Educational Psychology x2 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Developmental Constructivism
answer
Learners are building that knowledge themselves
question
Frederic Bartlett
answer
coins schema to explain how memory is constructive; people tent to remember what fits or matches what they already know
question
Schemes/Schema
answer
Construct webs of connections for new info in our mind
question
Jean Piaget
answer
administers intelligence test to students to identify those who needed to be remediated for extra help (notices different ages caused different mistakes) stages of development. known for his epistemological studies with children. His theory of cognitive development and epistemological view are together called "genetic epistemology"
question
Adaptation
answer
assimilation or accommodation (both try to restore harmony. change by which an organism or species becomes better suited to its environment.
question
Organization
answer
having new experiences is the process of learning (all learners strive to organize & adapt to their experiences in the environment)
question
Assimilation
answer
broadening schema- new version of a student (when you see a 65 year old woman in the same class). The part of the adaptation in which the external world is interpreted in terms of current schemes.
question
Cognitive Dissonance
answer
force accommodation (purple cow that flies- not normal) because purple cows is not something you are used to, you need accommodation to change your way of thinking. the state of having inconsistent thoughts, beliefs, or attitudes, especially as relating to behavioral decisions and attitude change.
question
Accommodation
answer
doesn't make sense to their schema - changing schema some how to make sense of new things/info
question
Equilibration
answer
things are equal harmony; nothing new
question
Disequilibrium
answer
something new, out of the ordinary
question
Equilibrium
answer
things are equal harmony; nothing new
question
Stages of Development
answer
Piaget's Stages: o Sensorimotor o Pre-operational o Concrete Operational o Formal Operational
question
Sensorimotor
answer
(Birth-2yrs) • Blanket & Ball study - Object permanence (8-12 months) [peek-a-boo] • Goal-Directed Behavior: if I cry, I get food (manipulate objects/actions for reinforcement) • babies use 5 senses/reflexes - cry, turn toward noise, suck for food...
question
Object permanence
answer
they don't realize if the object is there once you cover it
question
Goal-Directed Behavior
answer
if I cry, I get food (manipulate objects/actions for reinforcement)
question
Pre-operational
answer
(2yrs-6 or 7yrs) o Cant distinguish an other ways of separation by characteristic • Egocentrism • Classification • Centration • Irreversibility can recall past events and envision future ones (consequences for actions)
question
Egocentrism
answer
(3 mountain study) only seeing the world from one perspective; depending on which side you were standing, you only see that perspective.
question
Classification
answer
based on only one attribute
question
Centration
answer
can only focus on one thing (fuzzy, not both fuzzy and hard)
question
Animism
answer
confusing psych. Phenomena (thoughts ; feelings) w/ physical phenomena (imaginary friends and stuffed animals w/ personality- the bear is sad meaning they are sad)
question
Concrete Operational
answer
(6 or 7 yrs - 11 or 12 yrs) Decentration: Seeing more than one aspect at a time (class inclusion) • Conservation • Class Inclusion • Inductive reasoning (generalization)
question
Conservation
answer
(liquids in glasses test- even though they saw the same amount of water put into a long tube, because the long tube is taller, they look at that as being more)
question
Class Inclusion
answer
seeing more than one aspect
question
Inductive reasoning (generalization)
answer
making generalizations based on concrete observations
question
Formal Operational
answer
(11 or 12 yrs - Adulthood) o Ability to think abstractly) • Abstract Thinking • Hypothetical-deductive reasoning
question
Abstract Thinking
answer
use of metaphors ; analogies; capacity for metacognition; ability to envision other ways that world could be-Idealism
question
Hypothetical-deductive reasoning
answer
• Concrete: (inductive- coming up with ways to generalize things what we know before) can start to generalize and find patterns • Formal: (deduction- actually testing what you generalized) got capacity to test these ideas
question
David Kolb
answer
Experiential Learning: ideas only apply to people that are 12 yrs or more builds off of Piaget to develop a theory of stages "learning is the process whereby knowledge is created through the transformation of experience"
question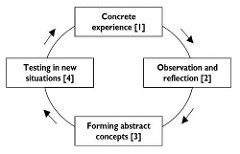
Experiential Learning

answer
Learning Styles o Accommodating o Converging o Diverging o Assimilating
question
Accommodating
answer
(Feel ; Do) but too much= imitating the world and letting environment take over your life {trying it out}
question
Converging
answer
(Think ; Do) testable; narrow to one hypothesis
question
Diverging
answer
(Feel ; Watch) opening up to new things(Feel ; Watch) opening up to new things
question
Assimilating
answer
(Think ; Watch) trying to broaden your original meaning or something {play}
question
Lev Vygotsky
answer
the reason for cultural differences is cuz we have acceptance of others o Core of his thinking: knowledge is relative- Truths of culture o Culture provides symbols ; tools that help children make sense of the world
question
Symbols ; Tools (ex)
answer
Symbols: Society transforms child Tools: Child can transform society o ex: cellphones (tools) -; selfies (symbols)
question
What Vygotsky believes about language
answer
YES: it means through which people construct their understanding about what is true YES: it is socially constructed YES: it is the basis by which people develop intersubjective order of the world NOT- it appears in the mind first, as a child internalizes a new idea, and then second as the child shares ideas with other people
question
Zone of Proximal Development
answer
more knowledgeable peeps help guide child (Can do if guided) • Scaffolding occurs through the support of the "more knowing other"
question
Actual development
answer
Can do Independently
question
Potential development
answer
Can do if guided (ZPD)
question
Cognitive Apprenticeship
answer
o Modeling: doing what the learner wants to accomplish; showing them how to do it by thinking aloud o Coaching: observation ; feedback o Scaffolding: support/construction o Articulation: student verbalizes thought process o Refection: evaluating/comparing ones thinking/performance with experts o Exploration: inquiry (asking questions); how to investigate, research, inquire
question
Mediated activity/action
answer
signs and tools medicate the ways in which we transform our understanding and our world
question
2 Levels of Development
answer
Inter-psychological level: talking to each other about it (social speech) Intra-psychological level: like legos- making it your own (private speech)
question
Internalization
answer
the transfer and transformation of cultural tools, ideas, language
question
Intersubjectivity
answer
unique understanding that is shared
question
Jerome Bruner
answer
Temporary support that has layers, that you little by little take it away as they become able to do it themselves (anxiety) | / F / scaffolding occurs (help by more Level | / D / knowledgeable peeps of | / Z / challenge | / goal / |_____/___________________ Level of competence (Boredom)
question
Scaffolding
answer
goal- to find the sweet spot that doesn't keep you bored, but doesn't give you anxiety either. o Get feedback form the student to find there they are at o Temporary support that has layers, that you little by little take it away as they become more able to do it themselves o Small steps- reduce the degrees of freedom o Modeling- often to get started/unstuck o Control frustration- encourage, find right balance of challenge (recruit interest) o Questions- keep focus; cueing (making critical features)
question
Constructivism Applied
answer
use them and manipulating topics o Core: I hear and I forget, I see and I remember, I do and I understand
question
Challenges of Constructivism Applied
answer
• Takes longer • Differentiation for learner's at different places takes a lot of preparation • Requires lots of formative assessment and realignment through questioning/altering • Motivation: what if students aren't interested/naturally curious or intrinsically motivated- dilemma of choosing their own adventure, they will only learn a narrow of sum stuff
question
Inquiry-Based Learning
answer
• Development Constructivism • problem solving (determine what- create hypothesis), data collection (gather info), analysis (examine/discuss), conclusion (determine solution) • mainly involving the learner and leading them to understand • learning by Scientific Method
question
Problem Based Learning
answer
• figuring it out themselves (model UN=ex) • Giving vocab after they create a definition themselves
question
Discovery Learning
answer
• moresory schools • Activities laid out by teachers that challenges students to learn in their own pace (they choose)
question
Situated Cognition
answer
all real learning has to be situated with real life situation (in context) {Learning ; Doing}
question
Cooperative Learning
answer
• based groups (success is defined if everyone in the group succeeds) • Re-teller, Questioner, Classifier, Predictor • Reciprocal Teaching
question
Think Pair Share
answer
make task ; instructions explicit ; precise; require students to produce a product; circulate, listen, encourage, challenge thinking {think alone, then with a partner, then as a class}
question
Reciprocal Teaching
answer
method of teaching reading comprehension. Group teaches each other what the meaning of the reading
question
Jigsaw
answer
a group is made up of 4 components that discuss with others from the same topic, but come back to form a group of 4 different topics
question
Higher Order Thinking Skills (HOTS)
answer
Bloom's taxonomy, for example, skills involving analysis, evaluation and synthesis (creation of new knowledge) are thought to be of a higher order, requiring different learning and teaching methods, than the learning of facts and concepts.
question
Convergent Thinking
answer
the person is good at bringing material from a variety of sources to bear on a problem, in such a way as to produce the "correct" answer. This kind of thinking is particularly appropriate in science, maths and technology.
question
Divergent Thinking
answer
broadly creative elaboration of ideas prompted by a stimulus, and is more suited to artistic pursuits and study in the humanities.
question
Critical Thinking
answer
the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgment. - Standards, Elements, & Intellectual Traits (Foundation for Critical Thinking)
question
Analysis
answer
Examine and break information into parts by identifying motives or causes. Make inferences and find evidence to support generalizations Questions like: List four ways of serving foods made with apples and explain which ones have the highest health benefits. Provide references to support your statements.
question
Evaluation
answer
Present and defend opinions by making judgments about information, validity of ideas or quality of work based on a set of criteria. Questions like: Do you feel that chicken is good for you and your family?
question
• Synthesis
answer
Builds a structure or pattern from diverse elements; it also refers the act of putting parts together to form a whole (Omari, 2006). Compile information together in a different way by combining elements in a new pattern or proposing alternative solutions. Questions like: Convert an "unhealthy" recipe for apple pie to a "healthy" recipe by replacing your choice of ingredients. Explain the health benefits of using the ingredients you chose vs. the original ones.
question
• Creativity
answer
the use of the imagination or original ideas, especially in the production of an artistic work.
question
• Torrance tests of creativity
answer
a test of creativity, originally involved simple tests of divergent thinking and other problem-solving skills, which were scored on four scales:
question
Fluency
answer
The total number of interpretable, meaningful, and relevant ideas generated in response to the stimulus.
question
Flexibility
answer
The number of different categories of relevant responses.
question
Originality
answer
The statistical rarity of the responses.
question
Elaboration
answer
The amount of detail in the responses
question
4C Model (Kaufman & Beghetto)
answer
Little-C: come up with own recipe for a dish. Mini-C: write short stories, turn drapes into a dress. People notice your creativity Pro-C: Creativity generates funds for you, travel photographer and graphic/interior designer. Big-C: Creativity has a lasting effect on the world: Da Vinci, Shakespeare, Beatles, Google
question
Stages of Creativity
answer
Preparation - Research: Collect information or data. Incubation - Percolation: Milling over collected information. Illumination - Light Bulb Idea: Aha moment. Verification - Actual Making, creating: Implementation
question
John Flavell
answer
used the term metamemory in regard to an individual's ability to manage and monitor the input, storage, search and retrieval of the contents of his own memory. Metacognition
question
Metacognition
answer
awareness and understanding of one's own thought processes.
question
Problem solving strategies
answer
Trial and Error - works well if the options for possible solutions of a problem are relatively few.
question
Algorithms
answer
step-by-step "recipes" that can solve any problem of a specific type (e.g., mathematical formulas). Algorithms never fail, but they are in short supply when it comes to typical problems facing human beings
question
Heuristics
answer
mental short-cuts that human beings automatically fall back on when making judgments and decisions under conditions of uncertainty. Heuristics are very fast and often accurate, but they can also seriously mislead
question
Insight
answer
occurs when a person has reached an impasse in attempts to solve a problem and then suddenly and effortlessly arrives at a solution.
question
Inquiry Process
answer
defined as "a seeking for truth, information, or knowledge -- seeking information by questioning
question
Amos Tversky & Daniel Kahneman
answer
Subjects when offered a choice formulated in one way might display risk-aversion but when offered essentially the same choice formulated in a different way might display risk-seeking behavior. For example, as Kahneman says, people may drive across town to save $5 on a $15 calculator but not drive across town to save $5 on a $125 coat. Thinking Fallacies too.
question
Anchoring & Adjusting heuristic
answer
a heuristic used in many situations where people estimate a number. According to Tversky and Kahneman's original description, it involves starting from a readily available number—the "anchor"—and shifting either up or down to reach an answer that seems plausible
question
Representativeness heuristic
answer
seen when people use categories, for example when deciding whether or not a person is a criminal. An individual thing has a high representativeness for a category if it is very similar to a prototype of that category.
question
Availability heuristic
answer
the ease with which a particular idea can be brought to mind. When people estimate how likely or how frequent an event is on the basis of its availability, they are using the availability heuristic.
question
Confirmation bias
answer
a tendency to search for or interpret information in a way that confirms one's preconceptions, leading to statistical errors.
question
Belief perseverance
answer
he tendency to cling to one's initial belief even after receiving new information that contradicts or dis- confirms the basis of that belief.
question
Framing bias
answer
people react to a particular choice in different ways depending on how it is presented; e.g. as a loss or as a gain. People tend to avoid risk when a positive frame is presented but seek risks when a negative frame is presented.
question
Dual Process Model of Thinking (Kahneman)
answer
provides an account of how a phenomenon can occur in two different ways, or as a result of two different processes. Often, the two processes consist of an implicit (automatic), unconscious process and an explicit (controlled), conscious process.
question
Benjamin Bloom
answer
It divides educational objectives into three "domains": cognitive, affective, and psychomotor (sometimes loosely described as "knowing/head", "feeling/heart" and "doing/hands" respectively). Within the domains, learning at the higher levels is dependent on having attained prerequisite knowledge and skills at lower levels. A goal of Bloom's taxonomy is to motivate educators to focus on all three domains, creating a more holistic form of education.
question
..Anderson & Krathwohl's Revision
answer
Knowledge;Remembering, Comprehension;Understanding, Application;Applying, Analysis;Analyzing, Synthesis;Evaluating, Evaluation;Creating
question
Concepts Learning
answer
refers to a learning task in which a human or machine learner is trained to classify objects by being shown a set of example objects along with their class labels. The learner simplifies what has been observed by condensing it in the form of an example.
question
Concept development strategies
answer
a strategy to help students to form a general mental understanding or construct (either an image or a model) from examples of a cluster of information or particular category
question
Nature vs. Nurture
answer
whether heredity or the environment most impacts human psychological development (behavior, habits, intelligence, personality, sexuality, aggressive tendencies, and so on).
question
Heritability
answer
proportion of observed differences on a trait among individuals of a population that are due to genetic differences. Factors including genetics, environment and random chance can all contribute to the variation between individuals in their observable characteristics
question
Aptitude tests
answer
An aptitude is the ability to learn or to develop proficiency in an area (if provided with appropriate education or training). It is like talent. Examples are various types of reasoning, artistic ability, motor coordination, musical talent. There are aptitude tests that measure mechanical and linguistic ability, as well as more specific skills, such as military flight and computer programming.
question
Achievement tests measure the extent to which a person has "achieved" something, acquired certain information, or mastered certain skills
answer
usually as a result of planned instruction or training. It is designed to efficiently measure the amount of knowledge and/or skill a person has acquired, usually as a result of classroom instruction.
question
Testing: standardization, reliability, validity
answer
reliability of a test refers to stability of measurement over time. When a person's data entry skills are measured on two occasions (with no special training in between), the two sets of scores should be similar
question
Validity
answer
the quality or correctness of a measure, that it measures what it's supposed to measure
question
Francis Galton
answer
the first to apply statistical methods to the study of human differences and inheritance of intelligence, and introduced the use of questionnaires and surveys for collecting data on human communities. Pioneer of Eugenics and "nature vs. nurture"
question
Eugenics
answer
the belief and practice which aims at improving the genetic quality of the human population.
question
Alfred Binet
answer
invented the first practical intelligence test, the Binet-Simon scale. His principal goal was to identify students who needed special help in coping with the school curriculum.
question
IQ
answer
a number used to express the apparent relative intelligence of a person: as. a : the ratio of the mental age (as reported on a standardized test) to the chronological age multiplied by 100.
question
Charles Spearman
answer
believed that intelligence is composed of practical intelligence. General intelligence factor
question
G Factor
answer
general intelligence factor, g, which underlies all intelligent behavior. Many scientists still believe in a general intelligence factor that underlies the specific abilities that intelligence tests measure.
question
Bell Curve
answer
a graph of a normal (Gaussian) distribution, with a large rounded peak tapering away at each end.
question
Robert Yerkes
answer
best known for his work in intelligence testing and in the field of comparative psychology. Army alpha and beta tests
question
Army Alpha ; Beta tests
answer
test measured "verbal ability, numerical ability, ability to follow directions, and knowledge of information". Scores on the Army Alpha were used to determine a soldier's capability of serving, his job classification, and his potential for a leadership position. Soldiers who were illiterate or foreign speaking would take the Army Beta, the nonverbal equivalent of the exam
question
Lewis Terman
answer
best known for his revision of the Stanford-Binet IQ test and for initiating the longitudinal study of children with high IQs called the Genetic Studies of Genius.
question
Stanford-Binet Tests
answer
a cognitive ability and intelligence test that is used to diagnose developmental or intellectual deficiencies in young children. The test measures five weighted factors and consists of both verbal and nonverbal subtests. The five factors being tested are knowledge, quantitative reasoning, visual-spatial processing, working memory, and fluid reasoning.
question
David Wechsler
answer
developed well-known intelligence scales, such as the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS) and the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC).
question
Raymond Cattell & John Horn
answer
Comprehension-knowledge, Fluid intelligence/Reasoning, Short-term memory, Long-term storage and retrieval, Processing speeds, Visual processing, Auditory processing. EMPIRICAL IQ TESTS. FLUID AND CRYSTALIZED INTELLIGENCE.
question
Cross Battery Assessment Model
answer
use information from multiple test batteries (i.e., various IQ tests) to help guide diagnostic decisions and to gain a fuller picture of an individual's cognitive abilities than can be ascertained through the use of single-battery assessments
question
Fluid Intelligence
answer
/reasoning is the capacity to think logically and solve problems in novel situations, independent of acquired knowledge. It is the ability to analyze novel problems, identify patterns and relationships that underpin these problems and the extrapolation of these using logic. It is necessary for all logical problem solving
question
Crystallized Intelligence
answer
the ability to use skills, knowledge, and experience. It does not equate to memory, but it does rely on accessing information from long-term memory. Crystallized intelligence is one's lifetime of intellectual achievement, as demonstrated largely through one's vocabulary and general knowledge. This improves somewhat with age, as experiences tend to expand one's knowledge.
question
Woodcock-Johnson Tests
answer
A set of intelligence tests that combines the other IQ tests and Cattle-Horn tests
question
Howard Gardner
answer
best known for his theory of multiple intelligences,
question
Multiple Intelligences Theory
answer
musical-rhythmic, visual-spatial, verbal-linguistic, logical-mathematical, bodily-kinesthetic, interpersonal, intrapersonal, and naturalistic. Intelligence isn't dominated by a single general ability.
question
Robert Sternberg
answer
the Triarchic theory of intelligence: intelligence is how well an individual deals with environmental changes throughout their lifespan. Sternberg's theory comprises three parts: componential, experiential, and practical.
question
Triarchic Intelligence Theory
answer
intelligence is how well an individual deals with environmental changes throughout their lifespan. Sternberg's theory comprises three parts: componential, experiential, and practical.
question
Peter Salovey ; John Mayer
answer
Emotional intelligence (EI) is the ability to monitor one's own and other people's emotions, to discriminate between different emotions and label them appropriately, and to use emotional information to guide thinking and behavior. There are three models of EI. The ability model, trait model "encompasses behavioral dispositions and self perceived abilities and is measured through self report". the mixed model is a combination of both ability and trait EI. It defines EI as an array of skills and characteristics that drive leadership performance
question
EQ
answer
Also, EI: Emotional Intelligence Quotient
question
Origins of Gifted vs. Special Education
answer
Galton said that if a parent deviates from the norm, so will the child, but to a lesser extent (Eugenics). Terman said the IQ was one's mental age compared to one's chronological age, based on the mental age norms he compiled after studying a sample of children. He defined intelligence as "the ability to carry on abstract thinking"
question
Differentiation
answer
mental autonomy or separation of intellect and emotions so that one is not dominated by reactive anxiety of a family or group emotional system. Thinking for yourself.



