Abnormal Psychology UGA Exam 1 – Flashcards
Unlock all answers in this set
Unlock answersquestion
Psychiatrists
answer
- Prescribe Medication - Medical Management - have gone through med school with a focus on Psych - M.D. / D.O
question
Psychologist
answer
- Licensed professional - clinical (PhD or Psy.D) - Counseling - School - Social workers
question
Clinical Psychologist
answer
- PhD or PsyD - focuses on diagnosing and treating mental, emotional, and behavioral disorders.
question
Counseling
answer
- maintains a focus on facilitating personal and interpersonal functioning across the life span. - The specialty pays particular attention to emotional, social, vocational, educational, health-related, developmental, and organizational concerns.
question
Psychotherapist
answer
- the use of psychological methods, particularly when based on regular personal interaction, to help a person change and overcome problems in desired ways.
question
School Psychologist
answer
- Testing in schools
question
Social Workers
answer
- M.S.W. or D.S.W - - community services, more popular
question
PhD
answer
- Doctor of Philosophy
question
Psy.D
answer
- Doctor of Psychology
question
Langer & Abelson Studies
answer
- (1974) 2 Groups: Psychoanalytic & Behavioral - Showed them the same video - Half of psychoanalytic & Behavioral were told it was a job applicant - Other half were told he was a mental hospital patient - LABELING PROMOTES PREJUDICE and DISCRIMINATION - The paradigm provided for the psychoanalytic effected what they saw and thought - Patient Paradigm
question
Freud
answer
- Psychoanalysis - Developed systematic theory to understand all human behavior
question
Psychoanalysis
answer
- (dreams, defense, motivation) - Is both a theory and a therapy - a system of psychological theory and therapy that aims to treat mental disorders by investigating the interaction of conscious and unconscious elements in the mind and bringing repressed fears and conflicts into the conscious mind by techniques such as dream interpretation and free association.
question
Oral stage of development
answer
- Early period of total dependence on parents - Early development is important later on in life - hemitaxia denotes the first psychosexual development stage wherein the mouth of the infant is his or her primary erogenous zone.
question
Anal stage of development
answer
- The anal stage is the second stage in Sigmund Freud's theory of psychosexual development, lasting from age 18 months to three years
question
Fixated
answer
- Never move beyond a particular stage - Dependent, no trust, stuck in a stage
question
Regress
answer
- Under pressure or stress, person is thrown back to issues associated with that stage - Break up can bring out disturbance if your early stage was neglected
question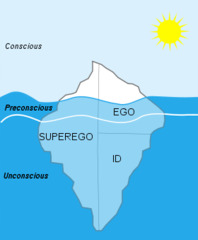
Iceberg Model

answer
- Freud treated the unconscious issues that came up as they went through different aspects of life - Conscious is the tip of the iceberg (EGO) - Preconscious is the water surface (Superego) - Subconscious is everything below the surface (Superego, ID)
question
Preconscious
answer
- The thoughts which are unconscious at the particular moment in question, but which are not repressed and are therefore available for recall and easily 'capable of becoming conscious'
question
The Goal of Therapy
answer
- in Psychoanalysis, is to make the unconscious conscious - Psychoanalysis is an insight oriented therapy - If you have insight, then you can control if and move your life better
question
ID
answer
- Present at birth - Gratification = Pleasure principle
question
EGO
answer
- Develops during first year of life - Consciousness = Reality principle
question
SUPEREGO
answer
- Develops through childhood - Oughts and Should's = Morality Principle
question
Defense Mechanism
answer
- Function: to protect the ego from anxiety - Can be too weak/strong - Operate on an unconscious level
question
Repression
answer
- Pushing anxiety provoking thought out of conscious awareness - Can't remember a traumatic experience because of anxiety
question
Projection
answer
- Attributing your own unacceptable impulse to someone else - Paranoid person, believe others will hurt damage them - But they have urges they can't accept and are more likely to
question
Displacement
answer
- Transfer or redirect an emotional impulse from a more to a less threatening object - Want to punch your friend but can't - "Kick the Cat"
question
Regression
answer
- Under threat returning to the way at an earlier stage - Throw a tantrum or become dependent as they would as a child
question
Rationalization
answer
- Giving a socially acceptable reason for an unacceptable action
question
Free Association
answer
- The person talks without usual filter in normal conversation - Begins to reveal patterns and themes in conversation
question
Resistance
answer
- The patient lives to avoid an important but unpleasant topic
question
Dream Analysis
answer
- 'Royal road to unconscious' - Dream interpretation
question
Interpretation
answer
- Therapist shares with patient their interpretation - Timing is important. if not ready they may reject
question
Transference
answer
- Patient acts toward the therapist as if the therapist was some important person in the patients past
question
Education of Psychoanalysis
answer
- There are more efficient and effective ways to do it - There is no great data base to show effectiveness, no investigation
question
Humanistic/Client-Centered
answer
- Carl Rogers - Defense mechanisims - IF people are given unconditional love and acceptance, they will be able to develop into healthy people - Conditional Love
question
Conditional Love
answer
- Can lead to 2 problems - Distort or deny truth about themselves to make them seem more lovable - Wall off some area of themselves - (Workaholics, dress a certain way)
question
Therapist Characteristics
answer
- Try to create an atmosphere of love and acceptance for the person to blossom
question
Genuiness
answer
- Openness, Spontaneous, Authentic
question
Unconditional Positive Regard
answer
- unconditional positive regard toward the client - Accept them for who they are, not what they do
question
Empathetic Understanding Engagement
answer
- Good listening skills - incorporated into other practices, but not largely used on its own.
question
Iatrogenic Treatment
answer
- Where the treatment makes the situation worse
question
Shame
answer
- The fear of disconnection
question
Vulnerability
answer
- In order for connection to happen, we have to be seen completely - People who had love and belonging believed they were worthy of love and belonging
question
Courage
answer
- People with worthiness had the courage to be imperfect
question
Behavioral Psychology
answer
- Freud and Rodgers both started their therapy with clients - Behavioral Psych was birthed in the laboratory (Control and Predict) - Behavioral Psych is easier to be measured
question
Classical Conditioning
answer
- Pavlov - a learning process that occurs when two stimuli are repeatedly paired; a response that is at first elicited by the second stimulus is eventually elicited by the first stimulus alone.
question
Unconditioned Stimulus
answer
- No learning required - A stimulus which, with no prior learning required, is capable of eliciting an unconditional response
question
Unconditioned Response
answer
- A response elicited by the unconditioned stimulus
question
Controlled Stimulus
answer
- An originally neutral stimulus, which, through association with the Unconditioned stimulus comes to elicit a close approximation of the unconditioned Response
question
Controlled Response
answer
- A response elicited by the controlled stimulus - a close approximation to the unconditioned response
question
Generalization
answer
- A phenomena that occurs in classical conditioning - to the extent that other stimuli resemble the Controlled stimulus they will elicit some degree of the C. Response - No additional learning is required for generalization
question
Discrimination
answer
- Actively present the similar stimulants, with no response given, so they learn eventually the correct C.S. - The patient learns that the other stimuli that are not the C.S do not reveal the response
question
Extinction
answer
- Break the association between the U.S. and the C.S breaking the response - The patient learns that the other stimuli that are not the C. stimulus do not reveal the response
question
Spontaneous Recovery
answer
- An increase in the C.Response to the C. Following a period of extinction, that's due to only the passage of time - some recovery
question
Operant Conditioning
answer
- a type of learning where behavior is controlled by consequences.
question
Positive
answer
- Behavior results in something being added
question
Negative
answer
- Behavior results in something being taken away
question
Reinforcement
answer
- There is an increase of behavior because of the consequences that behavior produces (Intensity, frequency, probability)
question
Punishment
answer
- The behavior decreases as a result of the consequences that behavior produces
question
Positive Reinforcement
answer
- Something added resulting in a increase of behavior - compliment, high five, paycheck
question
Positive Punishment
answer
- Behavior results in something being added resulting in a decrease in behavior - Speeding ticket, spanking
question
Negative Reinforcement
answer
- Behavior results in something being taken away resulting is an increase in behavior - (alarm clock, seatbelt, drugs to remove stress) - Escape of avoidance Immediate consequences of Behavior are the most influential, control behavior better than long term - Maladaptive behavior has 'short term gain but long term pain'
question
Negative Punishment
answer
- Behavior results in something being taken away resulting in a decrease in behavior - Time out, Phone away
question
Sit Down Study
answer
- Negative reinforcement by teacher - Positive reinforcement for the kid with attention
question
Stimulus Control
answer
- Behavior is prompted/controlled/qued/ by the things that recieve the behavior - Smoking because you see someone else do it - Having a specific study place
question
Functional Analysis of Behavior
answer
- the application of the laws of operant conditioning to establish the relationships between stimuli and responses.
question
Antecedent
answer
- Comes before behavior - sets the stage for behavior
question
Consequence
answer
- Comes after the behavior, influences the likelihood of the behavior
question
Shaping
answer
- Two main components: 1. Performing a task analysis 2. Teaching successive (in order) approximations of desired behavior
question
Modeling
answer
Two people (the model, the immitator) - Training complex behavior where shaping is not applicable - Adopt good and bad behaviors
question
Extinction (decreasing Behavior)
answer
- Withholding reinforcers for a previously reinforced behavior
question
Extinction Burst
answer
- Increase of behavior at beginning of extinction
question
D.R.O. (Differential Reinforcement of other behavior)
answer
- Reinforcing something other than the undesirable behavior - influencing baby to do something other than pulling her hair with hands in order to diminish hair pulling behavior
question
Time Out
answer
- Sending form good place, to a less desirable place
question
Cognitive Behavior Therapy
answer
- What does the world look like to them? - Appreciate clients phenommological world by listening to what they say/talk to themselves
question
Albert Ellis
answer
- Rational Emotional Therapy (R.E.T) - Irrational Beliefs - People feel bad because they think bad
question
Aaron Beck
answer
- Cognitive Behavior therapy - Automatic Thoughts - Collaborative Empiricism
question
Cognitive Triad
answer
- Bad me - bad world - bad future
question
Collaborative Empiricism
answer
- Client and therapist work together to consider data of clients life
question
Automatic Thoughts
answer
- Think without thinking about
question
Dr. Beck: Automatic Thoughts
answer
1. Examine automatic thoughts / teach them about Automatic thoughts 2. Examine their auto thoughts 3. Challenge the validity of those automatic thoughts 4. Modify those: specific automatic thoughts (stimulus control) 5. Try to change their cognitive Schema
question
Maintenance
answer
- The changed behavior continues over time - You want that behavior to continue
question
Generalization
answer
- The behavior is performed in non-training environments - (settings, caregivers, home, time)
question
Techniques for Promoting
answer
1. Intro to natural communities of reinforcement 2. Use indiscriminable contingencies 3. Program common stimuli 4. Eliminate Secondary gain
question
Intro to Natural Communities of reinforcement
answer
- Behavior is introduced to reinforcers that are naturally prevent in the individuals environment which come to maintain behavior
question
Reinforcement Trap
answer
- Keep bad behaviors going without being able to breakout of habit/situation
question
Efficacy
answer
- Does the treatment reduce significant benefit in highly controlled research situations? - the ability to produce a desired or intended result. - Efficacy is necessary but alone, is not efficient enough for effectiveness
question
Effectiveness
answer
- How useful is the treatment? - The results are not as impressive for efficient studies
question
Nomothetic Research
answer
- Seeks to determine general laws and Principles - Typically with large groups of people - Learning characteristics of the GROUP, not the individuals within the group
question
Idiographic Research
answer
- Focuses on the INDIVIDUAL - May or may not not generalize to the group - Clinical work - Clinical -> research (Clinical scientist, scientific practitioner)
question
Epidemiology
answer
- Study of frequency and distribution of an illness or condition in a population - Prevalence, Incidence - Risk Factor, Protective Factor (Fixed, Variable)
question
Prevalence
answer
- The proportion of the population that has the disorder at any given point in time
question
Incidence
answer
- Rate of new cases in a disorder in a given time
question
Risk Factor
answer
- Condition variable which, if present, INCREASES the likelihood of developing a disorder (fats, bad diet)
question
Protective Factor
answer
- Condition variable which, if present, DECREASES the likelihood of developing a disorder - Exercise, healthy habits
question
Naturalistic Observation
answer
- Watching the subjects in his/her natural environment and observing - Ethology - Correlational Data
question
Ethology
answer
- the study of human behavior and social organization from a biological perspective.
question
Correlational Data
answer
- measure of the extent to which two variables are related. - Is not as valid as experimental data - experimental data can cause cause and effect
question
Survey Methods
answer
- Asking people about their opinions, attitudes, and behaviors - Random Sample - Stratified Sample
question
Random Sample
answer
- Everybody has an equal chance of being selected
question
Stratified Sample
answer
- Sample is collected in such a way that it represents a population of Interest - matching population
question
Correlational Methods
answer
- Examine the extent to which changes in variable X change with or covary with changes in variable y - Correlation cannot cause causation but you cant have causation without correlation - Height changes with weight (positive) - Height goes up, weight goes down (negative)
question
Magnitude of Correlation
answer
- Size of the correlation - larger number (Positive or negative) is the largest correlation - Correlation cannot cause causation
question
Bidirectionally
answer
- Limitation of correlation - X is causing Y or Y is causing X?
question
Third Variable Problem
answer
- X and Y - Z variable could be prompting most things - Bars and churches (Z= population density/college town)
question
Case Studies
answer
- Detailed account of a person's life or behavior useful when: 1. Rare phenomenon/conditions 2. Generating Hypothesis to develop treatment approaches that can be tested later 3. Practicing Clintons who don't have time for large scale research
question
Experimental Designs
answer
- Allow you to move toward causation
question
Independent variable
answer
- treatment, what you can manipulate
question
Dependent Variable
answer
- outcome based on Independent variable
question
Group Design
answer
People are randomly assigned to one group or another
question
Single Subject Research Designs
answer
- the subject serves as his/her own control, rather than using another individual/group. - Reversal (ABA) - ABAB
question
Reversal Design

answer
- ABA - to Experimentally test something or a treatment, you must reverse or withdraw treatment
question
Limitations with Single Subject research designs
answer
1. Some behaviors will not reverse. Behaviors have to change in order for it to be an experiment 2. It would be unethical in some situations to withdraw treatment (cancer or disease)
question
Multiple Base-Line Design
answer
- Show if a third variable is present - You intervene on each individual after differing lengths of baseline, if behavior changes only at the point of intervention, then you have an experiment - Baseline and reversal are equivalent to control groups
question
Sroufe's Pathway
answer
a. Continuity of Maladaption b. Continuity of positive adaption c. Initial maladaption followed by positive change d. Initial positive adaption, followed by negative change
question
Pathways Model
answer
- Pathology may be though of as a secession of branchings which take the child away from pathways leading to confident development 1. Disorder is Deviant over time 2. Multiple pathways to similar outcomes 3. Different outcomes from the same pathway (A&C) 4. Change is possible at many points 5. Change is constrained by prior adaptation
question
1. Disorder is Deviant over time
answer
- Failure at any point in time is best viewed as placing an individual on a pathway potentially leading to disorder
question
2. Multiple pathways to similar outcomes
answer
- Individuals beginning on different pathways may nevertheless converge towards similar patterns of adaptation (B & C)
question
Equifinality
answer
- Equal Finally - Multiple pathways to similar outcomes
question
3. Different outcomes from the same pathway
answer
- The concept of secessive branches suggest that individuals beginning on a similar pathway may diverge ultimately showing different patterns of pathology or no pathology. - Multi-finality
question
4. Change is possible at many points
answer
- Despite every deviation, changes may lead individual back toward a more adaptive pathway (hopeful)
question
5. Change is constrained by prior adaptation
answer
- The longer a maladaptive pathway is followed/enjoined, the less likely the person will reclaim positive adaptation
question
Classification Benefits
answer
1. provides some description of the problem 2. Facilitates Communication among professionals 3. May lead to discoveries about the cause of the disorder 4. Can improve clinician's ability to predict the outcome/prognosis 5. Can lead to guidelines of selecting the best treatment for a disorder
question
Labeling
answer
- Problem with classification - Patient might be discriminated by the label they are given 1. Others may treat the patient according to the diagnosis 2. You may act according to the diagnosis (ADHD - why should i try to hard)
question
Reliability
answer
- The extent to which two clinician agree on diagnosis - Sets the ceiling on validity - Validity can't be better than reliability - Pre-req for validity - Reliability is not sufficient for validity
question
Validity
answer
- Usefulness of diagnosis/data - 3 types: 1. Ethological 2. Concurrent 3. Predictive
question
Ethological Validity
answer
- Where did it come from? - Based on past events
question
Concurrent Validity
answer
- Can the Diagnoses TEACH us something additional about the disorder? - Present time period
question
Predictive Validity
answer
- Prognosis - How is it going to turn out with this diagnosis? - Future time period
question
Catregorial Classification
answer
- Either you have it or you don't - Dead/alive, male/female, Tall/short
question
Continuous/Dimensional Classification
answer
- More or less of something - 4'10/5'6, - Measurement, quantitative
question
The Diagnostic & Statistical Manual (DSM)
answer
- a common language and standard criteria for the classification of mental disorders- Published by the American Psychiatric Association - Currently working with DSM 5 and previous - Refinement of criteria as time goes on
question
Axis I
answer
- Clinical Disorders - Almost everything
question
Axis II
answer
- Personality Disorders - Mental Insufficiencies/retardations
question
Axis III
answer
- General medical condition - Anything else (Diabetes, Heart disease)
question
Axis IV
answer
- Psychosocial and environmental problems - Divorce, poverty, abuse, homelessness
question
Axis V
answer
- Global assessment of functioning - Non-Axial System
question
Comorbidity
answer
- Has two or more diagnoses - Having one mental health problem predisposes one to have more than one problem - Anxiety and Depression
question
Diathesis
answer
- Predisposition toward a disorder - includes both genetics and history - If you lower risk factors, you can change your Diathesis
question
Stress
answer
- Current factors which combines with your diatheses - Influences the likelihood of developing a disorder



