Frontiers of Biotechnology – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Restriction Enzyme

answer
Enzyme that cuts DNA at a specific sequence of nucleotides
question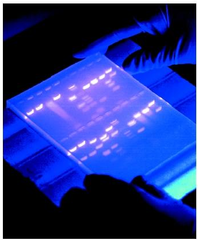
Gel Electrophoresis

answer
Separates DNA fragments by size using an electric current
question
Restriction Map

answer
diagram that shows the lengths of fragments between restriction sites in the strand of DNA
question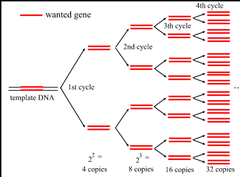
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)

answer
A method of producing thousands of copies of DNA segment using the enzyme DNA polymerase
question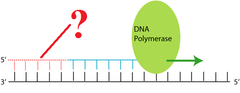
Primer

answer
A molecule (a short strand of RNA or DNA) whose presence is required for formation of another molecule (a longer chain of DNA)
question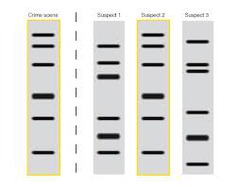
DNA Fingerprint

answer
Analysis of sections of DNA that have little or no known function, but vary widely from one individual to another, in order to identify individuals
question
Clone

answer
a group of genetically identical cells or organisms derived from a single cell or individual by some kind of asexual reproduction
question
Genetic Engineering
answer
A technology that includes the process of manipulating or altering the genetic material of a cell resulting in desirable functions or outcomes that would not occur naturally.
question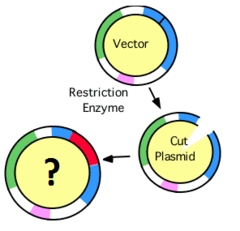
Recombinant DNA

answer
A section of DNA, often in the form of a plasmid, which is formed by joining DNA sections from two different sources.
question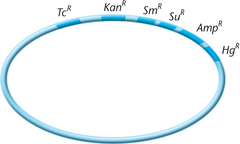
Plasmid

answer
A small, circular section of extra DNA that confers one or more traits to a bacterium and can be reproduced separately from the main bacterial genetic code.
question
Transgenic

answer
genetically modified organism whose source of new genetic material is a different species
question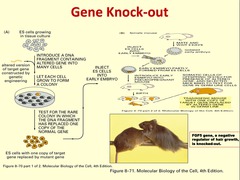
Gene Knockout

answer
genetic manipulation in which one or more of an organism's genes are prevented from being expressed
question
Genomics

answer
Study and comparison of genomes within a single species or among different species.
question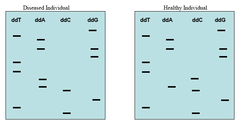
Gene Sequencing

answer
process of determining the order of DNA nucleotides in genes and genomes
question
Human Genome Project

answer
An international collaborative effort to map and sequence the DNA of the entire human genome.
question
Bioinformatics

answer
Application of mathematics and computer science to store, retrieve, and analyze biological data
question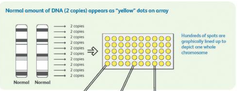
DNA Microarray

answer
A glass slide carrying thousands of different kinds of single-stranded DNA fragments arranged in an array (grid). A DNA microarray is used to detect and measure the expression of thousands genes at one time. Tiny amounts of a large number of single-stranded DNA fragments representing different genes are fixed to the glass slide. These fragments, ideally representing all the genes of an organism, are tested for hybridization with various samples of cDNA molecules.
question
Proteomics

answer
Study of the structure and function of proteins in the human body
question
Genetic Screening

answer
analyzing a group of people to determine genetic susceptibility to a particular disease
question
Gene Therapy
answer
The insertion of working copies of a gene into the cells of a person with a genetic disorder in an attempt to correct the disorder
question
9.1 Manipulating DNA
answer
Biotechnology relies on cutting DNA at specific places. Bacterial enzymes called restriction enzymes are used to cut DNA. Each restriction enzyme cuts DNA at a specific DNA sequence. After DNA is cut with a restriction enzyme, the fragments of DNA can be separated using gel electrophoresis. A restriction map of the DNA is made based on the lengths of the fragments. -Scientists use several techniques to manipulate DNA -Restriction enzymes cut DNA -Restriction maps show the lengths of DNA fragments
question
List a few of the ways that scientists can use to manipulate DNA.
answer
Artificial Nucleotides. Artificial copies. Chemical Mutagens. Computers. Enzymes. Bacteria.
question
What determines how DNA will be cut by a restriction enzyme?
answer
The sequence of DNA that the enzyme recognizes.
question
How does gel electrophoresis separate fragments from each other?
answer
DNA molecules, which have an overall negative charge, are drawn through a semisolid gel by an electric current toward the positive electrode within an electrophoresis chamber. The fragments are seperated by size.
question
Suppose you cut DNA. You know that you should find four DNA fragments on a gel, but only three appear, and one fragment is very large. Explain what happened.
answer
In order to get 4 bands you need four pieces of DNA. In order to get 4 pieces of DNA it needs to be cut 3 times. If this stand only gets cut twice than the restriction enzyme that you used only recognized 2 parts of the DNA and cut it. There for the enzyme you used could be the wrong enzyme or if it was the correct enzyme, during the reaction the enzyme broke down before it could cut the third time due to the environment. Even more unlikely is that you let the gel run to long and the smallest band ran off into the buffer.
question
What is the relationship between restriction sites and a restriction map?
answer
The map will show where the restriction sites are located on the DNA, and what the distance is between the sites.
question
Would a mutation in a gene always be detectable by using restriction maps? Why or why not?
answer
Usually, mutation cannot be detected by restriction mapping until mutation occurs in restriction sites. The mutation may be detectable after it is get mapped and taken away and then it is put under PCR. the mutation be detected.
question
9.2 Copying DNA
answer
The polymerase chain reaction rapidly copies segments of DNA. The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is based on the process of DNA replication. By combining the DNA to be copied, DNA nucleotides, primers, and specific polymerase enzymes, a desired segment of DNA can be copied in the laboratory. -PCR uses polymerases to copy DNA segments -PCR is a three step process
question
Briefly describe the function of polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
answer
The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) uses enzymes to mass replicate a portion of a DNA strand for easier analysis, such as searching for genes of interest.
question
Summarize the cycle involved in the PCR process.
answer
1. Separation of two strands of DNA by temperatures of around 90 degrees Celsius (194 degrees Fahrenheit) 2. Binding of DNA primer to the separated strands. Occurs at 50 degrees Celsius (131 degrees Fahrenheit) 3. Elongation of the strands using the DNA primer with heat-stable DNA polymerases. Occurs at 72 degrees Celsius (152 degrees Fahrenheit)
question
Describe how heating double stranded DNA separates the strands. Why does heating also inactivate DNA polymerases from many organisms?
answer
The hydrogen bonds between A & T and G & C are broken. G-C bonds require more heat to separate because they have 3 hydrogen bonds whereas A-T have only 2. Heating will denature the enzyme by destroying the precise 3-D structure.
question
Explain two reasons why primers are important in PCR.
answer
PCR needs two primers, each complementary to a different strand, because the primers define the region that will be amplified. In the first cycle, the double stranded DNA is heated, so that the hydrogen bonds holding the 2 strands together break, and the 2 strands fall apart. When the temperature goes down, complementary sequences will start to bind to each other. Because there are many more primers than template DNA, the chance that a primer will bind to its complementary sequence is much higher than that the 2 original full length template strands will find each other. One primer is designed to bind on one strand, the other primer will bind the other strand. The enzyme DNA polymerase will extend these primers, and use the template as a template.
question
9.3 DNA Fingerprinting
answer
DNA fingerprints identify people at the molecular level. DNA has many repeating base sequences. The number of repeats differ from person to person. DNA fingerprinting uses restriction enzymes and gel electrophoresis to detect these differences. By using DNA fingerprinting on several regions of DNA, one particular person can be identified. -A DNA fingerprint is a type of restriction map -DNA fingerprinting is used for identification
question
On what, in a person's DNA, is a DNA fingerprint based?
answer
It is based on non-coding DNA. This DNA has a high enough mutation rate that it is specific to individuals.
question
How are DNA fingerprints and restriction maps similar? Explain.
answer
A restriction map is a map of known restriction sites within a sequence of DNA. These might be like a fingerprint because fingerprints are judged by certain points as well and the shapes at those points determine who the print belongs to.
question
Briefly describe how restriction enzymes, gel electrophoresis, and PCR are used in DNA fingerprinting.
answer
Restriction enzymes are used to cut DNA sequences at specific areas. They have a nucleotide code on them. So when this restriction enzyme finds that code in your DNA it cuts it there. First your DNA is amplified using PCR, then cut into your restriction enzymes, then filtered to show your unique banding pattern with gel electrophoresis.
question
9.4 Genetic Engineering
answer
DNA sequences of organism can be changed. Clones, or identical genetic copies, of many organisms can be made. Organisms can also be implanted with genes that give then new traits. Often, genes are inserted into plasmids to make recombinant DNA. Genetically engineered plasmids are inserted into bacteria, producing a transgenic organism. Transgenic bacteria, plants, and animals are used in several different ways. -Entire organisms can be cloned -New genes can be added to an organism's DNA -Genetic engineering produces organisms with new traits
question
Why is the offspring of asexual reproduction a clone?
answer
With asexual reproduction there is only one parent. All genetic material comes from this sole parent.
question
What are plasmids, and how are they used in genetic engineering?
answer
Plasmids are DNA molecules, usually circular, that are independent of the chromosomal DNA. In bacteria these can replicate independently as well. In genetic engineering, plasmids are called vectors, and are used to isolate and multiply a specific gene. Since they are independent of chromosomal DNA, they can be transferred into other organisms.
question
Describe two applications of transgenic organisms.
answer
Genetic engineering in plants such as traits for resistance to frost, diseases, and some insects. Also, genetic engineering in animals can help scientists learn about diseases and cell growth.
question
How is the cloning of genes different from the cloning of animals?
answer
Cloning genes means you isolate/cut/remove a particular gene from the DNA sequence using rectriction enzymes. This gene usually will be inserted into other organism to produce a transgenic organism. Cloning animals means you clone animals. Asexual reproduction means to reproduce organisms without fusion between male gamete and female gamete.
question
How are restriction enzymes used to make both recombinant DNA and transgenic organisms?
answer
Restriction enzyme use is basically the same for both the production of recombinant DNA and for transgenic organisms since an organism can synthesize the DNA that has been inserted into it once it has been placed within the organism. In the case of unicellular organisms the restriction enzyme is first introduced to break apart the DNA and then the plasmid is introduced to create the desired effect. Then the organism can express those genes through further processing of the newly introduced DNA and through mitosis (which is how unicellular organisms reproduce) it can give that gene to its offspring.
question
9.5 Genomics and Bioinformatics
answer
Entire genomes are sequenced, studied, and compared. Through DNA sequencing, the genomes of several organisms, including humans, have been found and studied. Genomic data are organized and analyzed through bioinformatics. DNA microarrays are used to study interactions among genes in a genome. In addition, genomics has led to the study and comparison or proteins through proteomics. -Genomics involves the study of genes, gene functions, and entire functions -Technology allows the study and comparison of both genes and proteins
question
Describe the goals of the Human Genome Project.
answer
The goal of the Human Genome Project was to identify the location and function of every human gene.
question
Why is bioinformatics important in genetic research?
answer
Bioinformatics is important to genetic research because genetic data has a context. The context is biology. Life forms have certain rules of behavior. The same applies to tissues and cells, genes and proteins. They interact in certain ways and regulate each other in certain ways. The large-scale, complex data that is generated in genomics wouldn't make sense without the contextual knowledge of how life forms work.
question
Describe the difference between gene sequencing and DNA fingerprinting.
answer
Gene sequencing looks at the sequence of nucleotides in a sample whereas DNA fingerprinting does not. It looks at the pattern of fragments produced when the sample is digested.
question
How is the study of specific genes different from the study of a genome?
answer
A genome is a full set of chromosomes or genes rather than the study of one single gene.
question
9.6 Genetic Screening and Gene Therapy
answer
Genetics provides a basis for new medical treatments. Genetic screening is used to test people for genes that are linked to genetic disorders. One method to correct these faulty genes or to replace missing genes is gene therapy. Gene therapy is experimental, but has the potential to cure many diseases.
question
How does genetic screening use both old and new methods of studying human genetics?
answer
Genetic Screening applies the principle of synthetic lethality to a gene of interest in mammalian cells. Most "new methods" are recycled from the oldest ones, but the original old methods are no longer used as often. -Genetic screening can detect genetic disorders -Gene therapy is the replacement of faulty genes
question
Briefly describe the goals and methods of gene therapy.
answer
Gene therapy is an experimental technique that uses genes to treat or prevent disease. Researchers are testing several approaches to gene therapy, including: Replacing a mutated gene that causes disease with a healthy copy of the gene, inactivating a mutated gene that is functioning improperly, and introducing a new gene into the body to help fight a disease.
question
How is gene therapy similar to, and different from, making a transgenic organism?
answer
Transgenesis is much like gene therapy in that both transform cells for a specific purpose. However, whereas gene therapy targets only certain cells in order to cure a defect in them, transgenesis seeks to produce an entirely modified organism by incorporating the transgene into all the cells of the mature organism and changing the genome.
question
How are restriction enzymes and recombinant DNA important for gene therapy?
answer
Recombinant DNA is the technology that allows us to insert genes from one organism into another to make it produce a protein product, copy the gene multiple times, or give it a new trait. The discovery of recombinant DNA was considered the "birth" of modern biotechnology.
question
How is the cloning of genes different from the cloning of animals?
answer
The cloning of genes only requires that you clone the gene itself. Cloning an animal means cloning all of its genes and cells.



