CPR and First Aid – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
how to recognize an emergency

answer
look for unusual noises, sights, odors, appearances and behaviors example: screams, breaking glass, crashing metal
question
safety

answer
do not risk your own _________________ in orer to rescue or provide first aid to another person
question
Good Samaritan Laws

answer
state laws that help protect healthcare professionals and ordinary citizens from liability while giving emergency care to accident victims. You are protected if you are certified and obtain consent, act in good faith, are not paid, use reasonable skill and care, are not negligent (careless), and do not abandon the person
question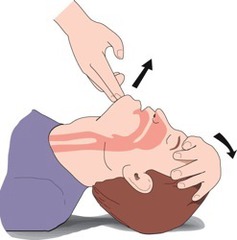
how to open an Airway

answer
tilt head, lift chin
question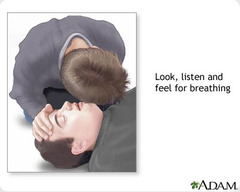
signs of life

answer
movement or breathing
question
ABCs
answer
Airway, Breathing, and Circulation (blood flowing through the body)
question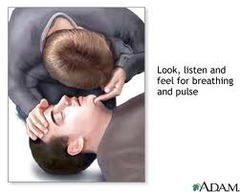
How to check Breathing

answer
look for movement of the chest, listen and feel for air movement by placing your ear and then your cheek at the mouth and nose of the victim
question
how to check Circulation
answer
place your index and middle fingers into the groove of the neck next to the voice box to feel the carotid artery pulse
question
index finger

answer
the finger next to the thumb; also called pointer finger
question
voice box
answer
larynx
question
Rescue Breathing
answer
an emergency technique in which a rescuer gives air to someone who is not breathing. To perform this, a person blows air into a victim's lungs to give him/her oxygen
question
how to give rescue breaths to an adult
answer
1. tilt head, lift chin, pinch the nose shut 2. take a breath and make a complete seal over the person's mouth 3. blow in to make chest clearly rise (1 second) 4. Begin CPR/administer AED if breaths go in OR assume unconscious choking if breaths do NOT go in
question
Steps to check an injured child or infant

answer
1. check scene, then check child 2. obtain consent from parent/guardian if present 3. Tap on shoulder and shout, "Are you okay?" 4. No response, call 911 or if alone, give 2 minutes of care then call 911 5. Open airway, check for signs of life for no more than 10 seconds 6. give 2 rescue breaths if not breathing 7. If breaths go in, check for pulse and severe bleeding. If breaths do NOT go in, begin rescue breathing. No pulse, begin CPR/AED 8. If breathing, place in recovery position and monitor ABCs
question
recovery position
answer
a side-lying position used to maintain a clear airway in unconscious patients without injuries who are breathing adequately
question
Rescue Breathing for Child/Infant (Age 1-12)
answer
1. give 1 rescue breath (for about 1 second) every 3 seconds, pinch nose shut, make seal over child's mouth and nose (infant), blow in to make chest clearly rise 2. After 2 minutes, recheck signs of life and pulse for no more than 10 signs 3. If pulse, but no breathing, continue. If NO pulse, begin CPR/Administer AED
question
unconscious choking/ no breaths go in
answer
tilt head farther back, give 2 rescue breaths, if chest does not rise, give 30 chest compressions; look for an object and remove it if seen; try 2 rescue breaths; continue these steps if breath does NOT go in. If breaths DO go in, check for signs of life and give care.
question
conscious choking

answer
victim can't cough, speak, cry or breath 1. check scene, check person 2. Have someone call 911 3. obtain consent 4. lean person forward, give 5 back blows with heel of your hand 5. give 5 quick, upward abdominal thrusts (or chest thrusts for infants, pregnant or obese people) 6. continue back blows and abdominal thrusts until object is forced out, the person can breathe or cough forcefully, OR the person becomes unconscious
question
two
answer
number of fingers used in chest compressions for infant
question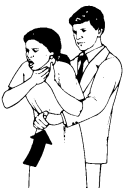
abdominal thrusts

answer
the act of applying pressure to a choking person's stomach to force an object out of the throat
question
choking when you are alone

answer
1. self-administer abdominal thrusts 2. place your fist above your navel (belly button) 3. cover your fist with your hand and thrust upward and inward 4. lean over the back of a chair, table or other firm object and quickly press your abdomen upward and inward
question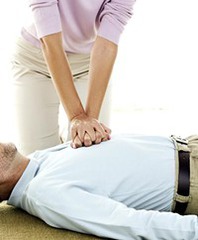
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)

answer
life saving technique that combines rescue breathing and chest compressions
question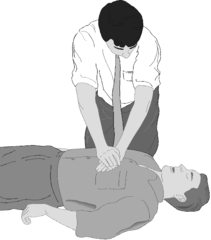
compressions

answer
techniques that allow the rescuer to artificially pump the heart, delivering blood to the body and bringing oxygen to the lungs
question
heart attack
answer
when an area of the heart muscle suffers damage and loses function due to lack of oxygen. The heart stops beating
question
cardiac arrest
answer
when the heart stops beating due to stroke, severe injuries, electrical shock, drug overdose, chest trauma, drowning or suffocation. Leads to unconsciousness, no pulse, no signs of circulation
question
signs of circulation
answer
consciousness, a pulse, pink nail beds, warm skin If a person does not have these, they are in cardiac arrest
question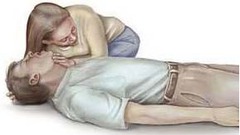
Adult CPR

answer
1. give 30 chest compressions and 2 rescue breaths 2. continue until scene becomes unsafe, you see a sign of life, AED is ready to use, you are too exhausted, or another trained responder arrives and takes over
question 12 years old" alt="Adult CPR skills >12 years old">
12 years old" alt="Adult CPR skills >12 years old">
Adult CPR skills >12 years old
 12 years old" alt="Adult CPR skills >12 years old">
12 years old" alt="Adult CPR skills >12 years old">answer
hand position: 2 hands in center of chest compression depth: 1 1/2 - 2 inches cycle: 30 compressions, 2 breaths rate: 30 compressions in 18 seconds or 100 per minute
question
Child CPR skills (1-12 years old)
answer
hand position: 1 or 2 hands in center of chest compression: 1-1 1/2 inches cycle: 30 compressions, 2 breaths rate: 30 compressions in 18 seconds
question
Infant CPR skills <1 year old
<img src="https://chmanchacentro.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/03/infant-cpr-skills.jpg" title="Infant CPR skills <1 year old" alt="Infant CPR skills
answer
hand position: 2 or 3 fingers on lower half of chest, one finger width below nipple line compression depth: 1/2 - 1 inch cycle: 30 compressions, 2 breaths rate: 30 compressions in 18 seconds
question
Automatic External Defibrillators (AEDs)

answer
portable defibrillators that are available in many public areas. The machine first determines if the victim needs a shock. If shock is needed, the machine talks the rescuer through administering the procedure
question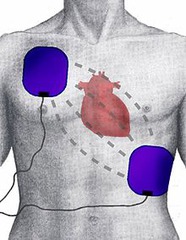
defibrillation

answer
shocking the heart back into beating again by delivering an electric current to the heart which will, in turn, return the heart to a regular rhythm
question
survival rate with AED

answer
30% or higher, according to the American Red Cross, if used within minutes after cardiac arrest
question
wound

answer
a break or tear in the soft tissue of the body
question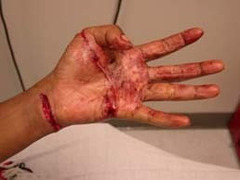
open wound

answer
wound that breaks the surface of the skin
question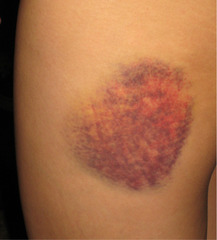
closed wound

answer
wound that does not break the surface of the skin
question
internal bleeding
answer
bleeding within the body that results from closed wounds such as bruises
question
external bleeding

answer
bleeding at the body surface that results from open wounds, such as cuts
question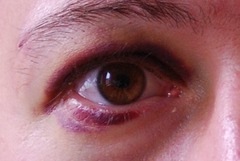
contusions

answer
simplest closed wound, also known as a bruise. They are caused when the body is subjected to a force
question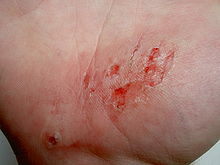
abrasions

answer
most common type of open wound which is characterized by skin that has been rubbed or scraped away
question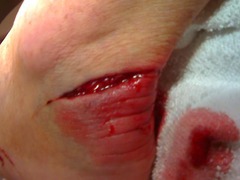
lacerations

answer
a cut with either jagged or smooth edges, usually from a sharp object. Can also result when a blunt force splits the skin
question
avulsions
answer
injury in which a portion of the skin and sometimes other soft tissue is partially or completely torn away
question
puncture
answer
when skin is pierced with a pointed object
question
caring for minor wounds
answer
1. wash hands, put on disposable gloves if available 2. place sterile or clean cloth on wound and apply direct pressure 3. Rinse wound with water and gently wash 4. Seek medical help if you can't remove dirt or debris from the wound. Apply antibacterial ointment 5. Cover wound with sterile dressing and bandage. Change dressing at least once a day, keeping wound clean and dry. Seek medical help if wound becomes infected--tender, swollen and red
question
caring for serious wounds with severe bleeding
answer
1. seek medical help immediately, protect yourself from blood by wearing disposable gloves 2. lay victim down, elevate feet and legs. Place in half-seated position if a head wound 3. find the wound by following the blood. Uncover wound if under clothing 4 place dressing over wound and apply direct pressure 5. raise wound above level of heart and continue to apply direct pressure if arm or leg is wounded 6. apply pressure at pressure point if bleeding continues 7. release pressure point and secure with bandage when bleeding stops. Do not remove dressings
question
pressure points
answer
areas where arteries lie over a bone
question
signs of internal bleeding
answer
bleeding from ears, nose, mouth or eyes, coughing up blood, bruises near skin surface
question
internal bleeding procedure

answer
1. lay person down, raise legs 8-12 inches (unless head injury--of so, put in reclining position) 2. lay vomiting person on left side 3. cover victim with warmth, seek medical help immediately
question
shock
answer
a condition in which some body organs are not getting enough oxygenated blood. It may occur when heart is not pumping properly, a considerable amount of blood is lost from the body hemorrhaging, dehydration or a systemic infection, or when the nervous system is damaged by injury or drugs
question
symptoms of shock
answer
anxious, restless, lethargic (slow-moving), unconscious, pale and cold skin, nauseous or vomiting, increased pulse and respiration rates, bluish tinge to skin, thirsty, dilated (enlarged) pupils
question
treating shock
answer
1. check ABCs and treat for injuries 2. lay victim on back 3. raise legs 8-12 inches 4. cover with blankets, coats 5. call for medical assistance 6. do not give victim anything to eat or drink
question
burn
answer
an injury to the skin and other tissues caused by heat, chemicals, electricity, or radiation. The degree refers to the depth of tissue damage
question
first degree burns
answer
burns that affect only the outer layer of the skin and look pink. Take 3-6 days to heal. No scars.
question
second degree burns
answer
burns that go into the inner skin layer and are red, swollen, and blistered. Take less than 3 weeks to heal. Scars possible.
question
third degree burns
answer
burns that go through all skin layers as well as tissue beneath the skin. Burns appear white, tan or charred black. Skin graft must be performed to heal. Some scarring. Take months to heal.
question
treating first degree burns
answer
apply cool water until pain stops, apply moisturizing lotion
question
treating second degree burns
answer
apply cool water until pain stops, apply antibacterial ointment, seek medical attention if severe
question
treating third degree burns
answer
cover with clean, dry cloth; treat for shock; seek medical attention immediately
question
thermal burns
answer
caused by contact with open flames, hot liquids or surfaces, or other sources of high heat Treat by removing victim from source, cool burn with water, check for bleeding and shock, seek medical attention
question
chemical burns

answer
caused by contact with chemicals that can burn the skin Treat by flushing burn with lots of cool water to remove chemical, or brush powdered chemical off skin with clean cloth
question
electrical burns

answer
direct exposure to electricity Treat by shutting off current, approach only if safe, cool burn with water, check breathing and for signs of bleeding, treat for shock, seek medical attention
question
special consideration for burns

answer
Seek medical help if severe 2nd degree, 3rd degree, chemical or electrical burns Never apply ointment or cream to severe burn Never remove clothing stuck to burn wound Always treat burns to face, hands and feet as severe.
question
fracture
answer
crack or break in a bone
question
dislocation
answer
injury in which a bone has been forced out of its normal position in a joint
question
open fracture
answer
skin is broken and bone ends may stick out of skin; obvious wound
question
closed fracture
answer
skin is unbroken. Injured bone causes pain and tenderness, loss of function, deformity, unnatural movement, swelling, bruising, grating sensation
question
treating a fracture
answer
check for bleeding, call for medical help, splint the area in position it was found, placing padding between splint and body, cover wounds with clean, dry dressing
question
splint
answer
device used to stabilize a body part Used to reduce pain, prevent further damage of tissues surrounding fracture, reduce bleeding and swelling
question
applying a splint
answer
1. Find materials to make splint (heavy cardboard, rolled newspapers) 2. hold splint close to injured area 3. place padding between splint and body 4. Use extra padding around body deformities, body hollows 5. Extend splint beyond joint above and below fracture 6. tie splint comfortably to body
question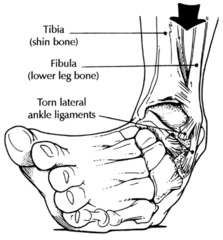
sprain

answer
injury in which the ligament in a joint is stretched too far or torn
question
ligament
answer
tissue that connects bone to bone
question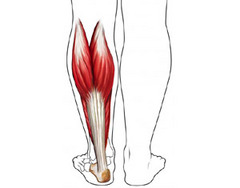
strains

answer
injury in which muscle or tendon has been stretched too far or torn
question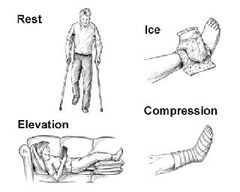
RICE method

answer
treating injuries to bones, joints and muscles 1. Rest--don't use injured area 2. Ice--use ice pack to reduce swelling 3. Compression 4. Elevation
question
compression of bone, joint or muscle injury
answer
wrap injured area with elastic bandage to prevent movement or swelling
question
elevation
answer
raise injured area above heart level when lying or sitting down
question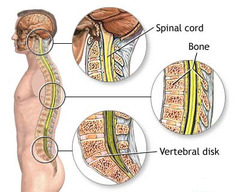
neck or spinal injuries

answer
no obvious signs or symptoms are possible; swelling and bruising; numbness, tingling or loss of feeling in arms and legs; unable to move arms or legs; pain, difficulty breathing; shock
question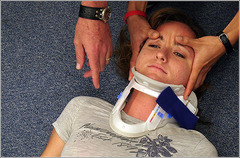
treating neck or spinal injury

answer
do not move person get medical help immediately steady and support head and neck by holding in position found if person MUST be moved keep your arms steady by placing them on your thighs, or place heavy objects on either side of head steady and support victim's feet
question
temperature at which death is likely

answer
106 degrees fahrenheit Danger: Do not leave a baby in a car on a hot day due to risk of death
question
shivering
answer
helps keep body warm by producing heat
question
hyperthermia hyper=above; therm=heat
answer
condition in which body's internal temperature is higher than normal Stage 1: Heat exhaustion Stage 2: Heat stroke
question
heat exhaustion

answer
condition in which the body becomes heated to a higher temperature than normal causes: exercising or working in hot, humid place when heavy sweating causes loss of body fluids
question
symptoms of heat exhaustion
answer
cold, moist skin; normal or above skin temperature; headache; nausea; extreme fatigue (tiredness)
question
treatment of heat exhaustion
answer
move to shady place; remove clothes; apply cool, wet towels; use fan; give victim half a glass of cool (not cold) water every 15 minutes
question
heat stroke

answer
condition in which the body loses its ability to cool itself by sweating because the victim has become dehydrated
question
symptoms of heat stroke
answer
hot, dry skin; higher than normal body temperature; rapid pulse; rapid, shallow breathing; could lose consciousness
question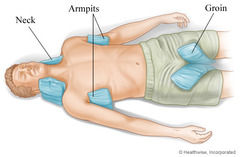
treatment of heat stroke

answer
seek medical help, move to cool place, cool body rapidly by immersing victim in cool (not cold) water or placing icepacks where large blood vessels are; only give food/water if not vomiting
question
prevention of heat-related illness

answer
drink at least 6-8 ounces of water 10 times a day when active in warm, humid weather
question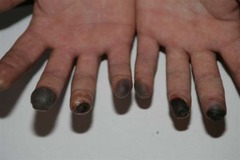
frostbite

answer
condition in which the body tissues become frozen, circulation ceases when ice forms within the tissues
question
symptoms of frostbite
answer
skin looks white, gray or blue; numbness; severe pain when warmth is returned to area
question
treatment of frostbite

answer
do not rub; remove wet or tight clothing; cover with dry, sterile dressing; warm the area slowly with warm, not hot water
question
hypothermia hypo=under therm=heat
answer
condition in which the internal body temperature becomes dangerously low because the body loses heat faster than it can generate heat
question
symptoms of hypothermia
answer
stiff muscles, cold skin; shivering; weakness and dizziness; slow breathing and heart rate`
question
treatment of hypothermia
answer
remove any wet clothing and wrap the person in blankets, towels, or newspapers; offer warm food or drink; do not use hot drinks, water or electric blankets
question
prevention of hypothermia

answer
wear several layers of clothing, a warm hat and go inside frequently to warm up
question
steps to checking an injured person

answer
1. Check the scene, remove hazards (dangers), determine how many victims 2. tap shoulder and shout, "Are you okay?" 3. Call 911 if no response 4. open airway, check for signs of life for no more than 10 seconds 5. No breaths go in, then look for severe bleeding and begin CPR/AED 6. If breathing, put in recovery position, check ABCs



