Human Anatomy & Physiology: The Integumentary System – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Another name for skin
answer
The Integumentary System
question
Epidermis
answer
Composed of epithelial cells, is the outermost protective shield of the body
question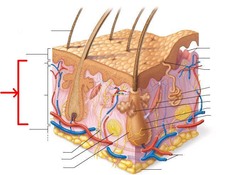
Dermis

answer
Makes up the bulk of the skin, is a tough, leathery lawyer composed mostly of dense connective tissue
question
Hypodermis
answer
The subcutaneous tissue just deep to the skin Not part of the skin, but shares some of skins protective functions Also called, the superficial fascia,because it is superficial to the tough connective tissue wrapping (fascia) of the skeletal muscles, consists mostly of adipose tissue
question
Keratinocytes
answer
To produce keratin, the fibrous protein that helps give the epidermis its protective properties
question
Melanocytes
answer
Spider-shaped epithelial cells that synthesize the pigment melanin, are found in the deepest layer of epidermis
question
Layers of Epidermis
answer
Deep to superficial 1. Stratum Basal 2. Stratum Spinosum 3. Stratum Granulosom 4. Stratum Lucidum (absent in thin skin) 5. Stratum Corneum
question
Stratum Basal
answer
The deepest epidermal layer, is attached to the underlying dermis along a wavy border line that resembles corrugated cardboard.
question
Stratum Spinosum (Prickly Layer)
answer
Several cell layers thick Contain intermediate filaments-pre keratin filaments
question
Stratum Granulosum
answer
Consists of one to five cell layers in which keratinocytes appearance changes drastically - keratinization begins
question
Stratum Lucidum (Clear Layer)
answer
Visible in only thick skin Consists of two or three rows of clear, flat, dead keratinocytes with indistinct boundaries
question
Stratum Corneum(Horny Layer)
answer
Outermost epidermal layer, broad zone to 20 to 30 cell layers thick
question
Dermis Composition
answer
Consists of papillary & reticular layers Made up of strong, flexible connective tissue
question
Papillary Layer
answer
Thin, superficial, is areolar connective tissue in which fine interlacing collagen and elastic fibers from a loosely woven mat that is heavily invested with small blood vessels. Dermal papillae contain capillary loops Friction ridges
question
Reticular Layer
answer
Deeper, accounting of about 80% of the thickness of the dermis, is coarse, dense irregular connective tissue Cleavage (tension) lines Flexure lines
question
3 Skin pigments
answer
Carotene, Melanin, Hemoglobin - determine skin color
question
Melanin

answer
Only one made in the skin - is a polymer made of tyrosine amino acids - its two forms range in color from reddish yellow to brownish black
question
Carotene
answer
Is a yellow to orange pigment found in certain plant products such as carrots Color most obvious in the palms and soles
question
Hemoglobin
answer
The pinkish hue of fair skin reflects the crimson color of the oxygenated pigment hemoglobin in the red blood cells circulating through the dermal capillaries
question
Cyanosis
answer
When hemoglobin is poorly oxygenated, both the blood and the skin of caucasions appear blue
question
Erythema
answer
Reddened skin may indicate embarrassment, fever, hypertension, inflammation, or allergy
question
Pallor
answer
Blanching, Becoming pale-low blood pressure or anemia (during fear, anger, emotional stress)
question
Jaundice
answer
Yellow cast- abnormally yellow skin tone usually signifies a liver disorder
question
Hair

answer
Consists of dead, keratinized cells Pili Are flexible strands produced by hair follicles and consist largely dead, keratinized cells Shaft- portion in which keratinization is complete Root- where kerantinization is still ongoing
question
Shaft
answer
Projects from the skin, extends about halfway down the portion of the hair embedded in the skin
question
Root
answer
Remainder of the hair deep within the follicle
question
Arrector pili
answer
"Goose bumps" Makes the hair stand straight up
question
First degree burns
answer
Burns where only epidermis is damaged. The area becomes red and swollen.
question
Second degree burns
answer
burns that involve injury to the epidermis and the upper region of the dermis. Skin is red and painful and blisters appear
question
Third degree burns
answer
Burn where entire thickness of skin is destroyed. The burned area appears blanched (gray-white) or blackened. Skin grafts must be done to repair area.



