Dermatology pictures – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Cholinergic urticaria. Usually seen on the trunk after exercise, the lesion tend to be smaller than in other forms of urticaria. Pathogenesis: Mast cells, increased histamine. Allergy, body temp fluctuations, Seasonal temperature. Symptoms: appears rapidly, within minutes. mean duration 80 min. itching, burning, tingling, warmth, irritation, pruritic wheals Sites: anywhere except palms and soles. Ddx: Acute urticaria, Chronic urticaria, Contact urticaria. Diagnostics: Intradermal inj. carbachol produce flare-up Treatment: Antihistamines, leukotrine inhibitors, immunosuppressives.
answer
An itchy, red, small sized rash have developed after excessive physical exertion for the first time.
question
Pemphigus vulgaris Erosions on the buccal mucosa, tongue and lips in pemphigus. Pathogenesis: Autoimmune, IgG antibodies (antidesmoglein 1 and 3) binds to keratinocyte desmosomes loss of cell-cell adhesion -> acantholysis Symptoms: Mucousal lesions precede cutaneous by weeks or months. intact bullae rare in mouth. Primary lesion on skin: flaccid blister filled with clear fluid on healthy or erythematous base. Nikolsky sign. Asboe-Hansen sign Sites: Start in mucosa then skin Ddx: Dermatitis herpetiformis, Drug-induced pemphigus, erythema multiforme Diagnosis: Histopathology from edge of blister. Direct IF on normal appearing perilesional skin. Indirect immunofluorescence using serum if DIF are positive. Treatment: Corticosteroids high dose. Immunosuppressives
acantholysis Symptoms: Mucousal lesions precede cutaneous by weeks or months. intact bullae rare in mouth. Primary lesion on skin: flaccid blister filled with clear fluid on healthy or erythematous base. Nikolsky sign. Asboe-Hansen sign Sites: Start in mucosa then skin Ddx: Dermatitis herpetiformis, Drug-induced pemphigus, erythema multiforme Diagnosis: Histopathology from edge of blister. Direct IF on normal appearing perilesional skin. Indirect immunofluorescence using serum if DIF are positive. Treatment: Corticosteroids high dose. Immunosuppressives" alt="Pemphigus vulgaris Erosions on the buccal mucosa, tongue and lips in pemphigus. Pathogenesis: Autoimmune, IgG antibodies (antidesmoglein 1 and 3) binds to keratinocyte desmosomes loss of cell-cell adhesion -> acantholysis Symptoms: Mucousal lesions precede cutaneous by weeks or months. intact bullae rare in mouth. Primary lesion on skin: flaccid blister filled with clear fluid on healthy or erythematous base. Nikolsky sign. Asboe-Hansen sign Sites: Start in mucosa then skin Ddx: Dermatitis herpetiformis, Drug-induced pemphigus, erythema multiforme Diagnosis: Histopathology from edge of blister. Direct IF on normal appearing perilesional skin. Indirect immunofluorescence using serum if DIF are positive. Treatment: Corticosteroids high dose. Immunosuppressives">
answer
There are painful blisters in the mouth for a long time, pain by eating and drinking.
question
Excoriated papules on the knees in dermatitis herpetiformis. Pathogenesis: deposition of IgA in papillary dermis -> neutrophil recruitment and complement activation. Result of an immunologic response to chronic stimulation of the gut mucosa by gluten. HLA genes. Symptoms: papules, excoriations, intensly pruritic, burning, stinging Sites: Symmetrically distributed over extensor surfaces (elbows, knees, buttocks, shoulders) Ddx: Bullous pemphigoid, Erythema multiforme, Scabies Diagnosis: Skin biopsy. Serum IgA Treatment: Gluten free diet. Dapsone
neutrophil recruitment and complement activation. Result of an immunologic response to chronic stimulation of the gut mucosa by gluten. HLA genes. Symptoms: papules, excoriations, intensly pruritic, burning, stinging Sites: Symmetrically distributed over extensor surfaces (elbows, knees, buttocks, shoulders) Ddx: Bullous pemphigoid, Erythema multiforme, Scabies Diagnosis: Skin biopsy. Serum IgA Treatment: Gluten free diet. Dapsone" alt="Excoriated papules on the knees in dermatitis herpetiformis. Pathogenesis: deposition of IgA in papillary dermis -> neutrophil recruitment and complement activation. Result of an immunologic response to chronic stimulation of the gut mucosa by gluten. HLA genes. Symptoms: papules, excoriations, intensly pruritic, burning, stinging Sites: Symmetrically distributed over extensor surfaces (elbows, knees, buttocks, shoulders) Ddx: Bullous pemphigoid, Erythema multiforme, Scabies Diagnosis: Skin biopsy. Serum IgA Treatment: Gluten free diet. Dapsone">
answer
There are intolerance to gluten products and complaints about a strong itch in patient's history.
question
Extensive papular eruption in secondary syphilis. Pathogenesis: Treponema penetrates intact mucous membranes or dermal abrasions -; lymphatics. Invasion of CNS early in disease. during second stage, multiplication and spread throughout the body. Symptoms: 1: afebrile, chancre at site of infection (painless papule becoming eroded and indurated with surrounding red areola), inguinal adenopathy. 2: mucocutaneous rash, generalized contender lymphadenopathy, exanthema may be macular, papular, pustular or mixed. 3: granulomatous lesions, gummas, indurated, nodular, papulosquamous or ulcerative with peripheral hyper pigmentation. Ddx: Drug eruptions, Candidiasis, Herpes simplex, Diagnosis: VDRL, RPR, ICE syphilis recombinant antigen test, FTA-ABS, TPHA, MHA-TP, TPPA Treatment: Penicillin (doxycycline)
lymphatics. Invasion of CNS early in disease. during second stage, multiplication and spread throughout the body. Symptoms: 1: afebrile, chancre at site of infection (painless papule becoming eroded and indurated with surrounding red areola), inguinal adenopathy. 2: mucocutaneous rash, generalized contender lymphadenopathy, exanthema may be macular, papular, pustular or mixed. 3: granulomatous lesions, gummas, indurated, nodular, papulosquamous or ulcerative with peripheral hyper pigmentation. Ddx: Drug eruptions, Candidiasis, Herpes simplex, Diagnosis: VDRL, RPR, ICE syphilis recombinant antigen test, FTA-ABS, TPHA, MHA-TP, TPPA Treatment: Penicillin (doxycycline)" alt="Extensive papular eruption in secondary syphilis. Pathogenesis: Treponema penetrates intact mucous membranes or dermal abrasions -; lymphatics. Invasion of CNS early in disease. during second stage, multiplication and spread throughout the body. Symptoms: 1: afebrile, chancre at site of infection (painless papule becoming eroded and indurated with surrounding red areola), inguinal adenopathy. 2: mucocutaneous rash, generalized contender lymphadenopathy, exanthema may be macular, papular, pustular or mixed. 3: granulomatous lesions, gummas, indurated, nodular, papulosquamous or ulcerative with peripheral hyper pigmentation. Ddx: Drug eruptions, Candidiasis, Herpes simplex, Diagnosis: VDRL, RPR, ICE syphilis recombinant antigen test, FTA-ABS, TPHA, MHA-TP, TPPA Treatment: Penicillin (doxycycline)">
answer
Patient has noticed a rash approximately 2.5 weeks ago. The rash not fuse and peel. There are no subjective complaints.
question
Granuloma annulare. Ring-shaped infiltrated edge, clinically annular element without peeling. Pathogenesis: proposed- Cell mediated immunity (type IV), immune complex vasculitis, abnormality of tissue monocytes. Symptoms: Localized=groups of 1-2mm papules in annular arrangement. Centers of lesions may be slightly hyperpigmented. Generalized=1-2mm papules coalesce into annular plagues measuring 3-6cm in diameter. Sites: dorsal surface of feet, hands and fingers, aural area of trunc. Ddx: Annular lichen planus, Tinea corporis, Leprosy Diagnosis: history and clinical Treatment: Localized=topical corticosteroids, cryotherapy, laser therapy Generalized=UVB, PUVA, Isotretinoin
answer
There is a history of diabetes mellitus.
question
Grouped blisters on the lower lip in herpes simplex. Pathogenesis: Intimate contact between susceptible person and person actively shedding virus. Invasion and replication in neurons, epidermal and dermal cells. Latency in dorsal ganglion. Symptoms: clustered vesicles on erythematous base. often progress to pustular or ulcerated lesions eventually form crust. Ddx: Cytomegalovirus, Erythema multiforme, Herpes zoster, Syphilis Diagnosis: PCR in specific instances. Tzanck smear: multinucleate giant cells. Treatment: topical, oral, intravenous antivirals: acyclovir, valacyclovir, famciclovir.
answer
Tingling, grouped rash developed a few days ago. Slightly itchy feeling was before.
question
The mother has itch in evenings, the child had also appeared itch and rashes on the body 2 weeks ago. Rash suppurated by scratching. Large red papule and nodules on the trunk in an infant with scabies. Pathogenesis: mite infestation. after 4 weeks a delayed type IV hypersensitivity reaction. Symptoms: pruritus worse at night, pruritic papules. Sites: Flexor aspects of wrists, interdigital webs of hands, dorsal feet, axillae, elbows, waist, buttocks, genitalia Ddx: Drug reactions, Folliculitis, Lichen planus, Psoriasis, Insect bites Diagnosis: light microscopy, ink test, tape test Treatment: Permethrin, Benzyl or sulfur
answer
The mother has itch at evenings, the itch and rashes appeared also to her child on the body 2 weeks ago and they suppurated by scratching.
question
Localized scleroderma (morphea) on the back of the hand. Pathogenesis: Overproduction of collagen (type I and III) by fibroblasts in affected area. mechanism of activation unknown. inflammatory, autoimmune. Symptoms: oval/linear/ill defined. Superficial/deep plaque like lesions, indurated Ddx: Lipodermatosclerosis, Linear atrophoderma of Moulin, Scleroderma, Lichen Diagnosis: Serum antibodies (RF, anti DNA, anti-MMP-1) Treatment: Superficial: Topical tacrolimus, corticosteroids Generalized/deep: systemic corticosteroids + MTX
answer
The patient suffers from early youth. Lesions are without significant subjective complaints it is difficult to take the involved skin in a fold.
question
Mature capillary hemangioma (port-wine stain). Pathogenesis: ecstatic papillary dermal capillaries in upper reticular dermis. Symptoms: macular, well circumscribed patches. Blanching is variable. May evolve later in life to a raised thickened plaque. Sites: face, upper trunk most common sites. Ddx: Cobb syndrome, infantile hemangioma Diagnosis: MRI for differential Sturge-Weber syndrome Treatment: cosmetic only
answer
Lesion of dilated blood vessels on the cheeks is since birth. There are no subjective disorders.
question
Pigmented macules (cafe-au-lait-spots) in neurofibromatosis. Pathogenesis: Increase in melanin content, presence of giant melanosomes. Symptoms: maculae brownish, sizes between millimeters to >10cm Ddx: Congenital nevi, post inflammatory hyperpigmentation, linear nevi hyperpigmentation. Diagnosis: Underlying genetic disorders. Treatment: no treatment
10cm Ddx: Congenital nevi, post inflammatory hyperpigmentation, linear nevi hyperpigmentation. Diagnosis: Underlying genetic disorders. Treatment: no treatment" alt="Pigmented macules (cafe-au-lait-spots) in neurofibromatosis. Pathogenesis: Increase in melanin content, presence of giant melanosomes. Symptoms: maculae brownish, sizes between millimeters to >10cm Ddx: Congenital nevi, post inflammatory hyperpigmentation, linear nevi hyperpigmentation. Diagnosis: Underlying genetic disorders. Treatment: no treatment";
answer
Lesions are since childhood, when brownish spots evolved in the skin. The neurological disease has also been diagnosed
question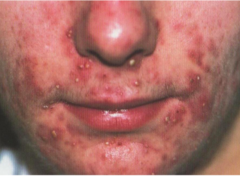 Plugging of follicle -; Lesions Symptoms: Comedones, papules, pustules, nodules in sebaceous distribution. Sites: face, upper chest, back Ddx: Folliculitis, Rosacea, Sebaceous hyperplasia Diagnosis: clinical Treatment: Topical: retinoid + antimicrobial (clindamycin, benzoyl peroxide) Systemic: Antibiotics (tetracyclines, trimethoprim, azitromycin) Hormonal therapy (estrogen) Isotretinoin" alt="Pustules and papules in acne. Pathogenesis: genetics, follicular hyperkeratinization, P acnes follicular colonization, Excess sebum production. Comedones -; Plugging of follicle -; Lesions Symptoms: Comedones, papules, pustules, nodules in sebaceous distribution. Sites: face, upper chest, back Ddx: Folliculitis, Rosacea, Sebaceous hyperplasia Diagnosis: clinical Treatment: Topical: retinoid + antimicrobial (clindamycin, benzoyl peroxide) Systemic: Antibiotics (tetracyclines, trimethoprim, azitromycin) Hormonal therapy (estrogen) Isotretinoin">
Plugging of follicle -; Lesions Symptoms: Comedones, papules, pustules, nodules in sebaceous distribution. Sites: face, upper chest, back Ddx: Folliculitis, Rosacea, Sebaceous hyperplasia Diagnosis: clinical Treatment: Topical: retinoid + antimicrobial (clindamycin, benzoyl peroxide) Systemic: Antibiotics (tetracyclines, trimethoprim, azitromycin) Hormonal therapy (estrogen) Isotretinoin" alt="Pustules and papules in acne. Pathogenesis: genetics, follicular hyperkeratinization, P acnes follicular colonization, Excess sebum production. Comedones -; Plugging of follicle -; Lesions Symptoms: Comedones, papules, pustules, nodules in sebaceous distribution. Sites: face, upper chest, back Ddx: Folliculitis, Rosacea, Sebaceous hyperplasia Diagnosis: clinical Treatment: Topical: retinoid + antimicrobial (clindamycin, benzoyl peroxide) Systemic: Antibiotics (tetracyclines, trimethoprim, azitromycin) Hormonal therapy (estrogen) Isotretinoin">
Pustules and papules in acne. Pathogenesis: genetics, follicular hyperkeratinization, P acnes follicular colonization, Excess sebum production. Comedones -; Plugging of follicle -; Lesions Symptoms: Comedones, papules, pustules, nodules in sebaceous distribution. Sites: face, upper chest, back Ddx: Folliculitis, Rosacea, Sebaceous hyperplasia Diagnosis: clinical Treatment: Topical: retinoid + antimicrobial (clindamycin, benzoyl peroxide) Systemic: Antibiotics (tetracyclines, trimethoprim, azitromycin) Hormonal therapy (estrogen) Isotretinoin
 Plugging of follicle -; Lesions Symptoms: Comedones, papules, pustules, nodules in sebaceous distribution. Sites: face, upper chest, back Ddx: Folliculitis, Rosacea, Sebaceous hyperplasia Diagnosis: clinical Treatment: Topical: retinoid + antimicrobial (clindamycin, benzoyl peroxide) Systemic: Antibiotics (tetracyclines, trimethoprim, azitromycin) Hormonal therapy (estrogen) Isotretinoin" alt="Pustules and papules in acne. Pathogenesis: genetics, follicular hyperkeratinization, P acnes follicular colonization, Excess sebum production. Comedones -; Plugging of follicle -; Lesions Symptoms: Comedones, papules, pustules, nodules in sebaceous distribution. Sites: face, upper chest, back Ddx: Folliculitis, Rosacea, Sebaceous hyperplasia Diagnosis: clinical Treatment: Topical: retinoid + antimicrobial (clindamycin, benzoyl peroxide) Systemic: Antibiotics (tetracyclines, trimethoprim, azitromycin) Hormonal therapy (estrogen) Isotretinoin">
Plugging of follicle -; Lesions Symptoms: Comedones, papules, pustules, nodules in sebaceous distribution. Sites: face, upper chest, back Ddx: Folliculitis, Rosacea, Sebaceous hyperplasia Diagnosis: clinical Treatment: Topical: retinoid + antimicrobial (clindamycin, benzoyl peroxide) Systemic: Antibiotics (tetracyclines, trimethoprim, azitromycin) Hormonal therapy (estrogen) Isotretinoin" alt="Pustules and papules in acne. Pathogenesis: genetics, follicular hyperkeratinization, P acnes follicular colonization, Excess sebum production. Comedones -; Plugging of follicle -; Lesions Symptoms: Comedones, papules, pustules, nodules in sebaceous distribution. Sites: face, upper chest, back Ddx: Folliculitis, Rosacea, Sebaceous hyperplasia Diagnosis: clinical Treatment: Topical: retinoid + antimicrobial (clindamycin, benzoyl peroxide) Systemic: Antibiotics (tetracyclines, trimethoprim, azitromycin) Hormonal therapy (estrogen) Isotretinoin">answer
Patient has rash on skin of the face from the 14 years of age. Patient's father also have been similar rash in history
question
Red papule and plaques in extensive lichen planus. Pathogenesis: cell-mediated immune response of unknown origin. Symptoms: papules are violaceous, shiny and polygonal. size 0.1->1cm. discrete or arranged in groups. White lines (Wickham striae) bound to papules Ddx: Guttate psoriasis, Pityriasis rosea, linea corporis Diagnosis: Direct IF (globular deposits of IgM and complement mixed with apoptotic keratinocytes) Histology (irregular acanthuses and colloid bodies in epidermis with destruction of basal layer. Upper dermis has a bandlike infiltrate of lymphocytes and histiocytes) Treatment: Topical steroids, UVB, PUVA,
1cm. discrete or arranged in groups. White lines (Wickham striae) bound to papules Ddx: Guttate psoriasis, Pityriasis rosea, linea corporis Diagnosis: Direct IF (globular deposits of IgM and complement mixed with apoptotic keratinocytes) Histology (irregular acanthuses and colloid bodies in epidermis with destruction of basal layer. Upper dermis has a bandlike infiltrate of lymphocytes and histiocytes) Treatment: Topical steroids, UVB, PUVA," alt="Red papule and plaques in extensive lichen planus. Pathogenesis: cell-mediated immune response of unknown origin. Symptoms: papules are violaceous, shiny and polygonal. size 0.1->1cm. discrete or arranged in groups. White lines (Wickham striae) bound to papules Ddx: Guttate psoriasis, Pityriasis rosea, linea corporis Diagnosis: Direct IF (globular deposits of IgM and complement mixed with apoptotic keratinocytes) Histology (irregular acanthuses and colloid bodies in epidermis with destruction of basal layer. Upper dermis has a bandlike infiltrate of lymphocytes and histiocytes) Treatment: Topical steroids, UVB, PUVA,";
answer
56g. old woman complaints about a extensive itch. There are reddish brown burnish populous elements on skin of both limbs.
question
Scarring alopecia secondary to discoid lupus erythematous. DLE Pathogenesis: autoimmune disease linked to HLA genes, immune signaling and environment. heat-shock protein induced in keratinocyte following UV exposure or stress. Symptoms: erythematous papule or plaque with slight to moderate scale. Hypo pigmentation of central area, hyperpigmentation of active border. Sites: Photodistributed Ddx: Rosacea, Lichen planus, Psoriasis, Tinea corporis, Granuloma annulare Diagnosis: Histology (thickening of basal membrane, hyperkeratosis, incontinence of pigment, atrophy of the epidermis) Treatment: Sun-protection, antimalarials, topical calcineurin inhibitors, topical retinoids
answer
There are prominent atrophy inside the lesion and "butterfly" form damage on central part of the face.
question
Severe atopic eczema. The eruption is confluent and excoriations are a common feature. Pathogenesis: primary immune dysfunction resulting in IgE sensitization, primary defect in epidermal barrier. Symptoms: xerosis, lichenification, eczematous lesions. excoriations, crusting, pruritus Sites: Adults: flexural, sparing groin and axilla Children: facial/neck/extensor involvement Ddx: Allergic contact dermatitis, Scabies, Tinea corporis, Seborrheic dermatitis Diagnosis: Serum IgE Treatment: Moisturization, Topical corticosteroids, Immunomodulators (tacrolimus, pimecrolimus)
answer
The patient suffers from 4 years of age. The skin of the folds is hyperemia, infiltrated and slightly lichenificated, separate excoriations are detectable
question
Small scabs on the back of the hans produced by minor trauma because of increased skin fragility in porphyria. Pathogenesis: deficiency of an enzyme in the heme production pathway Symptoms: Skin changes; Acute: erythema, edema and erosions. Chronic: skin fragility, blistering, scarring Sites: Acute-face, Chronic-back of hands Ddx: Pseudoporphyria Diagnosis: elevated porphyrins in plasma, urine and stool. Histology (sub epidermal bull with dermal papillae at the bases.) Treatment: Iron depletion, Erythropoietin
answer
Amount of porphyrin in urine is increased. Sun exposure provokes development of rash.
question
Subungual hyperkeratosis and yellowish discoloration due to a fungal infection. Pathogenesis: fungus spreads from plantar skin and invades nail bed. Symptoms: usually asymptomatic Ddx: Nail psoriasis, Melanonychia Diagnosis: Direct microscopy KOH, Culture Treatment: Systemic if involving luna region Topical: Efinaconazole, Amorolfine Systemic: Itraconazole, Terbinafine
answer
A patient suffers for many years; the nail changes it's color, crumbles and sheds. The KOH test is positive.
question
Symmetrical eruption on the back of the hands in erythema multiforme. Pathogenesis: Cell-mediated immunity -> destruction of epithelial cells. Epidermis infiltrated with CD8 -> cytokine release -> apoptosis of epithelial cells Symptoms: dull-red, pruritic macule or urticarial plaque expanding to maximum 2cm over 24-48h. In center a small papule, vesicle or bulla develops, flattens and clears. leaving inner ring. Sites: symmetrical, predominantly on aural extensor surfaces of extremities, spread centripetally to abdomen and back. Ddx: Allergic contact dermatitis, bulls pemphigoid, Drug eruptions, Irritant contact dermatitis. Diagnosis: clinical, histology (lymphocytic infiltrate along dermoepidermal junction) Treatment: Symptomatic (antihistamines, analgesics) Topical steroids
destruction of epithelial cells. Epidermis infiltrated with CD8 -> cytokine release -> apoptosis of epithelial cells Symptoms: dull-red, pruritic macule or urticarial plaque expanding to maximum 2cm over 24-48h. In center a small papule, vesicle or bulla develops, flattens and clears. leaving inner ring. Sites: symmetrical, predominantly on aural extensor surfaces of extremities, spread centripetally to abdomen and back. Ddx: Allergic contact dermatitis, bulls pemphigoid, Drug eruptions, Irritant contact dermatitis. Diagnosis: clinical, histology (lymphocytic infiltrate along dermoepidermal junction) Treatment: Symptomatic (antihistamines, analgesics) Topical steroids" alt="Symmetrical eruption on the back of the hands in erythema multiforme. Pathogenesis: Cell-mediated immunity -> destruction of epithelial cells. Epidermis infiltrated with CD8 -> cytokine release -> apoptosis of epithelial cells Symptoms: dull-red, pruritic macule or urticarial plaque expanding to maximum 2cm over 24-48h. In center a small papule, vesicle or bulla develops, flattens and clears. leaving inner ring. Sites: symmetrical, predominantly on aural extensor surfaces of extremities, spread centripetally to abdomen and back. Ddx: Allergic contact dermatitis, bulls pemphigoid, Drug eruptions, Irritant contact dermatitis. Diagnosis: clinical, histology (lymphocytic infiltrate along dermoepidermal junction) Treatment: Symptomatic (antihistamines, analgesics) Topical steroids">
answer
Itchy red rash with a blister in the center in hand skin appears regularly in autumn and winter months. Lesions of oral mucosa are also possible sometimes.
question
White scales as seen in psoriasis. Pathogenesis: epidermis infiltration by large number of activated T cells inducing keratinocyte proliferation. Vascular engorgement due to superficial blood vessel dilation. Accelerated turnover rate. Cells normally loosing their nuclei in stratum granulosum retain their nuclei (parakeratosis) Symptoms: Scling erythematous macule, papule or plaque. Non coherent, silvery plaques overlying a glossy homogenous erythema. Nailpitting, onycholysis. Sites: Plaque: extensor surfaces Guttate: trunk Inversus: flexural surfaces, armpit, groin, under breast and skin folds Pustular: palms and soles or diffusely over body Ddx: Allergic contact dermatitis, Lichen planus, Pityriasis, Seborrheic dermatitis, Syphilis Diagnosis: clinical, histology (basal cell hyperplasia, proliferation of sub epidermal vasculature, absence of normal cell maturation, and keratinization. Large number of activated T cells in epidermis) Treatment: Moisturizing, topical corticosteroids, tar preparations, vitamin D analog, UVB, PUVA, systemic corticosteroids, MTX, Biologicals
answer
Patient has papular elements with silvery scales on the two elbow, knee extensor surfaces for several years.
question
Pityriasis versicolor. Pathogenesis: Yeast infection. Malassezia. found in both spore and hyphen stage. Conversion from saprophytic to parasitic form by factors: genetic, warm humid environment, immunosuppression, malnutrition and cushings disease. Symptoms: 4 forms 1: numerous oval-round macules with pigmentary alteration over trunk/chest with occasional extension. 2: affects flexural regions, face or isolated areas on extremities. More often seen in immunocompromised 3: involves hair follicle. back, chest and extremities 4: multiple firm 2-3mm, monomorphic, red-brown papules. usually on torso and asymptomatic Sites: Trunk, back, abdomen, proximal extremities. Ddx: Erythrasma, Psoriasis guttata, seborrheic dermatitis, tine corporis, vitiligo Diagnosis: Clinical, woods light (coppery-orange), KOH examination, Culture, skin biopsy (fungal elements in stratum corneum) Treatment: Topical selenium sulfide, topical azoles, oral therapy (fluconazole/itraconazole)
answer
The brownish spots appeared on the back, chest and abdomen of patient after increased sweating at the beginning, after tah this spots formed more larger lesions with uneven polycyclic edges by merging.
question
Urticaria. Classification: Acute 6 weeks duration. Chronic inducible: Cold, Cholinergic, Contact, Delayed pressure, Solar, Heat, Vibratory, Aquagenic Pathogenesis: Weals due to cytokines, histamine, PAF from mast cells and basophils -> activate sensory nerves-> dilation of blood vessels -> leakage of fluid into surrounding tissues Clinical: Weals mm-cm in diam. each weal last minutes-hours and may change shape. severity based on daily weal/itch for 7 days. Ddx: contact dermatitis, vasculitis, mastocytosis. Diagnosis: history of weals lasting <24h, skin prick test/radioabsorbent test Treatment: Antihistamine p/o Avoidance of triggers
6 weeks duration. Chronic inducible: Cold, Cholinergic, Contact, Delayed pressure, Solar, Heat, Vibratory, Aquagenic Pathogenesis: Weals due to cytokines, histamine, PAF from mast cells and basophils -> activate sensory nerves-> dilation of blood vessels -> leakage of fluid into surrounding tissues Clinical: Weals mm-cm in diam. each weal last minutes-hours and may change shape. severity based on daily weal/itch for 7 days. Ddx: contact dermatitis, vasculitis, mastocytosis. Diagnosis: history of weals lasting <24h, skin prick test/radioabsorbent test Treatment: Antihistamine p/o Avoidance of triggers" alt="Urticaria. Classification: Acute 6 weeks duration. Chronic inducible: Cold, Cholinergic, Contact, Delayed pressure, Solar, Heat, Vibratory, Aquagenic Pathogenesis: Weals due to cytokines, histamine, PAF from mast cells and basophils -> activate sensory nerves-> dilation of blood vessels -> leakage of fluid into surrounding tissues Clinical: Weals mm-cm in diam. each weal last minutes-hours and may change shape. severity based on daily weal/itch for 7 days. Ddx: contact dermatitis, vasculitis, mastocytosis. Diagnosis: history of weals lasting
answer
Rash appeared to patient after exposure of cold water, they quickly disappeared, so the patient could not show this rash to the doctor.
question
Rosacea. Pathogenesis: theories (genetic, environmental, vascular, inflammatory, UV radiation) Cathelicidins -> infiltration of neutrophils -> nitric acid release -> vasodilation -> edema and cytokine release Clinical: red papules, dome-shaped, no comedones, telangiectasia, Sites: Nose, forehead, cheeks, chin Ddx: Acne vulgaris, seborrhoeic dermatitis, Contact dermatitis Diagnosis: Clinical, skin biopsy (chronic inflammation and vascular changes) Treatment: Oral tetracyclines (decrease inflammation), Topical Metronidazole, Brimonidine, Vascular laser
infiltration of neutrophils -> nitric acid release -> vasodilation -> edema and cytokine release Clinical: red papules, dome-shaped, no comedones, telangiectasia, Sites: Nose, forehead, cheeks, chin Ddx: Acne vulgaris, seborrhoeic dermatitis, Contact dermatitis Diagnosis: Clinical, skin biopsy (chronic inflammation and vascular changes) Treatment: Oral tetracyclines (decrease inflammation), Topical Metronidazole, Brimonidine, Vascular laser" alt="Rosacea. Pathogenesis: theories (genetic, environmental, vascular, inflammatory, UV radiation) Cathelicidins -> infiltration of neutrophils -> nitric acid release -> vasodilation -> edema and cytokine release Clinical: red papules, dome-shaped, no comedones, telangiectasia, Sites: Nose, forehead, cheeks, chin Ddx: Acne vulgaris, seborrhoeic dermatitis, Contact dermatitis Diagnosis: Clinical, skin biopsy (chronic inflammation and vascular changes) Treatment: Oral tetracyclines (decrease inflammation), Topical Metronidazole, Brimonidine, Vascular laser">
answer
The rash appeared to 40 years old woman on her face, after at a birthday party, in which alcoholic beverages was used for several days in a row.
question
Allergic vasculitis. Pathogenesis: Causing factor (direct injury by virus/bacteria, Indirect injury by antibodies, Indirect injury by complement activation) -> inflammatory response in the blood vessel Symptoms: Capillaritis: pigmented pupura characterized by petechiae Small vessel vasculitis: palpable purpura Medium vessel vasculitis: nodules and lived reticularis Large vessel vasculitis: infrequent in cutaneous features Diagnosis: Clinical, skin biopsy (inflamed blood vessel wall) Treatment: Depends on severity. general measures, systemic corticosteroids, immunomodulators
inflammatory response in the blood vessel Symptoms: Capillaritis: pigmented pupura characterized by petechiae Small vessel vasculitis: palpable purpura Medium vessel vasculitis: nodules and lived reticularis Large vessel vasculitis: infrequent in cutaneous features Diagnosis: Clinical, skin biopsy (inflamed blood vessel wall) Treatment: Depends on severity. general measures, systemic corticosteroids, immunomodulators" alt="Allergic vasculitis. Pathogenesis: Causing factor (direct injury by virus/bacteria, Indirect injury by antibodies, Indirect injury by complement activation) -> inflammatory response in the blood vessel Symptoms: Capillaritis: pigmented pupura characterized by petechiae Small vessel vasculitis: palpable purpura Medium vessel vasculitis: nodules and lived reticularis Large vessel vasculitis: infrequent in cutaneous features Diagnosis: Clinical, skin biopsy (inflamed blood vessel wall) Treatment: Depends on severity. general measures, systemic corticosteroids, immunomodulators">
answer
Rash appeared to patient after experienced moderate going tonsillitis.
question
Alopecia areata. Pathogenesis: autoimmune, T-ly around hair follicles -> pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines -> hair rejection Triggers: Viral infection, Trauma, Hormonal change, Emotional stressors Clinical: Most patients have no symptoms, bald patches found incidentally. Nail disease (pitting and ridging) 10-50% Diagnosis: clinically, skin biopsy Treatment: Topical steroids, Intralesional injection corticosteroids, systemic corticosteroids, immunotherapy
pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines -> hair rejection Triggers: Viral infection, Trauma, Hormonal change, Emotional stressors Clinical: Most patients have no symptoms, bald patches found incidentally. Nail disease (pitting and ridging) 10-50% Diagnosis: clinically, skin biopsy Treatment: Topical steroids, Intralesional injection corticosteroids, systemic corticosteroids, immunotherapy" alt="Alopecia areata. Pathogenesis: autoimmune, T-ly around hair follicles -> pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines -> hair rejection Triggers: Viral infection, Trauma, Hormonal change, Emotional stressors Clinical: Most patients have no symptoms, bald patches found incidentally. Nail disease (pitting and ridging) 10-50% Diagnosis: clinically, skin biopsy Treatment: Topical steroids, Intralesional injection corticosteroids, systemic corticosteroids, immunotherapy">
answer
The hair falls out at age 13 for the first time after a very serious infectious disease and the subsequent course of antibiotics. Then a new outbreak occurred at the age of 23 after a very severe and prolonged stress.
question
Balanoposthitis cancidomycetica. Balanitis Pathogenesis: specific skin conditions and infections affecting penis. Usually signs of skin condition elsewhere. Predisposing factors: Moisture, Infrequent washing, Overfrequent washing, DM, Chemical irritants, Minor trauma, Obesity Symptoms: Pink-red rash, redness/swelling/tenderness, Discharge or oozing, Itcing/discomfort, Phimosis Diagnosis: clinical, KOH/culture Treatment: Astringent compress + Topical anti fungal + Topical antiseptic + Mild topical steroid, Oral anti fungal/antibiotic
answer
Mainly it develops those male patients with diabetes mellitus.
question
Dermatomyositis. Inflammation of voluntary muscles in association with a skin rash Pathogenesis: Connective tissue disease. Factors: Genetic, Cancer, Autoimmune, Infectious, Drug-induced. Clinical: Reddish-bluish patches, purple eyelids "heliotrope", rash may affect cheeks, nose, shoulders, upper chest and elbows. Diagnosis: CK (incr), ANA, skin biopsy (similar to LE) Treatment: oral corticosteroid, immunosuppressives, Diltiazem, Hydroxychloroquine
answer
The patient has complaints of pain in a muscles and progressive weakness in proximal muscles of arms and legs.
question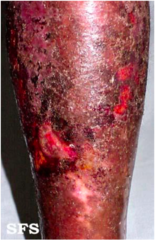
Microbial eczema.

answer
Lesions with diffuse erosive surface in the center and also pronounced moisturizing of the skin developed to patient after frostbite of the feet. Groups of micro vesicles are seen in periphery of rashes.
question
Erysipelas. Pathogenesis: almost all caused by Group A Beta Hemolytic Streptococci Clinical: Abrupt onset accompanied by fevers, child and shivering. Affected skin has sharp raised borders, bright red, firm and swollen. Diagnosis: characteristic rash, Leu (incr), CRP+, Blood culture+ Treatment: 10-14 days Oral/iv. penicillin / erythromycin
answer
Disease to patient started suddenly with a high fever, even 39-40, chills, headache, and also with nausea and vomiting.
question
Erythema multiforme. Pathogenesis: among others HSV; HSV infection of keratinocytes -> Langerhans precursors transport HSV DNA to distant keratinocytes-> HSV gene expressed-> Recreation of specific T-helper cells-> gamma-interferon-> inflammatory cascade Clinical: few to hundreds lesions erupt in 24h period. sharply demarcated, round, red/pink macules. Becomes papules. Enlarges to form plaques. Typical target lesion Diagnosis: clinical, Skin biopsy ( apoptotic keratinocytes, degeneration of basal keratinocytes, spongiosis, epidermal necrosis) Treatment: usually settles by itself, oral acyclovir, symptomatic (itch, pain)
Langerhans precursors transport HSV DNA to distant keratinocytes-> HSV gene expressed-> Recreation of specific T-helper cells-> gamma-interferon-> inflammatory cascade Clinical: few to hundreds lesions erupt in 24h period. sharply demarcated, round, red/pink macules. Becomes papules. Enlarges to form plaques. Typical target lesion Diagnosis: clinical, Skin biopsy ( apoptotic keratinocytes, degeneration of basal keratinocytes, spongiosis, epidermal necrosis) Treatment: usually settles by itself, oral acyclovir, symptomatic (itch, pain)" alt="Erythema multiforme. Pathogenesis: among others HSV; HSV infection of keratinocytes -> Langerhans precursors transport HSV DNA to distant keratinocytes-> HSV gene expressed-> Recreation of specific T-helper cells-> gamma-interferon-> inflammatory cascade Clinical: few to hundreds lesions erupt in 24h period. sharply demarcated, round, red/pink macules. Becomes papules. Enlarges to form plaques. Typical target lesion Diagnosis: clinical, Skin biopsy ( apoptotic keratinocytes, degeneration of basal keratinocytes, spongiosis, epidermal necrosis) Treatment: usually settles by itself, oral acyclovir, symptomatic (itch, pain)">
answer
Fern type erythema and plaques with raised edges and bright red border area are typical.
question
Erythema nodosum. Pathogenesis: hypersensitivity reaction with a number of causes (Throat infections, Sarcoidosis, TB, Pregnancy, Drugs, IBD) Clinical: Red lumps on shins or about knee/ankle. Nodules slightly raised above surrounding skin, hot and painful. Diagnosis: Clinically, skin biopsy (inflammation around septum between lobules of fat in subcutaneous tissue, without vasculitis) Treatment: Treat underlying infection, bed rest, tetracyclines(anti-inflammatory)
answer
Red unsharply demarcated knots of dense consistency have developed to 42 years old patient on her thighs. They are slightly painful by pressing.
question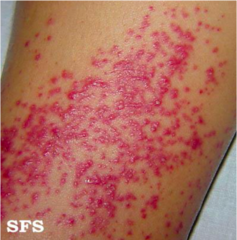
Folliculitis. Pathogenesis: infection, occlusion, irritation, skin disease.

answer
The first rash appeared to the patient after waxing procedures.
question
Herpes simplex. Pathogenesis: Intimate contact between susceptible person and person actively shedding virus. Invasion and replication in neurons, epidermal and dermal cells. Latency in dorsal ganglion. Symptoms: clustered vesicles on erythematous base. often progress to pustular or ulcerated lesions eventually form crust. Ddx: Cytomegalovirus, Erythema multiforme, Herpes zoster, Syphilis Diagnosis: PCR in specific instances. Tzanck smear (multinucleate giant cells) Treatment: topical, oral, intravenous antivirals: acyclovir, valacyclovir, famciclovir.
answer
The patient suffers from a skin disease on average 5-6 times per year, the disease regresses without initiating of therapy.
question
Pityriasis rosea Pathogenesis: Reactivation of HSV 6 and 7, Vaccination, Clinical: Herald patch (single plaque, oval, pink/red 2-5cm, scale trailing just inside the edge) Secondary rash (10-20 days after herald patch, more scaly patches on chest or back. Usually following Langers lines) Diagnosis: Clinically, skin biopsy (subacute dermatitis) Treatment: Bathing, moisturizing. Off-License (acyclovir, erythromycin), Topical steroid may resolve itch.
answer
The patient has complaints of severe itching after batching in the sauna, which provoked the manifestation of the disease and appearance of a new rash.
question
Pemphigus vulgaris. Pathogenesis: Autoimmune, IgG antibodies (antidesmoglein 1 and 3) binds to keratinocyte desmosomes loss of cell-cell adhesion -> acantholysis Symptoms: Mucousal lesions precede cutaneous by weeks or months. intact bullae rare in mouth. Primary lesion on skin: flaccid blister filled with clear fluid on healthy or erythematous base. Nikolsky sign. Asboe-Hansen sign Sites: Start in mucosa then skin Ddx: Dermatitis herpetiformis, Drug-induced pemphigus, erythema multiforme Diagnosis: Histopathology from edge of blister. Direct IF on normal appearing perilesional skin. Indirect immunofluorescence using serum if DIF are positive. Treatment: Corticosteroids high dose. Immunosuppressives
acantholysis Symptoms: Mucousal lesions precede cutaneous by weeks or months. intact bullae rare in mouth. Primary lesion on skin: flaccid blister filled with clear fluid on healthy or erythematous base. Nikolsky sign. Asboe-Hansen sign Sites: Start in mucosa then skin Ddx: Dermatitis herpetiformis, Drug-induced pemphigus, erythema multiforme Diagnosis: Histopathology from edge of blister. Direct IF on normal appearing perilesional skin. Indirect immunofluorescence using serum if DIF are positive. Treatment: Corticosteroids high dose. Immunosuppressives" alt="Pemphigus vulgaris. Pathogenesis: Autoimmune, IgG antibodies (antidesmoglein 1 and 3) binds to keratinocyte desmosomes loss of cell-cell adhesion -> acantholysis Symptoms: Mucousal lesions precede cutaneous by weeks or months. intact bullae rare in mouth. Primary lesion on skin: flaccid blister filled with clear fluid on healthy or erythematous base. Nikolsky sign. Asboe-Hansen sign Sites: Start in mucosa then skin Ddx: Dermatitis herpetiformis, Drug-induced pemphigus, erythema multiforme Diagnosis: Histopathology from edge of blister. Direct IF on normal appearing perilesional skin. Indirect immunofluorescence using serum if DIF are positive. Treatment: Corticosteroids high dose. Immunosuppressives">
answer
The patient's disease began with erosions in oral mucosa, which gradually increased at size and caused pain. Erosions formed also in the eye mucosa. Then appeared the rash on the skin.
question
Scabies Pathogenesis: mite infestation. after 4 weeks a delayed type IV hypersensitivity reaction. Symptoms: pruritus worse at night, pruritic papules. Sites: Flexor aspects of wrists, interdigital webs of hands, dorsal feet, axillae, elbows, waist, buttocks, genitalia Ddx: Drug reactions, Folliculitis, Lichen planus, Psoriasis, Insect bites Diagnosis: light microscopy, ink test, tape test Treatment: Permethrin, Benzyl or sulfur
answer
The patient has complaints of intense itching especially at night times, he tried antihistamine preparations in therapy, however, had no effect.
question
Primary syphilis. Pathogenesis: Treponema penetrates intact mucous membranes or dermal abrasions -; lymphatics. Invasion of CNS early in disease. during second stage, multiplication and spread throughout the body. Symptoms: 1: afebrile, chancre at site of infection (painless papule becoming eroded and indurated with surrounding red areola), inguinal adenopathy. 2: mucocutaneous rash, generalized contender lymphadenopathy, exanthema may be macular, papular, pustular or mixed. 3: granulomatous lesions, gummas, indurated, nodular, papulosquamous or ulcerative with peripheral hyper pigmentation. Ddx: Drug eruptions, Candidiasis, Herpes simplex, Diagnosis: VDRL, RPR, ICE syphilis recombinant antigen test, FTA-ABS, TPHA, MHA-TP, TPPA Treatment: Penicillin by injection (doxycycline)
lymphatics. Invasion of CNS early in disease. during second stage, multiplication and spread throughout the body. Symptoms: 1: afebrile, chancre at site of infection (painless papule becoming eroded and indurated with surrounding red areola), inguinal adenopathy. 2: mucocutaneous rash, generalized contender lymphadenopathy, exanthema may be macular, papular, pustular or mixed. 3: granulomatous lesions, gummas, indurated, nodular, papulosquamous or ulcerative with peripheral hyper pigmentation. Ddx: Drug eruptions, Candidiasis, Herpes simplex, Diagnosis: VDRL, RPR, ICE syphilis recombinant antigen test, FTA-ABS, TPHA, MHA-TP, TPPA Treatment: Penicillin by injection (doxycycline)" alt="Primary syphilis. Pathogenesis: Treponema penetrates intact mucous membranes or dermal abrasions -; lymphatics. Invasion of CNS early in disease. during second stage, multiplication and spread throughout the body. Symptoms: 1: afebrile, chancre at site of infection (painless papule becoming eroded and indurated with surrounding red areola), inguinal adenopathy. 2: mucocutaneous rash, generalized contender lymphadenopathy, exanthema may be macular, papular, pustular or mixed. 3: granulomatous lesions, gummas, indurated, nodular, papulosquamous or ulcerative with peripheral hyper pigmentation. Ddx: Drug eruptions, Candidiasis, Herpes simplex, Diagnosis: VDRL, RPR, ICE syphilis recombinant antigen test, FTA-ABS, TPHA, MHA-TP, TPPA Treatment: Penicillin by injection (doxycycline)">
answer
The patient complaints of non painful erosions on the genitals, which appeared two weeks ago as well as the lymph nodes in this area increased approximately 1 week ago



