexor muscles, bends the digits
answer
Deep digital flexor
question
Extends from the bones of the pelvis down to the trochanters of the femur, help extend the hip joint
answer
Gluteal muscles
question
main flexor of the stifle joint, propel and animal forward when they walk: Biceps femoris muscle Semimembranosus muscle Semitendinosus muscle
answer
Hamstring muscles
question
main extensor of the stifle joint, point of insertion is the tibia, (1&2)

answer
Quadriceps femoris muscle
question
extends the hock, called the calf in humans, attaches to the achilles tendon
answer
Gastrocnemius muscle
question
A thin, dome-shaped sheet of muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity
answer
Diaphragm
question
between the ribs, fibers are directed in an oblique direction so that when they contract, they rotate the ribs upward and forward, increase the size of the thoracic cavity and causes air to be drawn into the lungs
answer
External intercostal muscles
question
Fibers run at right angles to those of the external intercostal muscles, rotate the ribs backward, which decreases the size of the thorax and pushes air out of the lungs
answer
Internal intercostal muscles
question
Large, narrow, thin, long cells, Can be several inches long, Have many nuclei per cells
answer
Skeletal muscle cells
question
Microscopic, fiber-like structures that occupy most of the cytoplasm (sarcoplasm) in the skeletal muscle cells. Composed of filaments of the contractile protein actin and myosin and are packed together longitudinally in the muscle cells
answer
Myofibrils
question
The two contractile proteins of muscle that slide over each other to produce the shortening of the muscle cell that we refer to as muscle contraction
answer
Actin filaments and Myosin filaments
question
The organelle in a muscle cell that is equivalent to the endoplasmic reticulum of other cells, It stores calcium ions necessary to initiate the muscle contraction process
answer
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
question
A system of tubules in a skeletal muscle cell that extends from the sarcolemma (cell membrane) into the depths of the cell, Help carry an impulse caused by nerve stimulation of the muscle cell into its interior
answer
Transverse tubules (T tubules)
question
Large, dark bands in skeletal muscle fiber that alternates with lighter I bands to give a striped appearance to the skeletal muscle fibers under a microscope, are composed of the contractile protein myosin
answer
A band
question
Large, light bands in a skeletal muscle fiber that alternates with darker A bands to give a striped appearance to skeletal muscle fibers under a microscope, are composed of thin filaments of the contractile protein actin
answer
I band
question
The dark line in the center of the light band (I band) of skeletal muscle, disks to which the actin filaments are attached
answer
Z line
question
basic contracting unit of the skeletal muscle, consists of the actin and myosin filaments between the Z lines in a muscle cell,
answer
Sarcomere
question
The thin, delicate layer of connective tissue that surrounds each individual skeletal muscle fiber
answer
Endomysium
question
A group of skeletal muscle fibers bound together by a layer of fibrous connective tissue called the perimysium
answer
Fascicles
question
The fibrous connective tissue layer in skeletal muscle that surrounds groups of muscle fibers and binds them into groups called fascicles
answer
Perimysium
question
The tough connective tissue layer that covers and delineates individual muscles. It surrounds groups of skeletal muscle fascicles
answer
Epimysium
question
Sites where the ends of motor nerve fibers to connect to muscle fibers
answer
Neuromuscular Junction
question
a space between the end of the nerve fiber and the sarcolemma
answer
synaptic space
question
tiny sacs within the end of a nerve fiber in a neuromuscular junction
answer
synaptic vesicles
question
chemical neurotransmitter
answer
acetylcholine
question
one nerve fiber and all the muscle fibers it innervates
answer
motor unit
question
enzyme in the synaptic space that quickly removes the acetylcholine molecule from its receptor and splits it apart
answer
acetylcholinesterase
question
muscle contracts completely or not at all
answer
All-or-Nothing Principle
question
a large protein molecule that can store and release large quantities of oxygen
answer
Myoglobin
question
The type of metabolism in muscle in which the supply of available oxygen is sufficient to keep up with the energy needs of the muscle fibers
answer
Aerobic metabolism
question
The type of metabolism in muscle that occurs when the need for energy to produce muscular activity exceeds the available oxygen supply, creates lactic acid
answer
Anaerobic metabolism
question
Smaller than skeletal muscle cells, Longer than they are wide and have multiple branches
answer
Cardiac muscle
question
securely fasten the cells together and also transmit impulses from cell to cell to allow large groups of cardiac muscle cells to contract in a coordinated manner
answer
Intercalated disks
question
located in the wall of the right atrium, the heart's pacemaker
answer
sinoatrial (SA) node
question
stimulates the heart to beat harder and faster
answer
Sympathetic nervous system
question
cause the heart to beat more slowly and with less force
answer
Parasympathetic nervous system
question
sheets of cells in the walls of some hollow organs, as small discrete groups of cells
answer
Smooth muscle
question
Found in the walls of many soft internal organs: Sympathetic nervous system stimulation decreases visceral smooth muscle activity and Parasympathetic nervous system stimulation increases visceral smooth muscle activity
answer
Visceral smooth muscle
question
Small and delicate muscle, Made up of individual smooth muscle cells or small groups of cells
answer
Multiunit smooth muscle



